Prenatal development stages, ect.
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Definition of Prenatal Development Stages
The process of a baby growing and developing inside the mother’s womb, from conception (when the egg and sperm join) until birth.
Germinal Phase (Weeks 0–2), Where does it begin/end? Is it a zygote?
Begins at fertilization → ends at implantation.
The fertilized egg is a zygote.
Germinal Phase (Weeks 0–2), What day does implantation occur? Is it Germinal? How does it end?
Implantation occurs ~day 14.
“Germinal” = think germinate (like a seed sprouting).
Ends when the zygote attaches to the uterus → becomes an embryo
Embryonic Phase (Weeks 3–8), What body structures appear? Does brain development start?
Organ and body structure formation:
Arms, legs, torso, heart, brain begin developing.
Brain development starts very early (~week 3).
Embryonic Phase (Weeks 3–8), Does movement start? Why is it vulnerable? What does the brain appearance look like?
Movement begins by the end of this stage.
Vulnerability: most susceptible to toxins or damage.
Most people don’t know they’re pregnant during this phase.
→ Brain Appearance:
Early brain is smooth, later develops gyri and sulci (folds) to increase surface area.
More folds = more cortex = higher cognitive ability.
Fetal Phase (Week 9–Birth), is it the longest or shortest stage? What are the major developments?
Longest stage of prenatal development.
Major developments:
Growth, movement, and strength.
Hearing develops → fetus hears mother’s voice, heartbeat, and digestion.
Cognitive evidence: fetus remembers familiar rhythms (e.g., Cat in the Hat study)
Fetal Phase (Week 9–Birth), describe the attachment? What happens in a premature birth?
Attachment:
Baby recognizes mother’s voice after birth.
But attachment can form with any caregiver — it’s not exclusive to biological parents.
Premature birth:
Viability begins ~22 weeks (with medical support).
Female fetuses tend to survive prematurity better due to:
More developed lungs and immune system (testosterone redirects resources in males toward physical growth).
What’s the sequence of Early Brain Formation? What day?
Neural Plate (≈ Day 18)
Neural Groove (day 18–20)
Neural Tube (≈ Day 24)
What’s the neural plate?
Flat rectangle on the embryo’s back.
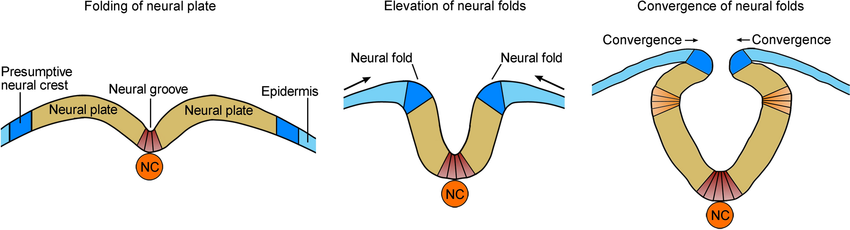
What’s the Neural Groove?
Indentation forms in the plate.
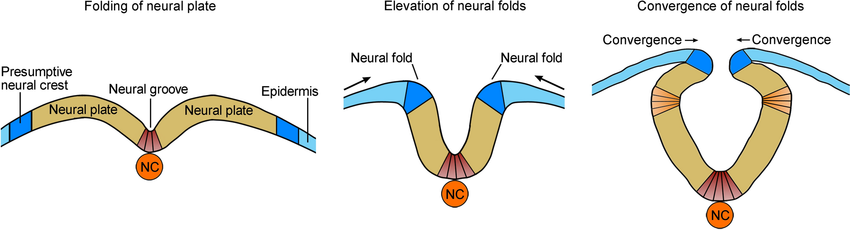
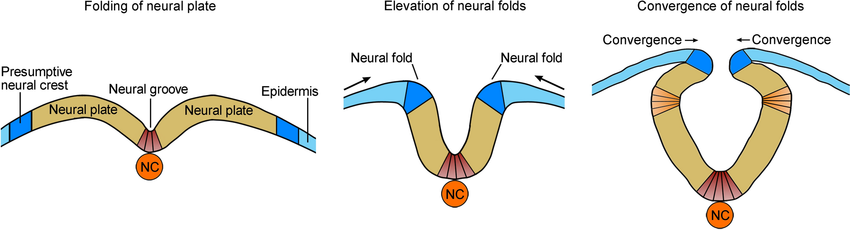
What’s the Neural Tube?
Groove closes into a tube.
Key factors in neurodevelopment (first 4), state definitions
Neurogenesis
Neuronal migration
Synaptogenesis
Myelination
Neurogenesis (formation of new neurons)
Neuronal migration (movement of neurons to their proper locations)
Synaptogenesis (forming synapses/connections)
Myelination (insulating axons to speed signaling
Key factors in neurodevelopment (last 3), state definitions
Synaptic pruning
Neurotransmitter system development
Hormonal influences
Synaptic pruning (removing weak or unused connections)
Neurotransmitter system development (brain builds the chemical signaling systems)
Hormonal influences (e.g., cortisol, thyroid hormone, sex hormones)