Alkanes
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
When do you use fractional distillation?
When boiling points are in a similar range.
What are alkanes?
Saturated hydrocarbons (single bonds only, C–C and C–H).
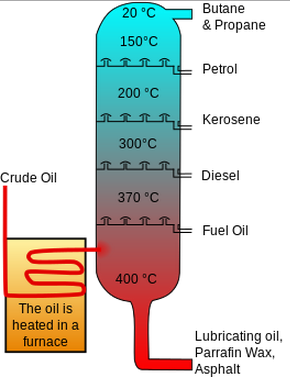
How does fractional distillation separate crude oil?
Crude oil is heated → vapour rises in the fractionating column (hottest at bottom, coolest at top).
Large molecules (strong van der Waals forces, high boiling points) condense at the bottom.
Small molecules (weaker forces, low boiling points) condense at the top.
Molecules of similar size/boiling point form useful fractions.
Why is vacuum distillation used for heavy hydrocarbons?
Distilled under a vacuum → reduced pressure → lowers boiling point → separation at lower temperatures → no thermal decomposition.
What is cracking?
Breaking large hydrocarbons into smaller ones by splitting strong C–C covalent bonds.
Why is cracking economically important?
Long-chain hydrocarbons are less useful → shorter-chain hydrocarbons → more volatile, less viscous, better fuels.
Compare thermal vs catalytic cracking.
Thermal cracking: High temp & pressure → mostly alkenes.
Catalytic cracking: High temp, slight pressure, zeolite catalyst → branched/cyclic alkanes & aromatics (motor fuels).
Why are branched/cyclic hydrocarbons useful in fuels?
Higher octane number → fuel does not ignite prematurely; burn more cleanly → less soot/pollution.