BIS2B Final - UC Davis
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
mycorrhizal fungi
symbiotic relationships between fungi and plants, the fungi colonizes the root system of a host plant, providing increased water and nutrition absorption while the plant provides fungus with carbohydrates formed from photosynthesis
For soils with high nutrient and water availability, mycorrhizal fungi are PARASITIC on plants.
inhibition
negative effect of one species on another preventing it from establishing as quickly (or at all) during succesion
keystone species
A species whose presence and role within an ecosystem has a disproportionate effect on other organisms within the ecosystem
foundation species
referred to a species that has a strong role in structuring a community
intermediate productivity hypothesis
diversity is maximized at intermediate levels of productivity
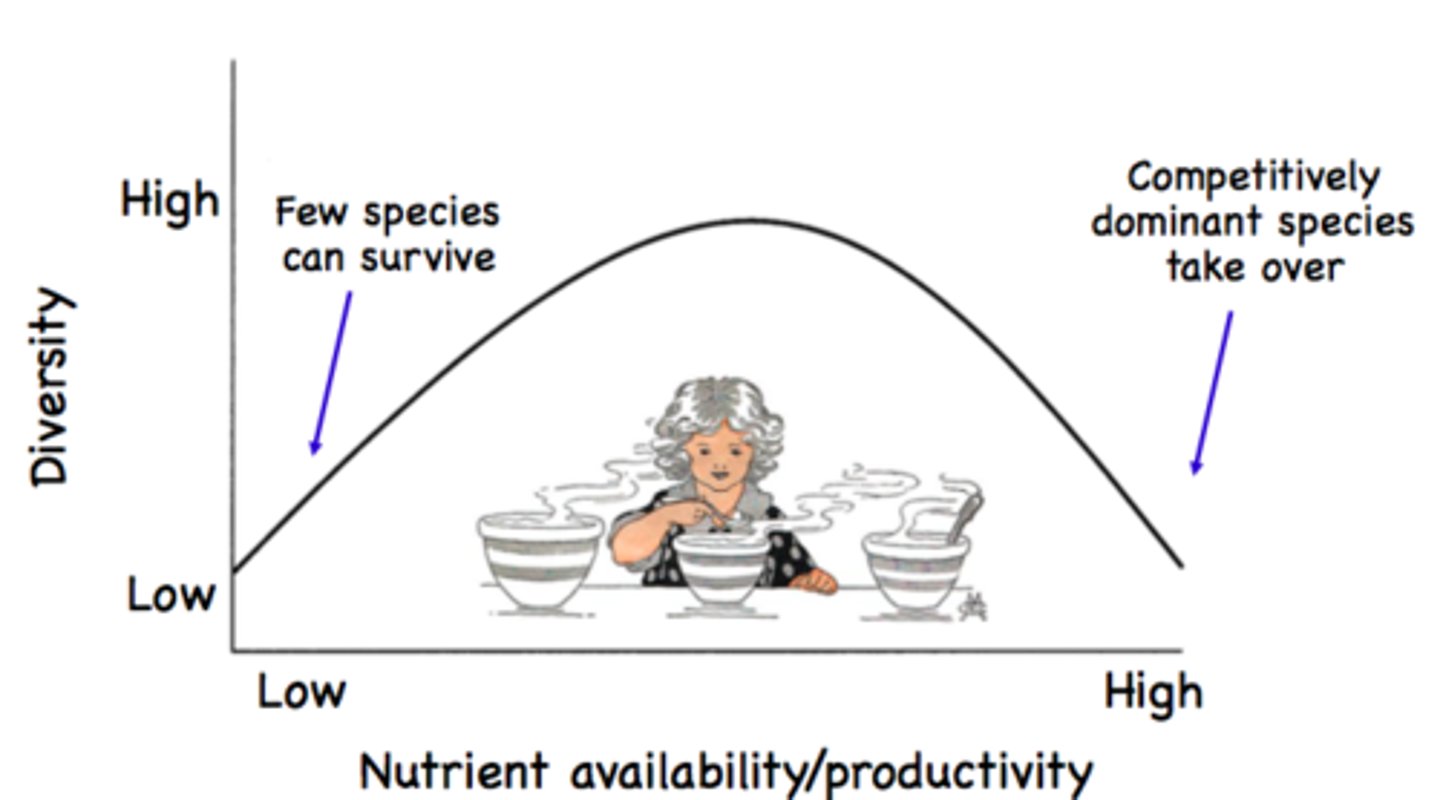
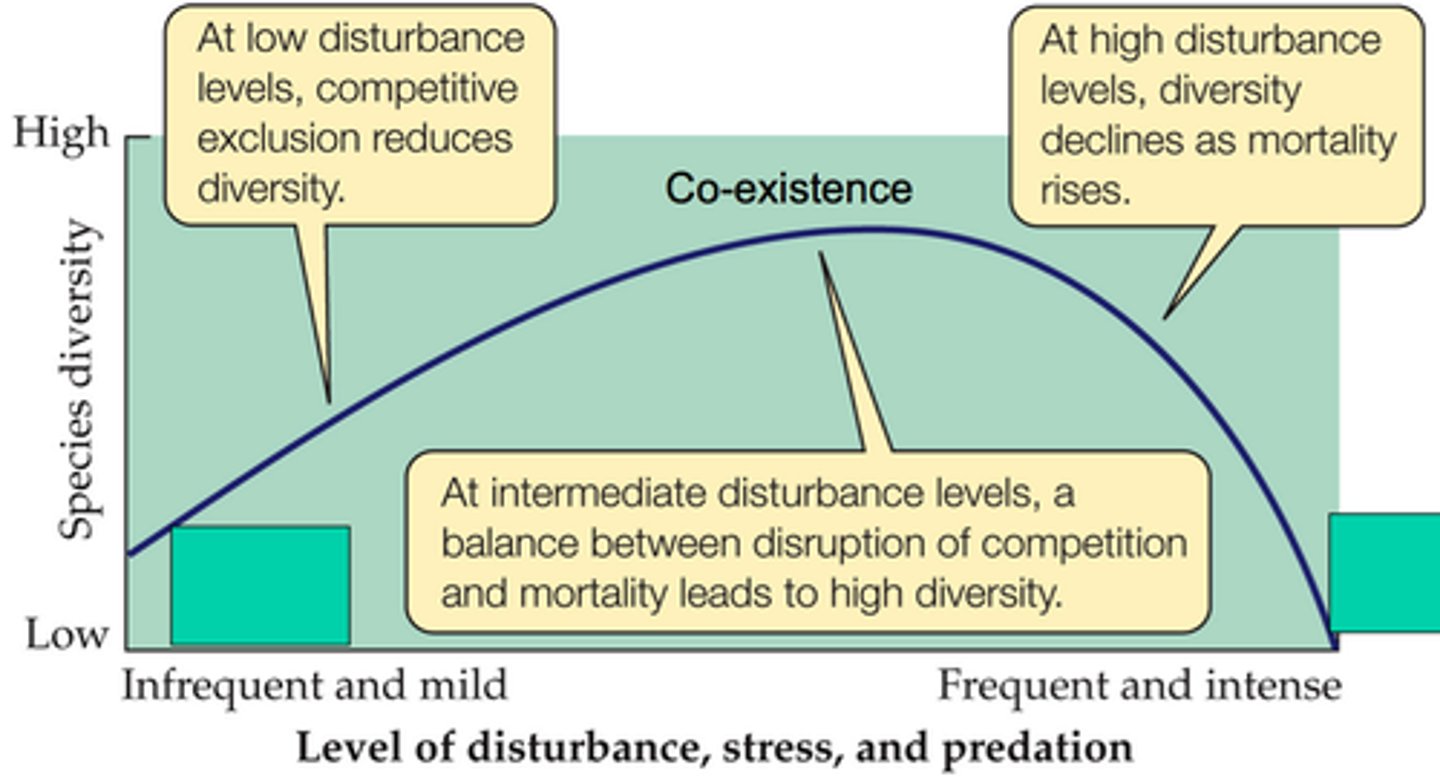
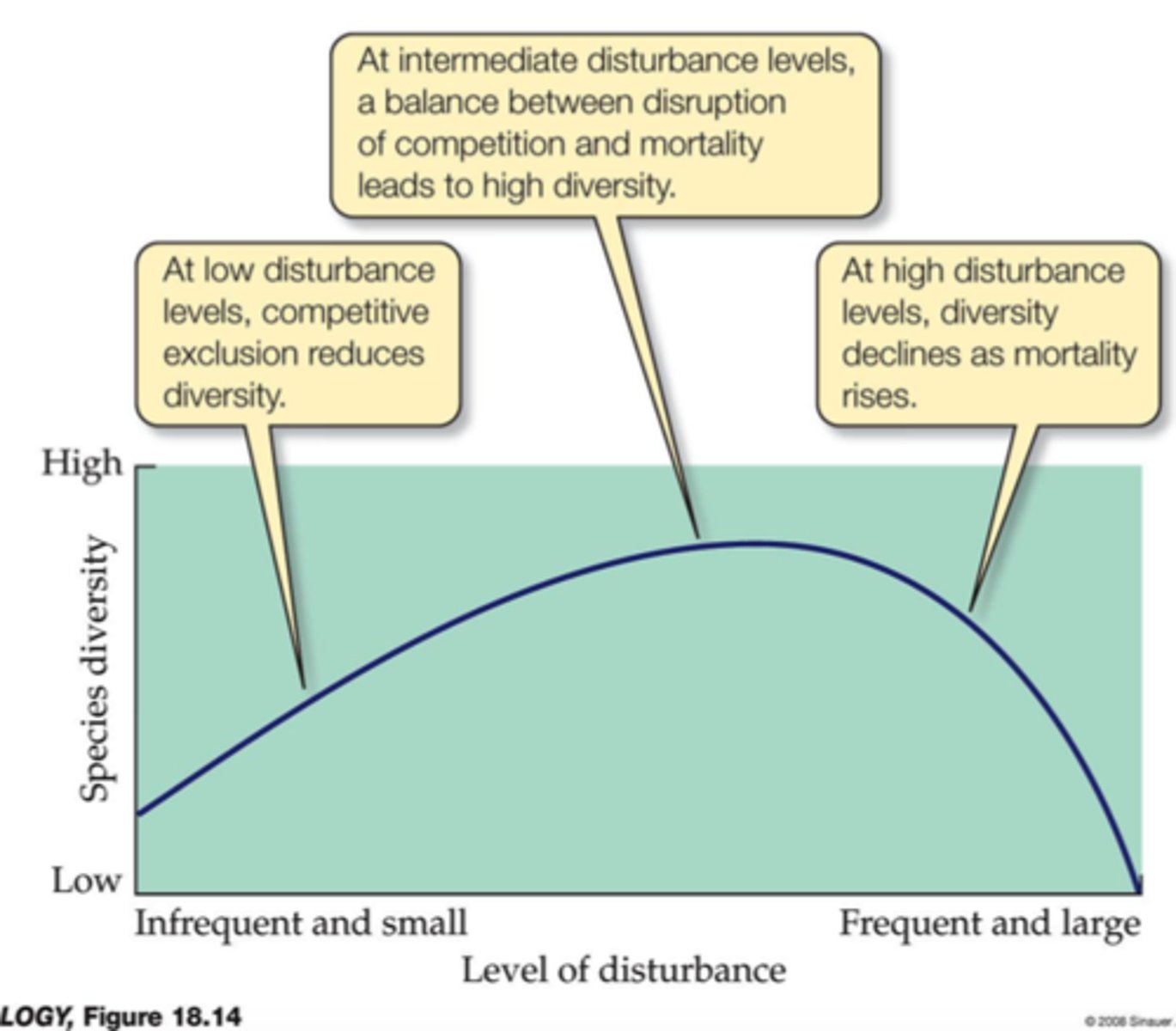
intermediate disturbance hypothesis
states that moderate levels of disturbance can create conditions that foster greater species diversity than low or high levels of disturbance
ecosystem regulating service
changing the quality of something instead of directly providing it
colonize
relates to a plant or an animal establishing itself in an area
ecological succession
process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time
logistic growth
takes place when a populations per capita growth rate decreases as population size approaches a maximum imposed by limited resources, the carrying capacity (k)
competitive interactions
interactions between organisms or species in which both of the organisms or species are harmed
facilitative encounters
encounters between organisms that benefit at least one of the participants and cause harm to neither
antagonistic interactions
interactions between organisms so that one organism benefits at the expense of another
realized niche
where the species actually lives
fundamental niche
an organism can take advantage of all the biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem without competition from other species or pressure from predators
invasion resistance
resistance to invasion from predators
fragmentation
the form of asexual reproduction wherein a parent organism breaks into fragments each capable of growing independently into a new organism
scaling law
scaling laws are linear on loglog scales and means that something observable is something measured
climax species
also known as late-successional k-selected or equilibrium species are plant species that will remain essentially unchanged in terms of species composition as long as it remains undisturbed
r-selected traits
rapid development, high production rate, small body size, short life span
k-selected traits
slow development, low reproductive rate, large body size
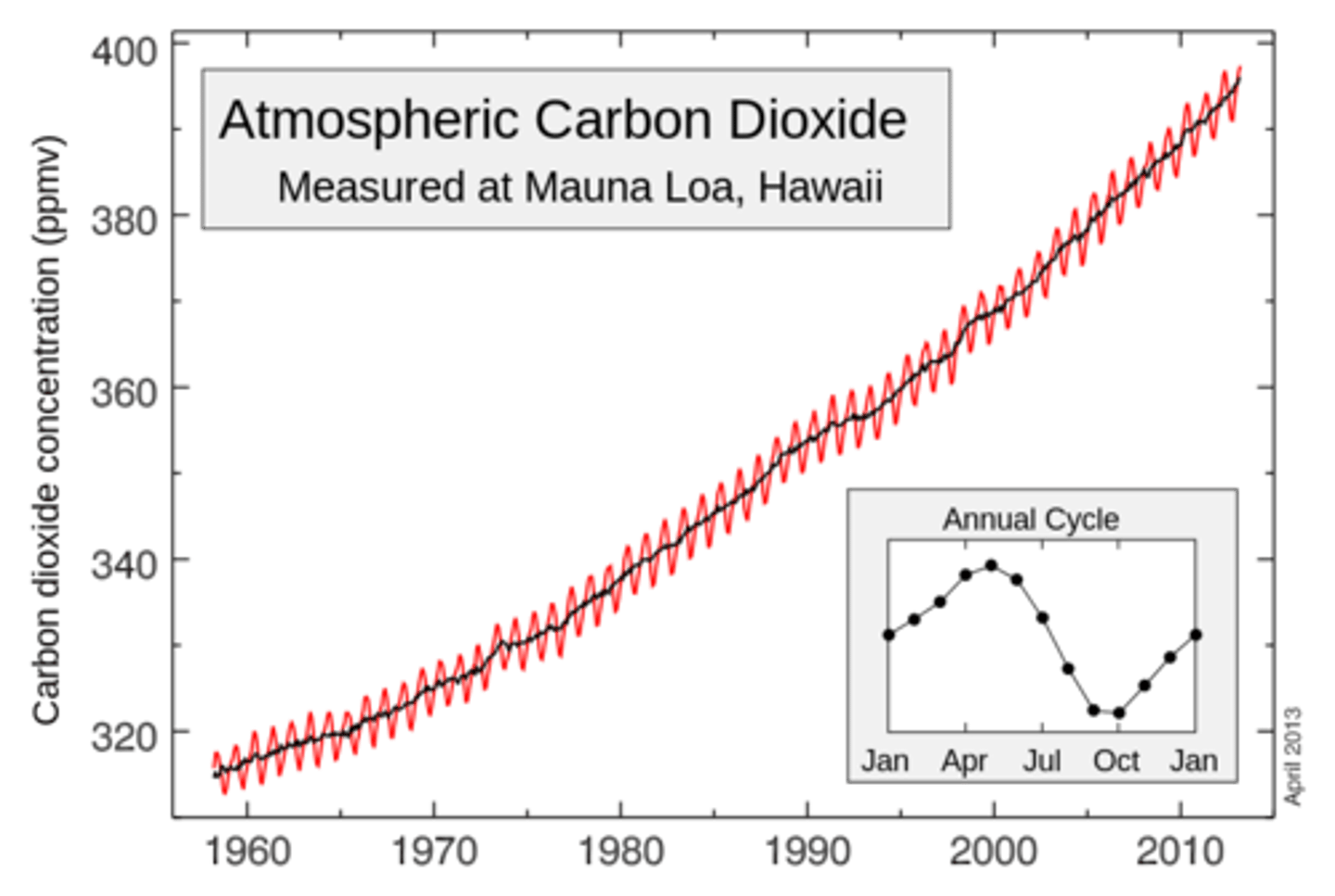
The Keeling curve
a graph of the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the earth's atmosphere based on continuous measurements
primary productivity
describe the rate at which plants and other photosynthetic organisms produce organic compounds in an ecosystem
Incipient speciation
when two groups are beginning to diverge, but there is not yet complete reproductive isolation between them
character displacement
the phenomenon where differences among similar species whose distributions overlap geographically are accentuated in regions where the species co-occur, but are minimized or lost where the species' distributions do not overlap.
competitive release
occurs when one of two species competing for the same resource disappears, thereby allowing the remaining competitor to utilize the resource more fully than it could in the presence of the first species
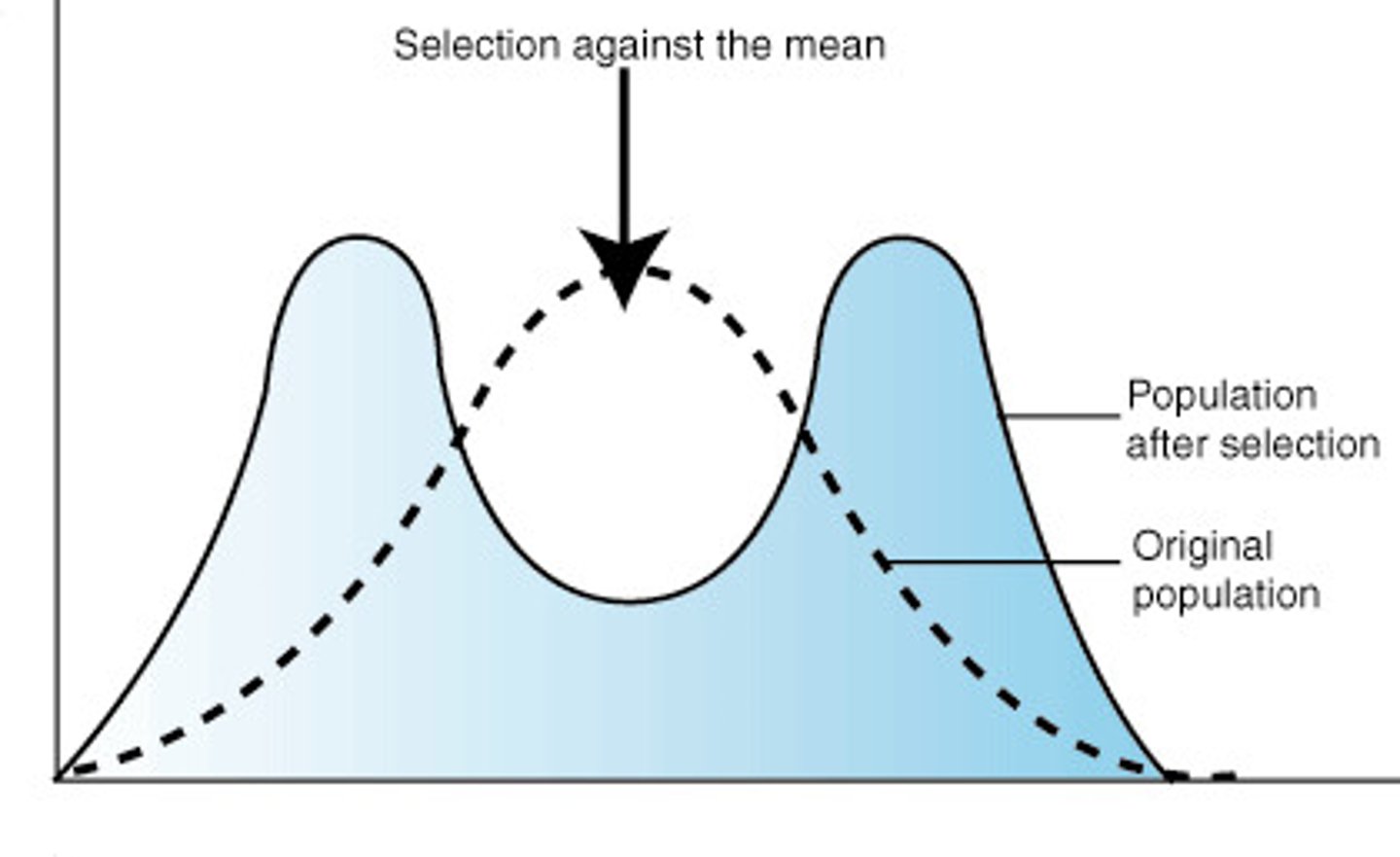
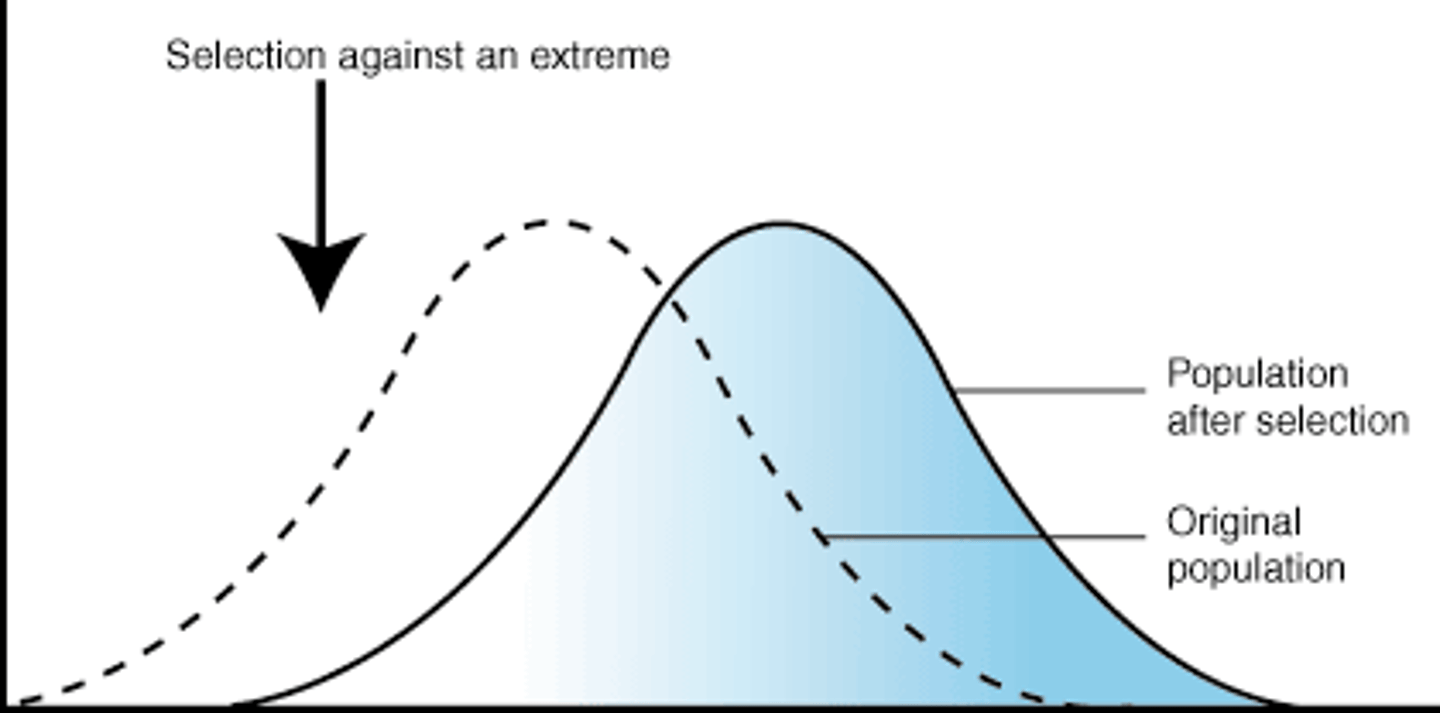
disruptive selection
changes in population genetics in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values
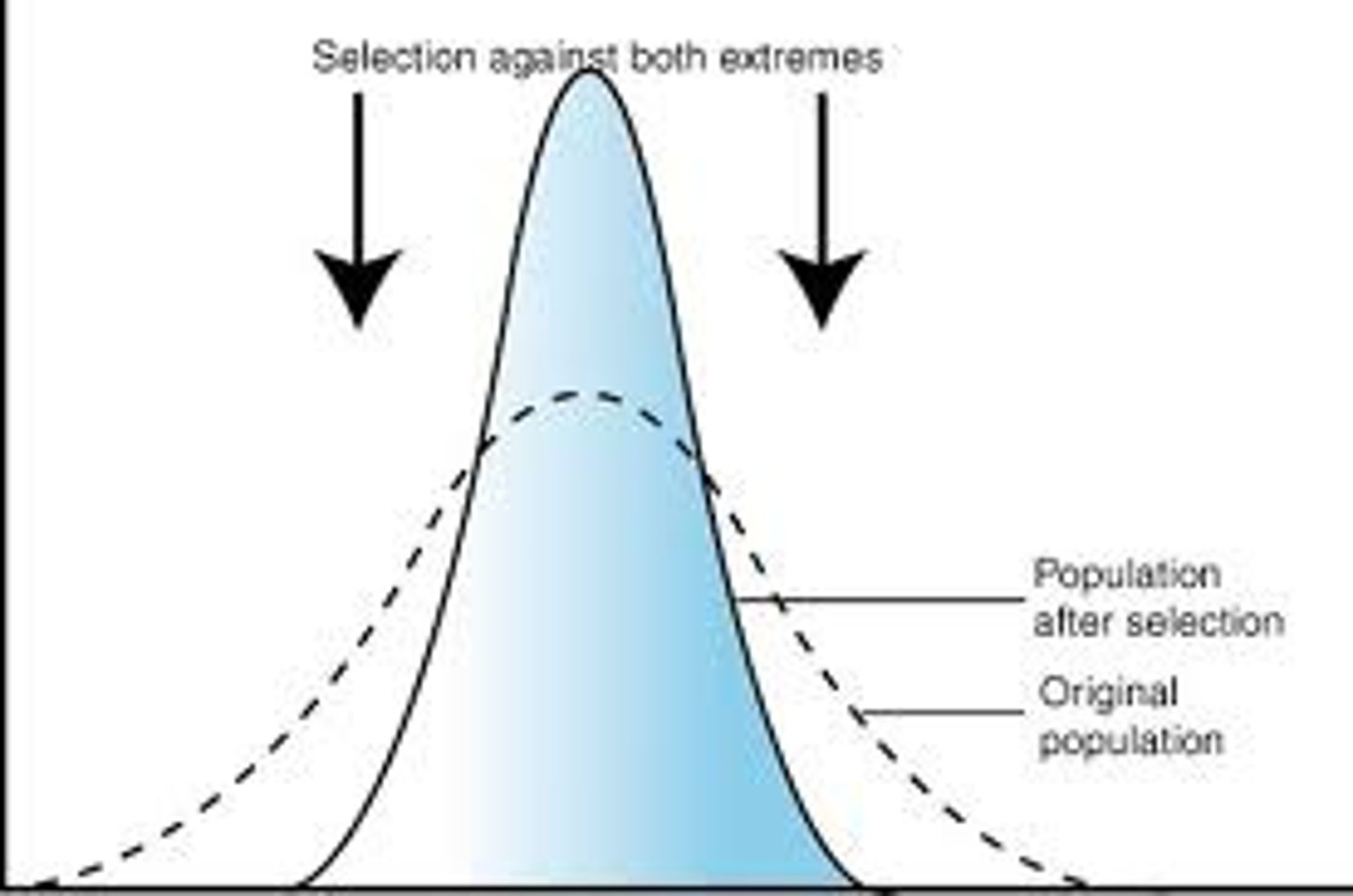
stabilizing selection
when extreme phenotypes on both ends of the spectrum are unfavorable
directional selection
a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction
competitive exclusion principle
states that two species that compete for the exact same resources cannot stably coexist
assortative mating
the type of mating that occurs when an organism selects a mating partner that resembles itself (homozygotes match)
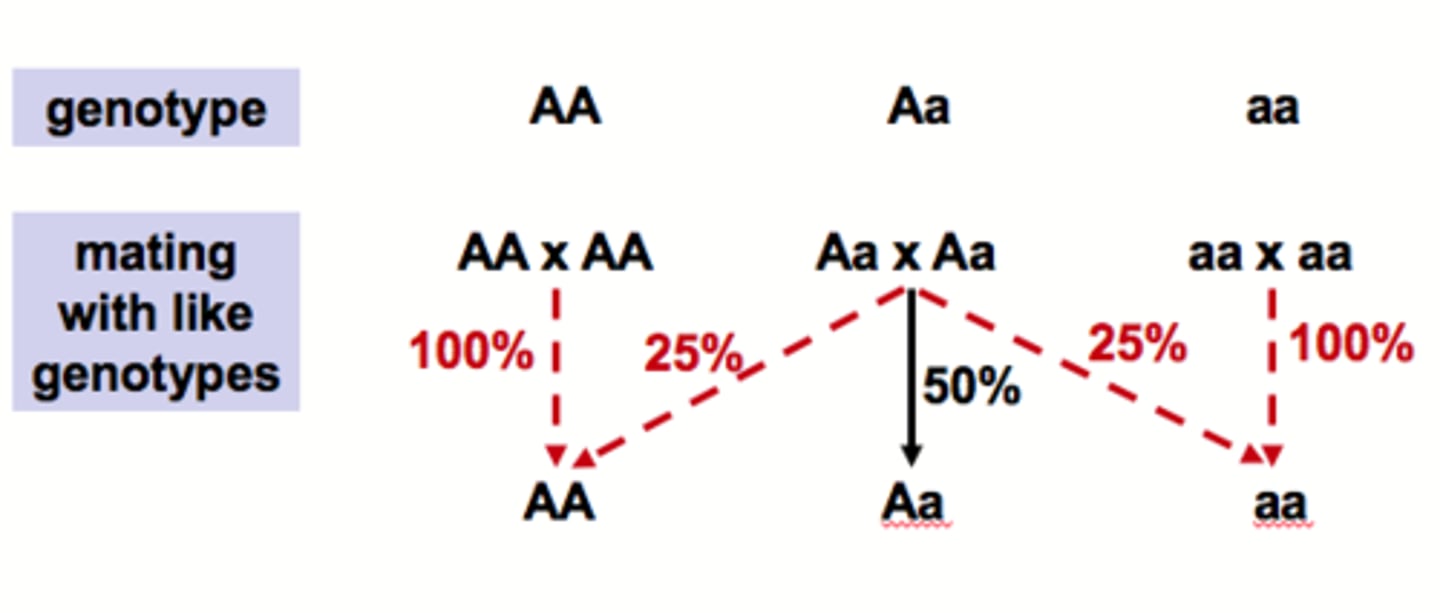
disassortative mating
Dissimilar phenotypes mate preferentially
Favors heterozygosity

genotype x environment interaction
Phenotypic variation arising from the difference in the effect of the environment on the expression of different genotypes.
heterozygote advantage
Greater reproductive success of heterozygous individuals compared to homozygotes; tends to preserve variation in gene pools.
allopatric speciation
speciation that happens when two populations of the same species become isolated from each other due to geographic change
Hybrid inviability
a post-zygotic barrier, which reduces a hybrid's capacity to mature into a healthy, fit adult. The relatively low health of these hybrids relative to pure-breed individuals prevents gene flow between species.

founder effects
the reduced genetic diversity which results when a population is descended from a small number of colonizing ancestors
Behavioral isolation
Mating rituals within species. Prezygotic mechanism that has been favored by selection for reinforcement of reproductive isolation. Example: mating dance by birds.
hybrid inviability
A postzygotic barrier in which hybrid zygotes fail to develop or to reach sexual maturity
Activities that have altered ecosystems
Fossil fuel emissions (global warming, rise in sea level, greenhouse gasses, loss of coral reefs, ocean acidification)
Industrial agriculture (increases biological availability)
More: deforestation, habitat destruction, species extinction
ecological isolation
Species occur in the same area, but they occupy different habitats and rarely encounter each other. Example: prezygotic mechanism that prevents hybrid mating between benthic and limnetic forms within lakes in the wild
inbreeding depression
when individuals with similar genotypes - typically relatives - breed with each other and produce offspring that have an impaired ability to survive and reproduce (lowers fitness)
adaptive radiation of certain lineages
an event in which a lineage rapidly diversifies with the newly formed lineages evolving different adaptations
key innovations
a novel phenotype trait that allows subsequent radiation and success of a taxonomic group
lineage
temporal series of organisms, populations, cells, or genes
sexual selection
natural selection arising through preference by one sex for certain characteristics in individuals of the other sex
ecological speciation
the process which ecologically based divergent selection between different environments leads to creation of reproductive barriers between populations
vacant ecological niches
the possibility that in ecosystems or habitats more species can exist that are present in a particular time, because many are not being used by potentially existing species
series of events in chronological order
origin of photo synthesis
origin of aerobic metabolism
origin of eukaryotes
Cambrian explosion
colonization of land
carboniferous coal formation
end - cretaceous astroid impact
spread of grassland
angiosperms
flowering plants
pleistocene
ice age
late Cenozoic
Ice age in Northern Hemisphere
mammoths, first humans, modern organisms
deleterious alleles
alleles that lower fitness
Demographic stochasticity refers to __________.
random year-to-year variations in a population's birth and death rates
theory of island biography
a theory that demonstrates the dual importance of habitat size and distance in determining species richness (larger island=greater number of species because lower extinction rates and lower in reserves geography closer to other reserves due to higher colonization rates)
Chronological order of events
origin of photosynthesis, origin of aerobic metabolism, origin of eukaryotes, Cambrian explosion, colonization of land, carboniferous coal formation, end-cretaceous astroid impact, spread of grassland.
Cambrian explosion
A burst of evolutionary origins when most of the major body plans of animals appeared in a relatively brief time in geologic history; recorded in the fossil record about 545 to 525 million years ago.
Carboniferous Period
354 to 290 mya. refers to the rich coal deposits found in rocks of this age.cooler period, much of the land covered by forest swamps. Very large plants and trees became prevalent. amniotic egg, which prevents dessication of the embryo inside.
negative frequency dependent selection
Phenotypes favored only when rare. Example is left-handed fighting ability
adaptive radiation
An evolutionary pattern in which many species evolve from a single ancestral species (Darwins finches had very different phenotypes but all came from the same generation)
founder event
A type of bottleneck that occurs when only a few individuals establish a new population.
Vicarience
speciation due to isolation by geographic separation-blocks mating
Bottleneck
process in which a large population declines in number, then rebounds
reproductive barriers
serve to isolate the gene pools of species and prevent interbreeding
key innovation
an adaptation which enhances the diversification rate of a lineage (sympatric speciation, autopolyploid, allopolyploid)
divergent selection
evolution in which species that were once similar to an ancestral species diverge; occurs when populations change as they adapt to different environmental conditions; eventually resulting in a new species
ecological specialization
the concentration of homogeneous groups and activities into different sections or urban areas-divergent selection in different environments lead to creation of reproductive barriers between populations.
Late Cenozoic Ice Age
The last great ice age that ended 10,000 years ago, lasting for the past 2 million years. (cooling climate)
Important global events during the Cenozoic era
adaptive radiation of MAMMALS, diversification and dominance of angiosperms, Pleistocene glacial cycles.
Human sister lineage
chimpanzees
vicariance
the geographical separation of a population, typically by a physical barrier such as a mountain range or river, resulting in a pair of closely related species
temporal isolation
when species that could interbreed do not because the different species breed at different times
autopolyploid speciation
an individual or strain whose chromosome consists of more than two complete copies of the genome of a single ancestor species
duplication - > post zygotic - > sterile
prezygotic isolating mechanism
occurring before breeding; produces a fertilized egg, or zygote
allopolyploid speciation
genetic makeup of two different species (HYBRID)
helpful hint: ALLOsin "donkeeey"
gamete incompatibility
proteins on egg that allow sperm binding do not bind with sperm from another species
commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
positive frequency dependent selection
Phenotypes are favored only when common. Example is warning coloration
symbiosis
A close relationship between two species that benefits at least one of the species.
obligate
at least one species could not grow and reproduce without the other
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited. (fur color, height, skin color)
random mating
no selective mating in which animals chose mate depending on phenotype
Scaling Laws
linear on log-log scale.
something measurable is equal to something observable
Fragmentation
A means of asexual reproduction whereby a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals. (small parts)
antagonistic interaction
one benefits, other is harmed
competitive interaction
both harmed
intermediate disturbance
Moderate levels of disturbance can create conditions that foster greater species diversity.
intermediate predation hypothesis
diversity is maximized at intermediate levels of predation
Tolerance
lack of species on others
Facilitation
An interaction in which one species has a positive effect on the survival and reproduction of another species without the intimate association of a symbiosis
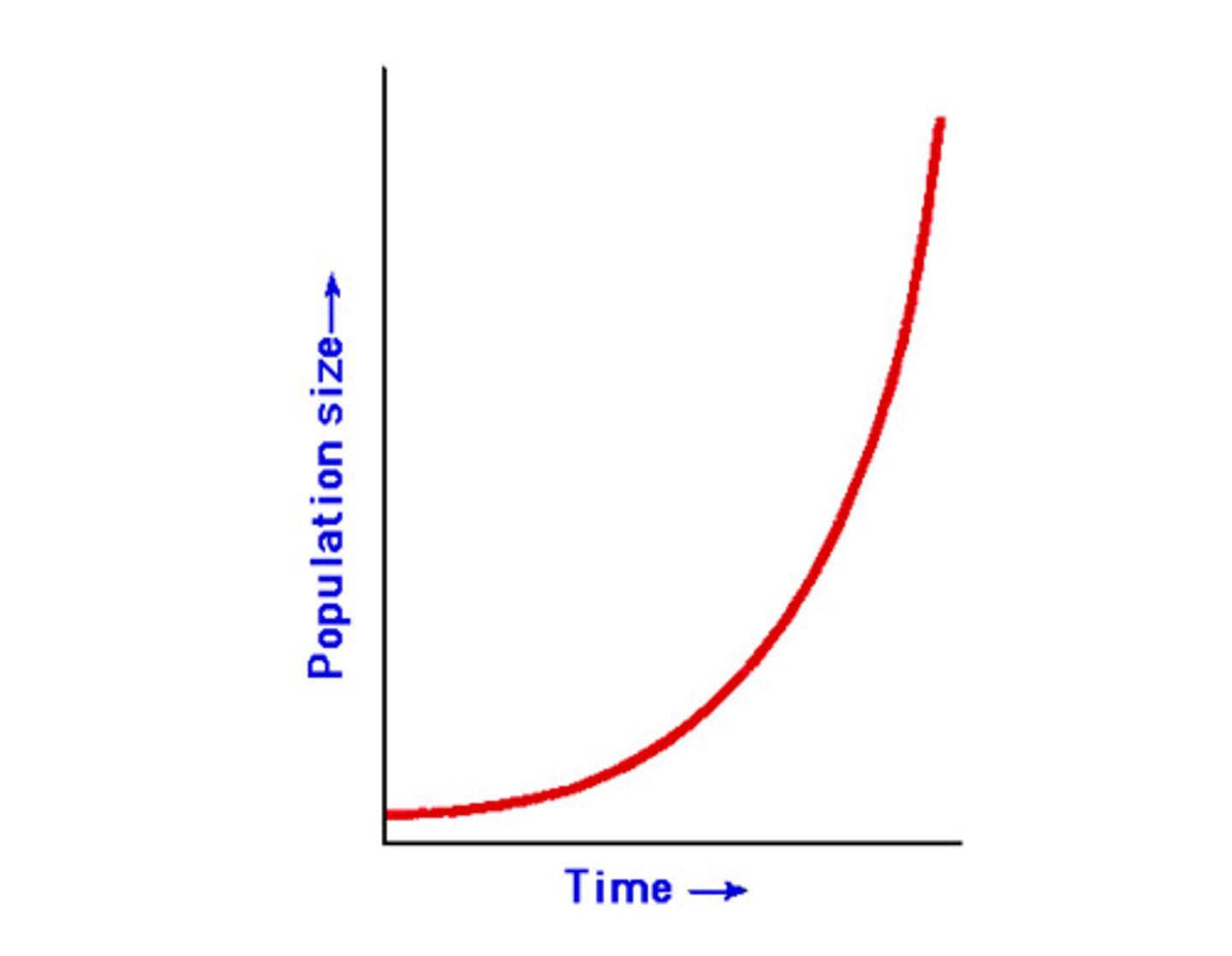
exponential growth
Growth pattern in which the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate
mychorrhizae
specialized mutualistic associations between roots and fungi
symbiotic relationship
close interaction between species in which one species lives in or on the other
A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit is
mutualistic relationship
a symbiotic relationship in which one benefits and has no effect on the other
commensalism
parasitic relationship
only the infecting organism benefits from the relationship
active protection
Some organisms (crustaceans) are given food and shelter in exchange for protection
vigilance behavior
scanning the environment for predators
allopatric
geographic isolation
Dobzhansky-Muller incompatibility
breakup of "coadapted gene complexes" by independent mutations in isolated populations (creates low fitness)