micro ch 9 monopoly
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
monopoly
1 firm produces all of the output in a market
a firm that controls all (or nearly all) of the supply of a good or service
(if more than 1 firm produces same products, then not considered this)
any price
since a monopoly faces no significant competition, it can charge ? it wishes, subject to the demand curve
very few monopolies exist, but for ex., US postal service
barriers
the legal, technological, or market forces that discourage or prevent potential competitors from entering a market
can range from the simple and easily manageable, like the cost of renting retail space, to the extremely restrictive
ex., there are a finite number of radio frequencies available for broadcasting
once an entrepreneur or firm has purchased the rights to all of them, no new competitors can enter the market
a perfect competition market has none
inelastic
completely ? demand for a monopolistic firm
when prices change, qty demanded is the same bc no other competitors can produce same goods
monopoly market power determinants
2 primary factors
firm’s demand curve
firm’s cost structure
5 monopoly types
natural monopoly
control of physical resource
legal monopoly
patent, trademark, and copyright
intimidating potential competitors
natural monopoly
Occurs when economies of scale are large compared to market demand
Common in industries with high fixed costs and low marginal costs (e.g., airplane manufacturing)
Happens when market demand is less than the quantity needed to reach the lowest average cost
Only one firm can efficiently supply the whole market
can also arise in smaller local markets for products that are difficult to transport.
control of a physical resource- monopoly
company has control of a scarce physical resource
legal monopoly
sometimes the government erects barriers to entry by prohibiting or limiting competition
ex., USPS
most are utilities (products necessary for everyday life that are socially beneficial)
barriers to entry created by the govt
innovation protection
a patent
trademark
copyright
patent
gives inventor the exclusive legal right to make, use or sell the invention for a limited time (in US- 20 years)
idea is to provide limited monopoly power so that innovative firms can recoup their R&D investment, but then to allow other firms to produce the product more cheaply once the patent expires
trademark
legal protections on words, phrases, designs, or marks that identify a specific product or service
an identifying symbol or name for a particular good (e.g., Nike “swoosh)
a firm can renew a trademark repeatedly, as long as it remains in active use
copyright
legal protections on creative works of the mind
no one can reproduce, display, or perform the work wo authr’s permission
author’s life + 70 years
patent law
inventions
copyright
books
songs
art
trade secrets
another way to protect invention
even if company doesn’t have a patent on an invention, competing firms aren’t allowed to steal their secrets
e.g., Coca-cola formula
intellectual property
implies ownership over an idea, concept, or image, not a physical piece of property
combo of patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secret law
predatory pricing
firm uses threat of sharp price cuts to discourage competition
after new entrant has gone out of business, incumbent firm can raise prices again
a violation to US antitrust law, but difficult to prove
profit maximizing qty of output
monopolist ? will be equal to total revenues-total costs
perceived demand for a perfect competitor
demand curve is flat (firm can sell either a low quantity QI or a high quantity Qh at exactly the same price P).
demand curve perceived by a monopoly
perceived demand curve mostly downward sloping
thus if the it chooses a high level of output Qh, it can charge only a relatively low price (PI)
if it chooses a low level of output Q1, it can then charge a higher price Ph
challenge is to choose combo for price and qty that maximizes profits
monopolist
can charge any price for its product, but the demand for the firm’s product constrains the price
none (even one protected by high barriers to entry) can require consumers to purchase its product
total revenue curve will start low, rise, then decline
copyright legislation, as well as all of the above
Intellectual property law is a body of law that includes
A. the right of inventors to produce their inventions
B. the right of inventors to sell their inventions
C. trademark, patent and trade secret legislation
D. copyright legislation, as well as all of the above
natural monopoly
A ___________ exists when the quantity demanded in the market is less than the quantity at the bottom of the long-run average cost curve.
A. natural monopoly
B. monopoly
C. oligopoly
D. monopolistic competition
predatory pricing
The use of sharp, temporary price cuts as a form of ________ would enable traditional US airplane companies to discourage new competition from smaller airplanes manufacturers.
A. natural monopoly
B. monopolistic competition
C. predatory pricing
D. oligopolistic competition
local electricity distributor
Which of the following is most likely to be a monopoly?
A. local fast-food restaurant
B. local electricity distributor
C. local bathroom fixtures shop
D. local television broadcaster
total cost and revenue curve for health pill monopoly
total revenue first rises, then falls
total cost curve is upward sloping
profits will be highest at the qty of output where total revenue is most above total cost
profit maximizing level of output not the same as revenue maximizing level output (bc profits take costs into account and revenues don’t)
theoretical, not real world
loss minimization
profit maximizing monopolist would achieve ? when price is btw avg total cost and avg variable cost
profit maximizing choice
for the monopoly is to produce at the qty where marginal revenue =marginal cost
MR=MC
profit maximizing level of output
monopoly could seek out ? by
increasing qty by a small amount
calculating marginal revenue and marginal cost
either increasing output as long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost or reducing output if marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue
marginal cost
change in total cost from producing a small amount of additional output
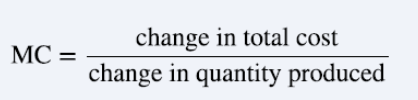
key difference
perfectly competitive firm
in case of perfect competition, marginal revenue is equal to price (MR=)
for monopolist
marginal revenue isn’t equal to the price bc changes in qty of output affect the price
marginal revenue
change in total revenue from selling a small amount of additional output
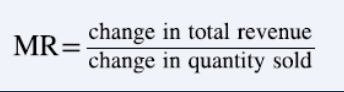
sign of possible monopoly
firm earns profits year after year, while doing or more less the same thing, wo ever seeing increased competition eroding these profits
P=MC
monopolist has no motivation to operate at an output level where P=MC, once a barrier is in place and no longer has to worry about competition
Predatory pricing
A large airline provides most of the flights between two particular cities. A new, small start-up airline decides to offer service between these two cities. The large airline immediately slashes prices on this route to the bone, so that the new entrant cannot make any money. After the new entrant has gone out of business, the incumbent firm raises prices again. We would call the behavior of the large airline...
Option A
Predatory pricing
Option B
Aggressive marketing
Option C
Competitive pricing
Option D
Multi-level marketing
completely inelastic
For a monopolistic firm, the demand for its product is
Option A
completely inelastic
Option B
completely elastic
Option C
neither b or c
Option D
unitary elastic
copyright legislation, as well as all of the above
intellectual property law is a body of law that includes
Option A
the right of inventors to produce their inventions
Option B
the right of inventors to sell their inventions
Option C
trademark, patent and trade secret legislation
Option D
copyright legislation, as well as all of the above
Price is between average total cost and average variable cost.
The profit maximizing monopolist would achieve loss minimization when...
Option A
Price is above average total cost.
Option B
Price is below average variable cost.
Option C
Price is between average total cost and average variable cost.
Option D
Total cost equals total revenue.
during the author's life plus 70 years
Copyright protection legislation provides protection for original works
Option A
during the author's life plus 20 years
Option B
until the author is 75 years of age
Option C
until the author is 70 years of age
Option D
during the author's life plus 70 years
start low, rise, and then decline.
The total revenue curve for a monopolist will
Option A
start high, rise, and then decline.
Option B
start low, decline, and then rise.
Option C
start high, decline, and then rise.
Option D
start low, rise, and then decline.
demand curve and its cost structure
The two primary factors determining monopoly market power are the firm's
Option A
demand curve and its cost structure
Option B
demand curve and level of wealth within its market
Option C
revenues and size of its customer base
Option D
variable cost curve and its fixed cost structure
By determining where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
How does the monopoly determine the level of output that maximizes profit?
Option A
By determining where total revenue equals marginal cost.
Option B
By multiplying price by marginal cost.
Option C
By determining where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
Option D
A monopoly does not need to calculate where maximum profit occurs because they have no competition and can set any price they want for their product.
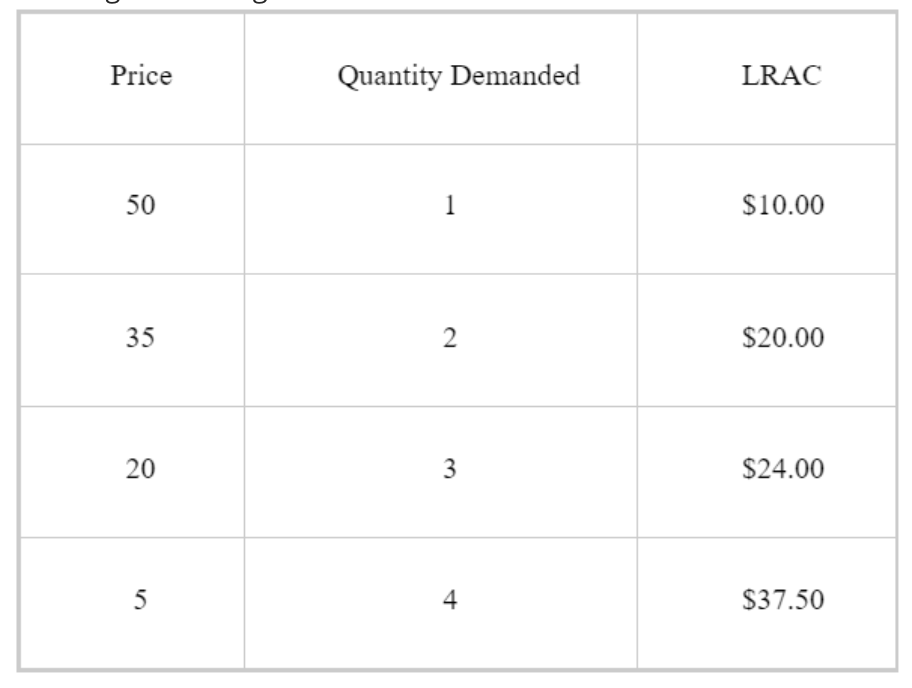
50
At what price Long run average cost were the lowest?
Option A
20
Option B
50
Option C
5
Option D
35
20 years
In the United States, a pharmaceutical company's exclusive patent rights last for
Option A
70 years.
Option B
25 years.
Option C
20 years.
Option D
10 years.
$3.90 or less
if a firm holds a pure monopoly in the market and is able to sell 5 units of output at $4.00 per unit and 6 units of output at $3,90 per unit, it will produce and sell the sixth unit if its marginal cost is
Option A
$3.50 or less
Option B
$3.40 or less
Option C
$4.00 or less
Option D
$3.90 or less
$3.40 or less
if a firm holds a pure monopoly in the market and is able to sell 5 units of output at $4.00 per unit and 6 units of output at $3,90 per unit, it will produce and sell the sixth unit if its marginal cost is
Option A
$3.50 or less
Option B
$3.40 or less
Option C
$4.00 or less
Option D
$3.90 or less
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where marginal revenue intersects marginal cost.
How can a monopolist identify the profit-maximizing level of output if it knows its marginal revenue and marginal costs?
Option A
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where marginal revenue larger than marginal cost.
Option B
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where marginal revenue smaller than marginal cost.
Option C
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where marginal revenue intersects marginal cost.
predatory pricing
The use of sharp, temporary price cuts as a form of ________ would enable traditional US automakers to discourage new competition from smaller electric car manufacturers.
Option A
oligopolistic competition
Option B
predatory pricing
Option C
monopolistic competition
Option D
natural monopoly
that firm could set up barriers to entry to discourage competition
If it was possible for one company to gain ownership control all of the uranium processing plants in the US, then
Option A
government will deregulate to ensure the company's monopoly.
Option B
they will strive to reach efficiencies only they know how to make.
Option C
the factors of market demand and supply will set the price.
Option D
that firm could set up barriers to entry to discourage competition
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where there is the greatest difference between total revenue and total cost.
How can a monopolist identify the profit-maximizing level of output if it knows its total revenue and total cost curves?
Option A
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where there is the least difference between total revenue and total cost.
Option B
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where there is the greatest difference between total revenue and total cost.
Option C
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where there is the no difference between total revenue and total cost.
downward sloping
The slope of the demand curve for a monopoly firm is
Option A
vertical, parallel to the y-axis
Option B
upward sloping
Option C
downward sloping
Option D
horizontal, parallel to the x-axis
there is a single seller in a particular industry
For a pure monopoly to exist,
Option A
there is a single seller in a particular industry
Option B
there is only one seller, therefore no industry
Option C
there are a few sellers in a given industry
Option D
there are limited sellers in a particular industry
local electricity distributor
Which of the following is most likely to be a monopoly?
Option A
local bathroom fixtures shop
Option B
local electricity distributor
Option C
local television broadcaster
Option D
local fast-food restaurant
Predatory pricing
A large airline provides most of the flights between two particular cities. A new, small start-up airline decides to offer service between these two cities. The large airline immediately slashes prices on this route to the bone, so that the new entrant cannot make any money. After the new entrant has gone out of business, the incumbent firm raises prices again. We would call the behavior of the large airline...
Option A
Competitive pricing
Option B
Aggressive marketing
Option C
Predatory pricing
Option D
Multi-level marketing
Has no motivation to operate at an output level where P=MC, once a barrier is in place and no longer has to worry about competition.
Allocative efficiency is an economic concept regarding efficiency at the social or societal level. It refers to producing the optimal quantity of some output, the quantity where the marginal benefit to society of one more unit just equals the marginal cost. The rule of profit maximization in a world of perfect competition was for each firm to produce the quantity of output where P = MC, where the price (P) is a measure of how much buyers value the good and the marginal cost (MC) is a measure of what marginal units cost society to produce. A monopolist...
Option A
Will prefer to operate where price < average total cost.
Option B
Will experience greater profits if it sets prices equal to average total cost.
Option C
Would try to achieve allocative efficiency to compete with the other firms who own a larger market share.
Option D
Has no motivation to operate at an output level where P=MC, once a barrier is in place and no longer has to worry about competition.
In a legal monopoly, barriers to entry are created by the government.
How is a legal monopoly different from a natural monopoly?
Option A
In a legal monopoly, the monopolist has purchased the necessary certificate from the local government that allows the formation of a monopoly.
Option B
A legal monopoly applies to government-run institutions, whereas a natural monopoly applies to all other resources
Option C
In a legal monopoly, the Federal Trade Commission has paid a firm to be the only producer of a product in a given area.
Option D
In a legal monopoly, barriers to entry are created by the government.
Has no motivation to operate at an output level where P=MC, once a barrier is in place and no longer has to worry about competition.
Allocative efficiency is an economic concept regarding efficiency at the social or societal level. It refers to producing the optimal quantity of some output, the quantity where the marginal benefit to society of one more unit just equals the marginal cost. The rule of profit maximization in a world of perfect competition was for each firm to produce the quantity of output where P = MC, where the price (P) is a measure of how much buyers value the good and the marginal cost (MC) is a measure of what marginal units cost society to produce. A monopolist...
Option A
Will experience greater profits if it sets prices equal to average total cost.
Option B
Would try to achieve allocative efficiency to compete with the other firms who own a larger market share.
Option C
Has no motivation to operate at an output level where P=MC, once a barrier is in place and no longer has to worry about competition.
Option D
Will prefer to operate where price < average total cost.
Three firms control the production of a precious gem globally
Which of the following is NOT an example of a monopoly?
Option A
The government-run postal service.
Option B
A utility (e.g. water, sewer, electricity) provided primarily by one company
Option C
In the 1930s, ALCOA (The Aluminum Company of America) controlled most of the bauxite, a key mineral used in making aluminum.
Option D
Three firms control the production of a precious gem globally
producing output where MR = MC and charging a price along the demand curve
A monopolist is able to maximize its profits by
Option A
producing output where MR = MC and charging a price along the demand curve.
Option B
setting the price at the level that will maximize its per-unit profit.
Option C
setting output at MR = MC and setting price at the demand curve's highest point.
Option D
producing maximum output where price is equal to its marginal cost.
raise prices, cut production, and realize positive economic profits.
In the event that Only1Corp. obtains control of all the natural gas producers in the US, it would most likely
Option A
raise prices, cut production, and realize positive economic profits.
Option B
have a patent giving it exclusive legal rights to make, use, and sell for a limited time.
Option C
have legal protection to prevent copying its methods of production for commercial use.
natural monopoly
A ___________ exists when the quantity demanded in the market is less than the quantity at the bottom of the long-run average cost curve.
Option A
monopoly
Option B
natural monopoly
Option C
oligopoly
Option D
monopolistic competition