balanced equations + associated calculations
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Why must chemical equations be balanced?
So the reacting ratios are correct → so can then be used to calculate reacting masses, percentage yield, atom economy
What are the rules for balancing equations?
Not ok to change any small numbers of a formula
Add large numbers in front of a formula
Large numbers can be x/2 or halves if in front of a diatom e.g ½ O₂ is okay but not ½ H₂O
What are the state symbols?
s) = solid
(l) = liquid
(aq) = aqueous
(g) = gas
STATES OF MATTER
metals are..
diatoms are mostly..
ionic compounds are…
most simple molecules are..
acids are..
when in solution, ionic compounds are..
solids
gases
solids
gases
aqueous
aqueous
What does aqueous mean?
Dissolved in water
* when compounds are dissolved in water, they dissociate into separate ions
What do ionic equations only show?
The ions / species that change in a reaction
What is the ionic equation for:
Explain how to form an ionic equation for a precipitate reaction
The simplest ionic equation will always be:
____ (aq) + _____ (aq) → _____ (s)
The only product present is the precipitate and the only two reactants are the aqueous ions that make the precipitate
Write the ionic equation for magnesium nitrate solution + sodium hydroxide solution → solid magnesium hydroxide (precipitate)
Mg²⁺ (aq) + 2OH⁻ (aq) → Mg(OH)₂ (s)
Define atom economy
A measure of what proportion of the products of a reaction are the desired product + how much is waste
Higher the atom economy, the less…
waste that is produced
What is the equation for atom economy?

What does the % yield tell us?
The practical efficiency of the process
Reasons why percentage yield is less than 100%
Incomplete reaction
Side reactions
Loss of product during washing
Loss of product transferring product
What is the equation for percentage yield?
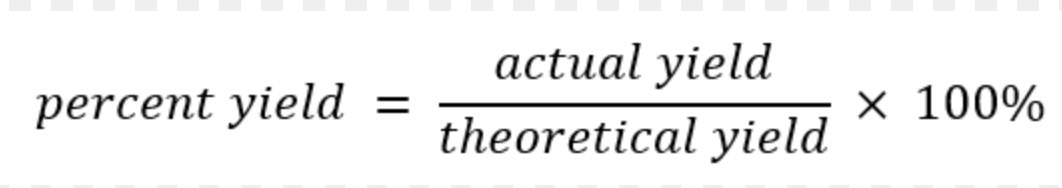
Rearrange the formula to make actual yield the subject
(percentage yield x theoretical yield) / 100
Rearrange the formula to make theoretical yield the subject
actual yield x 100 / percentage yield
The theoretical mass is also the…
expected mass
10.0g of calcium carbonate was decomposed to give 3.60g of calcium oxide. What is the % yield of calcium oxide in this reaction?
What is the equation for percentage purity? ADD PIC
The concentration of a solution is measured as what?
the number of moles of solute per decimetre cubed of solution (moldm⁻³)
What is concentration also known as?
Molarity
What is the triangle that links moles, concentration + volume?

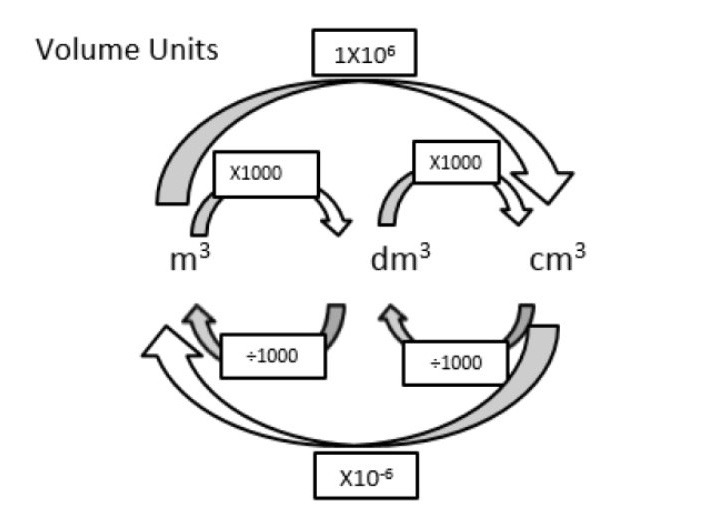
How to convert from cm³ to dm³
divide by 1000
7.55g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 500cm³ of water - what is the concentration of the solution in moldm⁻³
calculate the moles of NaCl
mass/ Mr → 7.55/58.5 = 0.1291
convert volume from cm³ to dm³
500/1000 = 0.5 dm³
calculate concentration
0.1291/0.5 → 0.258moldm
How to calculate concentration in g dm⁻³
conc in mol dm⁻³ x Mr
What is a standard solution?
A solution whose concentration is known accurately → its concentration is usually given in mol dm⁻³ or g dm⁻³
When making a standard solution, what is important?
Mass of substance is accurately measured
All substance weighed out is successfully transferred to volumetric flask used to make up solution
What is the procedure that will make that happen?

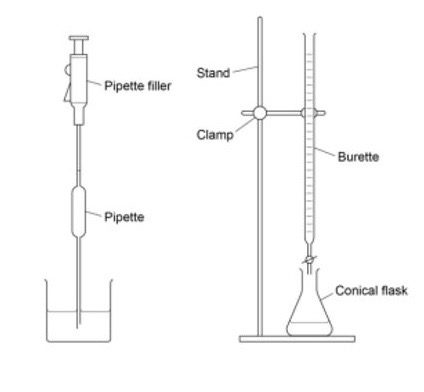
What is a titration?
A technique where a solution of a known concentration is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution
Briefly explain what an acid base titration involves
The standard solution is added to a burette to a known volume in the conical until the reaction is complete
Often an indicator is used to signal the end of the reaction → the endpoint
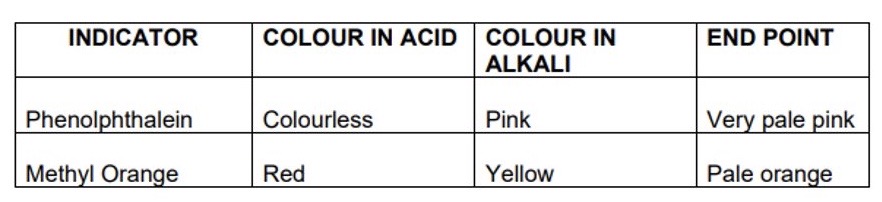
What colours do these indicators make?
Phenolphthalein
Methyl orange
The accuracy of the results of the titration will be a reflection of what?
The care you have taken whilst performing it → when done carefully, titrations give a very accurate, precise results
Titrations of unknown solutions are done in what 2 steps?
A rough titration used to determine the approximate amount of standard solution needed to neutralise an unknown solution
Subsequent more accurate titrations that you will use for your calculations
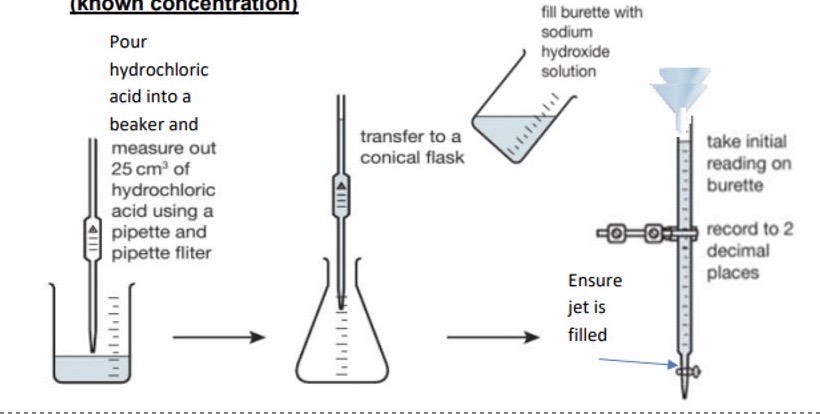
Explain in detail the method of the rough titration
Rinse burette with deionised water, then rinse with the standard solution + fill burette incl. area below tap with the solution → take initial reading + record to 2.d.p, ending in a 5 or 0
Rinse pipette with deionised water, then rinse with unknown concentration solution + transfer 25cm³ of the solution from your beaker into your conical flask using pipette
Add 3-4 drops of indicator to your conical flask + place under your burette → don’t add more than 4 drops as indicators are weak acids so anymore will affect the end point
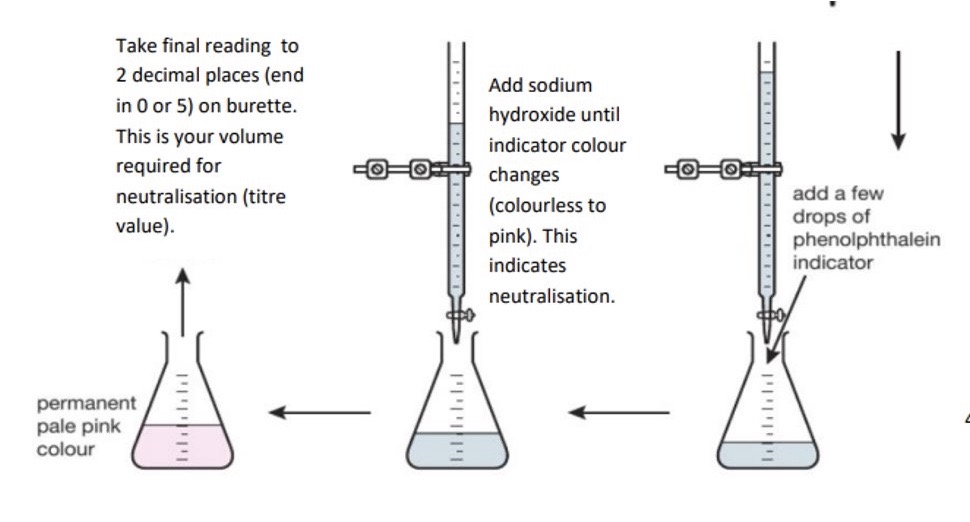
The solution in conical flask will change colour depending on its pH + indicator used
Remove filter funnel + add solution from burette, with constant swirling of flask until indicator just changes colour → indicates neutralisation
Write down final burette reading to 2.d.p - ending in 0 or 5 → this is the volume of solution from burette required for neutralisation (titre value)
Empty conical flask + wash thoroughly with deionised water
Refill burette if necessary → if there’s less than 25cm³
What can you add to make sure all your solution has reacted
Add deionised water
Why should we always overfill the burette + let some solution out into waste beaker?
It ensures that the area below the tap (jet) is also filled → prevents titre volume from being too high
Why is it important to rinse pipette + burette with the solution that will be in the apparatus?
This removes any drops of deionised water that would lower the concentrations of the solutions + effect the end point - titre value
Why is a conical flask used?
Easy to swirl so there are no spillages
Why do we remove the filter funnel from burette when carrying out the titration?
Ensures no additional drops enter from the burette + lower titre
Explain the method of subsequent titrations
At start of titration, instead of adding a small amount of solution from burette at a time, add 2cm³ less than your previous titre value to your conical flask
Then add dropwise from burette whilst swirling until you see the endpoint
Continue with titration until you have concordant titre values → only use the concordant values to calculate average titre which is used in the calculations
Close to the endpoint, what can you do to ensure all reagents are in solution
Use deionised water to wash the sides of your conical flask → won’t affect the end point as water isn’t a reagent
What are concordant values?
Values that are within 0.1cm³ of each other
Give an example of a titration + its method
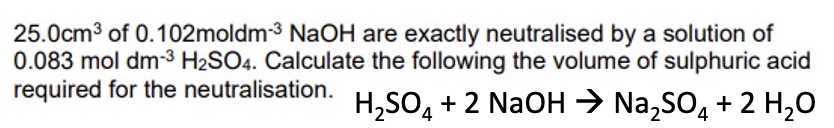
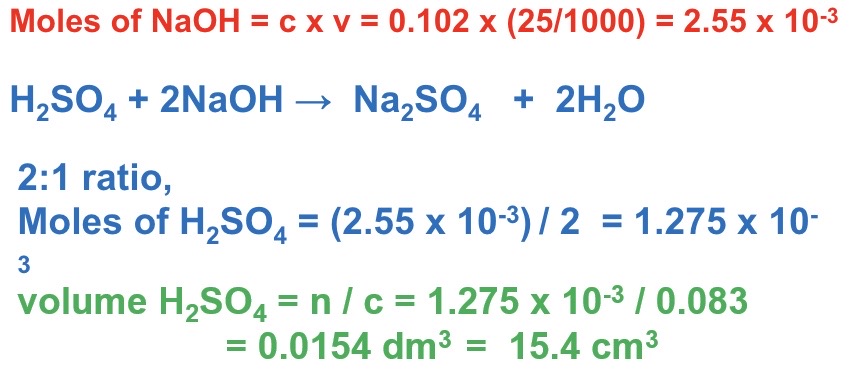

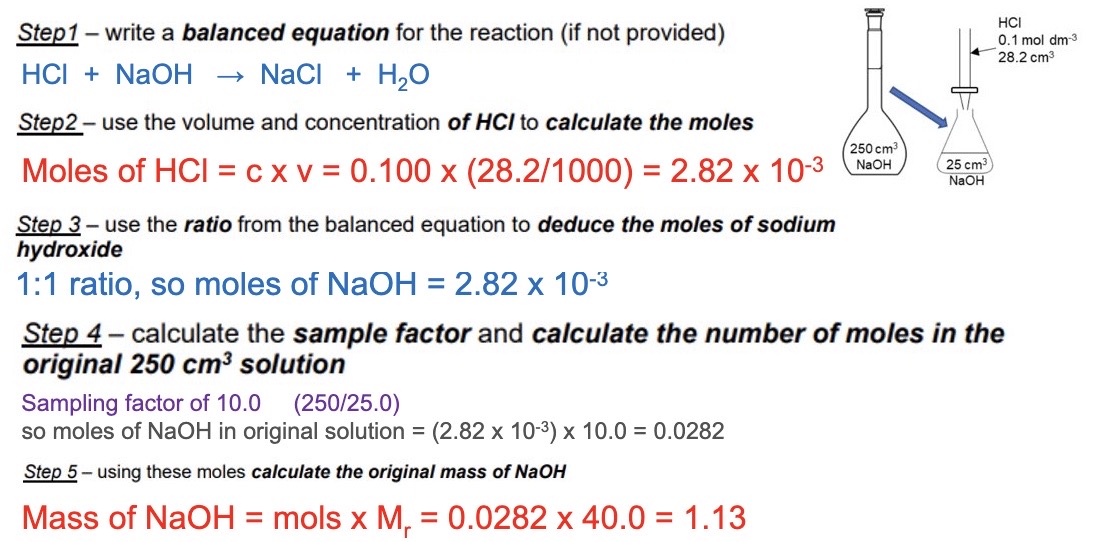
Every time you make a measurement with a piece of apparatus, there is a small..
margin of error in that measurement due to the apparatus itself
What are errors like this called?
Apparatus error + can’t be avoided → can be reduced by using the most precise equipment available
What is the equation for calculating the apparatus error for each piece of equipment?

When you calculate apparatus error, what does that actually mean?
The result of the experiment should be within __% of the correct value
When you design experiments, you should aim to ensure that the total apparatus error is minimised by doing what?
Working on a suitable scale + with suitable apparatus
For apparatus that is read more than once, what should you do when calculating the apparatus error?
Multiply the error you are given by the no. of readings
How can you reduce the amount of uncertainty without changing the equipment used?
By increasing the measured amount → decrease the % uncertainty
In a titration, how could we increase the titter volume + lower burette’s % uncertainty?
Decrease conc. of solutionI in burette
Increase volume / conc. of solution in conical flask
Explain how to complete a back titration question asking to calculate mass / percentage yield :


