Cardiovascular 1,2 & 3
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
How is Heart Rate Variability (HRV) determined?
By measuring the time intervals between each R wave on an electrocardiogram.
What are the main factors that influence Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)?
Cardiac output: The total volume of blood pumped by the heart each minute.
HR & SV
Stroke volume: The amount of blood ejected with each heartbeat.
Baroreceptors: Sensors that help regulate blood pressure.
How does HR and SV impact Cardiac output (CO)?
Heart Rate:
PNS and SNS
Stroke Volume:
Contraction length
Mean arterial pressure (Afterload)
Preload (End diastolic volume)
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
An average pressure in a patient's arteries during one cardiac cycle, influenced by cardiac output and vascular resistance.
What is Total Peripheral Resistance? (TPR)
The overall resistance to blood flow in the systemic circulation, influenced by:
blood vessel diameter
blood viscosity.
What is pulse pressure?
The difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings,
Indicating the force that the heart generates each time it beats
Pulse Pressure = Systolic BP - Diastolic BP
What is stroke volume?
The amount of blood ejected with each heartbeat.
What are the three primary regulators of stroke volume?
Preload
Afterload: An increased afterload decreases stroke volume.
Contractility: The strength of ventricular contractions.
What happens when you have a greater preload?
Increases the strength of the contraction and increases cardiac output
What is afterload?
The resistance the left ventricle (LV) must overcome to eject blood into the aorta. A higher resistance in the aorta leads to increased afterload, which limits stroke volume.
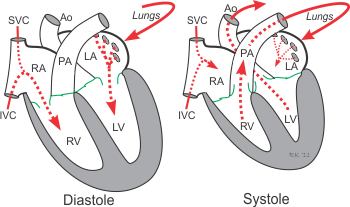
What occurs during systole?
The phase of the cardiac cycle where the heart muscles contract, pumping blood from the heart chambers into the arteries.
Systole→Squeeze
What is Diastole?
The phase of the cardiac cycle where the heart muscle relaxes, allowing the atria and ventricles to fill with blood. This occurs after systole and is vital for ensuring sufficient blood volume in the heart before the next contraction.
Diastole→DIe down (Relaxes)
What is the first mechanism to happen within the SNS to lower high BP?
Release of Norepi is decreased and less NE binds to the alpha receptors on arterial smooth muscles leading to vasodilation.
Which nerve communicates/activates the parasympathetic NS?
Vagus nerve
What is the Sympathetic NS stimulated through?
cardiac accelerator nerves
sympathetic cardiac nerves
Stimulate and activate SA and AV node
What does a drop in hematocrit mean?
A drop in hematocrit indicates a reduced proportion of red blood cells in blood, which can signal anemia or fluid overload.
Does a drop in hematocrit result in decreased stroke volume?
Not directly; a drop in hematocrit indicates a reduced proportion of red blood cells, which can affect blood viscosity and oxygen-carrying capacity but does not directly determine stroke volume. Stroke volume is primarily influenced by __________, __________, and __________.
What is cardiovascular drift?
A gradual increase in heart rate during prolonged exercise at a constant intensity, accompanied by a decrease in stroke volume.

What is the Fick equation?
A mathematical formula used to calculate cardiac output based on oxygen consumption and the difference in oxygen content in arterial and venous blood.
What is the Frank-Starling mechanism?
An increase in the heart's preload (the volume of blood filling the heart) leads to a stronger contraction and increased stroke volume.
This ensures that cardiac output matches the volume of blood returning from the body, maintaining efficient circulation.
What regulates the Frank starling mech.?
Venous return
volume of blood, from the system, back to the heart
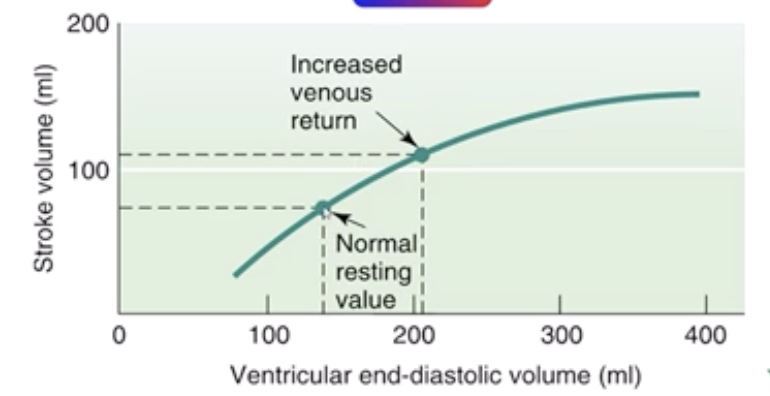
What influences venous return?
Venoconstriction
Via SNS
a-VO2 Difference
The difference in oxygen content between arterial and venous blood, indicating how much oxygen is used by tissues.
If someone is NOT fit:
There will be more O2 on the venous side
V→Very unfit (Bad)
If some IS fit:
There will be more O2 on the arteriole side
A→Always Fit (Good; A+)
What is endothelium mediated vasodilation?
The process by which the endothelium (inner lining of blood vessels) releases substances that cause relaxation of the vascular smooth muscle, leading to dilation of the blood vessels and increased blood flow.
Nitric Oxide
How does emotion affect HR and BP?
HR and BP increase in an emotionally charged environment
Increase in Sympathetic nervous system activity
What happens at the onset of exercise?
Theres a rapid increase in HR, SV, CO
Plateau in submaximal (below lactate threshold) exercise
What does the rate of recovery depend on?
Duration & intensity of exercise
Training state of subject
The more Hot, humid environment the LONGER the recovery
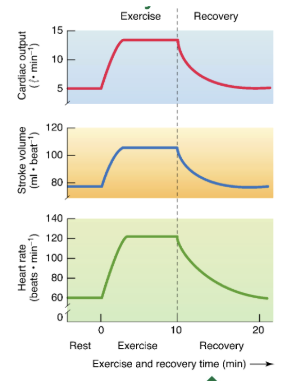
With incremental exercise, what happens?
Increased HR & CO plateaus at 100% VO2 max
Decreased vascular resistance and increased Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
What is Double product?
Double product, or rate-pressure product, is a measure of myocardial oxygen consumption calculated as heart rate multiplied by systolic blood pressure.
Used to determine how HARD the heart is working
With intermittent exercise what does HR, BP, and recovery depend on?
Fitness level of person
Temp and humidity or environment
Duration and intensity of exercise
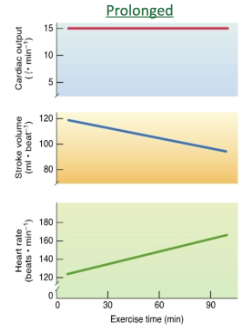
Prolonged exercise
Cardiac output is maintained BECAUSE we can have an increase in HR (CARDIOVASCULAR DRIFT)
Theres a DECREASE IN STROKE VOLUME
Increase in body temp→dehydration→a drop in plasma volume→ Decreased venous return (VR) → Decreased stroke volume
What causes a decrease in SV?
Increase in body temp→dehydration→a drop in plasma volume→ Decreased venous return (VR) → Decreased stroke volume
What is cardiovascular drift?
When the HR is able to increase despite a drop in stroke volume
The a-VO2 Difference indicates the difference in oxygen content between __________ and __________ blood, indicating how much oxygen is used by tissues.
arterial; venous
If someone is NOT fit, there will be more O2 on the __________ side.
venous
If someone IS fit, there will be more O2 on the __________ side.
arterial
Short term and Long term regulation of BP
Short term
baroreceptor reflexes that quickly adjust heart rate and vascular resistance.
Long term
kidneys control blood volume and release hormones like renin to activate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), ultimately stabilizing blood pressure.
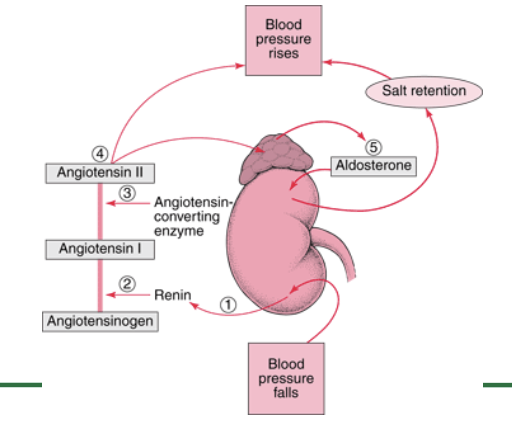
Explain the process of how the kidneys regulate BP
When blood pressure drops, the juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys detect the change and release renin. Renin then converts angiotensinogen (produced by the liver) into angiotensin I. As angiotensin I passes through the lungs, the enzyme ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) converts it into angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that narrows blood vessels and increases blood pressure. Angiotensin II also stimulates the adrenal glands to release aldosterone, which signals the kidneys to retain sodium and water, increasing blood volume and further raising BP. Additionally, the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) promotes water retention, further stabilizing BP. If BP becomes too high, the kidneys counteract this by excreting excess sodium and water, reducing blood volume and lowering BP back to normal.
4o
How do baroreceptors regulate short term BP?
Barorecpeptors sense the increase in blood pressure→baroreceptors use sensory neurons to deliver the information to the cardiovascular control center (IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA) → The goal is to lower the BP through the AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM:
What variables affect HR?
Baroreceptors→Through ANS
PNS: Ach released via vagus nerves and slows HR by inhibiting SA and AV node
SNS: Norepi is released via sympathetic cariac acceleratory nerves & increases HR by stimulating SA and AV nodes
what is the connection between less ventricular myocardium contractions and sympathetic nerves?
The less Nor epi. or epi. being released the weaker the contraction
How does the SA node know to decrease its activity if it is innervated by both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves?
Ach that attaches to the muscarinic receptors on the SA node, inhibit the SA node. (PARASYMPATHETIC)
Describe CO2 dioxide transport from the exercising muscle to the lungs
During exercise, muscles produce more CO₂ as a byproduct of increased metabolism→CO₂ diffuses into the blood and is transported to the lungs in three forms: mainly as bicarbonate (~70%), bound to hemoglobin (~20–23%), and dissolved in plasma (~7–10%) →It travels through the veins to the right heart, then to the lungs, where it's released into the alveoli and exhaled→This process helps remove metabolic waste and maintain acid-base balance during physical activity.
4o
What is the role of carbonic anhydrase?
Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the conversion of carbon dioxide and water to bicarbonate and protons, aiding in CO2 transport and pH regulation.
What is the short-term regulation of decreased blood pressure?
Baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and aortic arch detect the drop.
They trigger increased sympathetic activity → vasoconstriction, increased HR, and cardiac output → raises BP quickly.
What does the Fick equation describe?
The relationship between oxygen uptake, cardiac output, and arterial-venous oxygen difference.
V˙O2=Q×(a−v)O2
What factor increases heart rate and blood pressure before an event?
✅ Anticipatory Response (Sympathetic Activation)
Triggered by mental prep and adrenaline
HR and BP increase due to increased sympathetic nerve activity and epinephrine release
How does increased blood viscosity affect blood pressure?
✅ Peripheral Resistance (or Total Peripheral Resistance, TPR)
Thicker blood = more resistance to flow
Increases afterload and raises blood pressure
What is the relationship between resistance and blood flow?
As resistance increases, blood flow decreases.
What is true about intrinsic regulation of blood flow to skeletal muscles?
✅ Local metabolites (like CO₂, H⁺, K⁺, adenosine) cause vasodilation
This is autoregulation, matching blood flow to metabolic demand
Oxygen demand = local control of vasodilation
Which is true about the Fick equation
✅ It shows that oxygen uptake depends on:
Cardiac output (Q) and
Arterial-venous O₂ difference
→ It quantifies the body’s ability to deliver and use oxygen.
Whats the difference between the cardiovascular control center and the respiratory control center?
The CVC controls heart rate, blood pressure, and blood vessel tone to manage circulation,
The CVC responds to pressure and chemical signals to adjust cardiac output
RCC controls breathing rate and depth to maintain proper oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
the RCC responds mainly to CO₂ and pH to regulate ventilation.