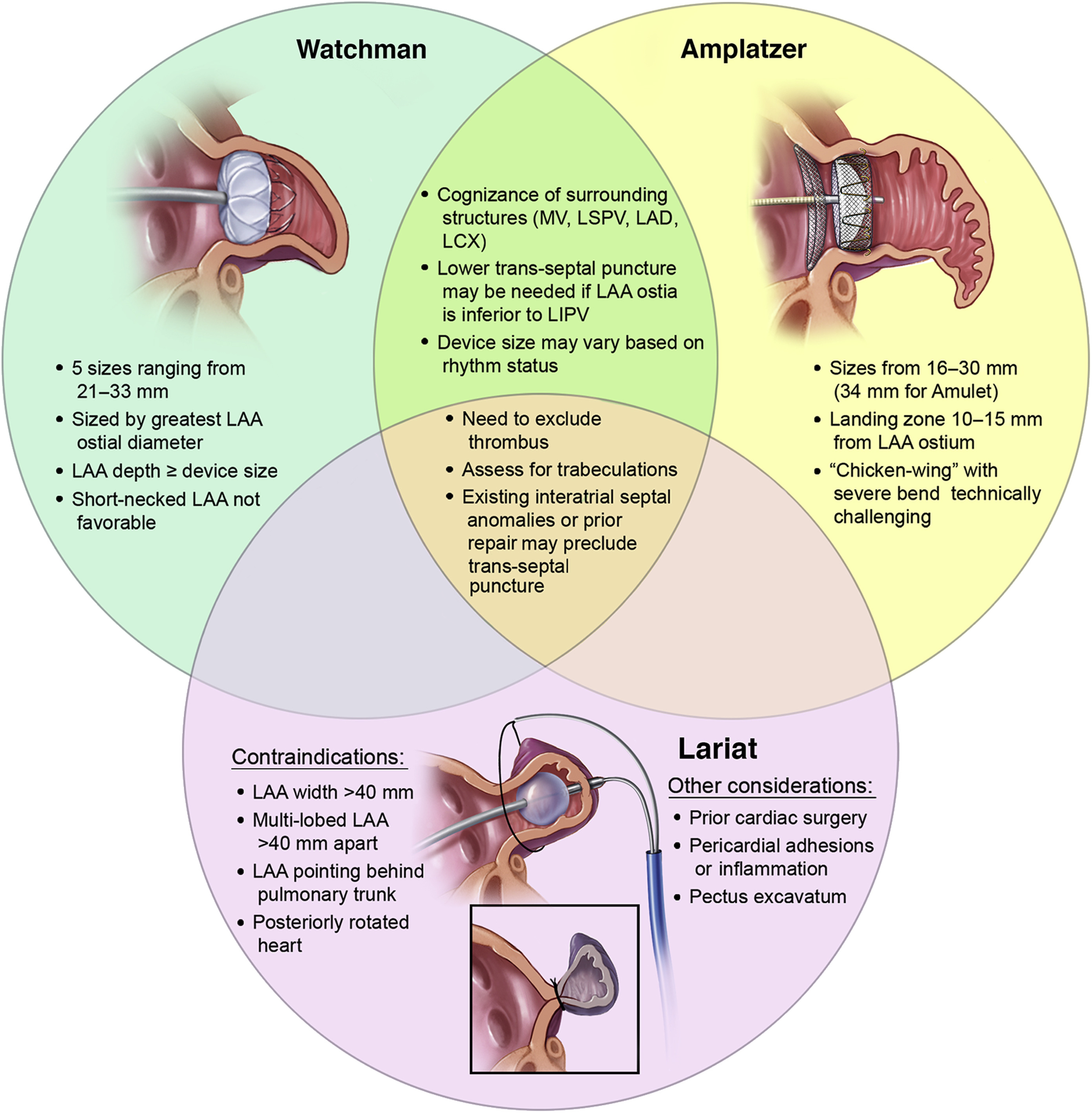
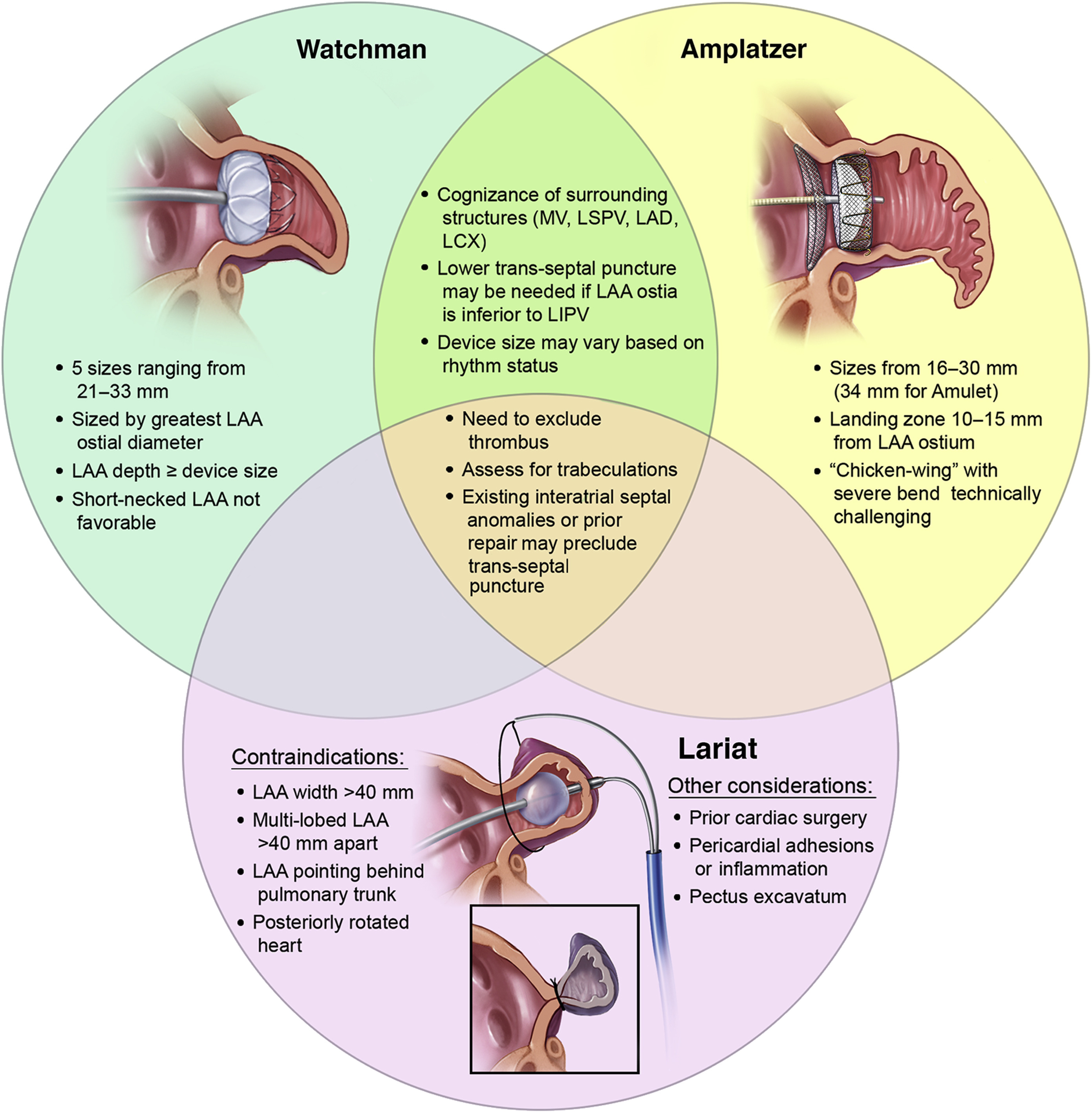
Cardiac anatomy
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
355-410
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What is the most anterior structure of the heart
Hint chamber
RV,
Lateral chest x ray projection identifies RV dilation/hypertrophy by showing RV and it’s outflow track.
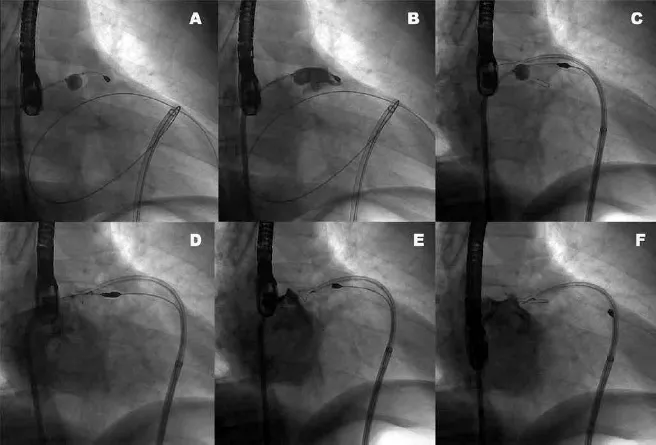
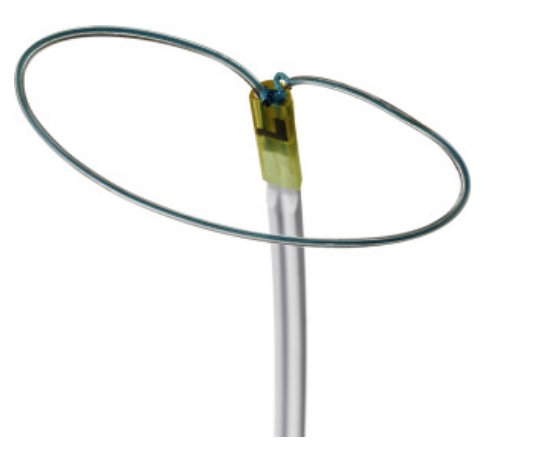
what device is being deployed in this fluoroscopy
device
access
function
Lariat device
Epicardial
Closing t
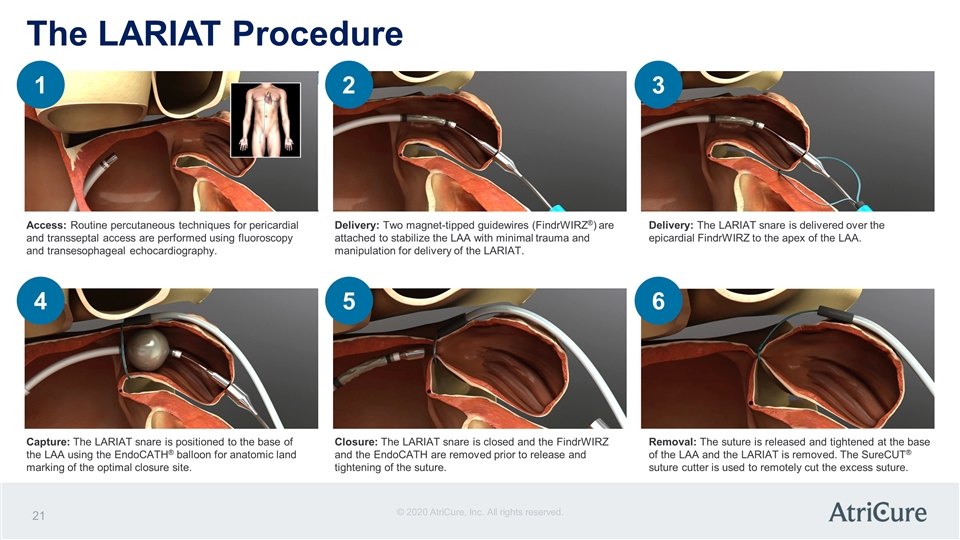
what device is this
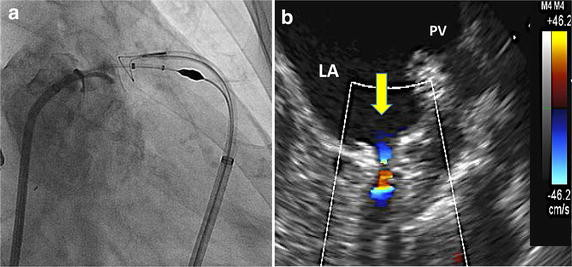
Study this image
completed
Cannulation of the femoral artery should be ___.
Precisely in the inguinal fold
above the inguinal fold
1 finger breath below the inguinal fold
6cm below the inguinal fold
1 finger breadth below the inguinal fold
However, it's important to note that relying solely on the inguinal fold can be misleading due to anatomical variations among patients. The inguinal crease may not accurately correspond to the location of the common femoral artery, potentially increasing the risk of complications.
T or F TEE is commonly used for a pericardiocentesis
False
An elevated RVedp is found in which pathology?
lv infarct
MR
RV infarct
A.S.
RV infarct
What is the correctorder of a quad bypass as they would appear on the Aorta
SVG
OM
RCA
LAD
DIAG
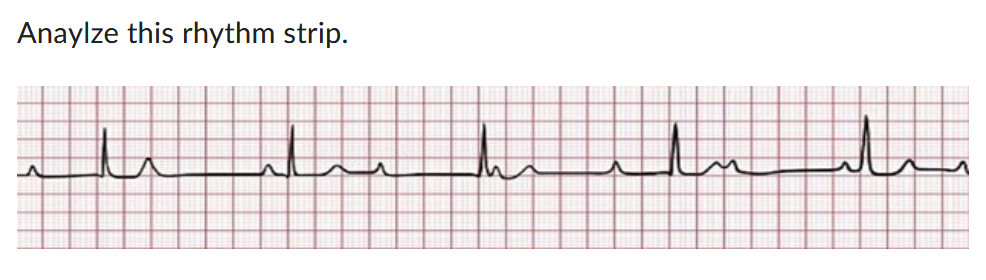
3rd degree
st elevation in leads V1 & V2 is an infarction in
Septal
When reviewing an IVUS or OCT image for evaluation of lesion,
T or F for each
Flow dynamics pd/pa is visible
lesion length is visible
lumen dimension is visible
F
T
T
Would you use a scoring/cutting balloon on a fibrous plaque blockag?
True
What heart block is most likely to become lethal
2nd degree heart block type 2
ST segment elevation in leads V5, V6, I, aVL indicates which culprit vessels? Choose the
CX
What are the three symptoms of a RP bleed
hypotens
abdominal or flank pain
tachycardia
Midazolam is the generic name of ______ that causes _____
Versed
Sleepiness
Proper dosage of heparin for peripheral interventions?
Typically, 70-100 units/kg administered intravenously.
Which catheter is the BEST option to use to cannulate an LAD with a high takeoff?
AL1
what interventional device utilizes the use of high pressure heparinzed saline to remove
thrombus
angiojet
Lisinopril belongs to which drug class
ACEi
Yes or no is diabetes a contraindication of coronary stenting
NO
Which of these meds are used for preop known contrast allergy
Solumedrol
Diphenhydramine
Hydralazine
ancef
famotidine
solumedrol
diphenhydramine
famotidine
The posterior tibial pulse is located where on the body
Near the medial malleolus
A drug often used to treat spasm, Verapamil belongs to which drug class?
CCB
what NYHA class is this …
Patients experience
symptoms with less than
ordinary activity, meaning
they are comfortable at rest
but experience limitations
during minimal exertion.
CLASS 3
THIS IS CLASS 2
Characterized by marked
limitation of physical activity,
where comfortable at rest,
but less than ordinary activity
results in fatigue, palpitations,
or dyspnea
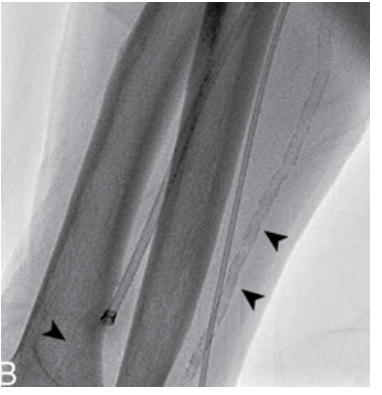
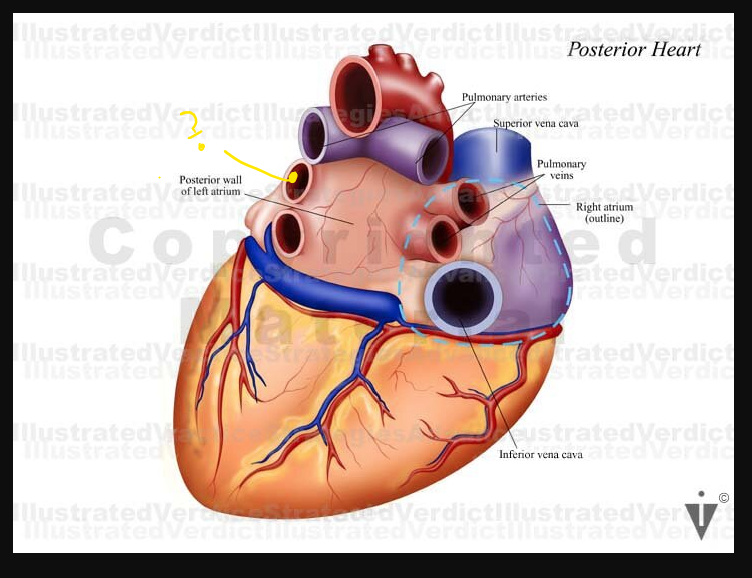
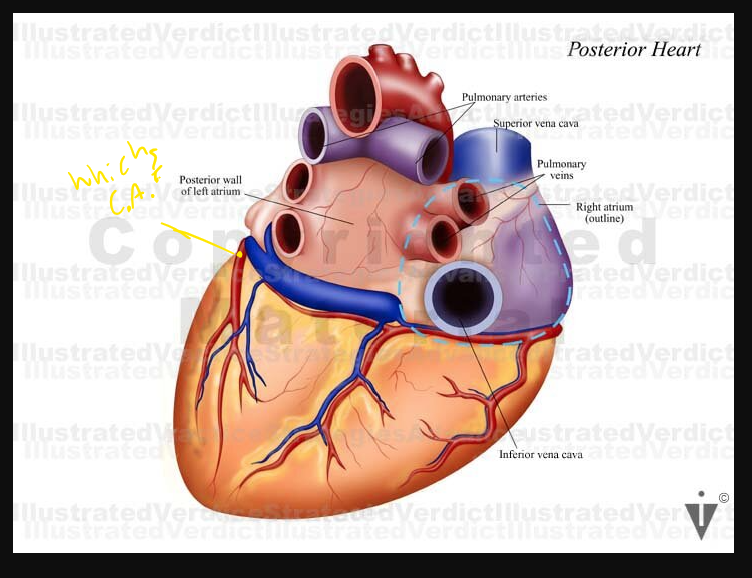
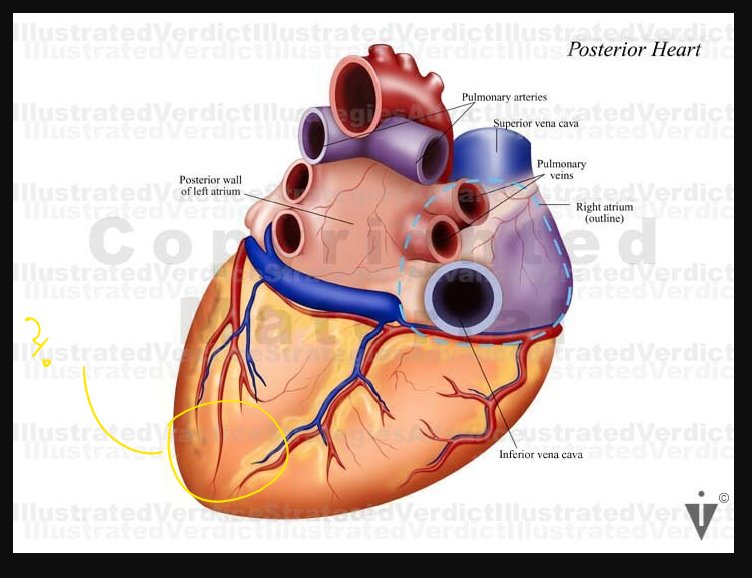
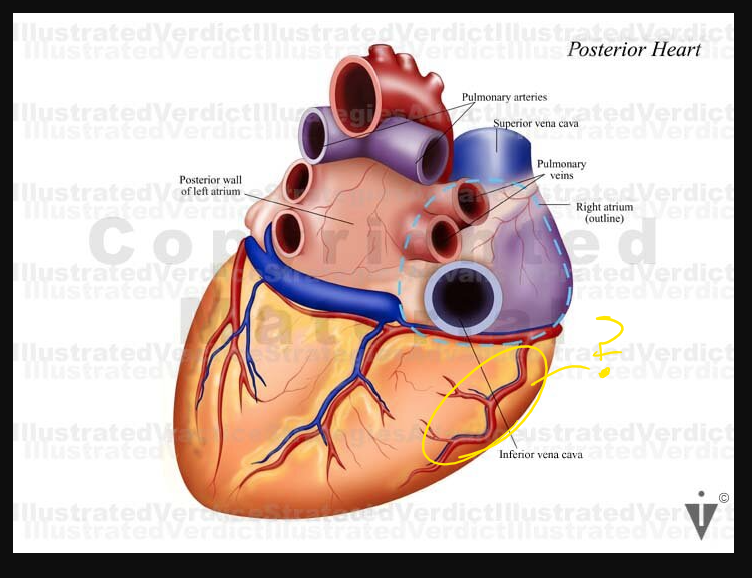
what are these arrows pointing at
Calcification
When performing a thermodilution cardiac output, 10 cc of injectate enters into the ___,
and the temperature change is measured in the ___
RA
PA
Afterload is most impacted by ________?
the systemic vascular resistance
Preload is mostly impacted by
Increased filling pressures

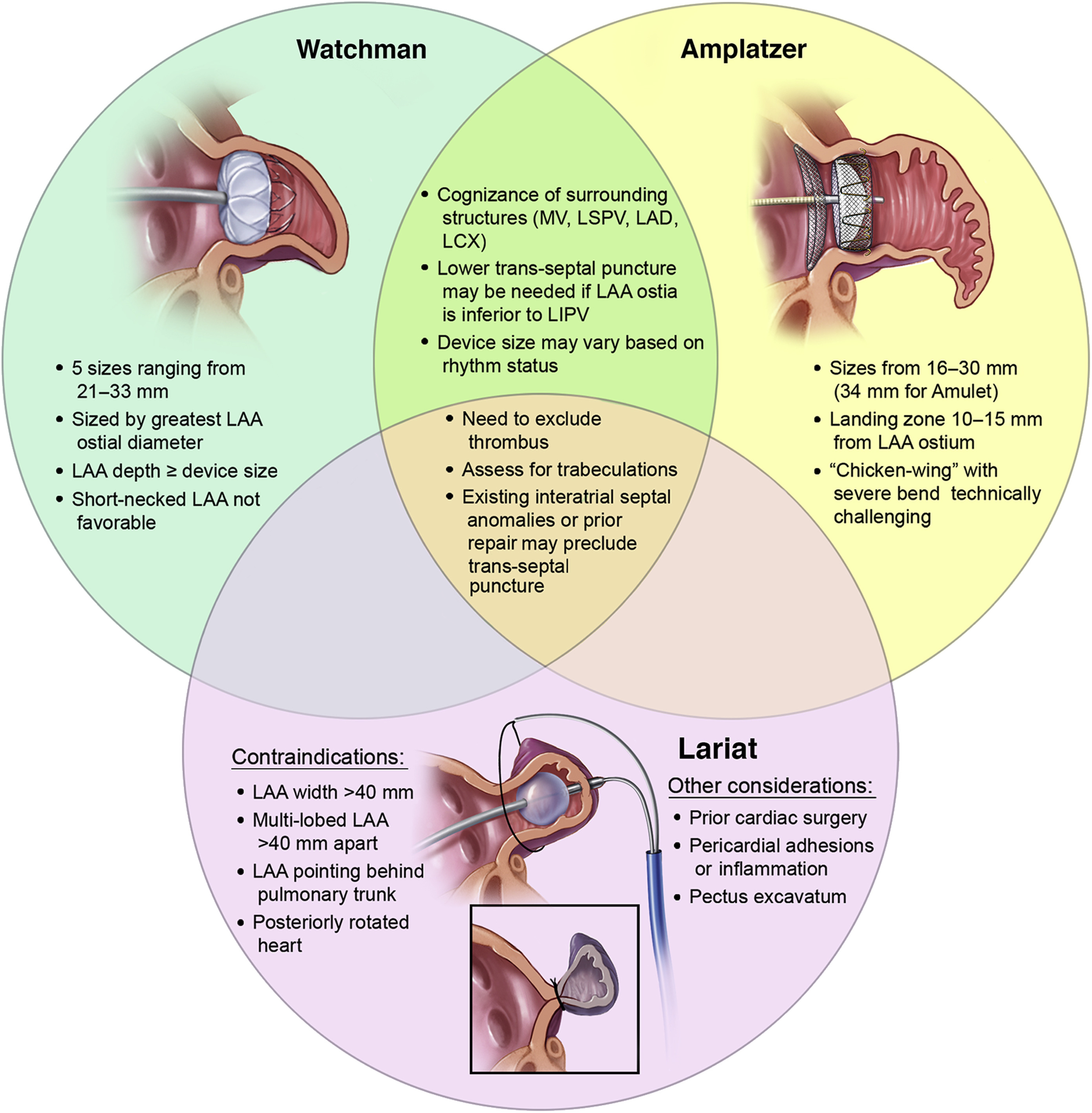
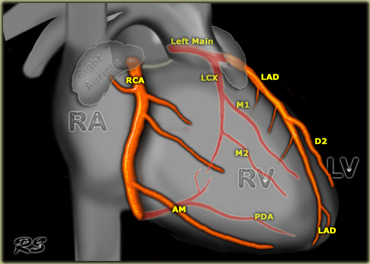
Identify the structural heart device and access.
What vessel can be viewed on the anterior side of the heart
LAD
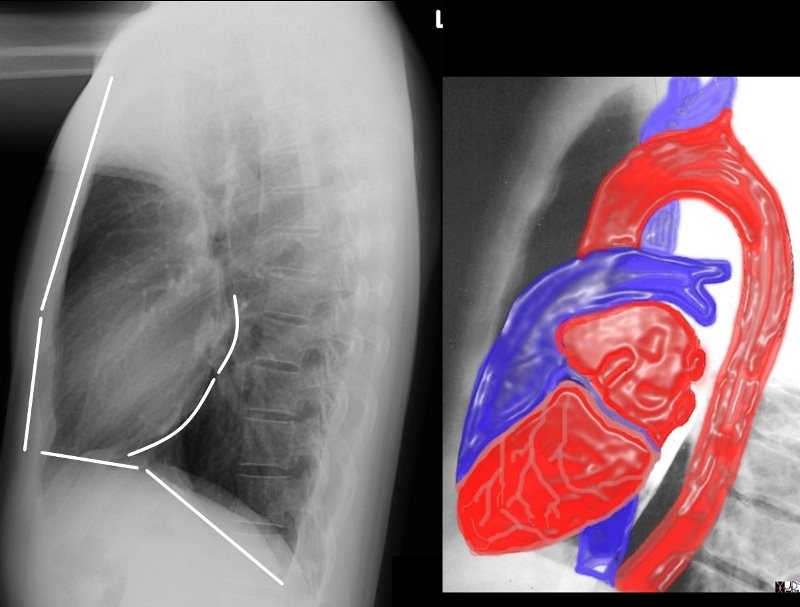
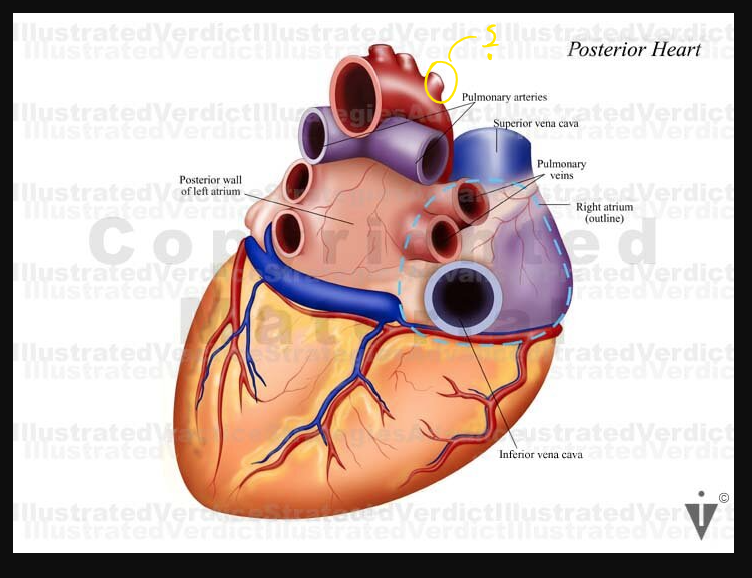
In a lateral chest x ray the coronary sinus is orientated _____ and located near the ______ aspect of the heart
orientated horizontally
near the posterior inferior aspect of the heart
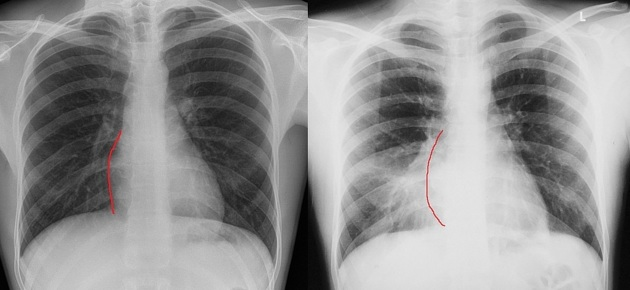
Which structure forms the patents right cardiac border?
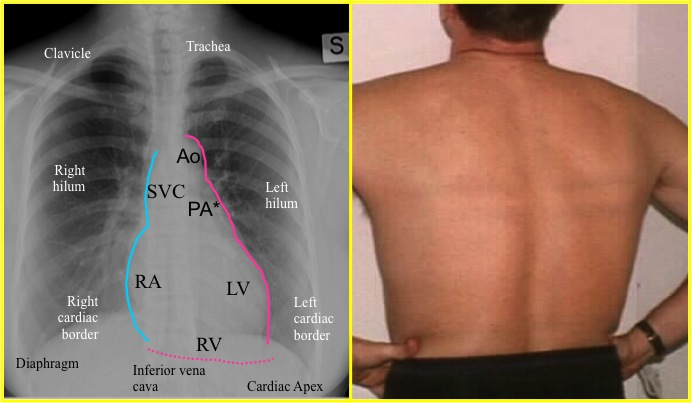
what structure normally appears as a circle on the superior aspet of the cardiac silhouette in the AP chest radiograph
Transverse aortic arch or the aortic knob
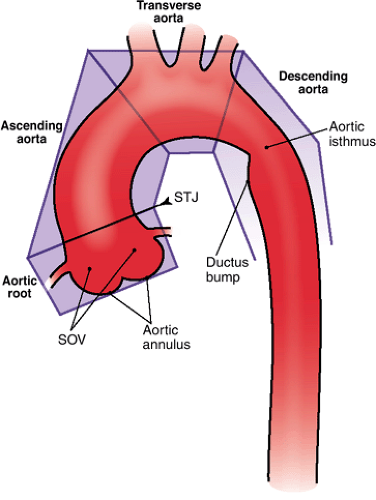
What is another name for the aortic knob
Transverse aortic arch
When viewing the heart in LAO projection what structures form the right cardiac border
Right atrium and right ventricle.
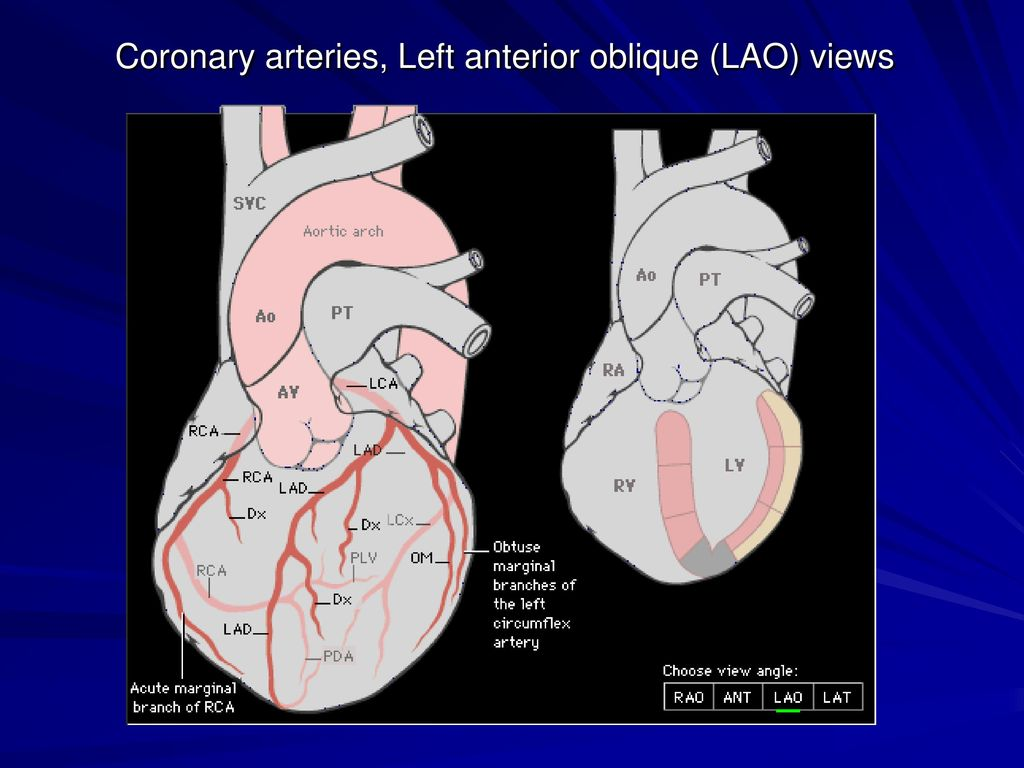
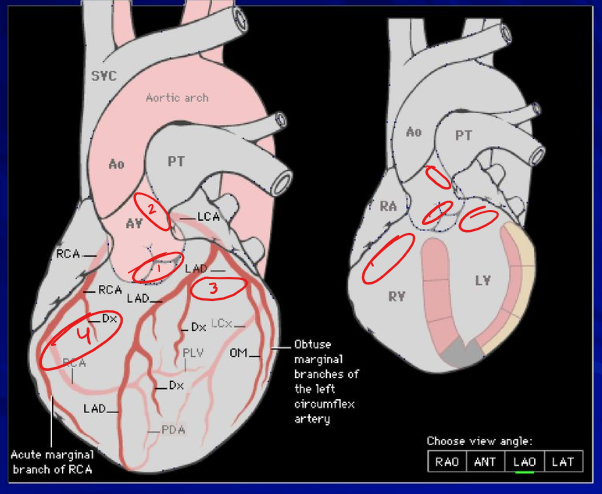
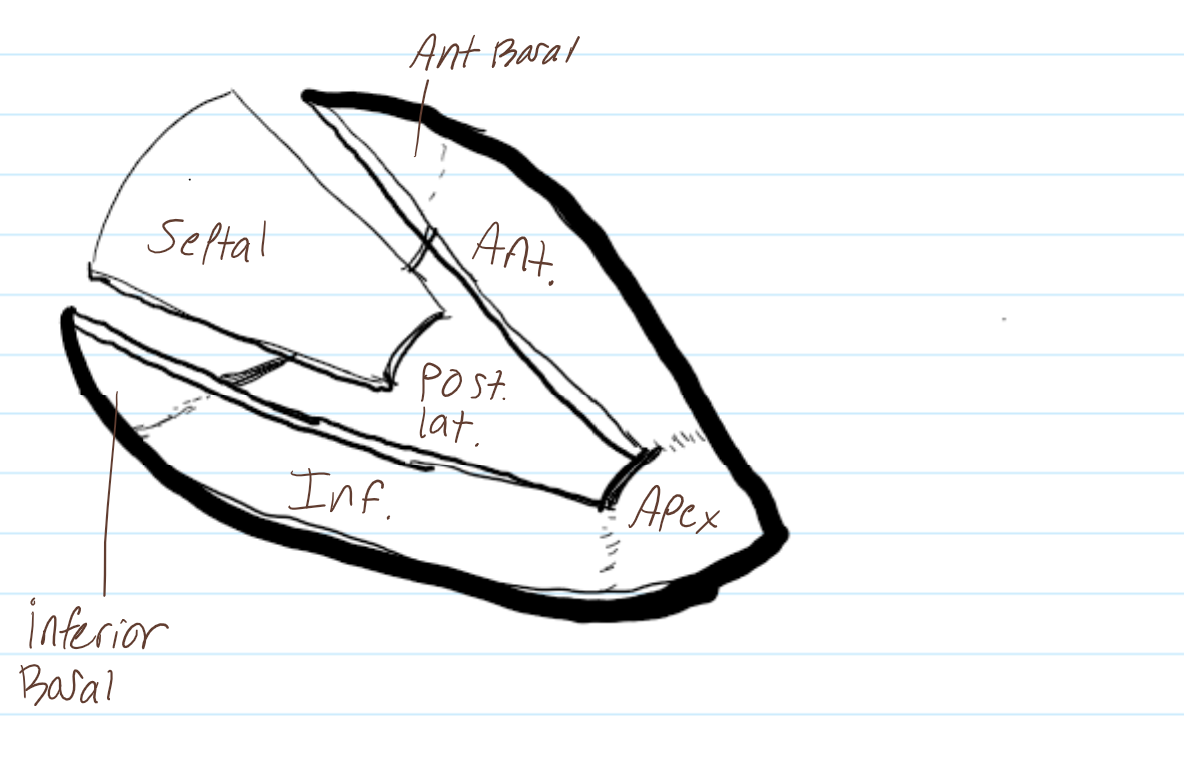
LABEL THEM
AO
PA
MITRAL
TV
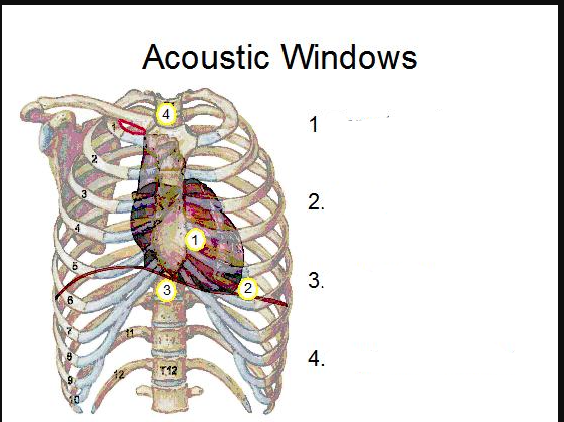
1/2?
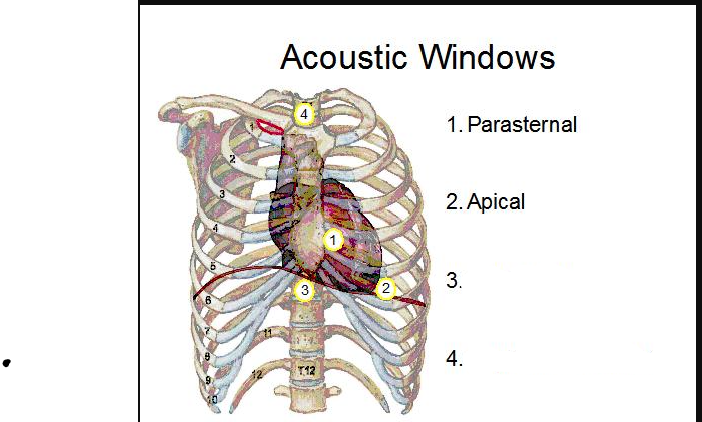
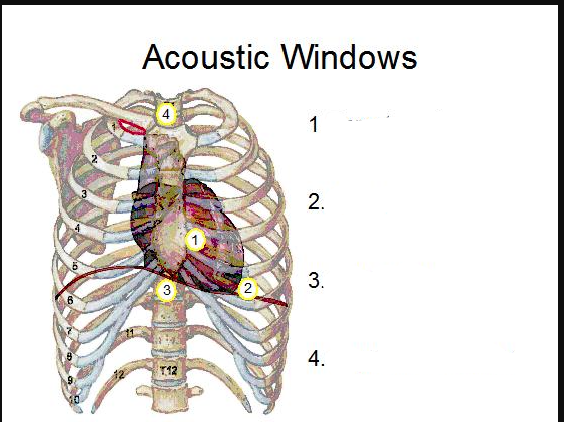
3/4
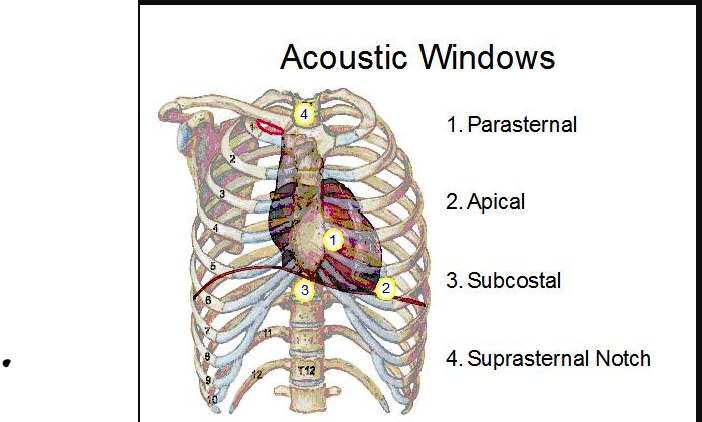
What standard echo transducer position is shown
Apical 4 chamber
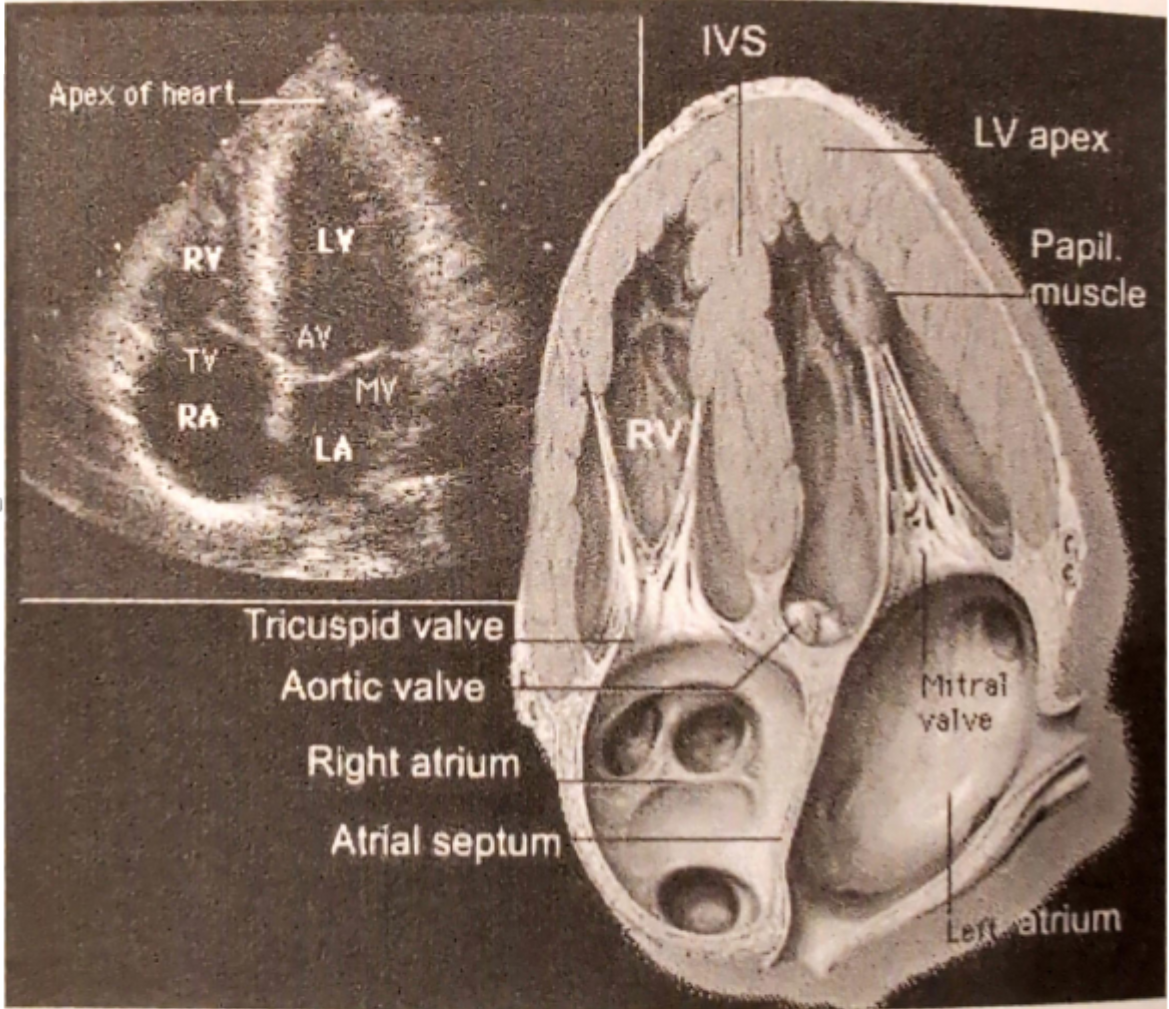
review this image
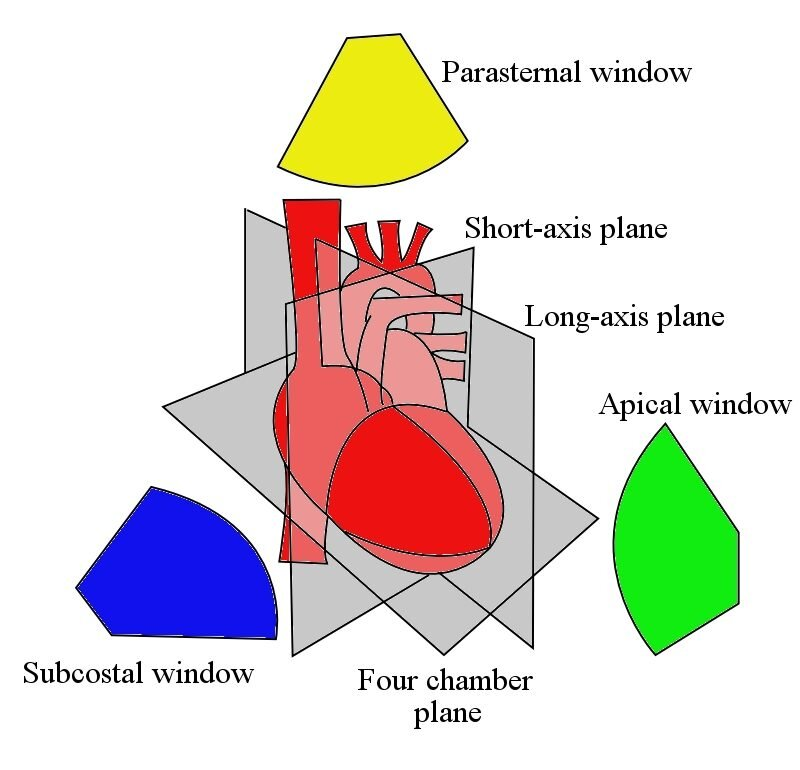
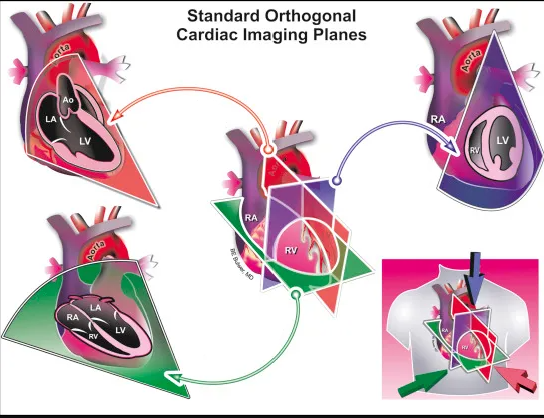
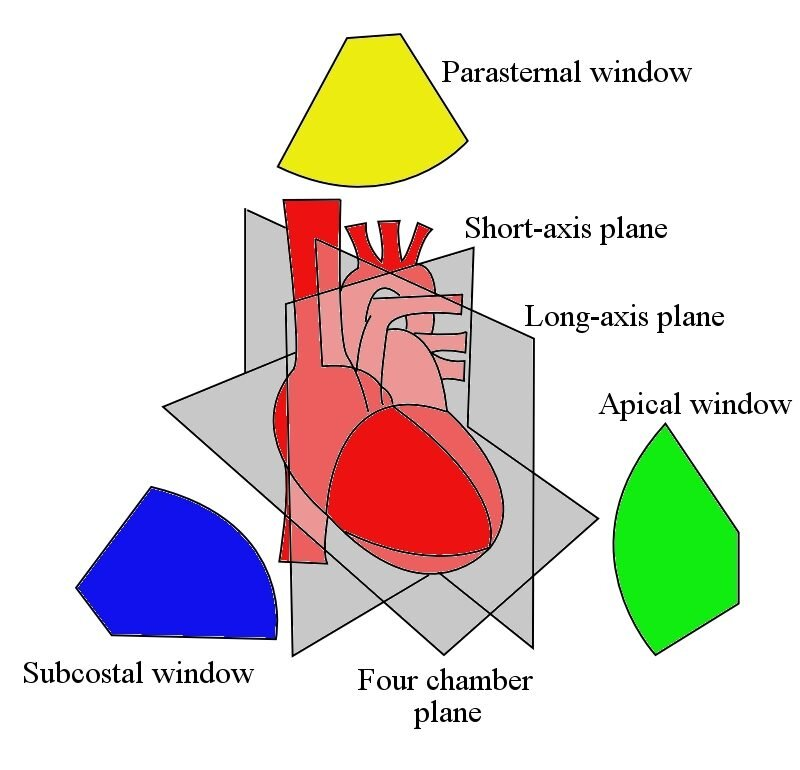
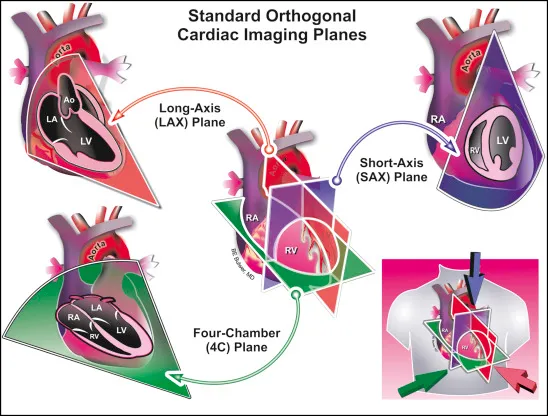
name these views
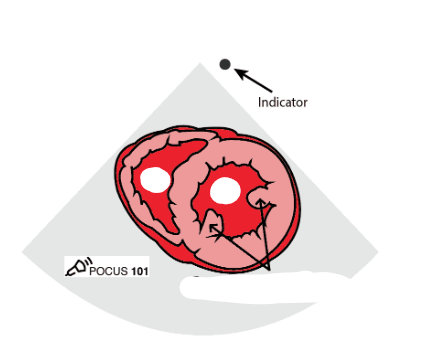
what view
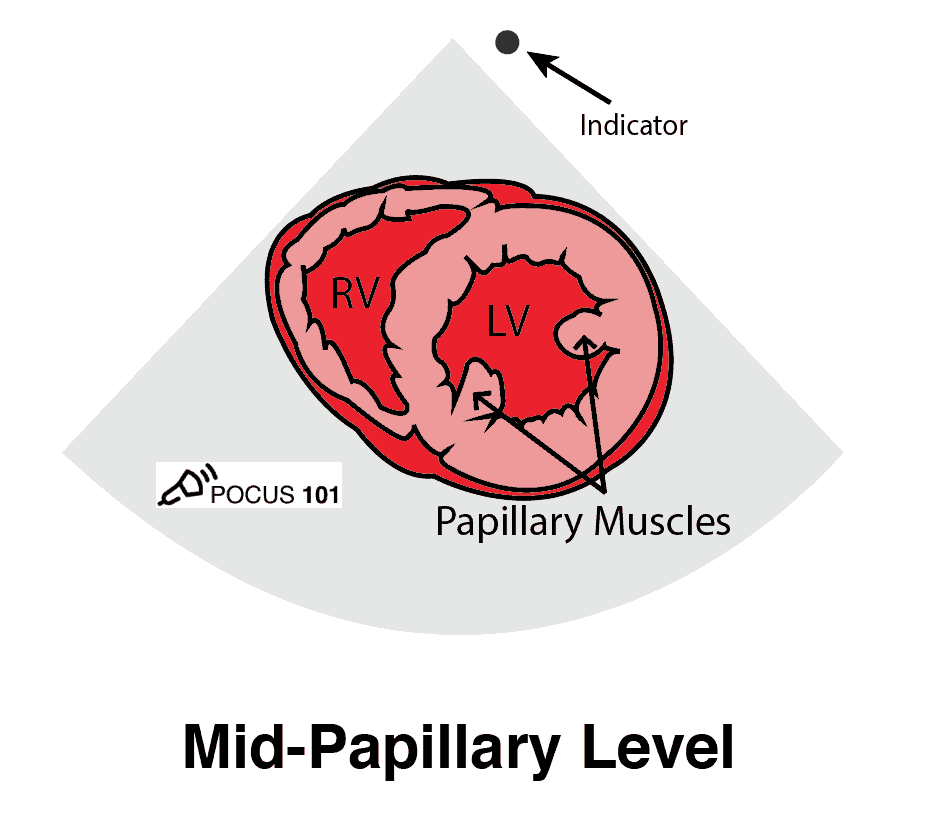
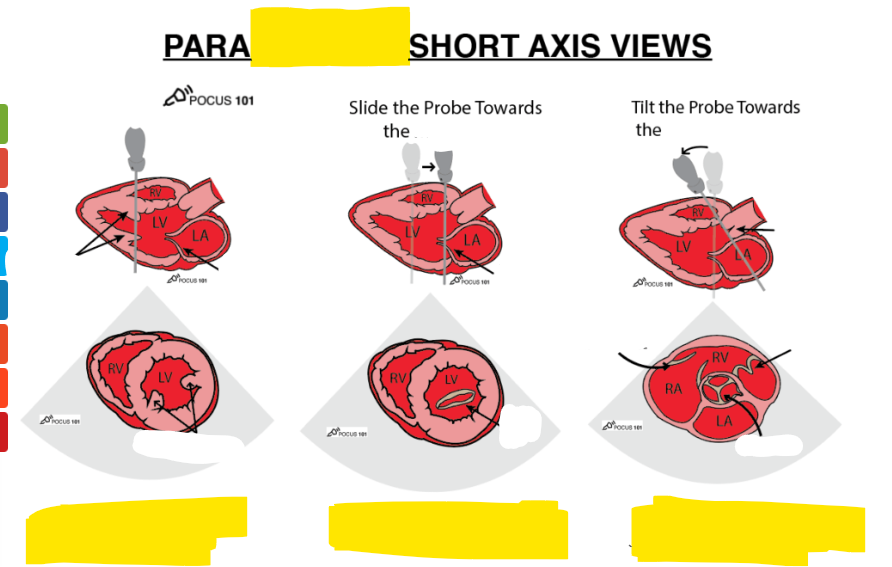
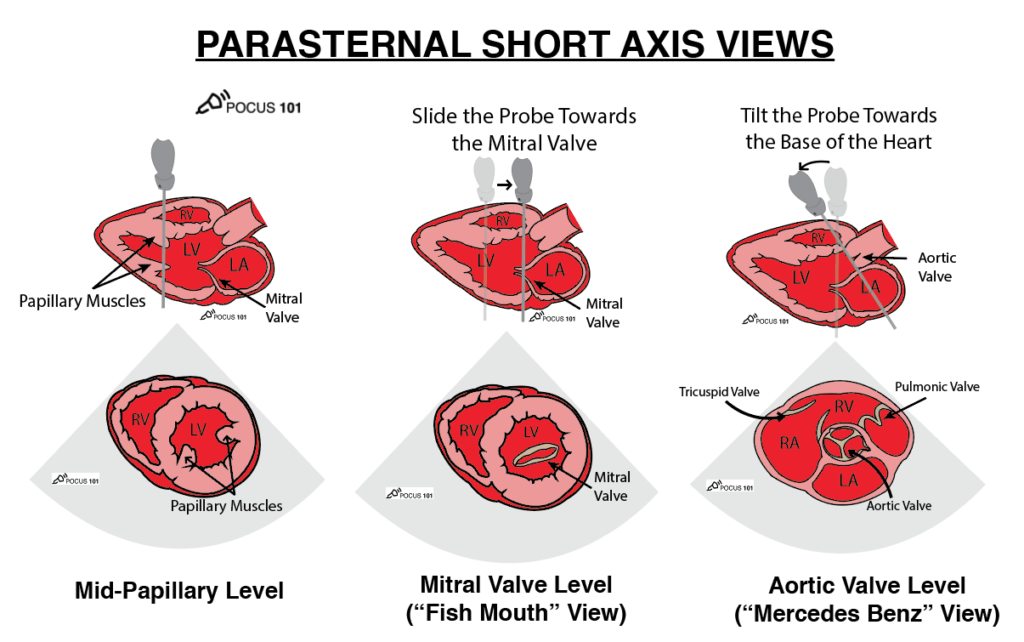
what are these 3 views
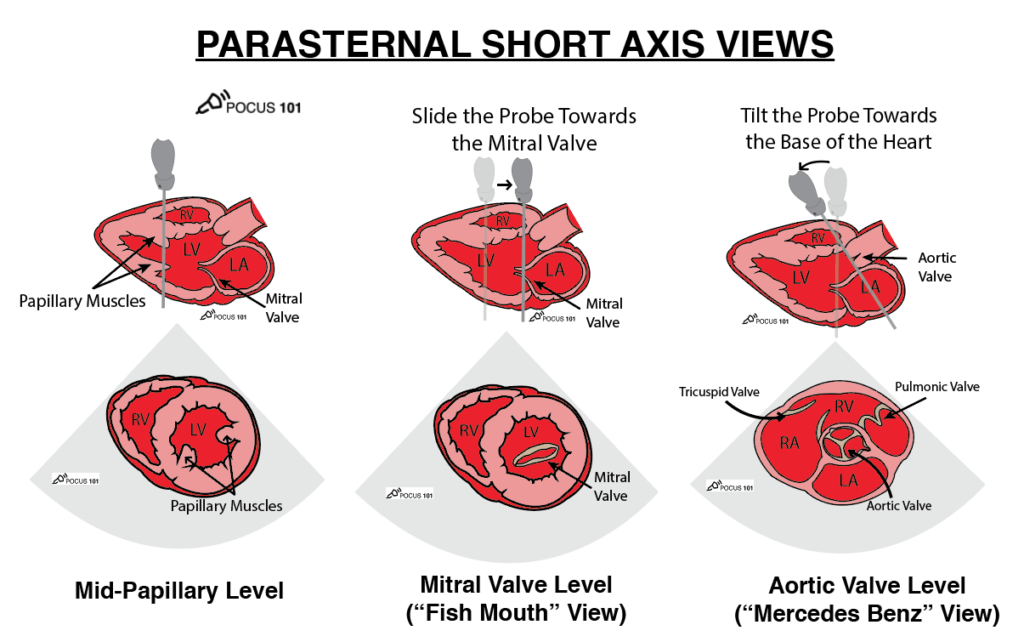
label structures
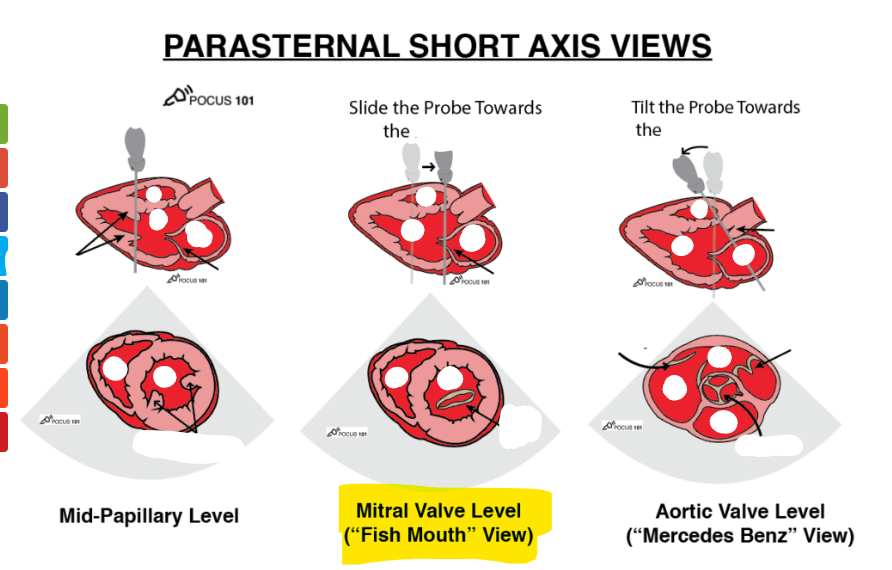
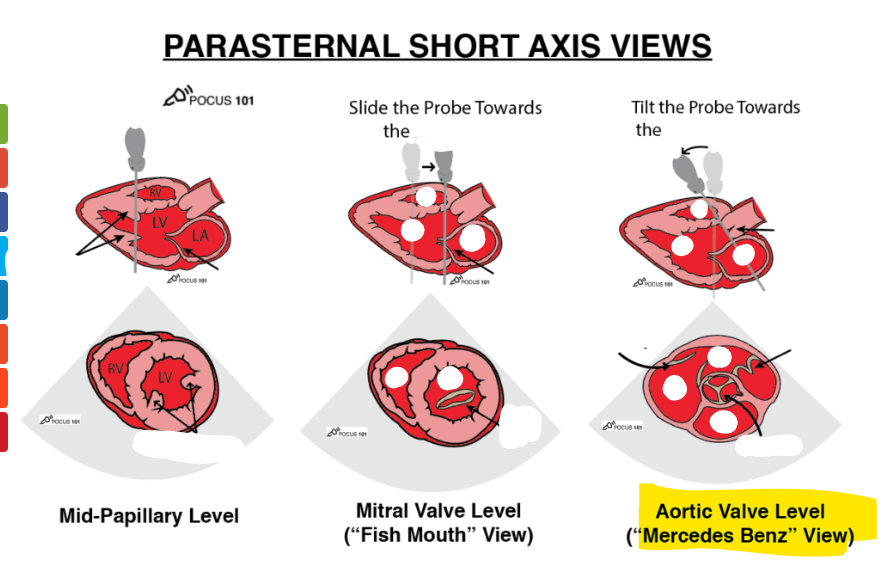
label structures
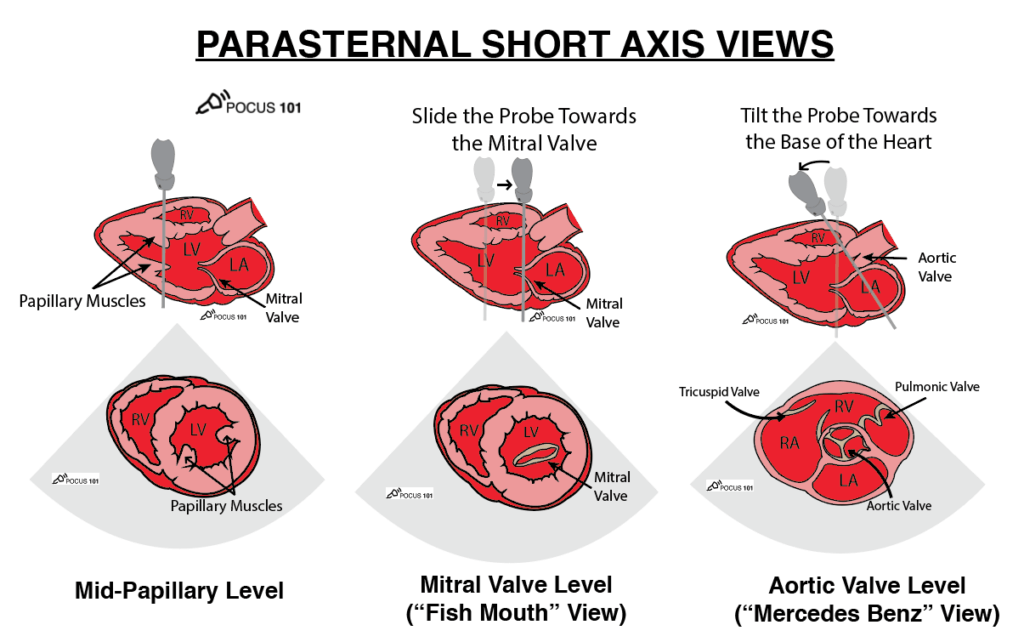
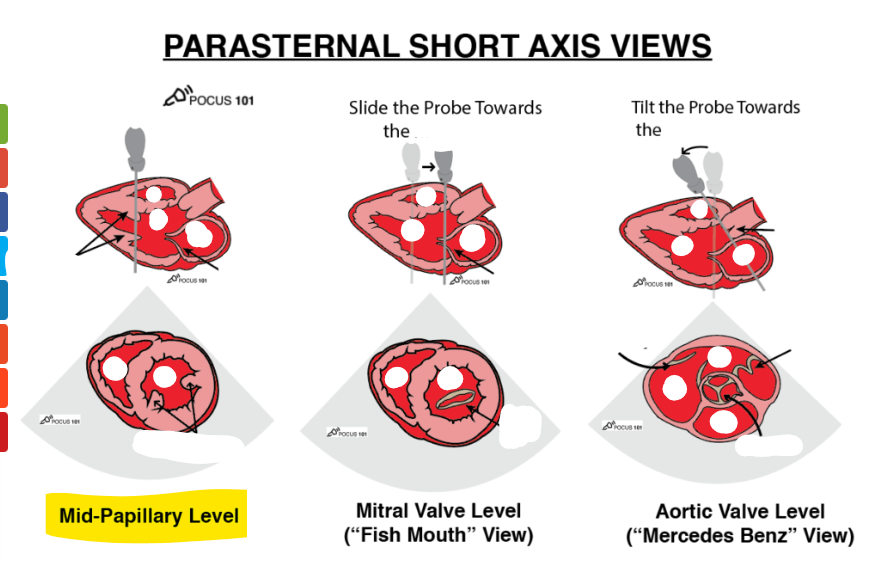
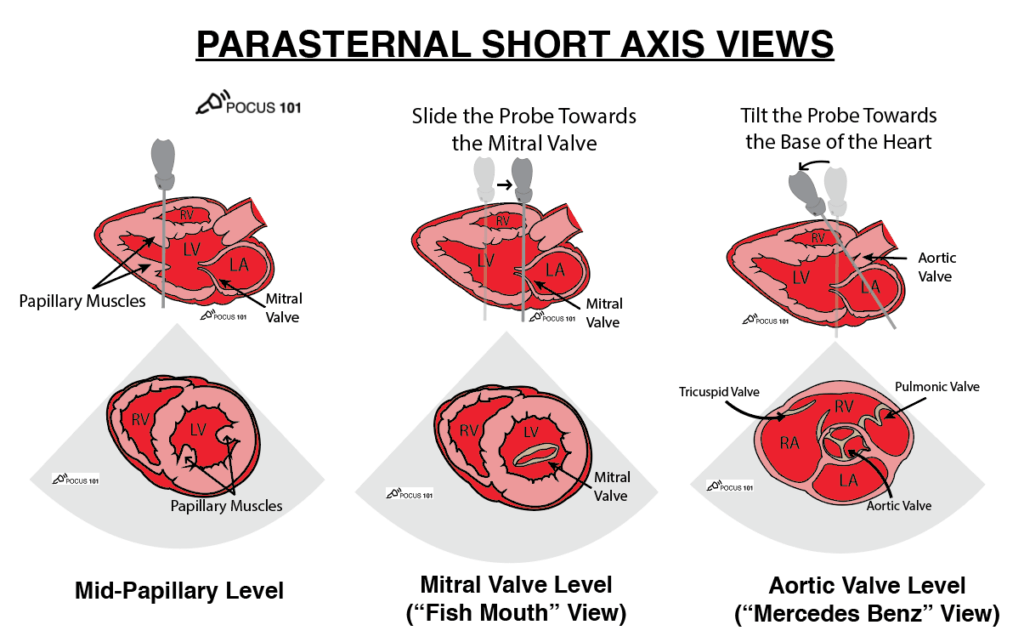
label structures
which heart valves are attached to the chordae tendinea
The heart valves attached to the chordae tendineae are the mitral valve and the tricuspid valve. These structures prevent the valves from inverting during ventricular contraction.
The MV and the TV have chordae tendinea attached to prevent ************** during ***** *****
These structures prevent the valves from inverting during ventricular contraction.
What valves are opened during ventricular systole
The aortic and pulmonary valves are opened during ventricular systole, allowing blood to be ejected from the heart into the aorta and pulmonary artery.
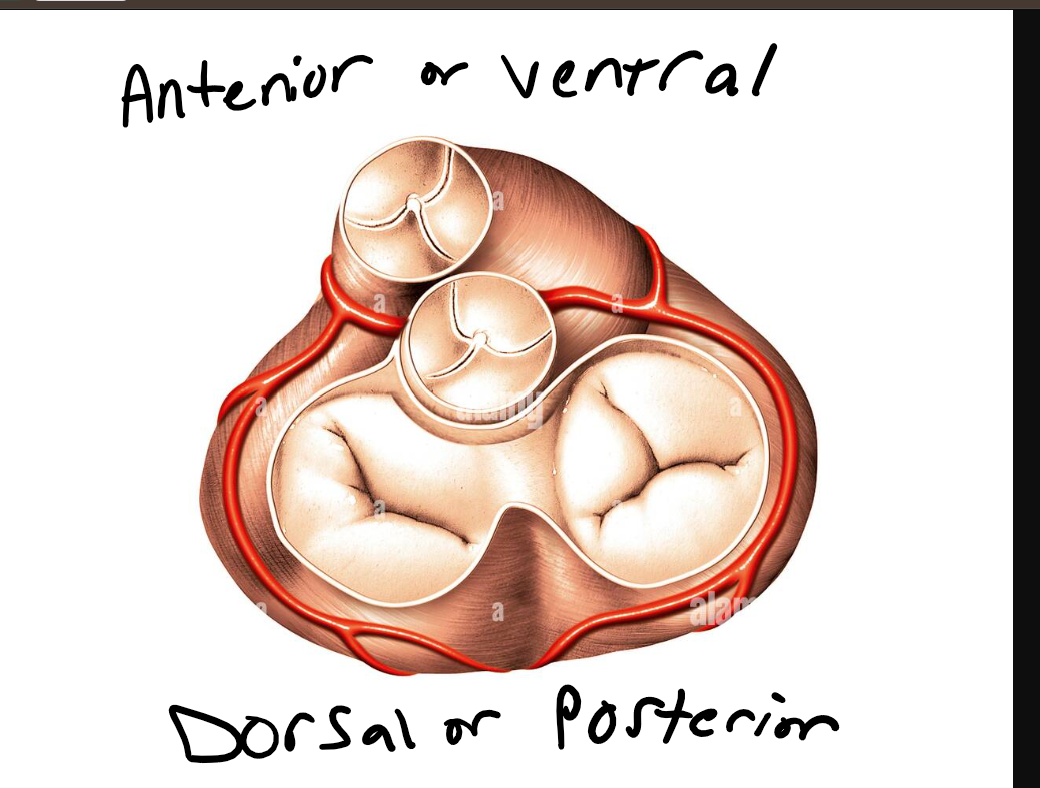
What anchors the heart valves in fibrous rings that are connected by triangular pads ( Trigone ) that create a rigid structure around the valves
The cardiac skeleton
Annulis
Annuli Fibrosi
what is the most front facing cardiac valve or anteriorly positioned
pulmonic valve
What is the largest cardiac valve
TV
but just slightly larger orifice
RA does not generate as much pressure as LA so orifice area is larger for both to admit same amount of blood
The worm like muscle strains within the RV chambers are termed
trabeculae carneae.
They are found chiefly in the RV where they provide a mesh in which to entrap transvenous pacemaker leads
and to distinguish native LV and RV
Trabeculae carneae
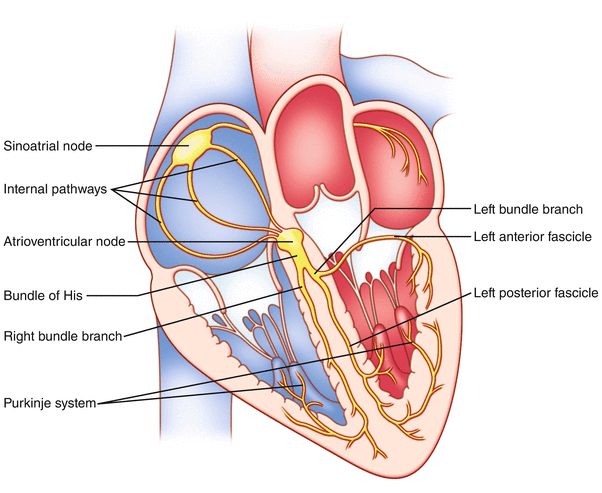
The left bundle branch is divided by what two
Left
anterior and posterior fascicle
The diaphragmatic surface of the LV is also called the
inferior surface of the heart.
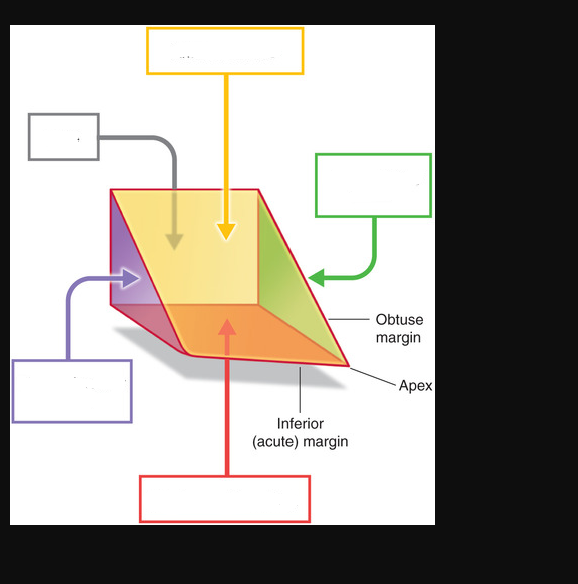
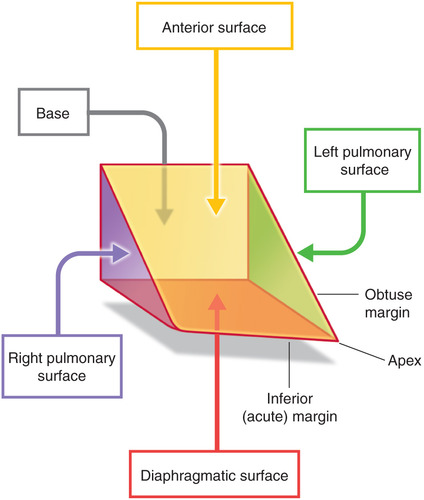
label the surfaces of the heart
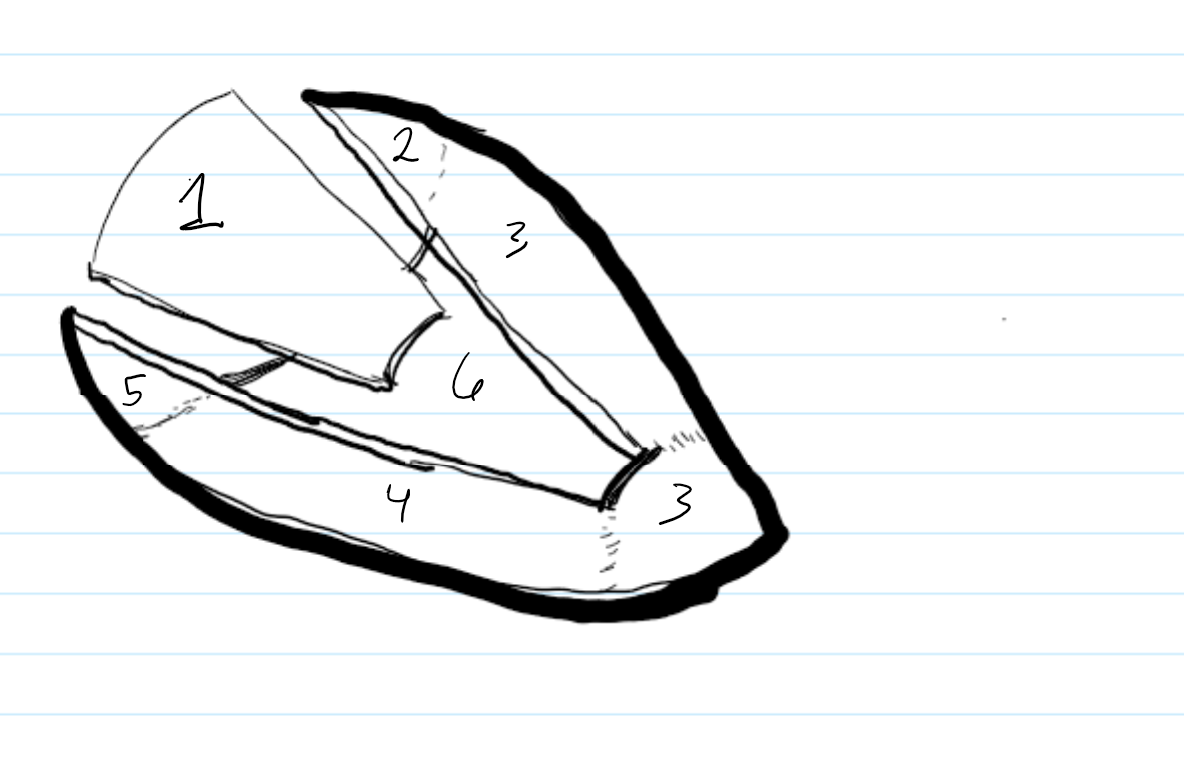
what angle is this rao or lao
RAO
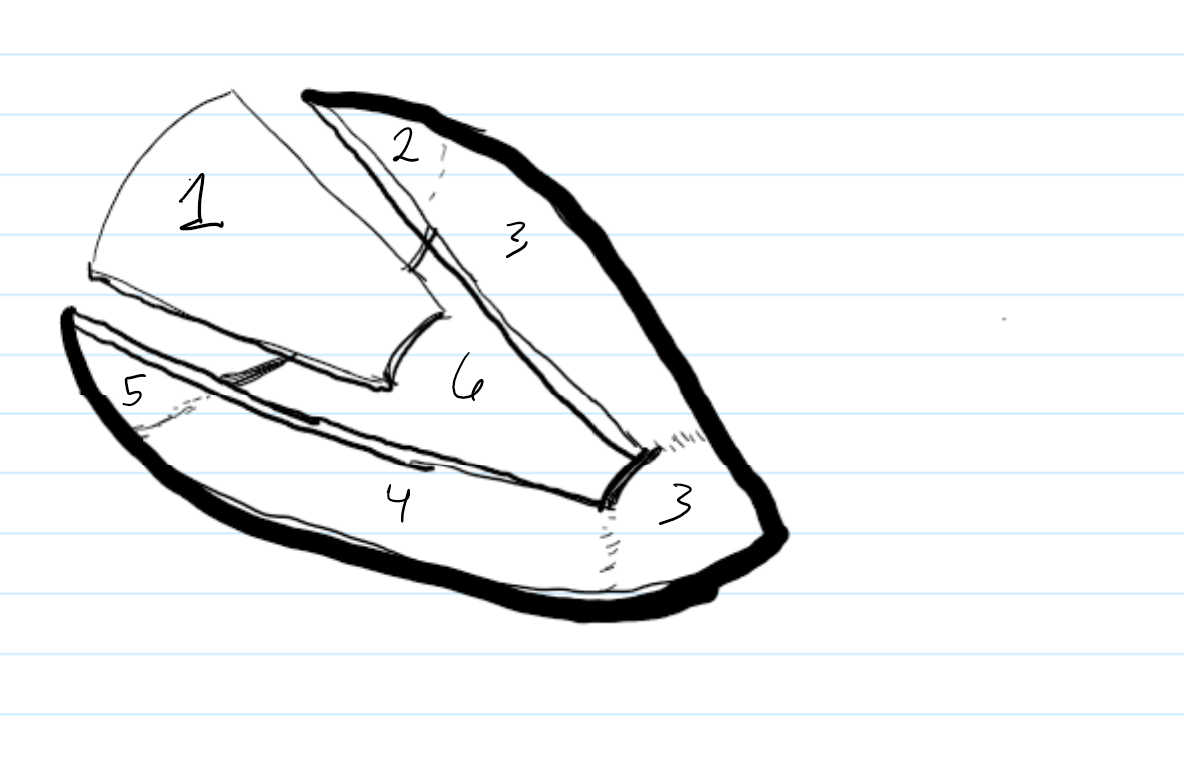
label the surfaces in this RAO image
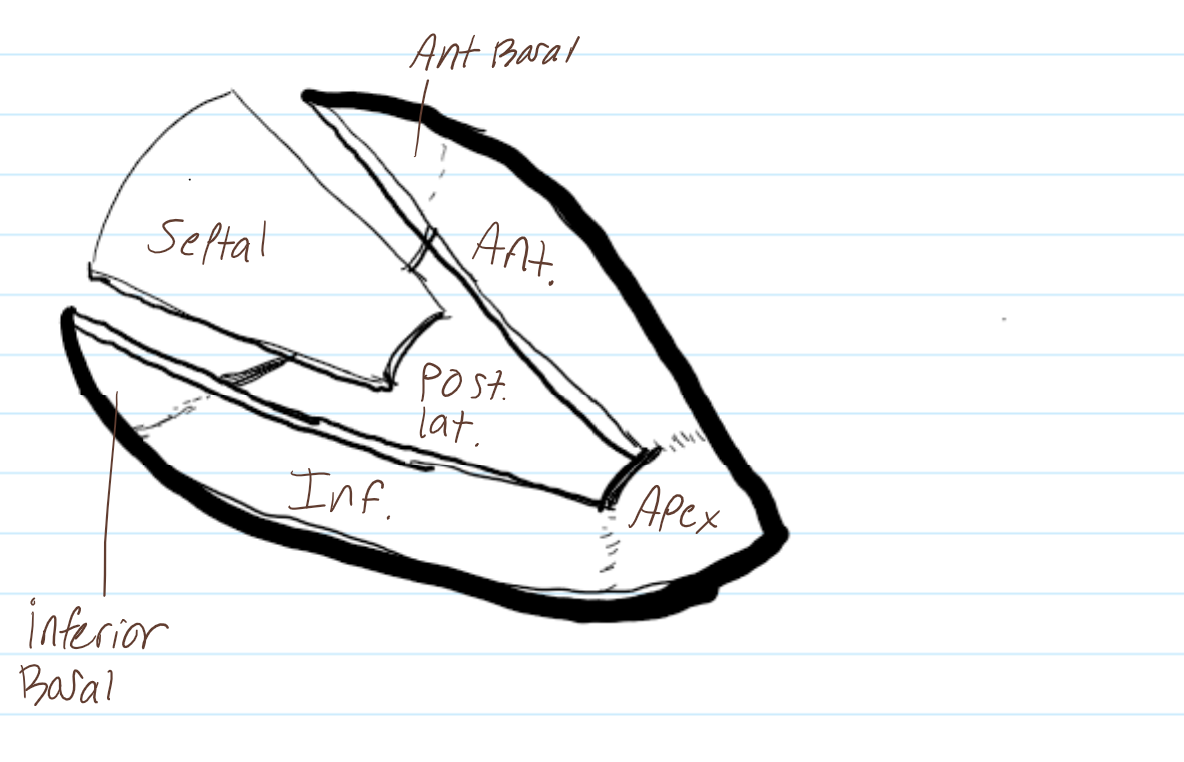
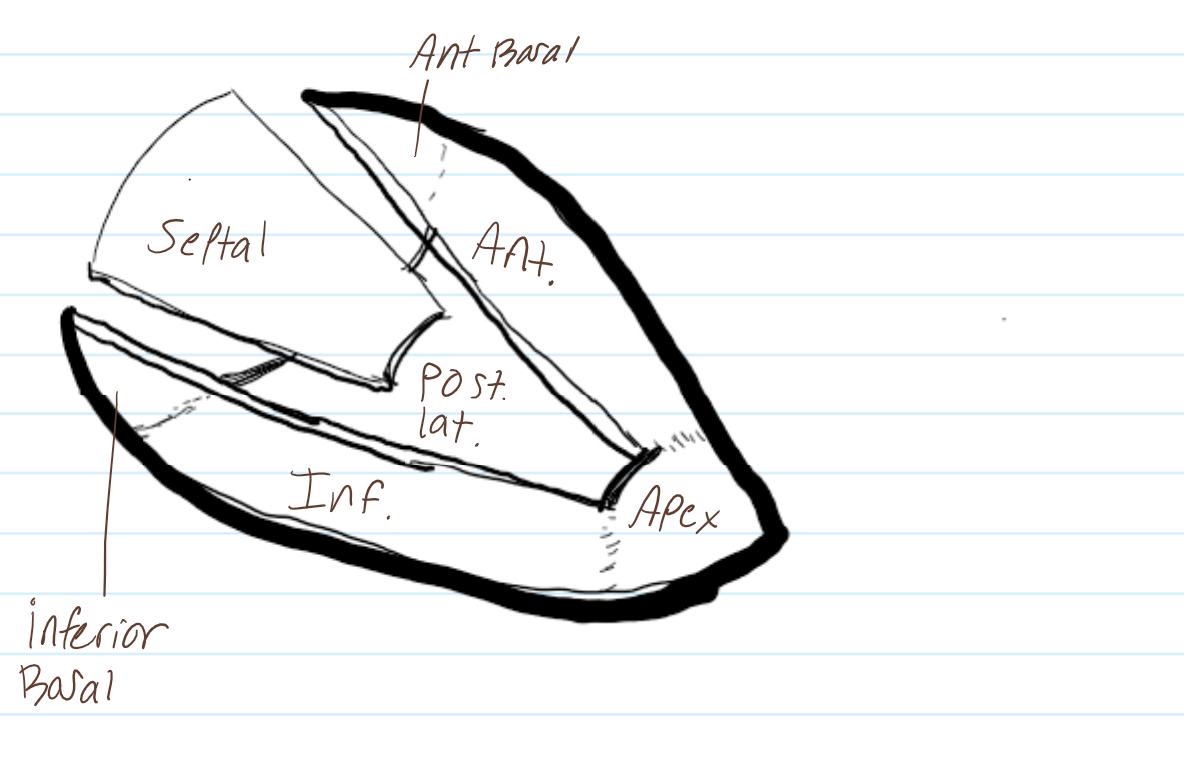
review this image
review complete
The RVOT is also known as the 2x
Infundibulum
Conus Arteriosus
The infundibulum is also known as the 2x
RVOT
Conus Arteriosus
The normal pacemaker of the heart is the
sinoatrial node (SA node)
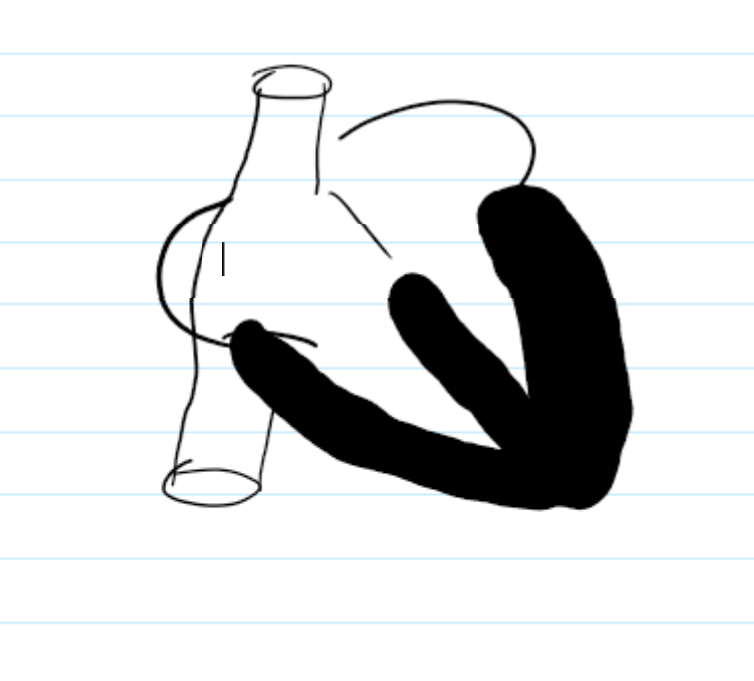
Sa node lies at the junction of the
right atrium and superior vena cava.
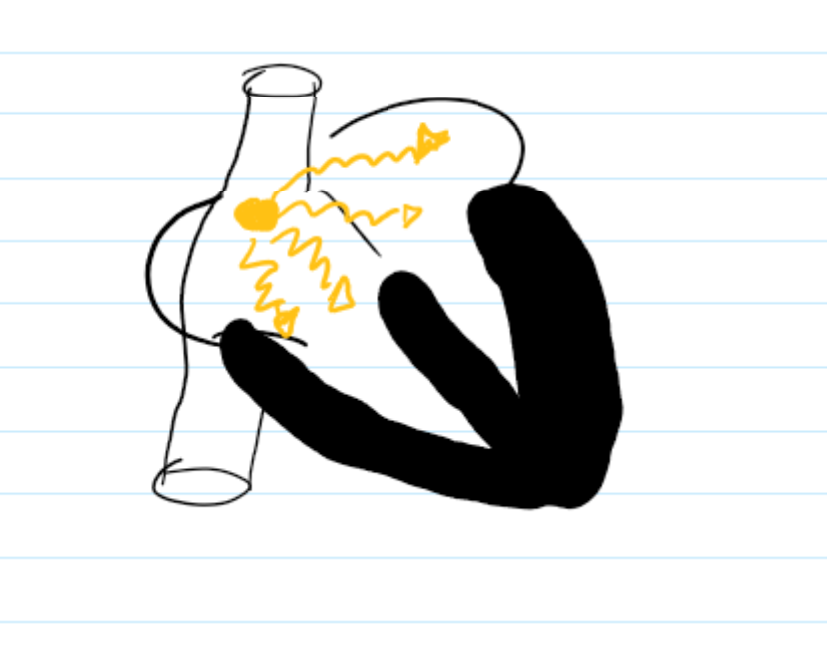

in biventricular lead placement, access to the coonrary sinus is sometimes difficult due to obstruction by the
Thebesian valve, the valve of the coronary sinus
the cells are separated by intercalated discs while the sarcomere are separated by ** ******
Z lines
What ions are involved in muscle contraction in the heart
*****
*****
sodium
and minor role chloride
missing 2
calcium
potassium
sodium
and minor role chloride
Ion movement in cardiac contraction
Depolarization
phase 0 is…..
**** Influx
Depolarization
Sodium influx Na+
Initial repolarization phase 1
***** and **** efflux
K+ and Cl- efflux
Plateau phase
phase 2
***** influx
Phase 2
Ca 2+ influx
Repolarization phase 2
*****efflux
K+ efflux
Restine membrane potential phase 4
maintained by na+/K+, ATPase, and ** leak channels
K+ leak channels
What is the central anatomic structure of the sarcomere which is believed to have a globular heads spiraling from its side which facilitate cross bridge linking btx two filamints
and
is it thick or thin filament
Myosin is a thick filament protein that plays a crucial role in muscle contraction by interacting with actin filaments.
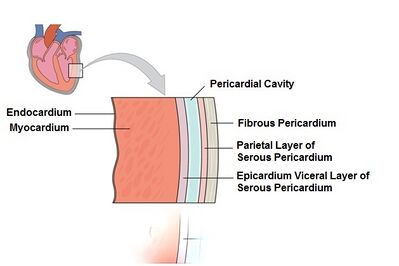
The epicardium is also termed the ***** of the pericardium
visceral pericardium
What type of tissue grows over implanted valves and stents
endothelium
inside lining of all organs, quickly grow over implanted devices to make the surface less thrombogenic
What refers to the walls of a body cavity
Parietal
What type of tissue lines inside of closed body cavities,
Serous membranes - Simple squamous epithelium that secretes serous fluid, providing lubrication.
What type oof tissue lines the cavities that open to external environment
mucous membranes
secretes mucus for protection and moisture
What kind of tissue covers the external surface of the body
cutaneous membrane
stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized)
The ______ peritoneum covers the organs in the abdominal cavity, reducing friction and providing a smooth surface for movement.
visceral
The ______ peritoneum lines the abdominal cavity walls and diaphragm, forming the outer layer of the peritoneal sac.
parietal
The peritoneum provides ______ between organs, allowing for smooth movement, and helps protect them from friction and damage.
lubrication and cushioning
It acts as a sack not engulfing the organs just cushioning them
the main function of the pericardium and its fluid is to
provide lubrication and protection for the heart, reducing friction during heartbeats.
how much pericardial fluid is contained in the pericardial sac
approximately 15 to 50 milliliters
CaO2 and CvO2 stands for what
arterial oxygen content and venous oxygen content, respectively.
(CaO2 - CvO2) gives you an idea of ____________ by the tissues
the oxygen extraction used
How much oxygen is extracted by the tissues
When finding Fick CO you are using arterial and venous ____ _____ not arterial and venous oxygen saturation percentage
contents
This is if you either use the actual oxygen contents from blood samples or (Ao sat - Pa sat) x hgb x Constant …. which would just be avo2 diff which uses the o2 content of both as CaO2 - CvO2 then you would convert from d/cl to L/min
We can determine pt’s blood flow (CO) if we know 3 things
VO2(oxygen consumption),
CaO2
CvO2.
just don’t forget to use proper units and conversion factors.
usually cardiac output will give you dL so divide the number by 10
to turn ml/min to L/min you need to do what
divide by 1000
How many joules should be used for the initial defibrillation shock in a patient with VF or pulseless VT?
120-200 Joules
What is the recommended dose of epinephrine during a cardiac arrest?
and whats the time on that
1mg every 3-5 min
What medication is typically administered after unsuccessful shock in a patient with VF/pulseless VT?
E