Medical Anatomy chapter 5
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
cervical vertebrae
small body, uncinate process, pedicles and laminae, biford spinous process, transverse process, anterior and posterior articular processes fused into a pillar, articular pillar, superior and inferior articular processes and facets, large triangular vertebral foramen
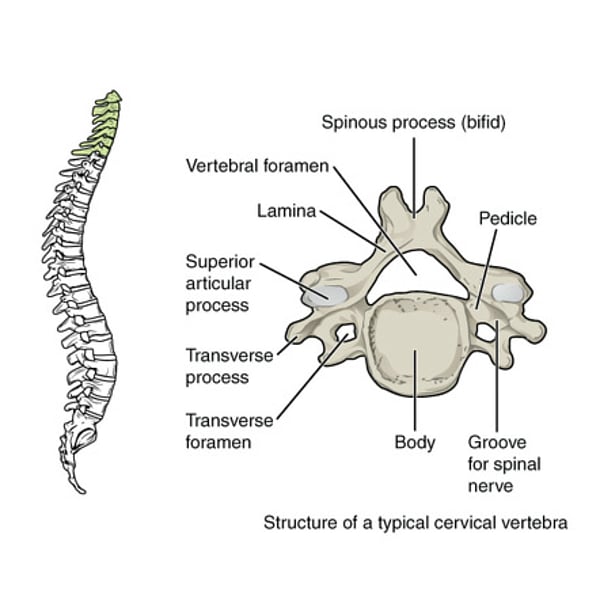
what is this
uncinate process
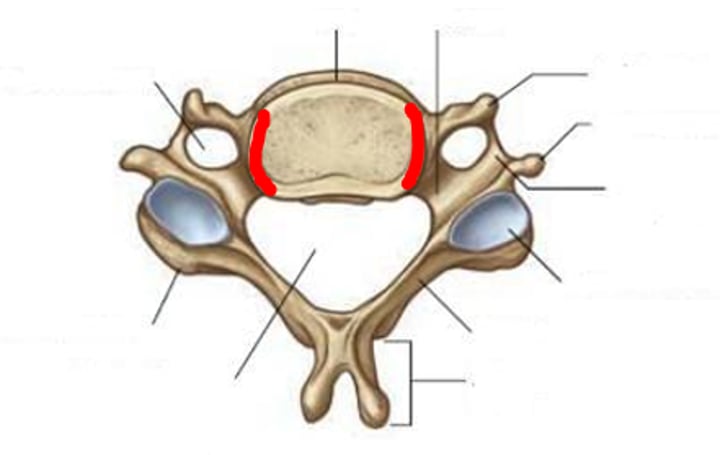
what is this
transverse foramen
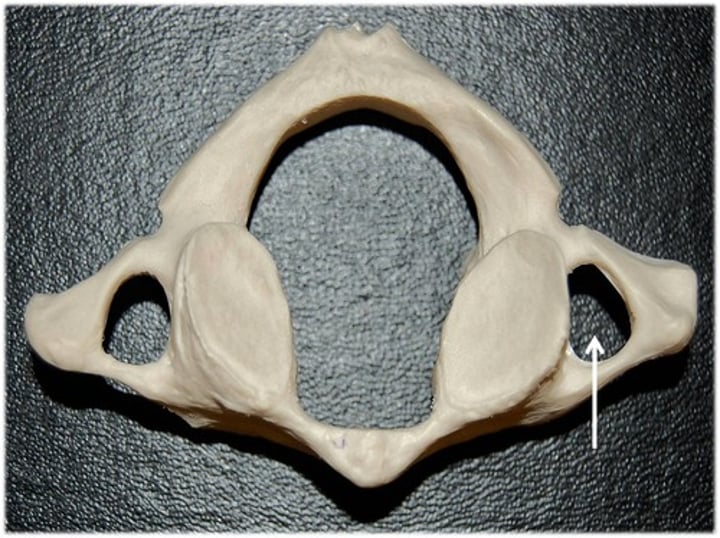
atlas
no vertebral body, anterior arch instead. anterior tubercle for muscle attachment, superior anterior process and facet and inferior articular facet
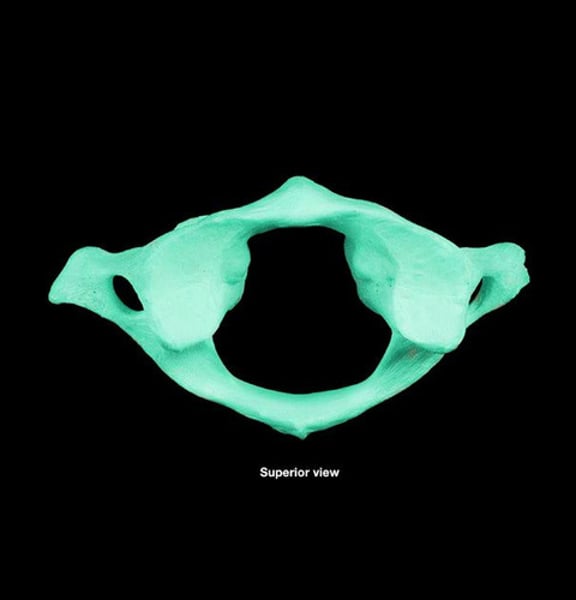
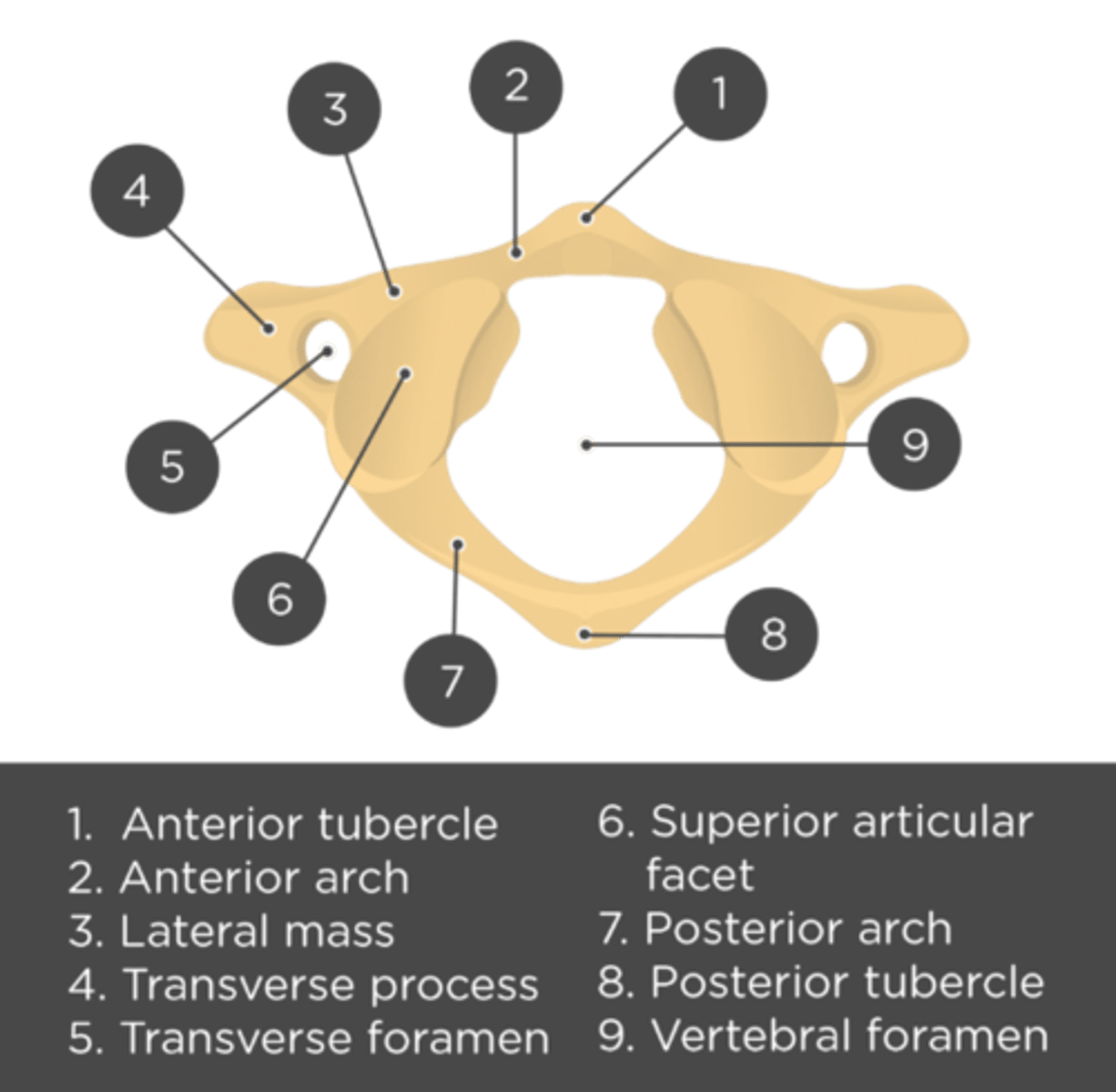
what attaches to the anterior tubercle of the atlas
Longus colli muscles and the anterior longitudinal ligament
what goes through the transverse foramen
vertebral artery and vein
atlanto-occipital joint
articulation between the atlas and the cranium. btw occipital condyles and the superior articulating processes of the atlas.
what movement does the atlanto occipital joint have
flexion and extension no rotation
Axis
dens (odontoid process), facet for anterior arch of atlas, 3 synovial joints, paired joints btw articulating facets
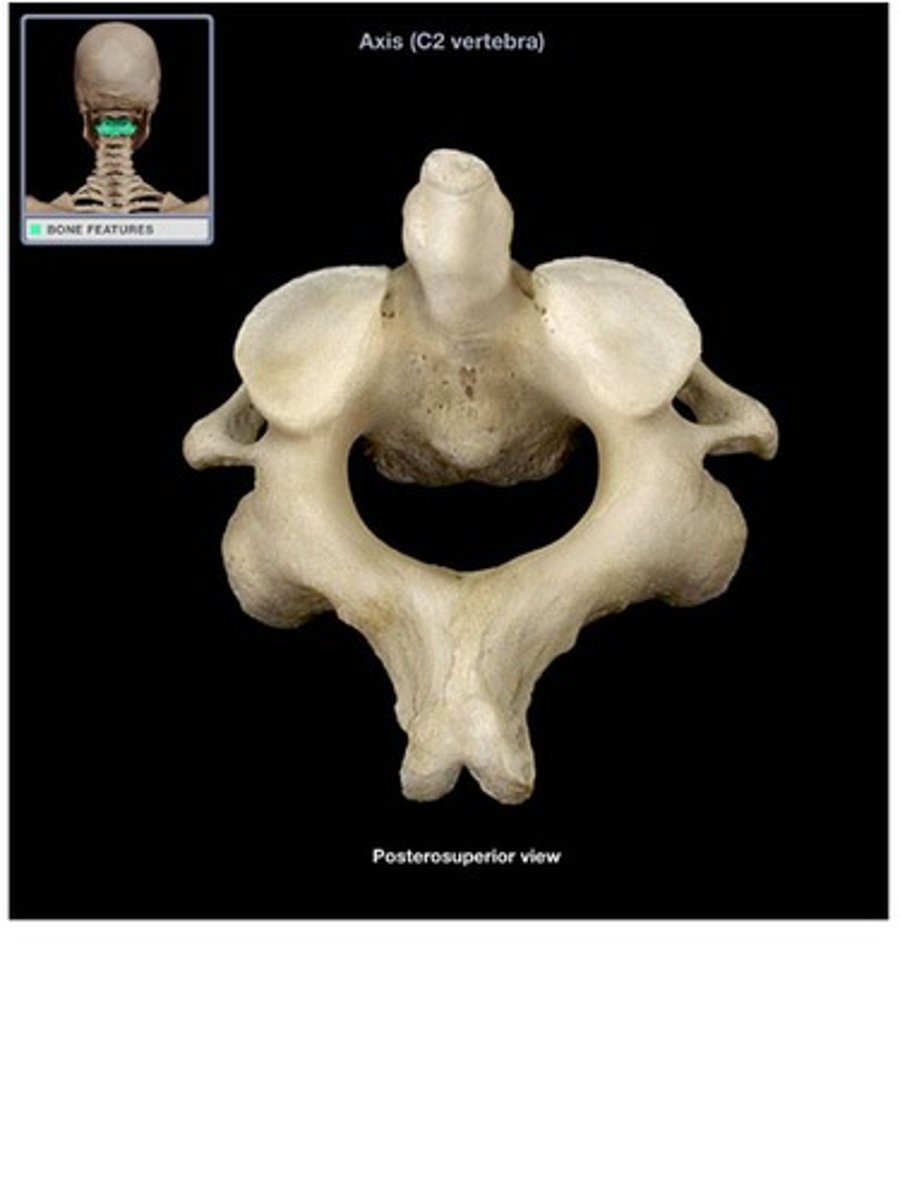
atlantoaxial joint
series of three articulations between the atlas (C1) vertebra and the axis (C2) vertebra, consisting of the joints between the inferior articular processes of C1 and the superior articular processes of C2, and the articulation between the dens of C2 and the anterior arch of C1
sacrum
bone formed from five vertebrae fused together near the base of the spinal column
what are the features of the sacrum
fused transverse processes, anterior and posterior sacral foramina, passage of the primary rami of the sacral nerves, roughened dorsal surface. median sacral crest with 4 tubercles (spinous process), make up the median acral crest. The lateral sacral crest is the remnants of the transverse process. Sacral ala and body and the sacral canal is continuous with the C5 foramen.
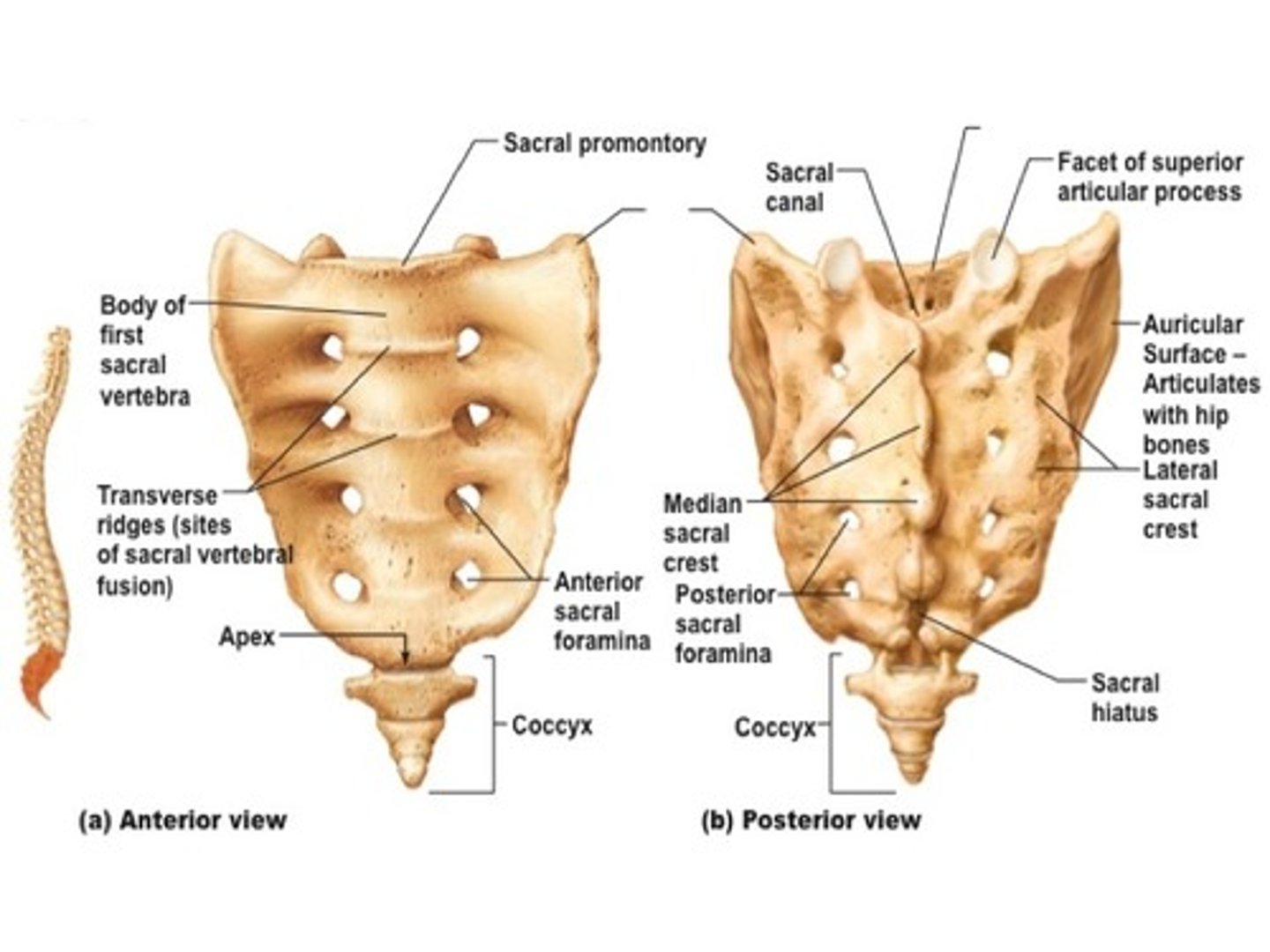
what does S5 tubercle not have that others do
tubercle, and no posterior element that fuse opens and normal defect.
what is the sacral hiatus used for clinically
epidural as there is no spinal chord as it finishes at S2
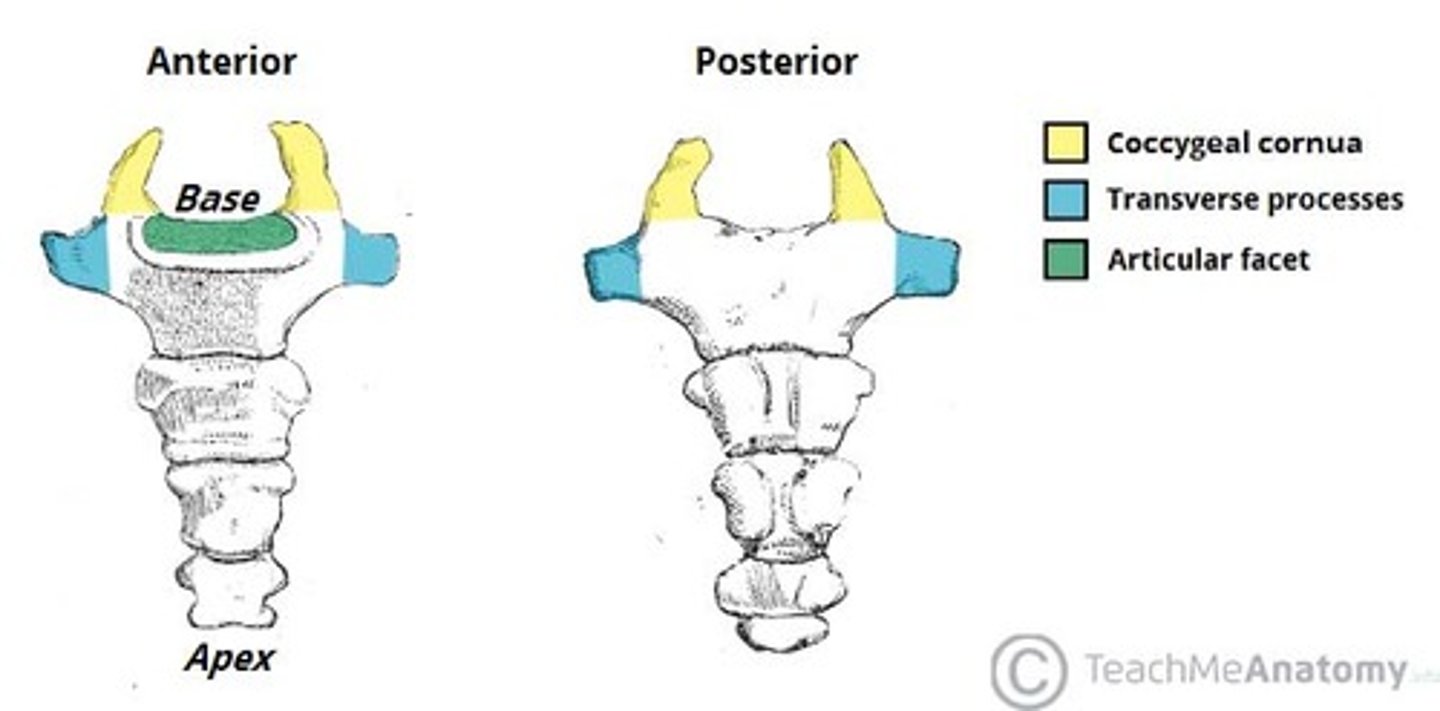
Coccyx segments
2-4 these articulate at the sacrococcygeal joint.
lumbosacral joint
pertaining to the joint between the last lumbar vertebra and the sacrum
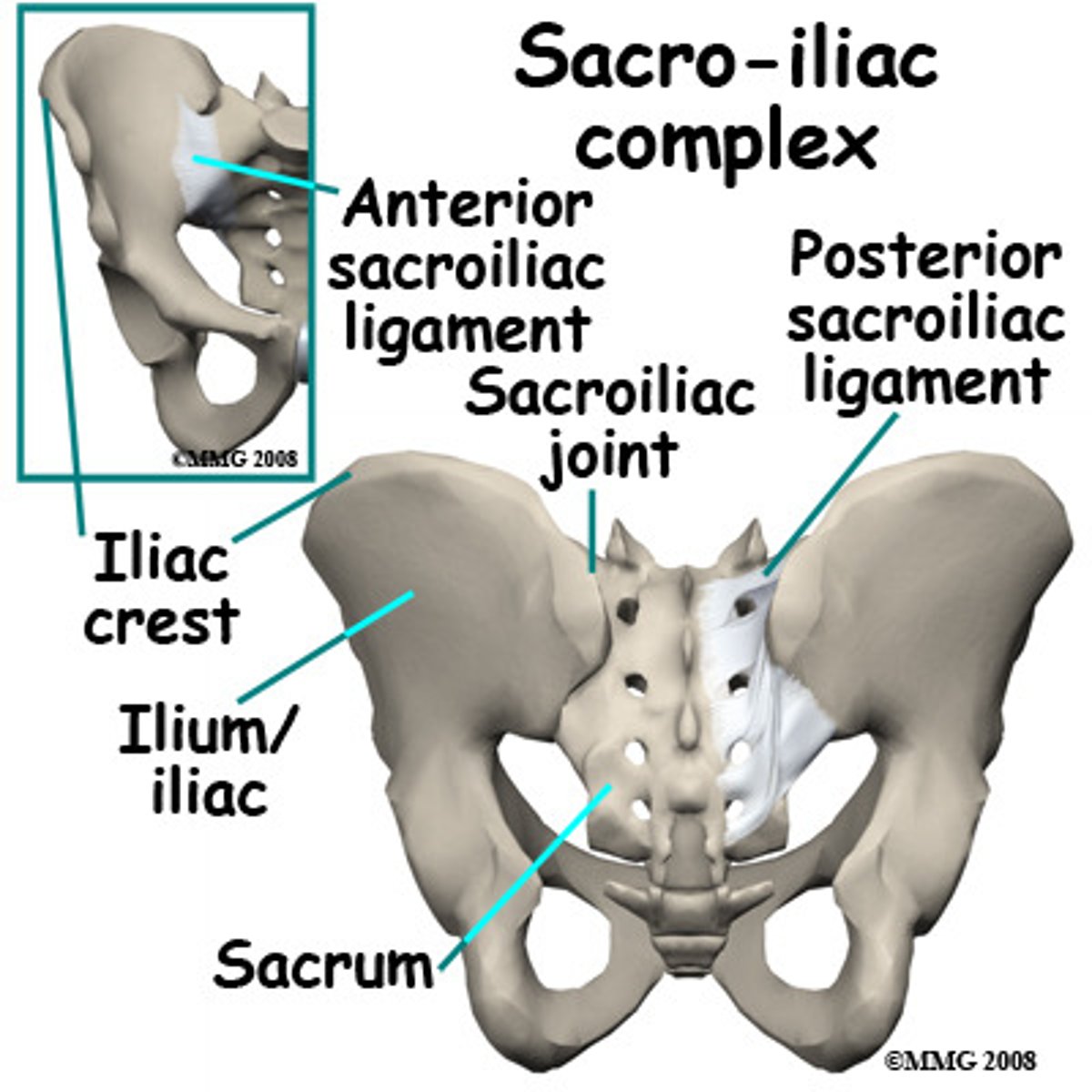
sacroiliac joint
the joint between the sacrum and the ilium
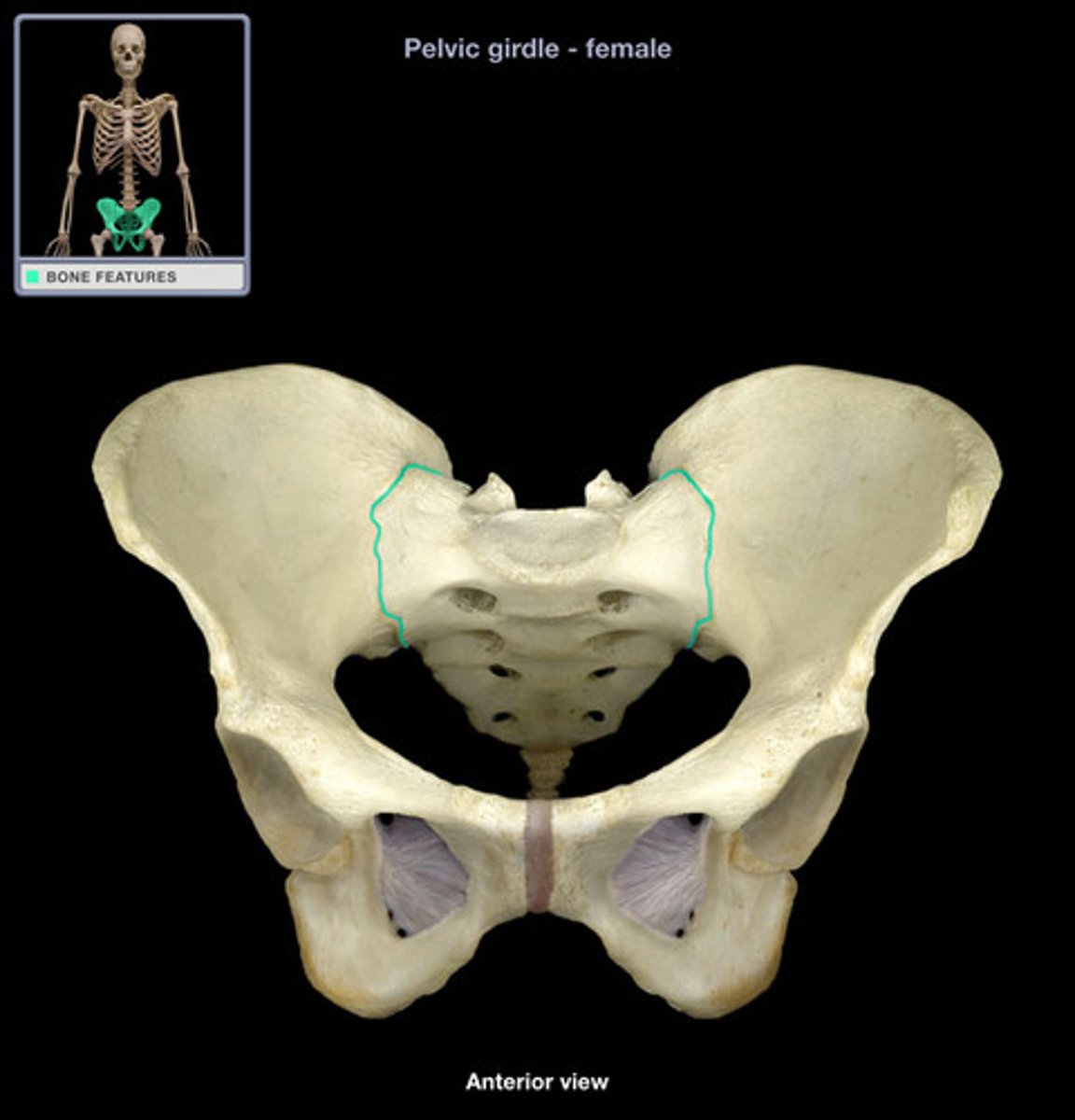
what movement does the sacroiliac joint have
not a great range 2-5 degrees, flexion extension and some rotation partly synovial partly syndesmotic.
on the sacral side what cartilage does the sacroiliac joint have
hyaline
on the iliac side what cartilage does the sacroiliac joint have
fibrocartilage
coccygeal cornu
hornlike projections found on each side of superior aspect of coccyx
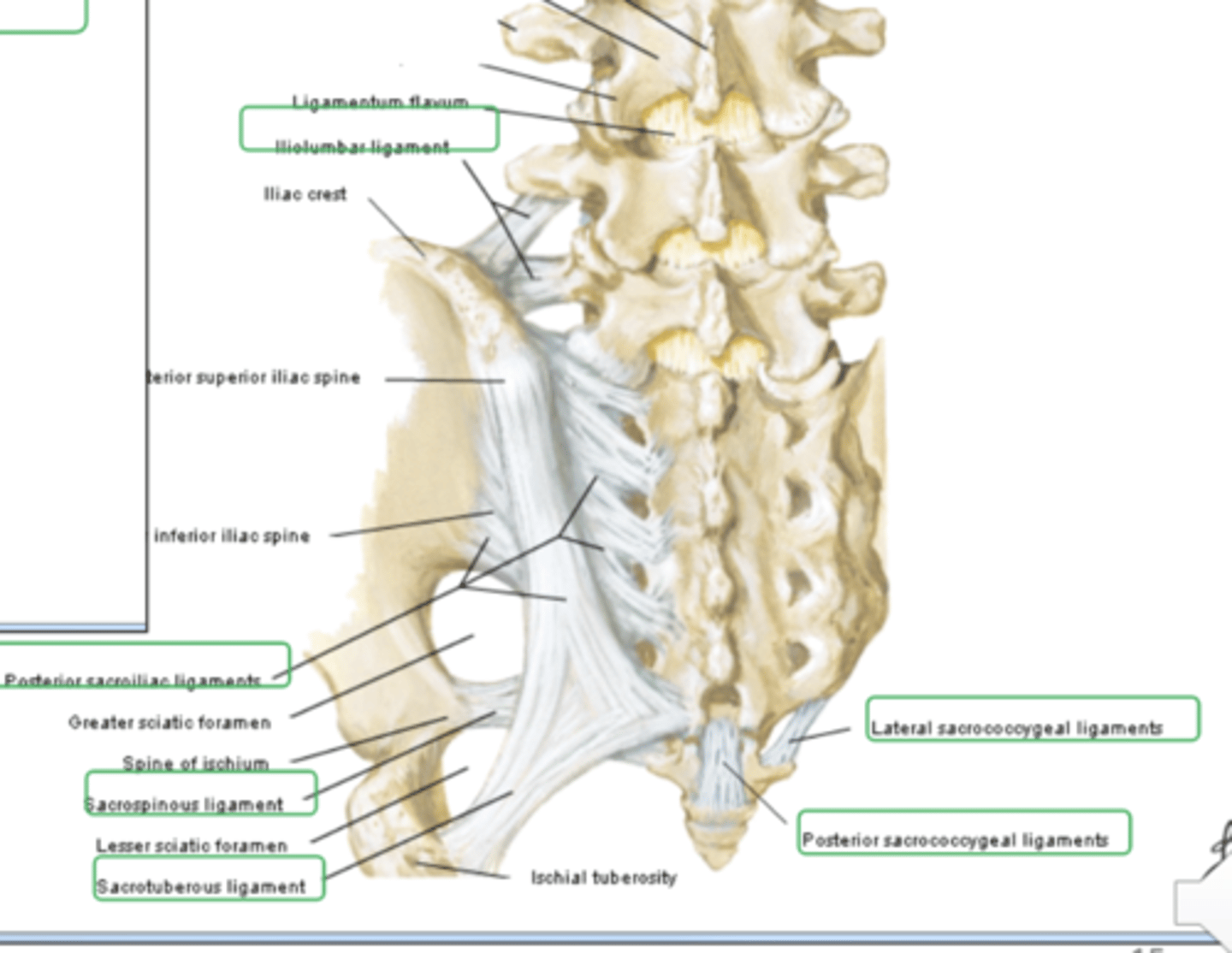
sacrococcygeal symphysis
between sacrum and coccyx
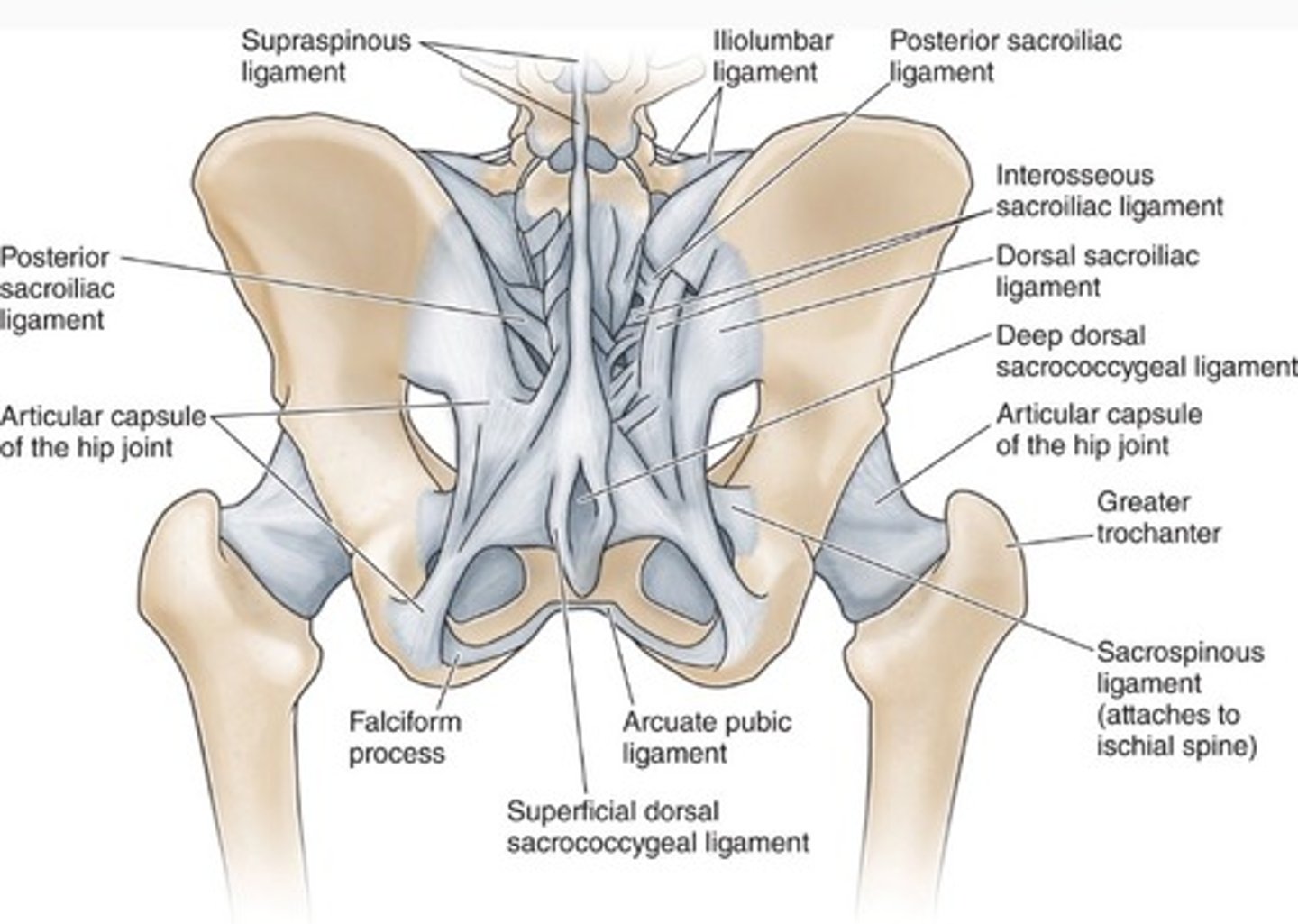
anterior and posterior sacrococcygeal ligaments
attach sacrum to coccyx
what movement does the sacrococcygeal symphysis
anterior and posterior movement
AP lower cervical
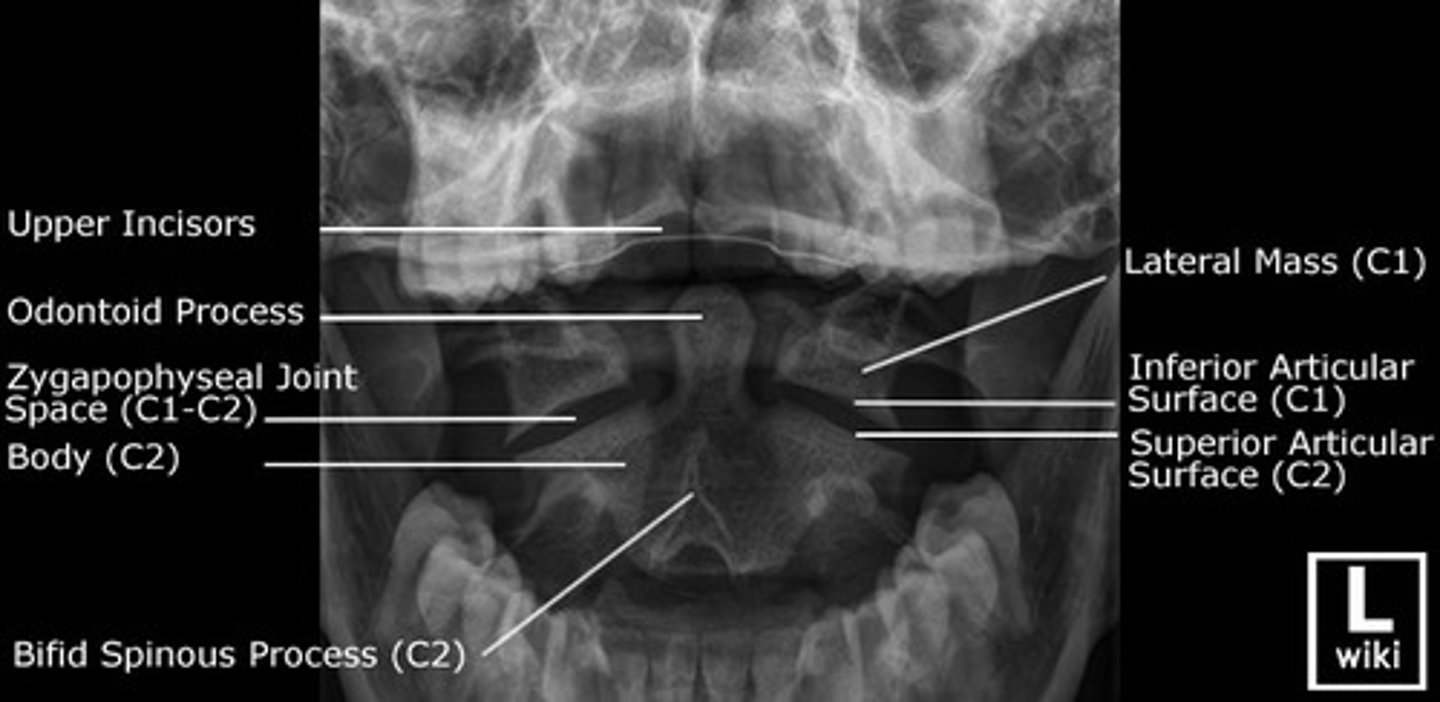
AP open mouth
Used to visualize C1 and C2
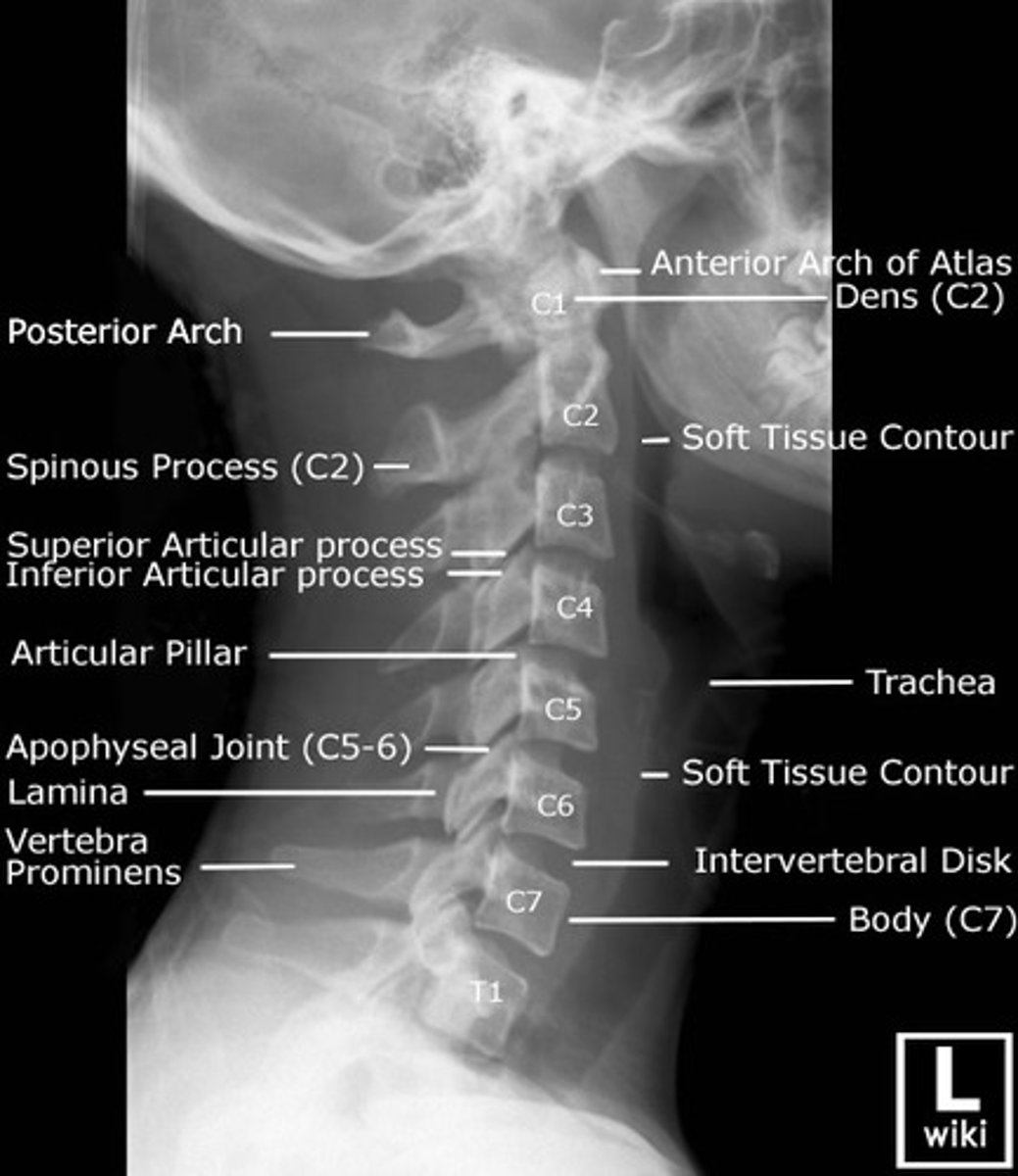
Lateral cervical
side of neck
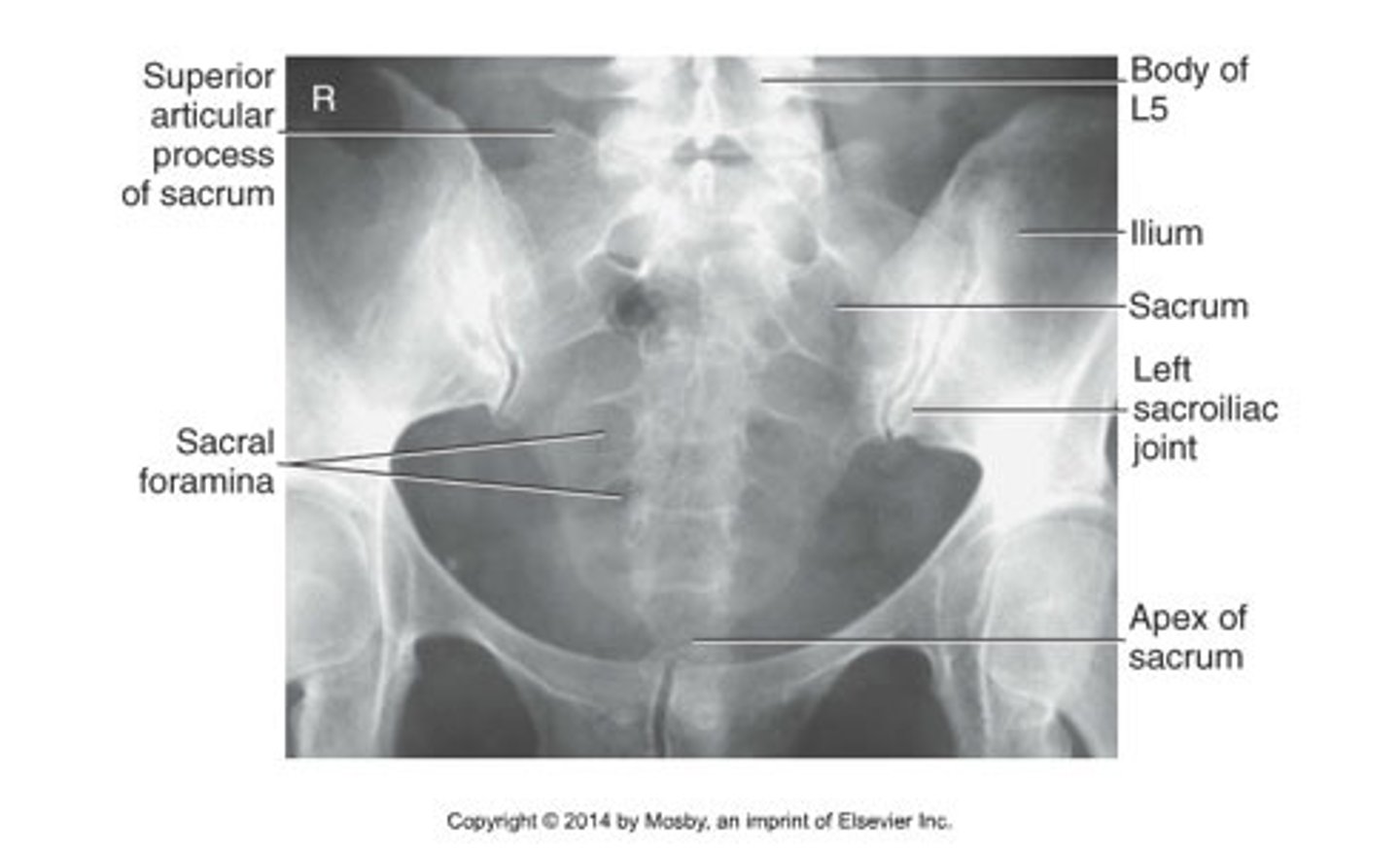
AP sacrum
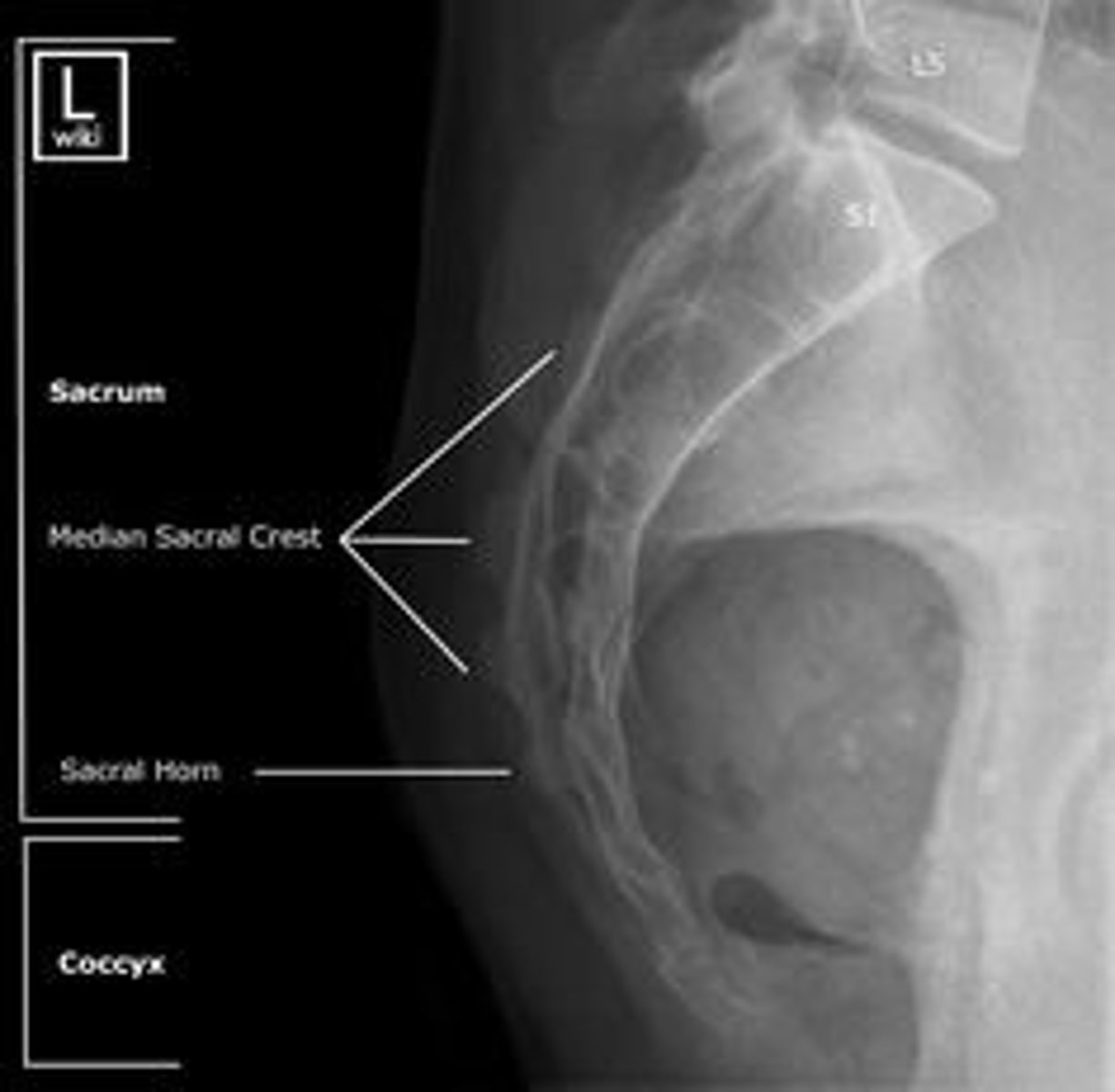
Lateral sacrum
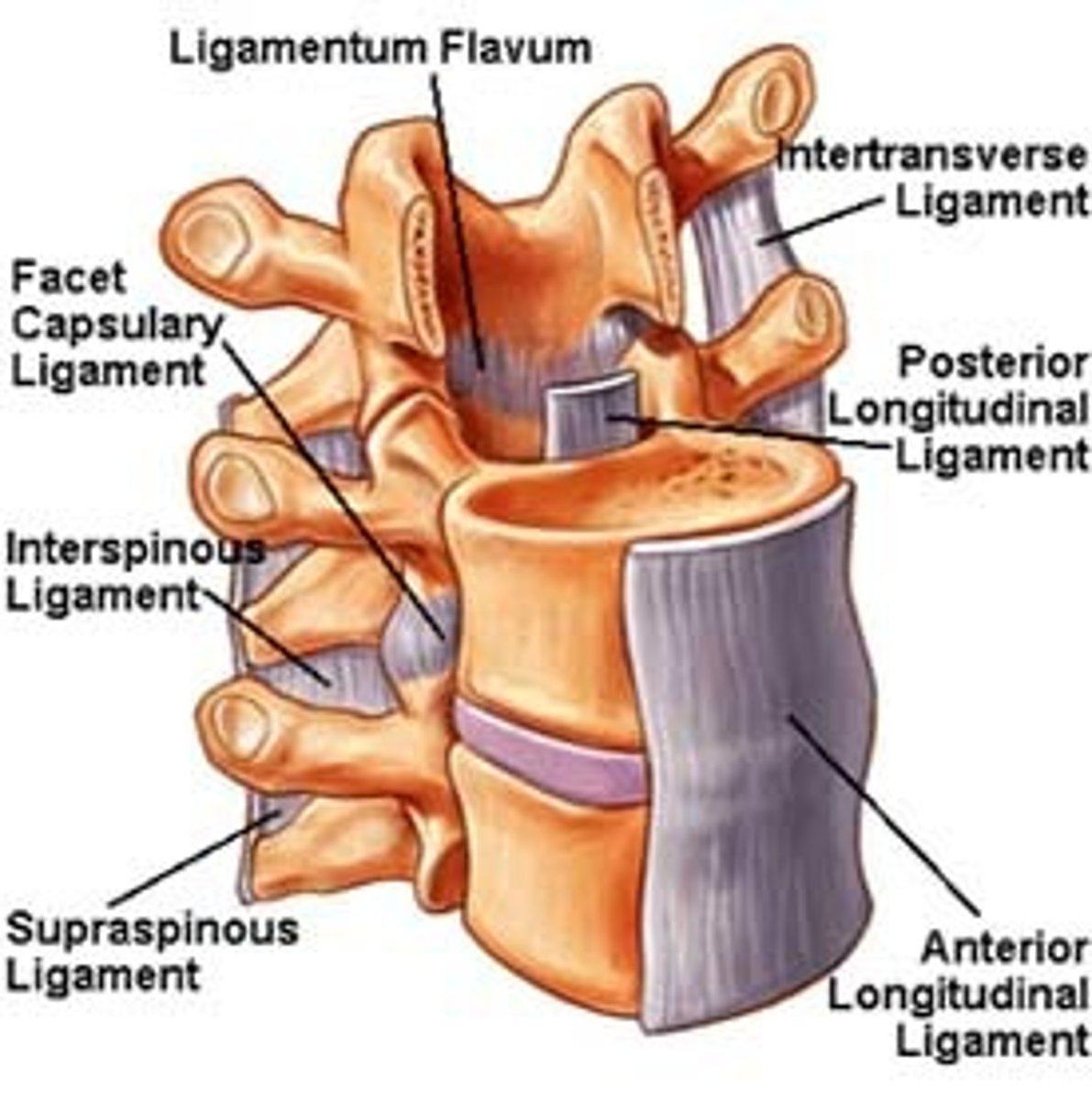
spinal ligaments
anterior longitudinal ligament, ligament flavum, supraspinous ligaments, interspinous ligament, capsular ligament, posterior longitudinal ligament
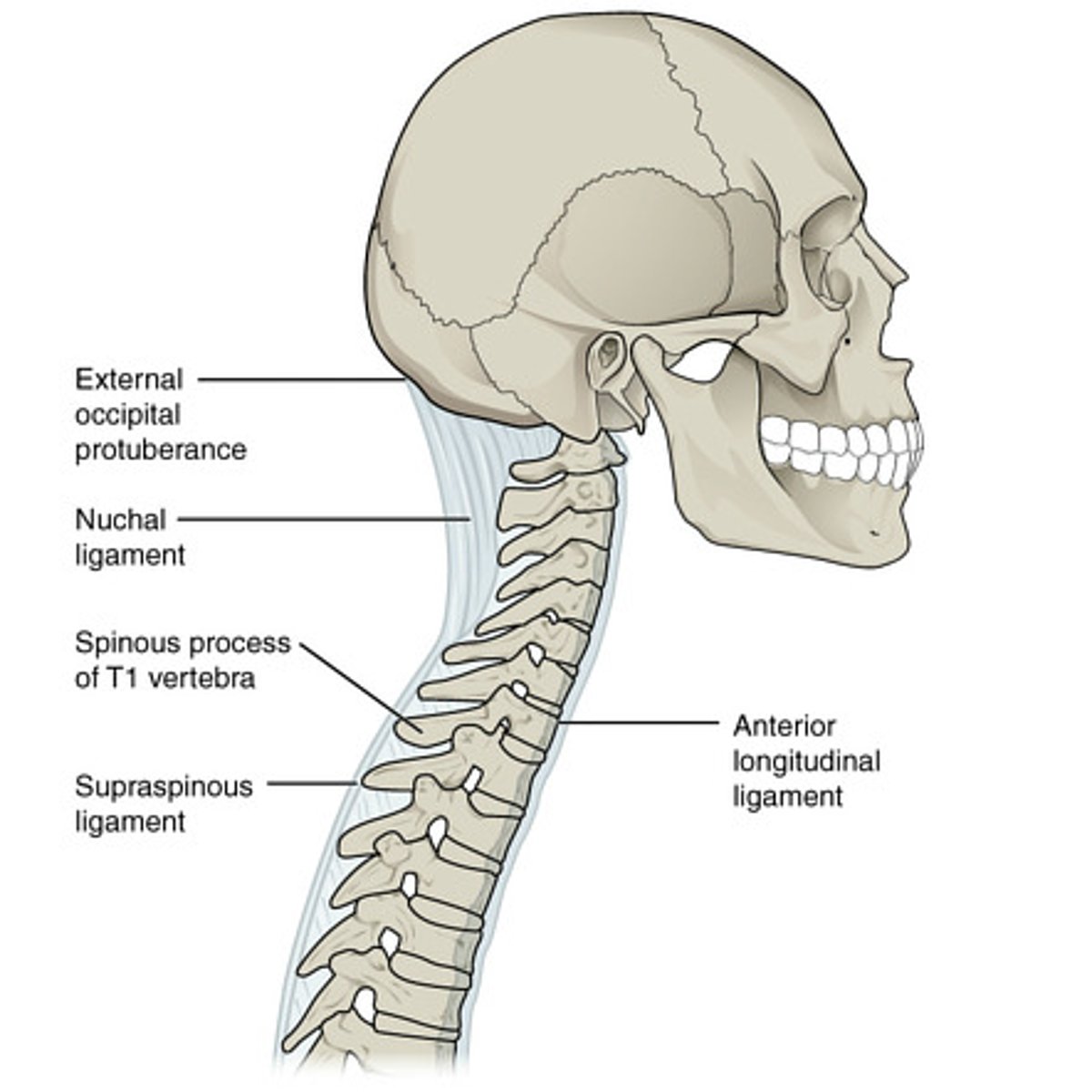
anterior longitudinal ligament
flow from C1 to sacrum inferiorly, anterior side of vertebral disks, assists to limit extensions of the whole spinal region
ligament flavum
between lamina to lamina. C1 to sacral canal, yellow due to elastin fibres. Restricts too much flexion
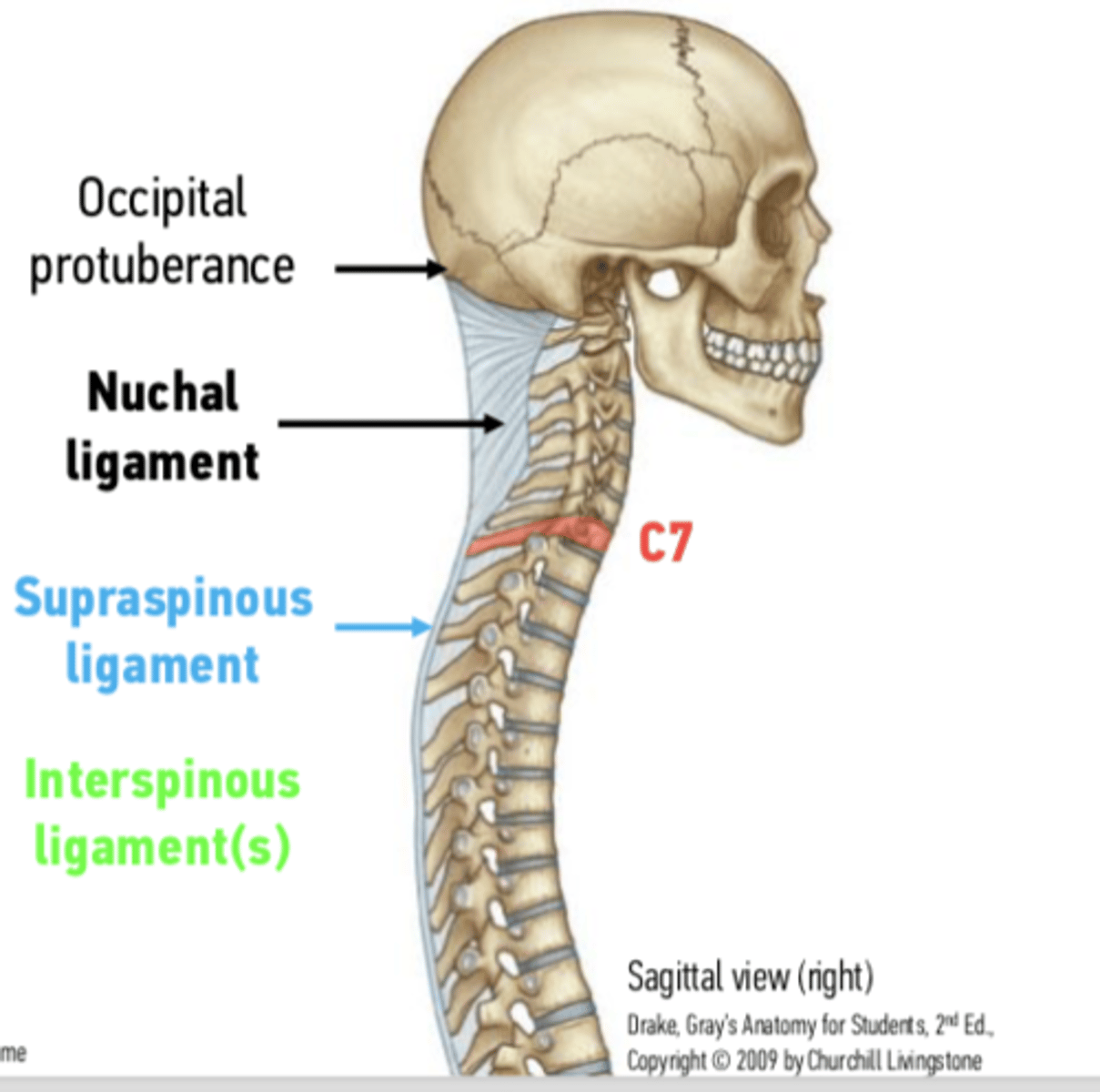
supraspinous ligament
tip of spinous process to tip of the spinous process of L5 up to become continuous with nuchal ligament, resists flexion
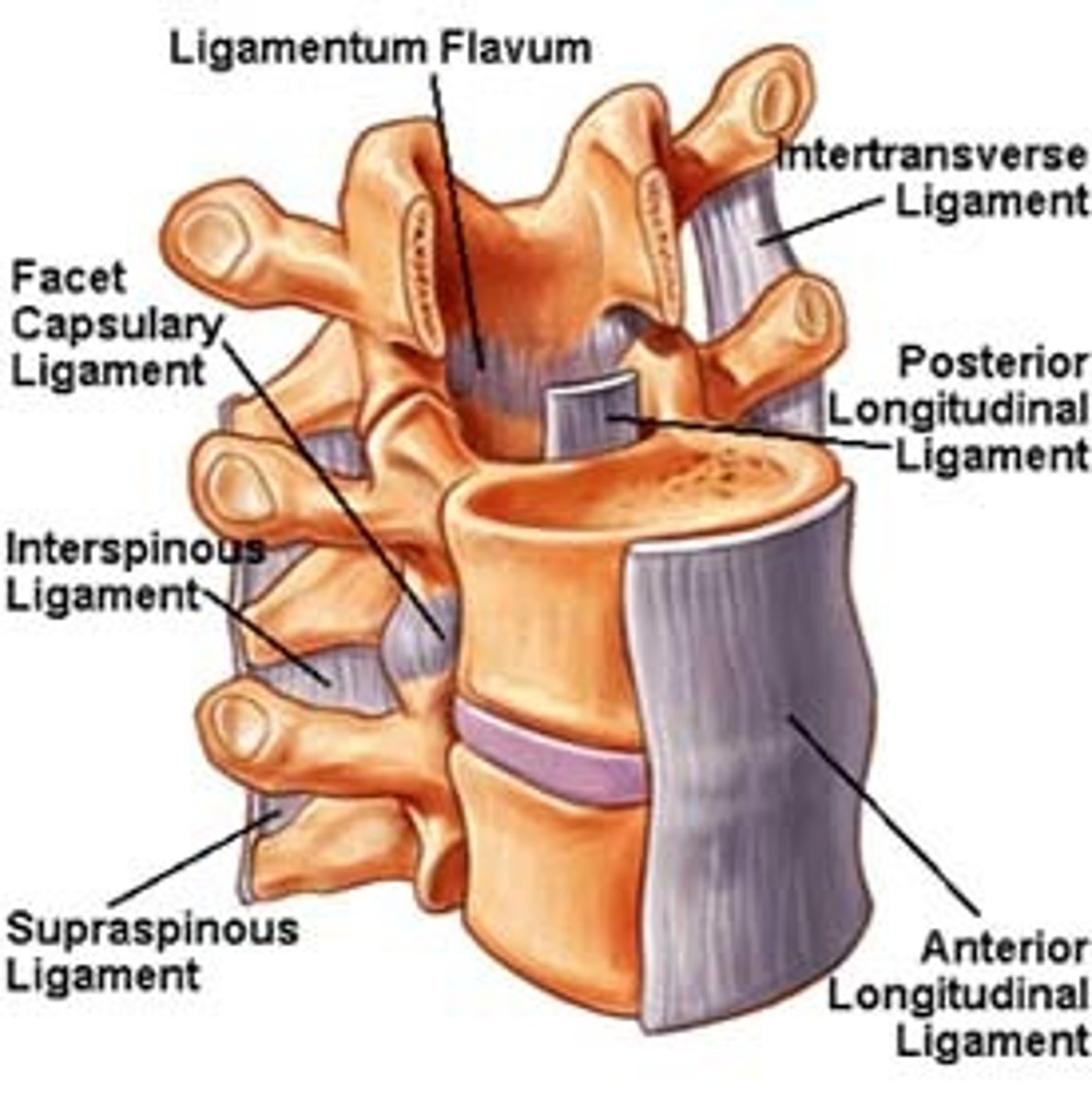
interspinous ligament
between spinous processes AP are long limited width. Lay largely midline resisting flexion
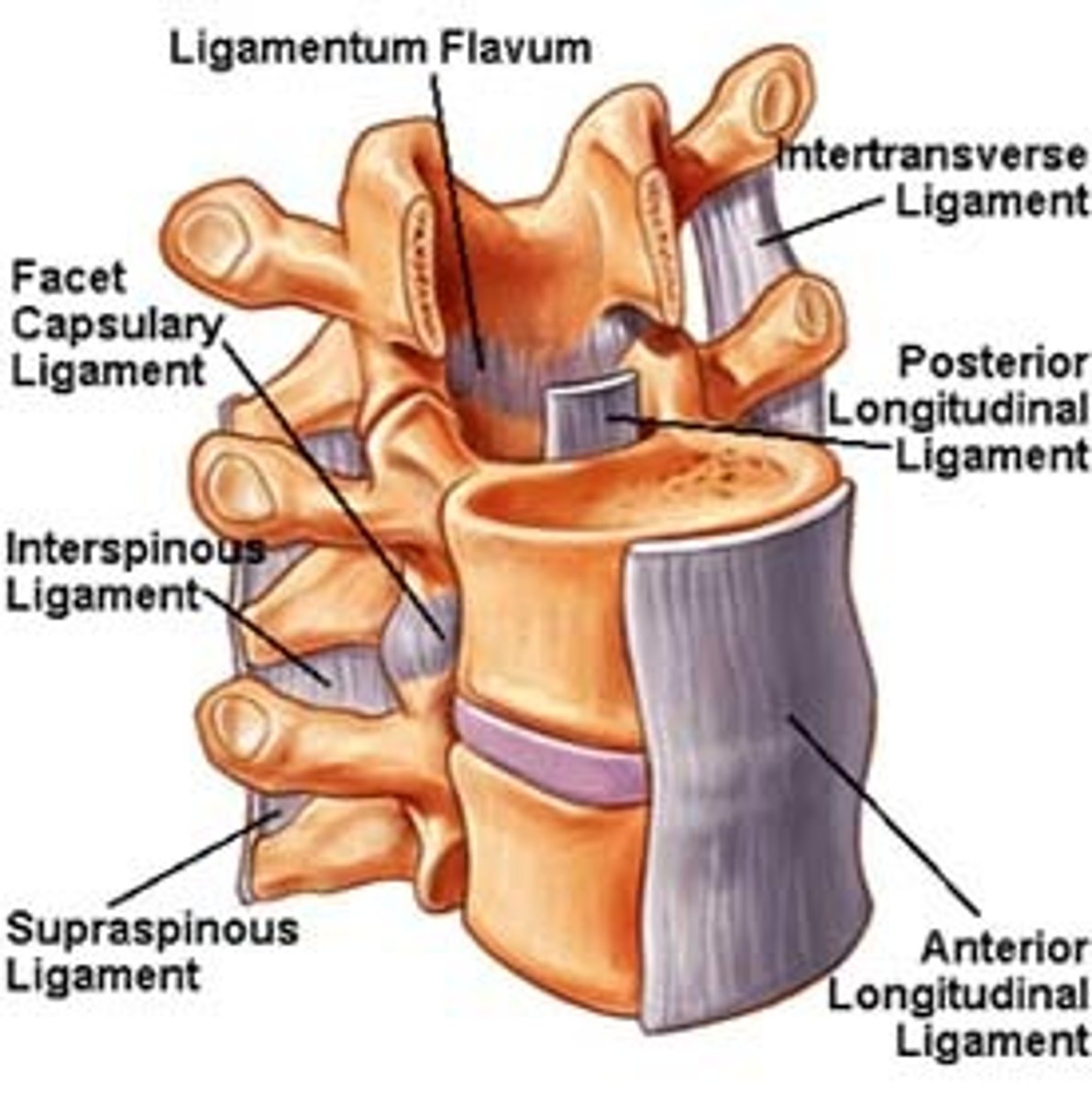
capsular ligament
facet joints are true synovial joints they have a capsule which is reinforced by this
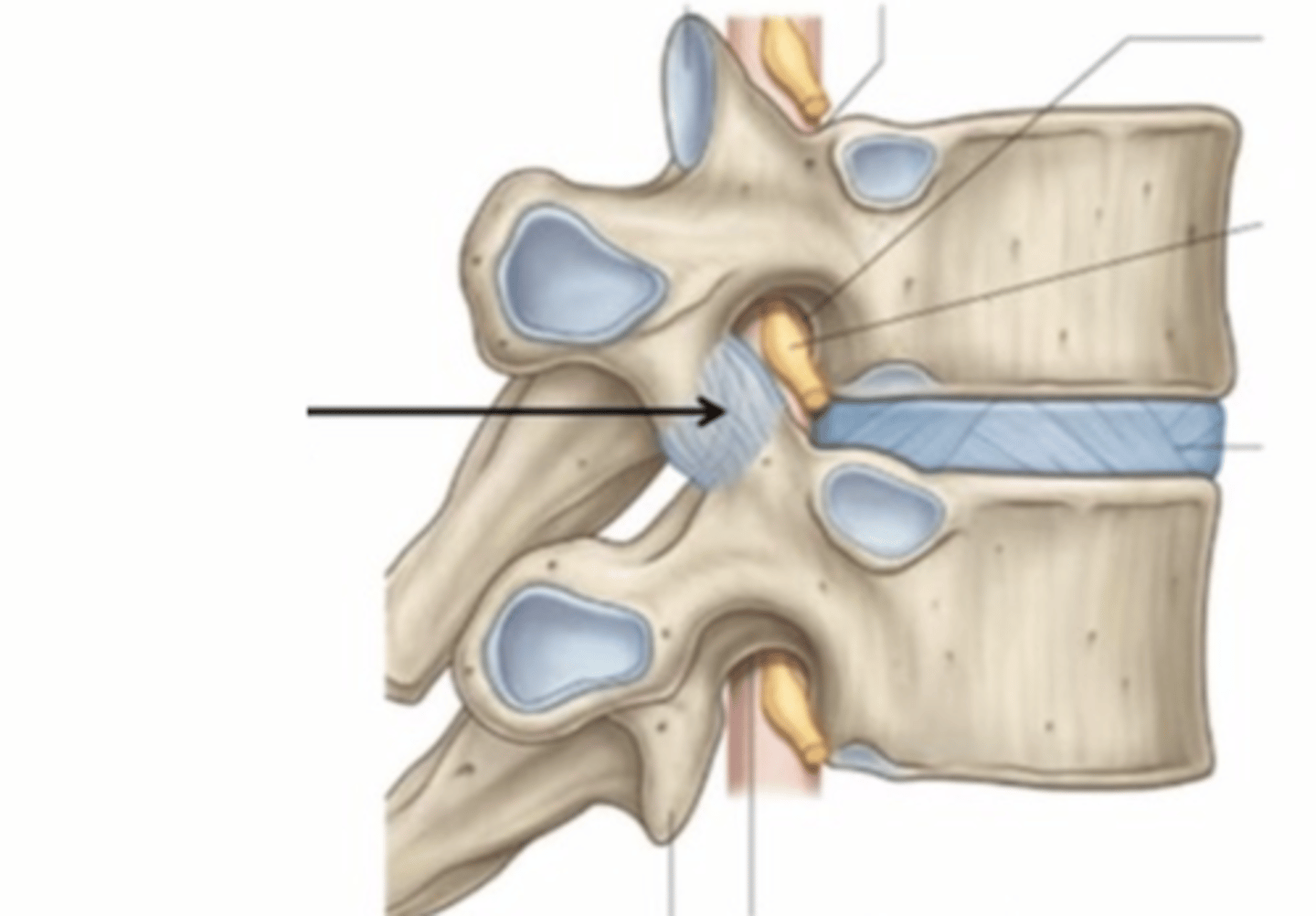
posterior longitudinal ligament
C2 - sacral canal strong connection to posterior of the annulus fibrosis of the intervertebral disks. Has a gap where posterior vertebral body is. This is due to the vein that needs to drain the medullary cavity of the vertebral body,
what vein drains the medullary cavity of the vertebral body
basivertebral veins
Ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament
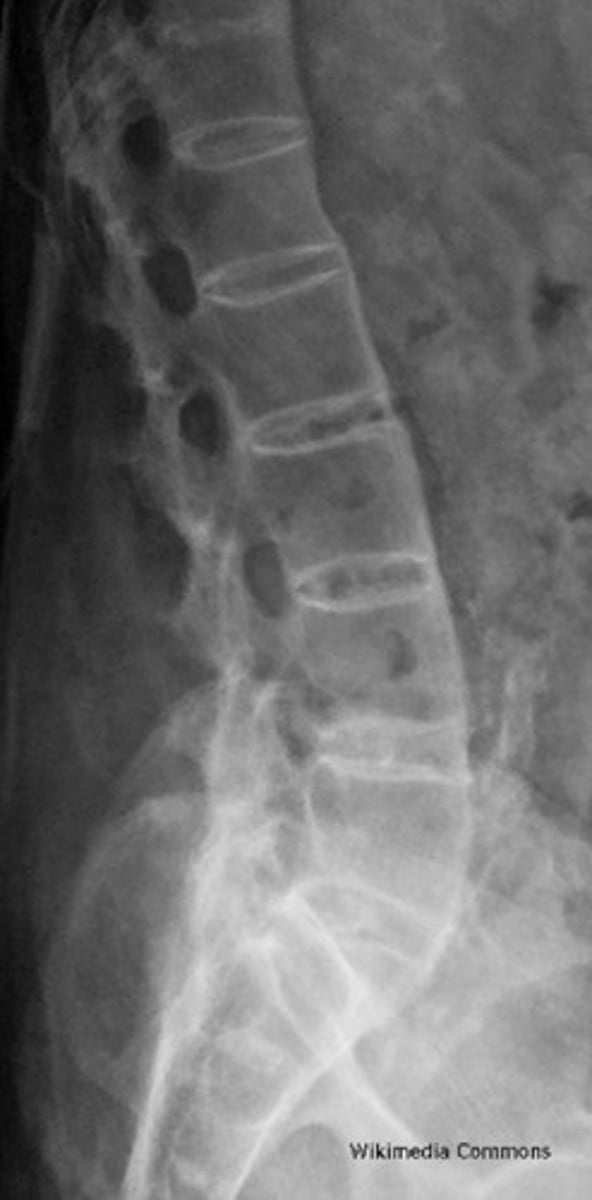
ossification of the interspinous ligament and supraspinous ligament
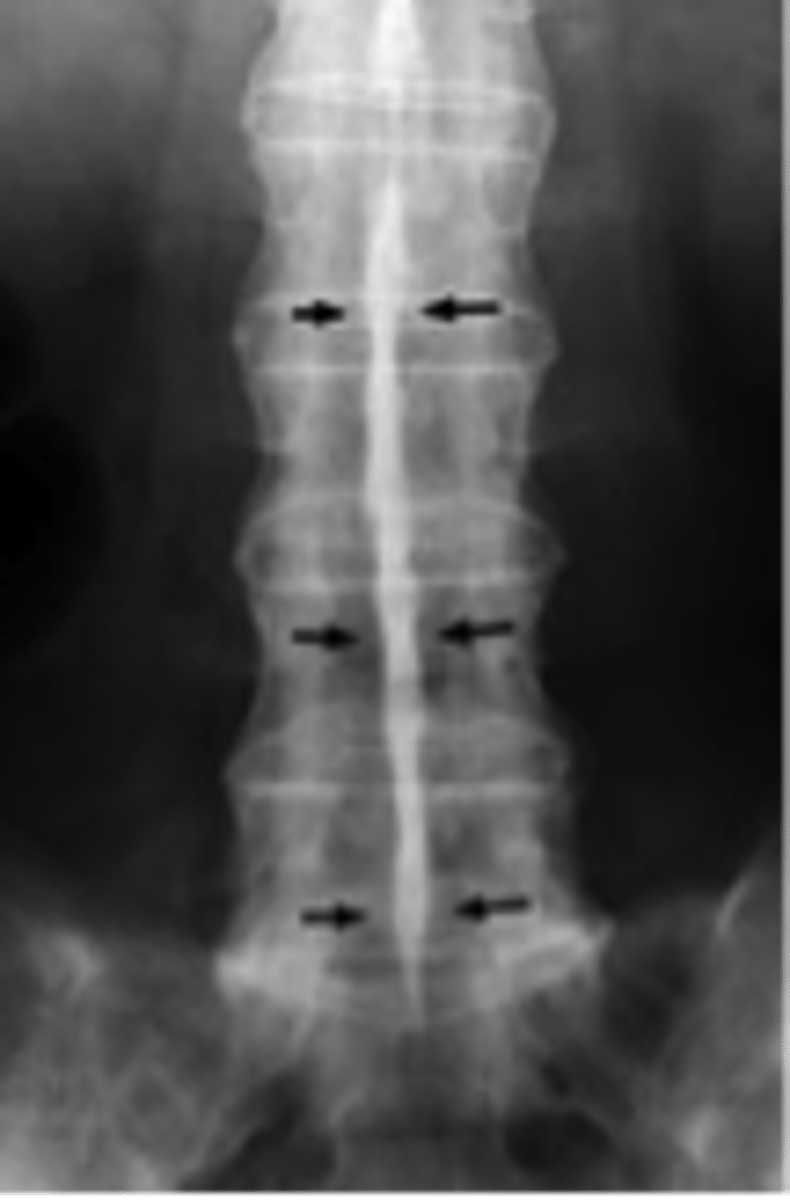
what happens when ligaments ossificate
less movement loss of joint space
lumbosacral ligament
iliolumbar ligament, short posterior sacroiliac ligaments long posterior sacroiliac ligament, posterior sacrococcygeal ligament, anterior sacroiliac ligament, nuchal ligament, cruciform ligament alar ligament
iliolumbar ligament
from iliac crest towards the transverse process L4 to L5
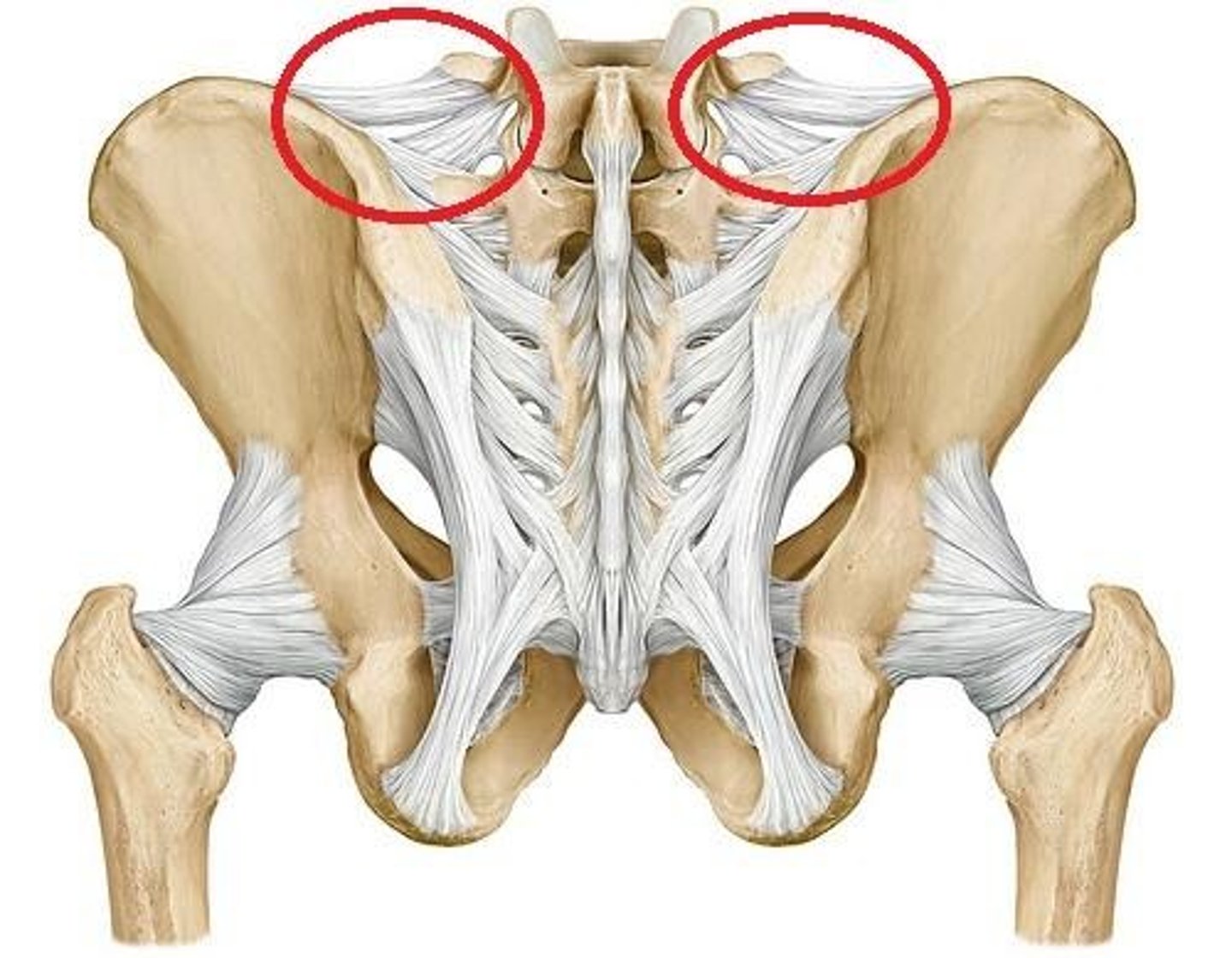
short posterior sacroiliac ligaments
from iliac crest to the dorsal access of the sacrum
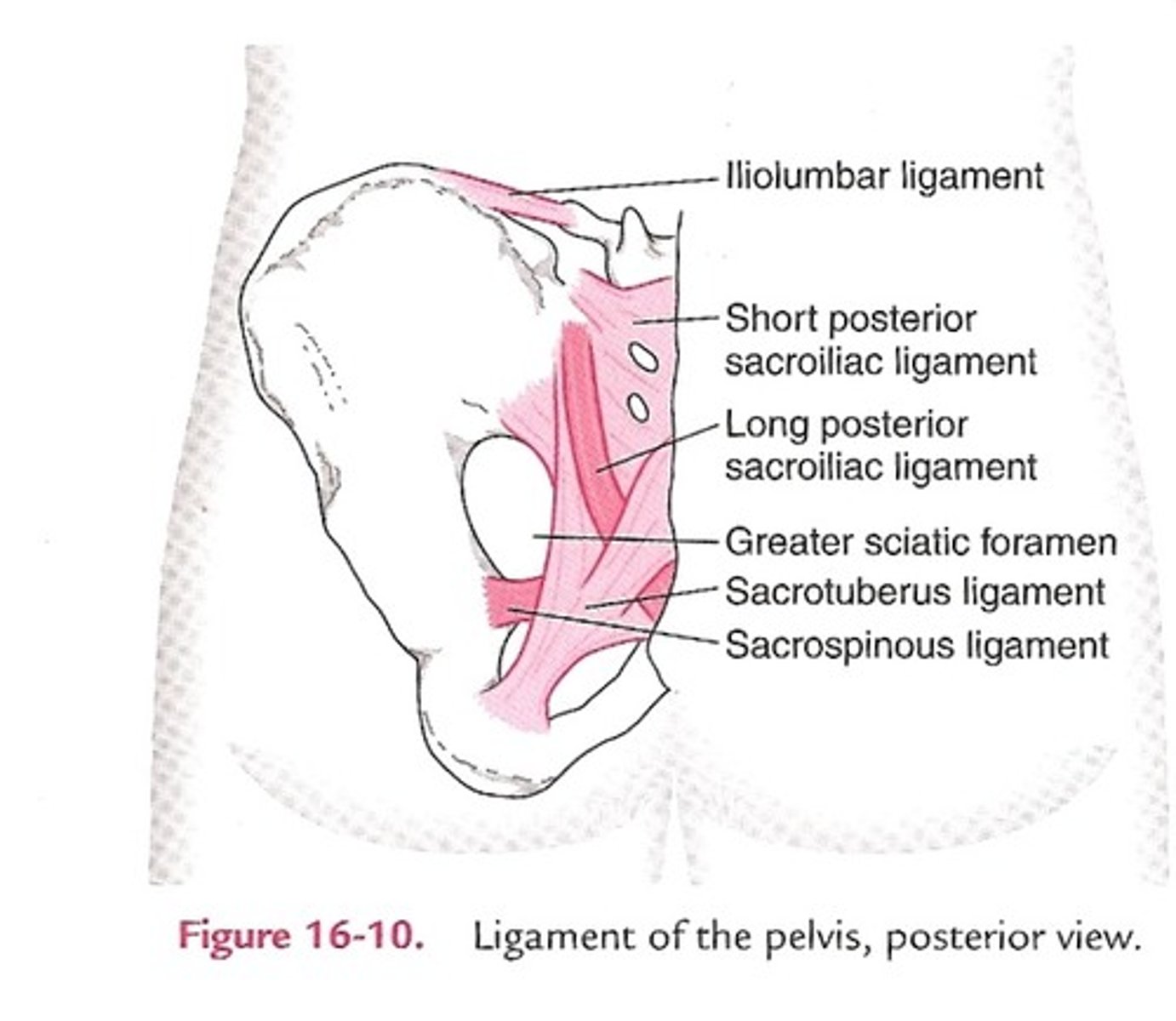
long posterior sacroiliac ligament
comes down to fuse with Sacro tuberous ligament
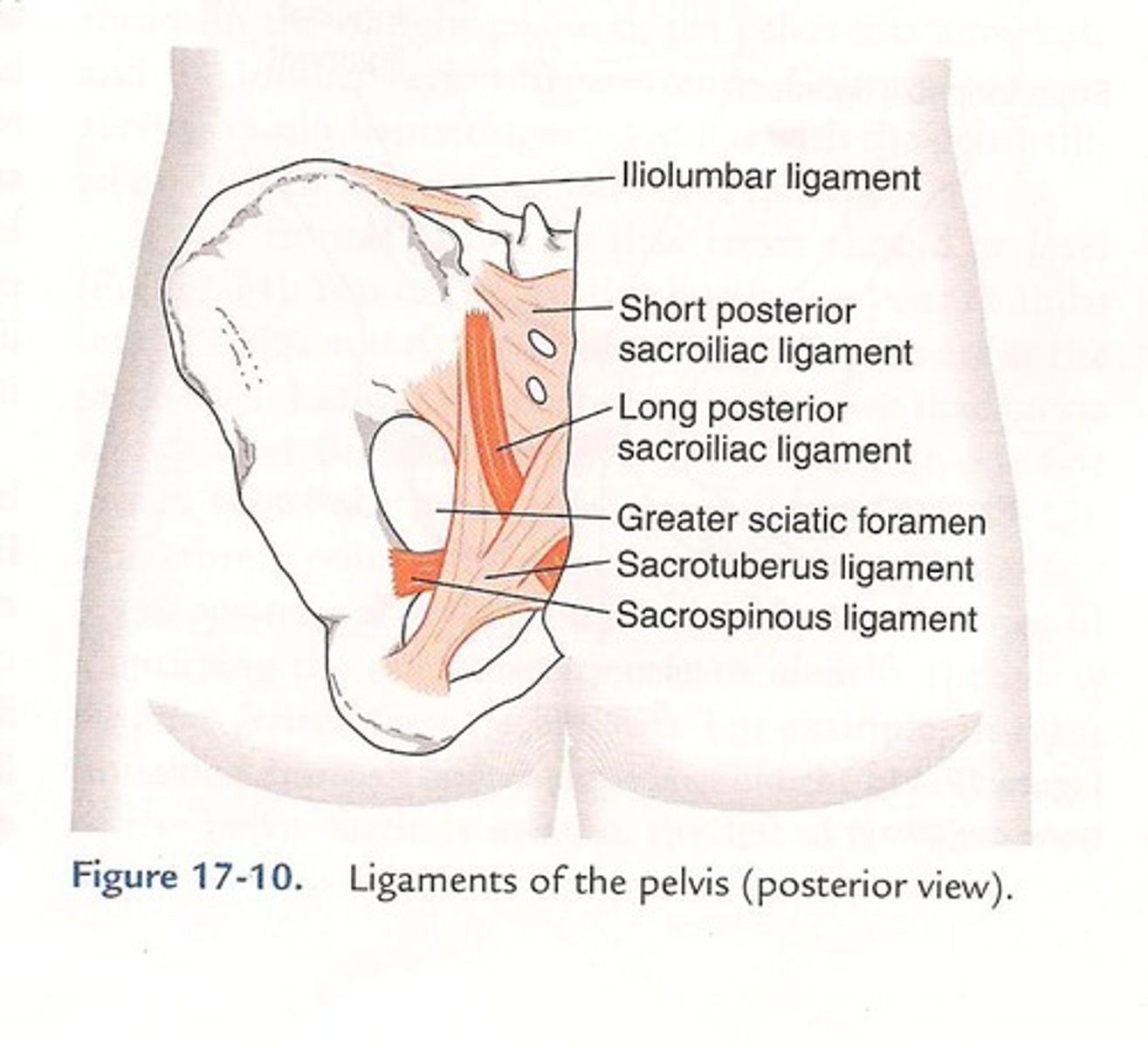
posterior sacrococcygeal ligament
between dorsal aspects of sacrum and coccygeal reinforces sacrococcygeal joint
anterior sacroiliac ligament
strong ligament between the sacrum and the ilium portions of the hip bone that supports the anterior side of the sacroiliac joint
Nunchal ligament
this is homologues to the supraspinous ligament, tips of cervical vertebrae, limits flexion of the neck and extends from external occipital tuberance process to C7. Provides attachment sites for cervical muscles
cruciform ligament
ligament longitudinal posterior side of the C2 vertebral body to anterior part of the foramen magnum transverse between lateral mass of axis to the lateral mass of the axis on contralateral side
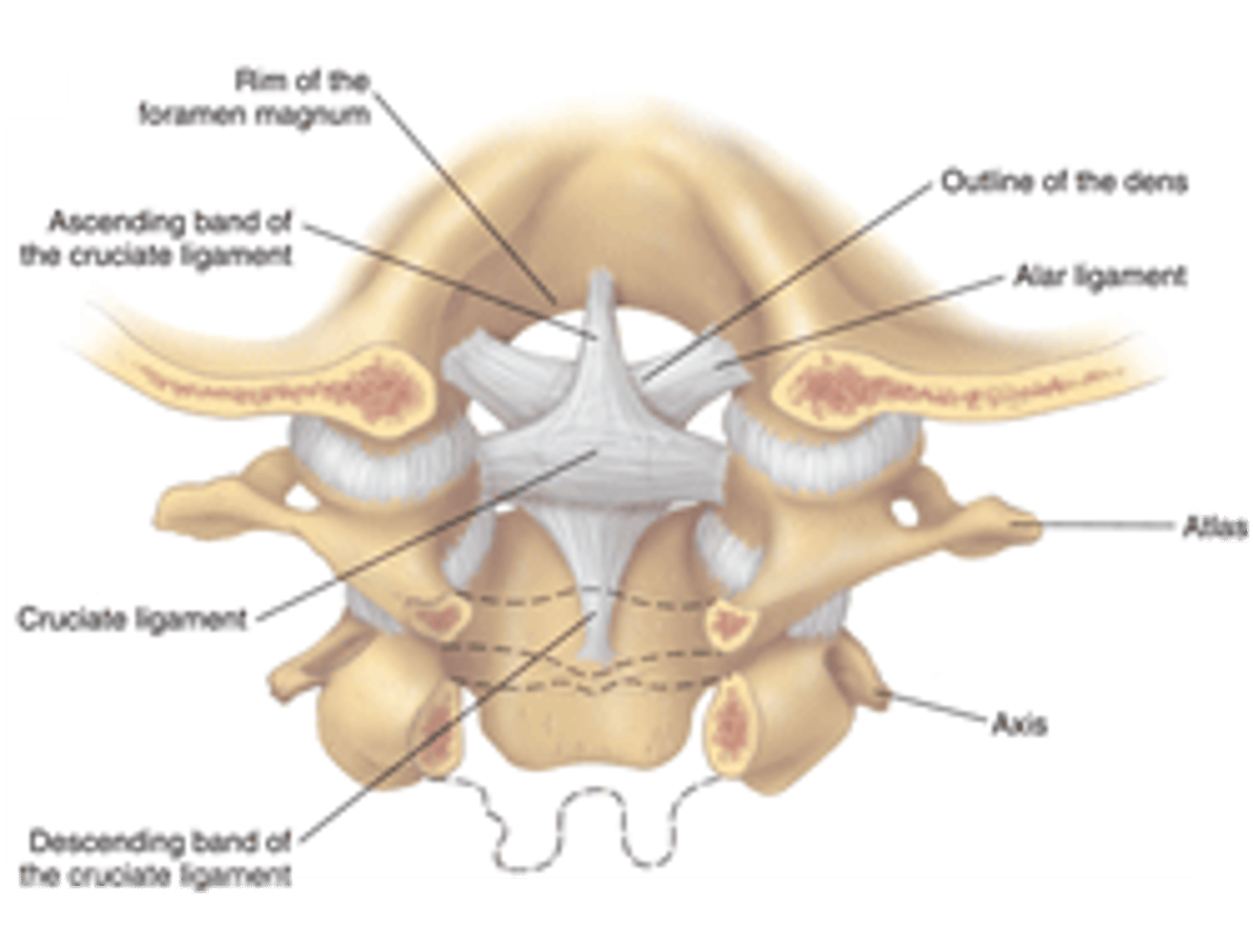
foramen magnum
A large opening at the base of the skull through which the brain connects to the spinal cord.
what does the transverse cruciform ligament prevent
the dense from moving posteriorly into the C1 vertebral foramen and compress whatever is in it we will lose stability in the medial atlanto axial joint and too much flexion and extension
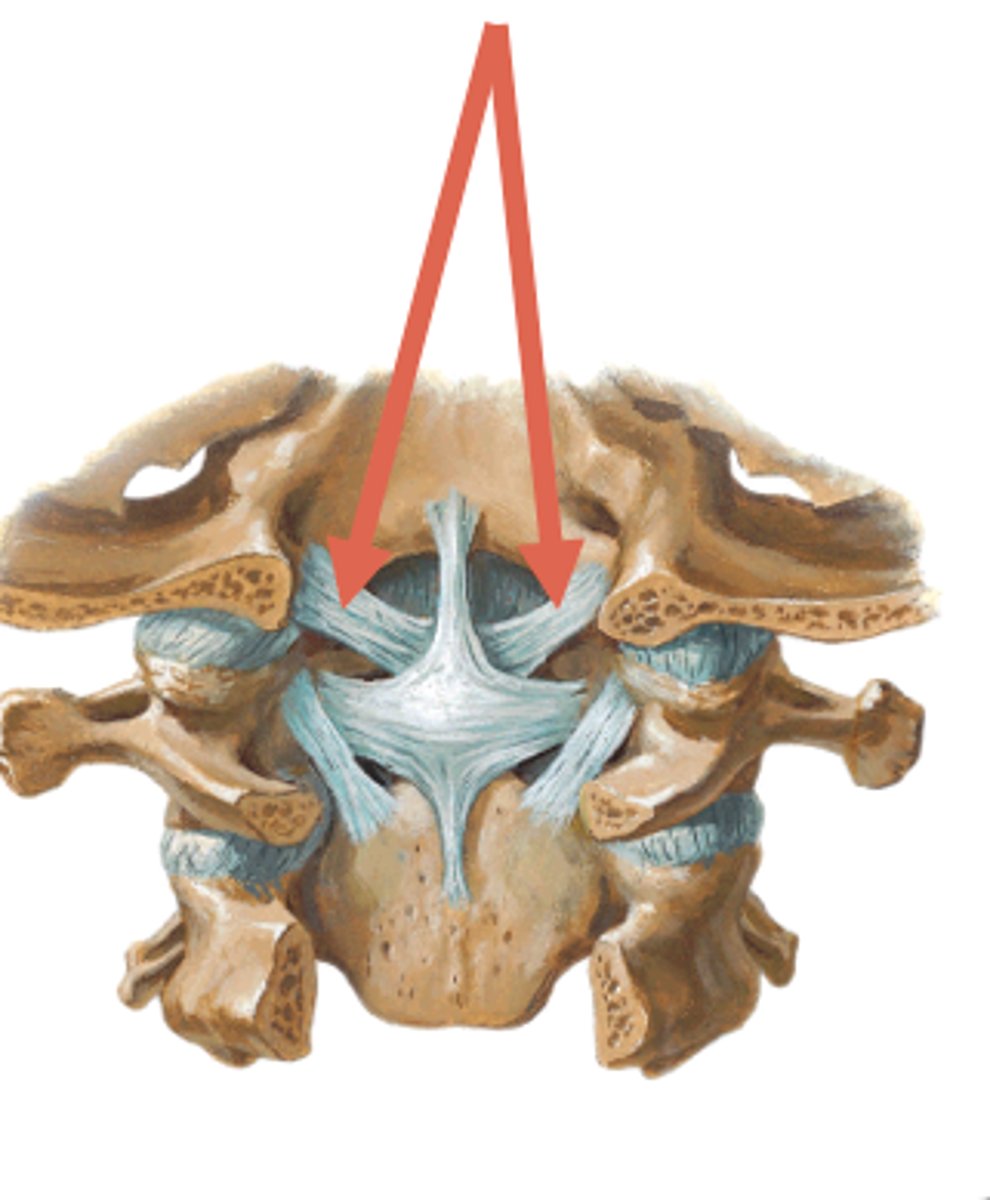
alar ligament
tip of dens to the cruciform ligament and insets onto the lateral margins of the later foramen, limits lateral flexion and rotation too much movement means risk of compression of the brain
tectorial membrane
continuation of posterior longitudinal ligament to the anterior margin of the foramen magnum
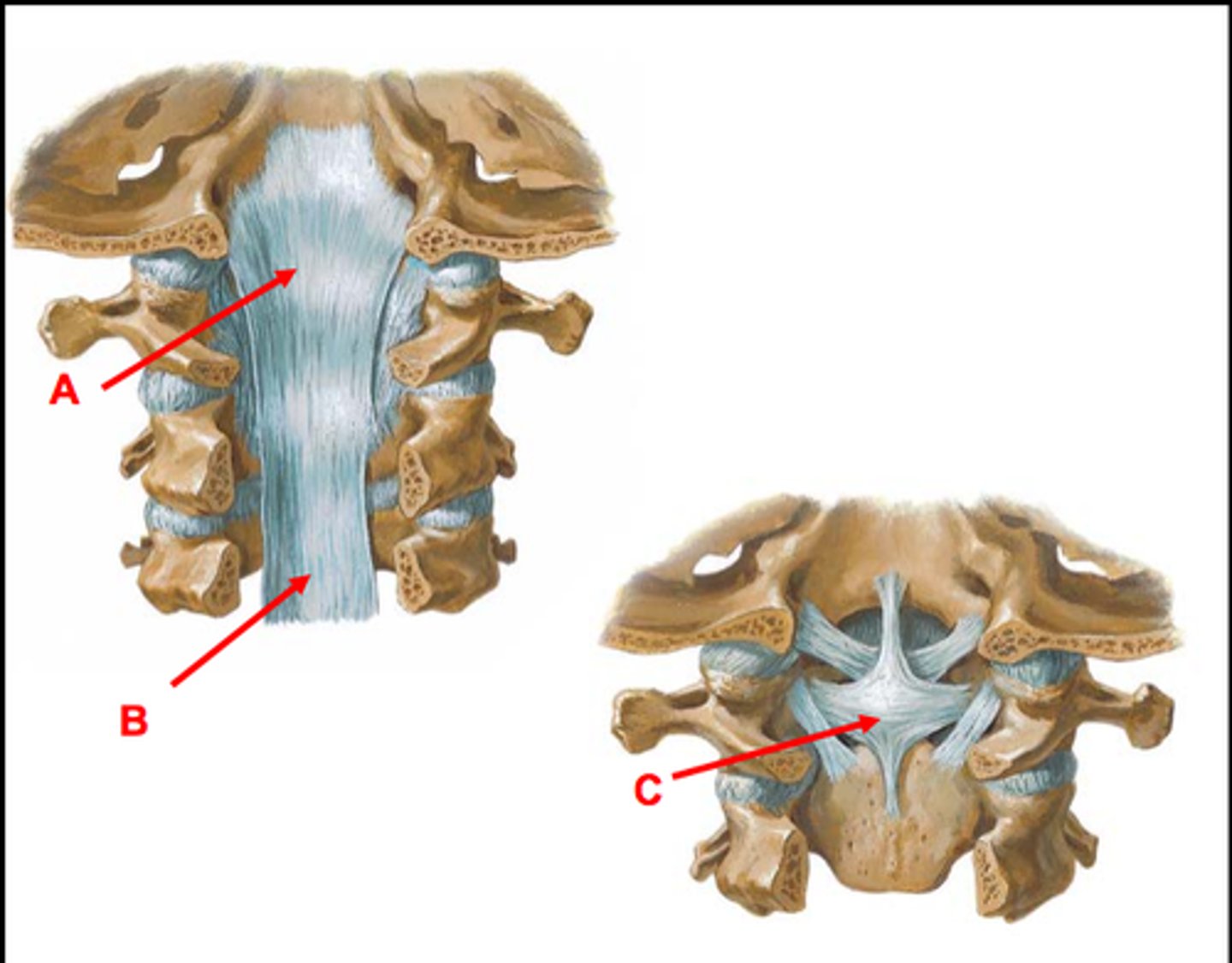
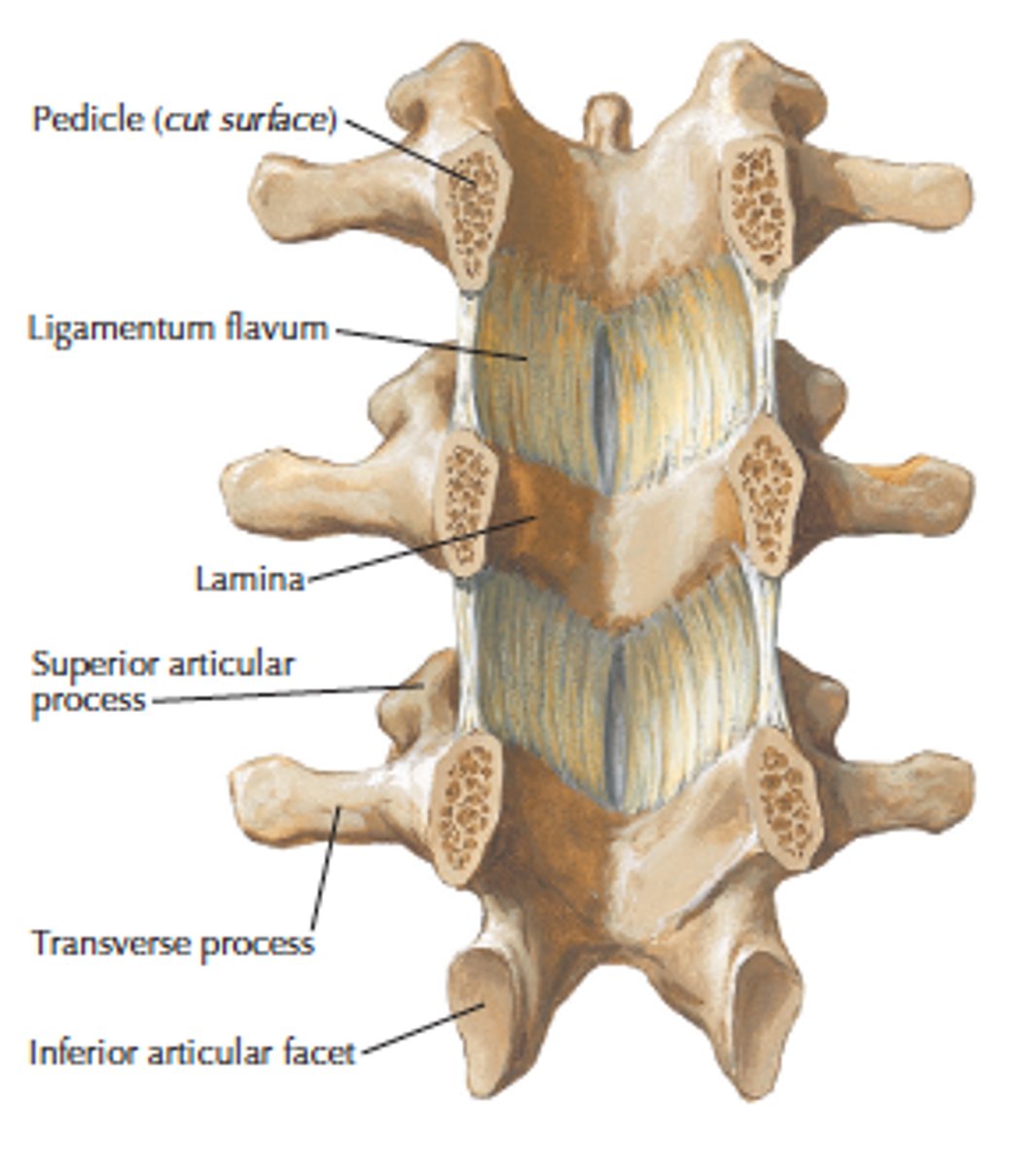
vertebral foramen boarders
by vertebral body, pedicle and intervertebral foramina, lamina and spinous process and or ligaments
what does the vertebral foramen contents
spinal chord, meninges nerve rooms epidural fat
what is the spine supplied by
anterior and posterior spinal arteries, anterior branch from vertebral artery, posterior from vertebral artery, anterior lives in the anterior median fissure, posterior just laterally to the posterior lateral sulcus basivertebral artery and internal vertebral plexus
Larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
What are the 3 unpaired cartilages of the larynx?
thyroid, cricoid, epiglottis
What are the 6 paired cartilages in the larynx?
retinoid, corniculate, cuneiform
Where does the larynx lie?
between the pharnyx and trachea and C3-6
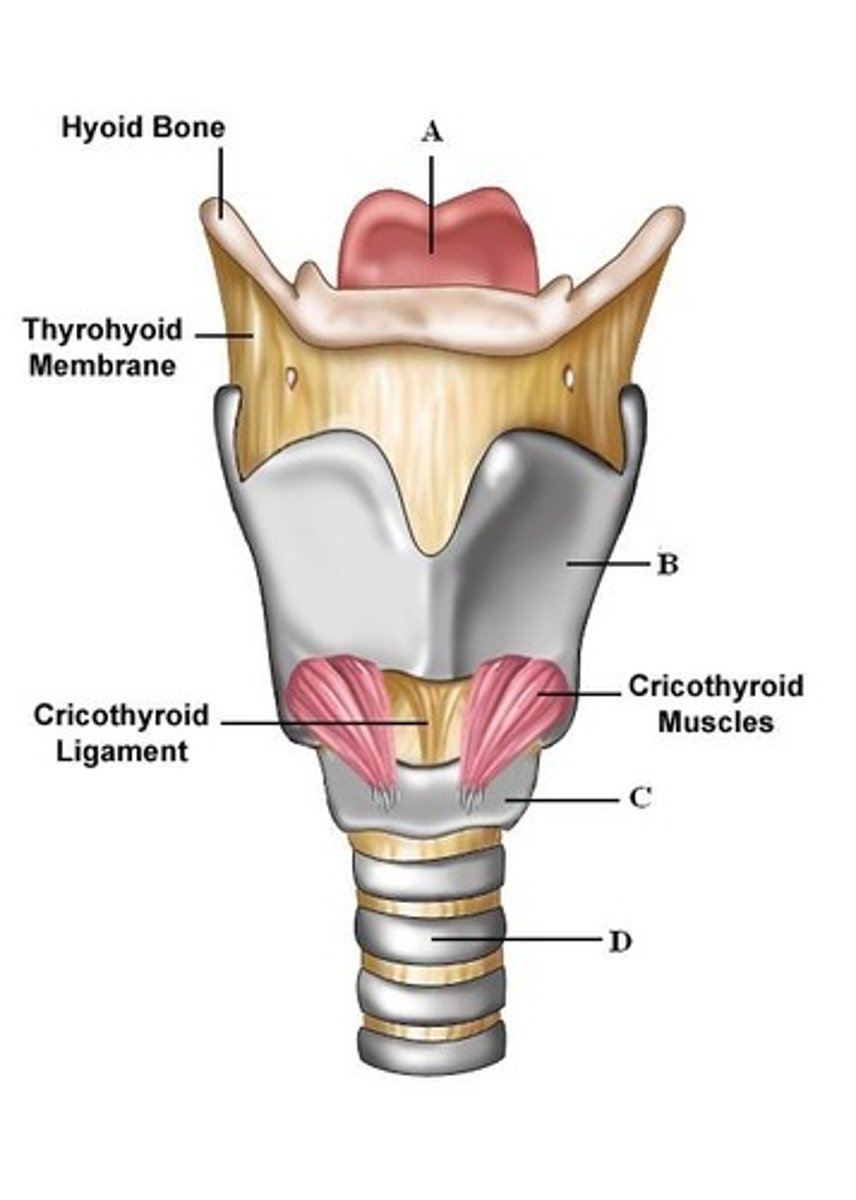
hyoid bone
a U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
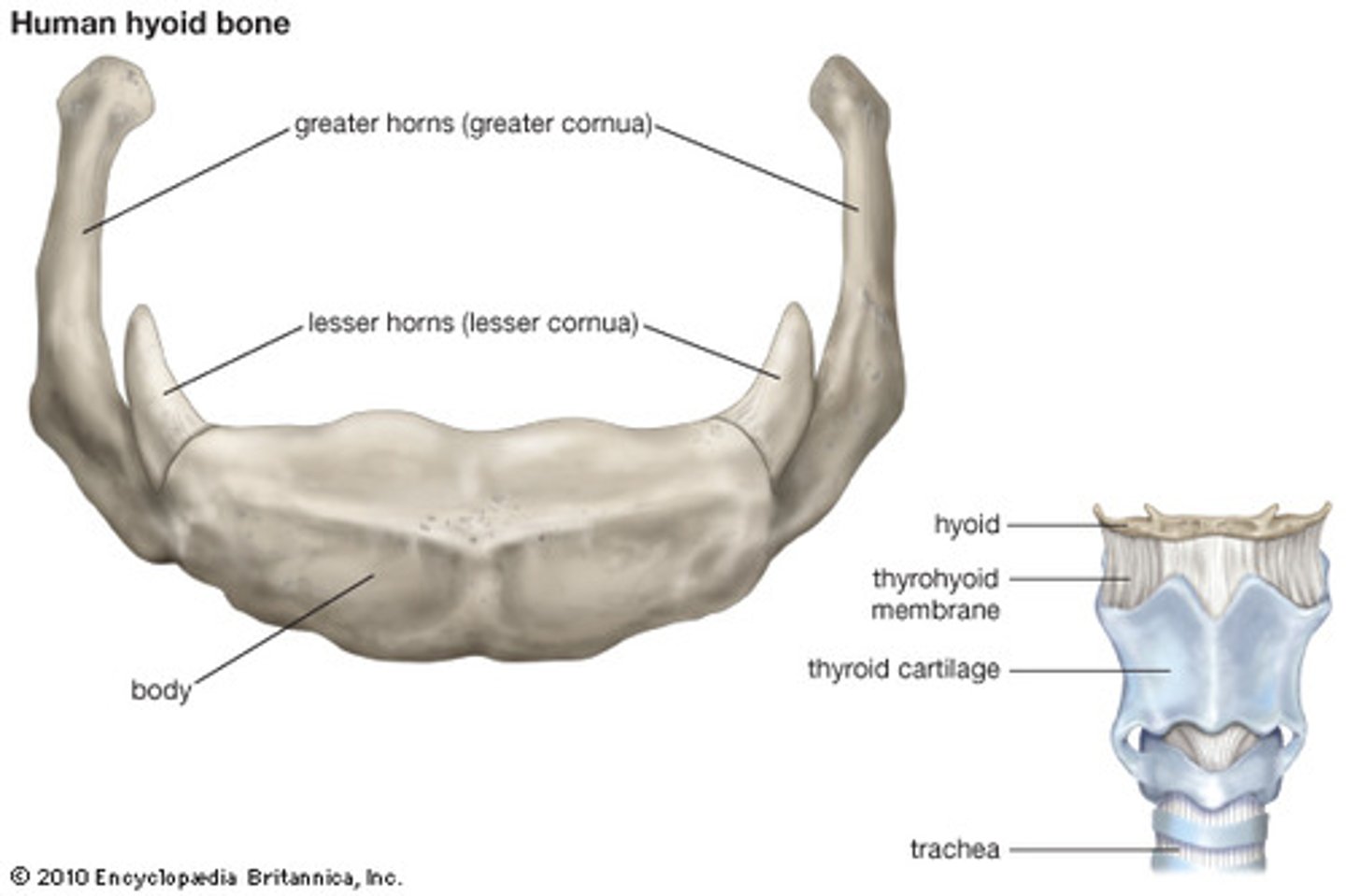
thyroid cartilage
made up of laminae and superior thyroid notch and laryngeal prominence
tracheal rings
rings of cartilage that provide structural support to the trachea and bronchi
cricothyroid membrane
A thin sheet of fascia that connects the thyroid and cricoid cartilages that make up the larynx.
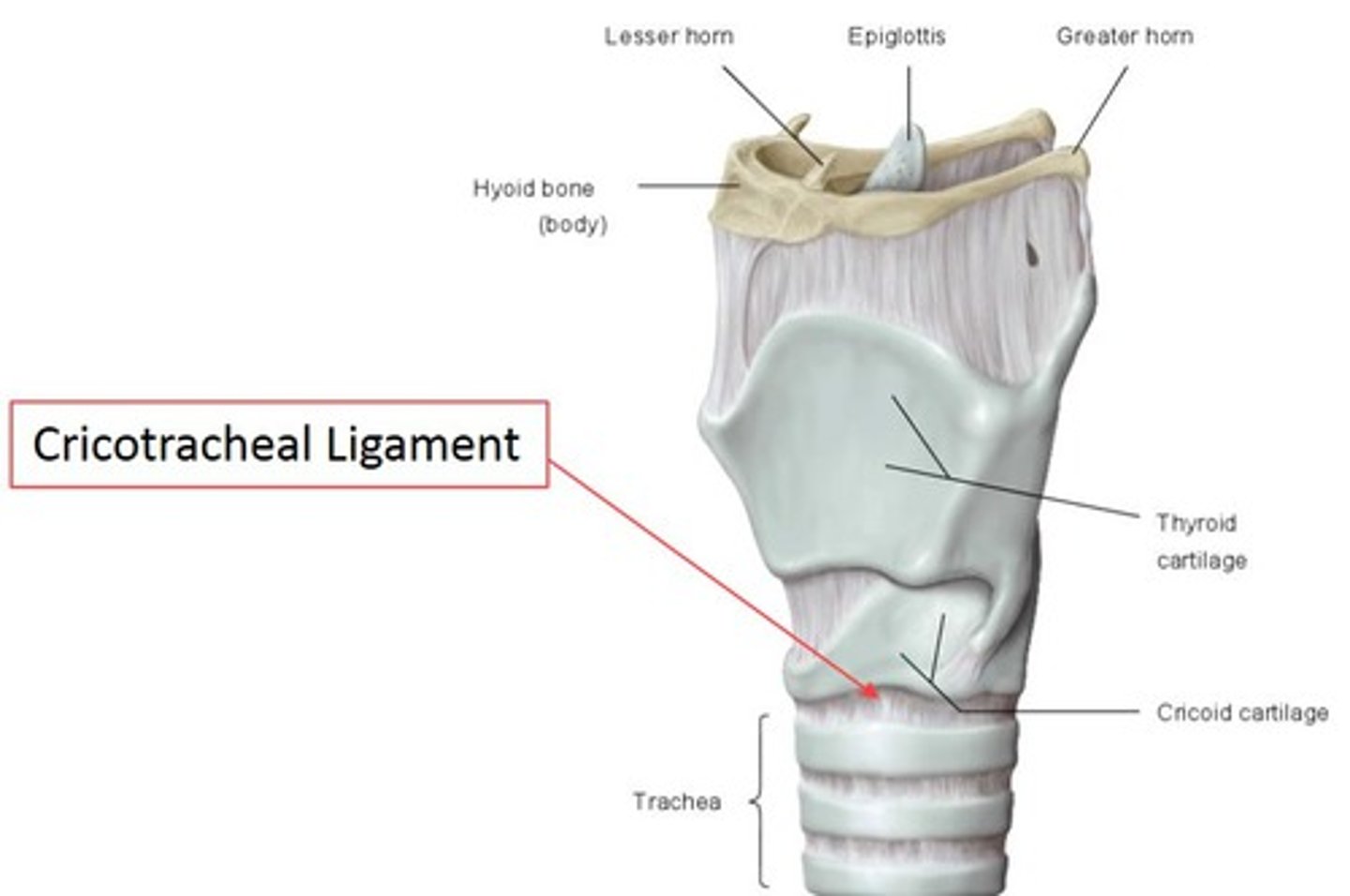
cricotracheal ligament
connects lower border of cricoid cartilage with upper border of first tracheal ring
thyrohyoid membrane
stretches across the space between the greater cornu of the hyoid and the lateral thyroid
epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
Paired corniculate cartilages
horn-shaped pieces of elastic cartilage, are located at the apex of each arytenoid cartilage
Paired arytenoid cartilages
ride on the high-backed upper surface of the cricoid cartilage, forming the posterior point of attachment for the vocal folds
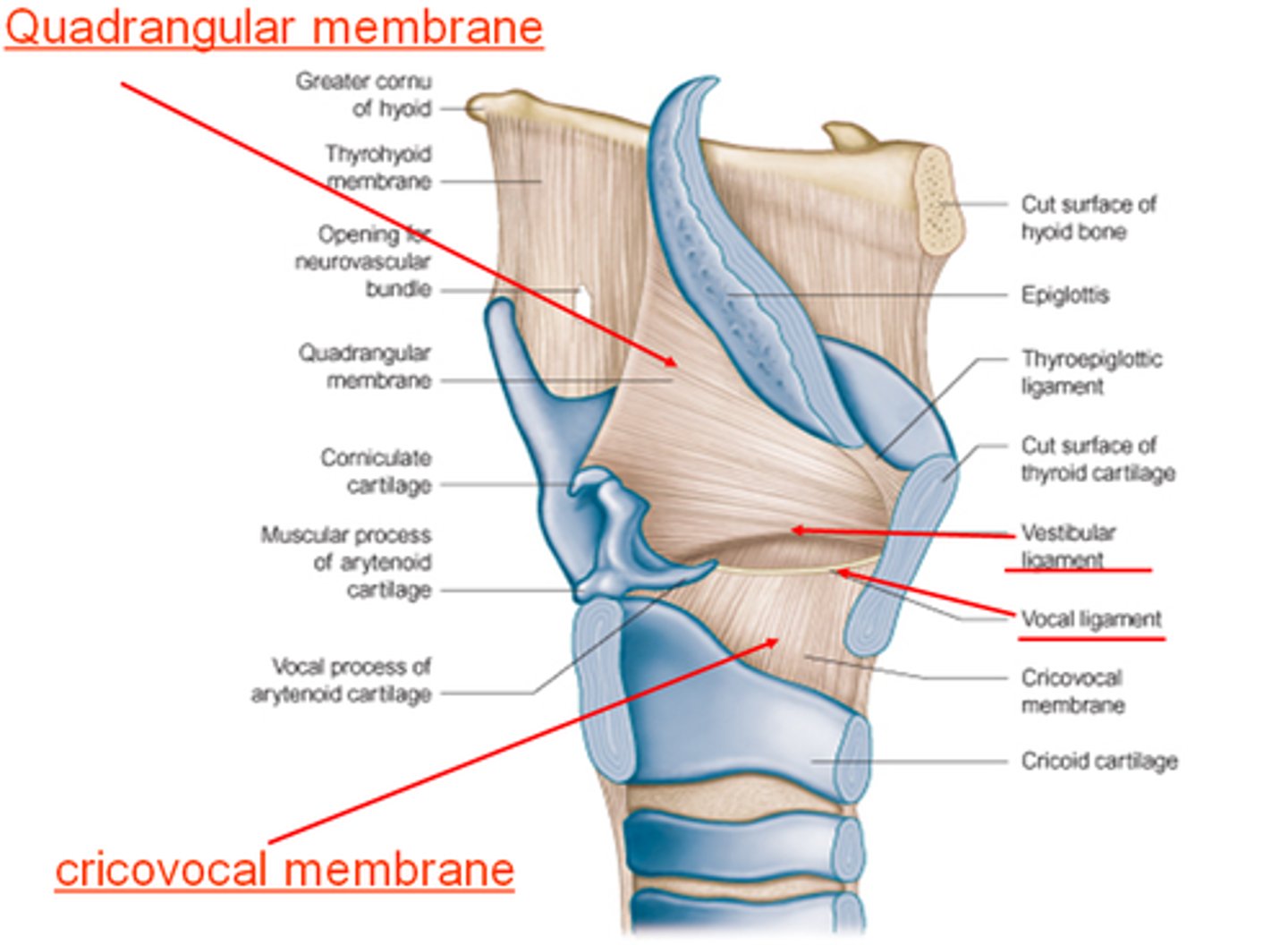
quadrangular membrane
Submucosal sheet of elastic tissue, extending between the lateral parts of the arytenoid and epiglottic cartilages
Superior free margins in aryepiglottic folds form "Aryepiglottic Ligament"
Inferior free margins in aryepiglottic folds form "Vestibular Ligament"
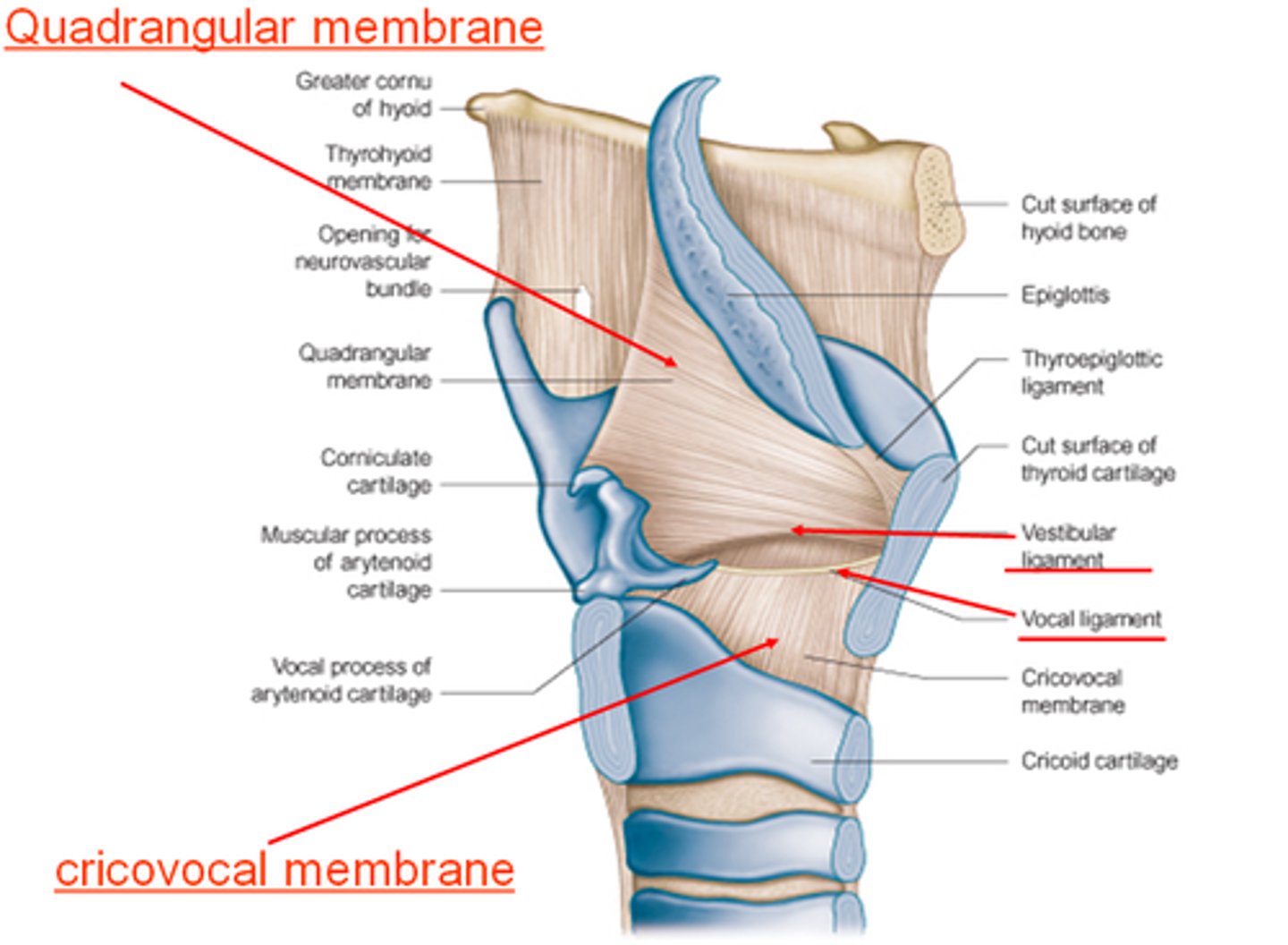
vocal ligament
These are also called the true vocal folds.
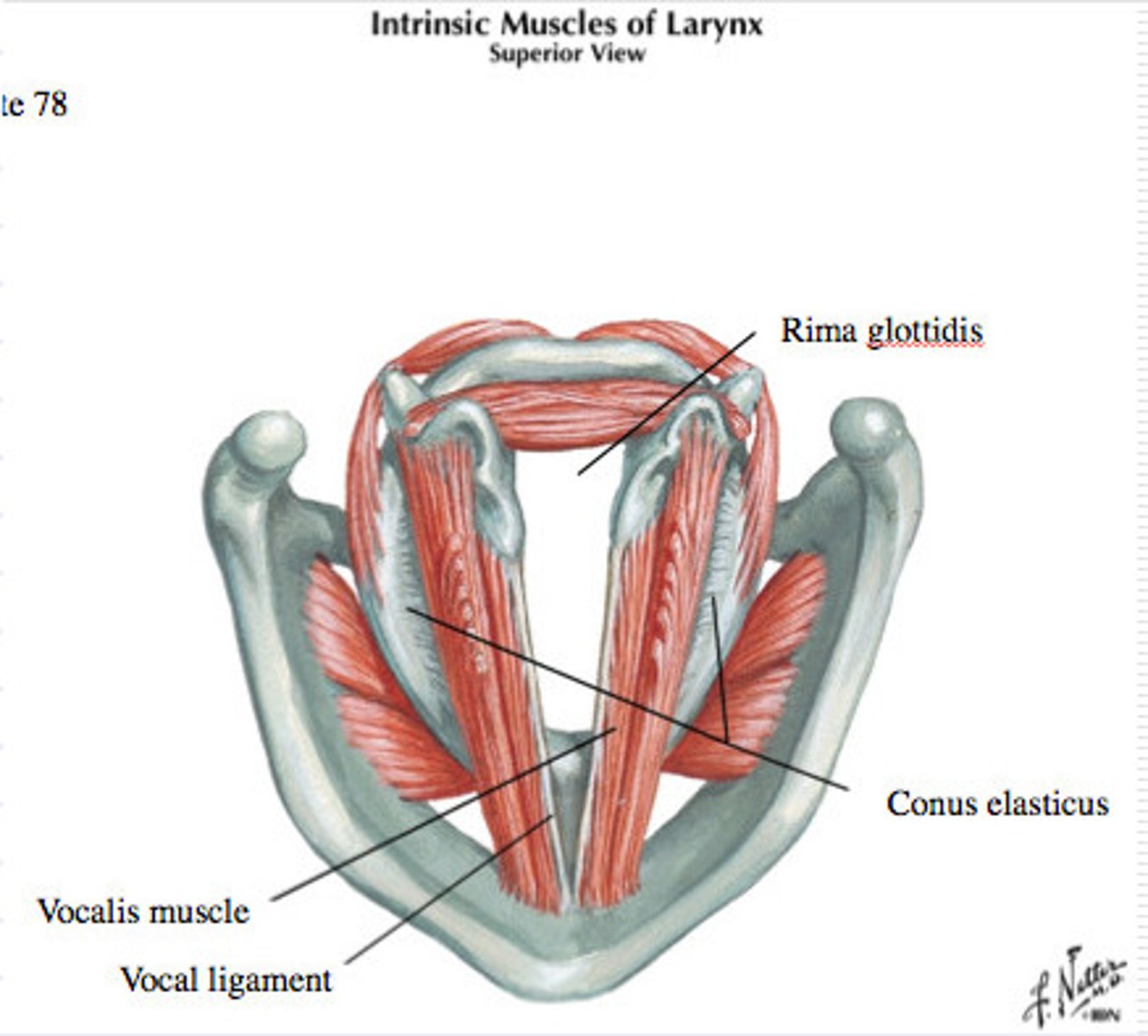
what do the vocal ligaments
extends from arytenoid cartilage to the posterior laryngeal prominence. Producing sound tension and length by arotinoid cartilage, adduct or abduct changes tension pitch and quality
what does the quadrangular membrane do
lateral part of the epiglottis to the superior part of the aretoid cartilage free boarders superior and inferiorly.
vestibular ligament
make up the false vocal chords
cricothyrotomy
emergency airway procedure through an incision in the neck, through the cricothyroid membrane
tracheotomy
where the tube is introduced into tracheal rings
intubation
the insertion of a tube into a body canal or cavity, as in endotracheal intubation
costophrenic angle
extreme outermost lower corner of each lung where diaphragm meets the ribs. Where the chest and diaphragm meet
how to palpate the hyoid
move inferiorly from the mandible
palpate thyroid cartilage
extend cervical spine and palpate the thyroid cartilage
how do you palpate the thyrohyoid membrane
palpate between thyroid laminae and hyoid bone
palpating cricoid cartilage
lies inferior to the thyroid cartilage
palpate cricothyroid membrane
thyroid laminae and cricoid cartilege
jugular notch palpation
superior extent on manubrium ending at the clavicular notches laterally
palpate CCA
cricoid cartilage to thyroid
cricothyrotomy placement
laryngeal prominence and cricoid cartilage, draw a dashed line horizontally though the cricothyroid membrane
tracheotomy placement
halfway between jugular notch and cricothyroid cartilage
how to find the external jugular vein
compression of the EJV just superior to the subclavian
Valsalva manoeuvre, abdominojugular reflux compressing the liver and decreases blood flow
fovea dentis
articulates with the dens of C2; located on the posterior border of the anterior arch
nunchal ligament is continuation of what
supraspinous ligament
what restricts the extension of the ligament
anterior longitudinal
vertebrobasilar system
right and left vertebral artery and basilar artery
V1
V1: pre-foraminal segment origin to the transverse foramen of C6. subclavian artery inferiorly C6 transverse foramen superiorly
V2
V2: foraminal segment from the transverse foramen of C6 to the transverse foramen of C2
V3
V3: atlantic, extradural or extraspinal segment starts from C2, where the artery loops and turns lateral to ascend into the transverse foramen continues through C1 to pierce the dura
V4
V4: intradural or intracranial segment from the dura at the lateral edge of the posterior atlanto-occipital membrane to their confluence on the medulla to form the basilar artery
uncovertebral joint
Growth of the unicate processes in the cervical vertebrae that presses on the intervertebral disc and can lead to tearing of intervertebral discs in the cervical region