MGMT 340 EXAM 3 SEO
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Leadership
the ability to influence a group toward the achievement of a vision or set of goals
Trait Theories of Leadership
focus on personal qualities and characteristics.
The search for personality, social, physical, or intellectual attributes that differentiate leaders from non-leaders goes back to the earliest stages of leadership research.
Leader Emergence
Who becomes a leader?
Behavioral theories
imply we can train people to be leaders.
Initiating Structure
which a leader is likely to define and structure his or her role and those of employees in the search for goal attainment. It includes behavior that attempts to organize work, work relationships, and goals
Consideration
to which a person’s job relationships are characterized by mutual trust, respect for employees’ ideas, and regard for their feelings.
Contingency Theories
Fiedler Contingency model, Least preferred coworker questionnaire (LPC), and situational leadership theory (SLT)
Fiedler’s model
effective group performance depends upon the proper match between the leader’s style and the degree to which the situation gives control to the leader
Situational leadership theory (SLT)
•a contingency theory that focuses on the followers.
•Successful leadership is achieved by selecting the right leadership style, which is contingent on the level of the followers’ readiness (“the extent to which people have the ability and willingness to accomplish a specific task.”).
Leader-member exchange (LMX)
because of time pressures, leaders establish an unique relationship with each follower
Charismatic Leadership
a style where leaders inspire and motivate followers through charm, persuasiveness, and a compelling vision
Key characteristics of a charismatic leader
vision and articulation, personal risk, sensitivity to follower needs, unconventional behavior
Vision and articulation
has a vision—expressed as an idealized goal—-that proposes a future better than the status quo; and is able to clarify the importance of the vision in terms that are understandable to others
Personal risk
willing to take on high personal risk, incur high costs, and engage in self-sacrifice to achieve the vision
sensitivity to follower needs
perceptive of other's’ abilities and responsive to their needs and feelings.
unconventional behavior
engages in behaviors that are perceived as novel and counter to norms
Transactional leadership
Contingent reward, active management by exception, passive management by exception
contingent reward
Leader attains follower agreement on
what needs to be done, and gives promised or
actual rewards in return for adequate performance
transformational leadership
inspire followers to transcend their own self-interests for the good of the organization
They change followers’ awareness of issues by helping them to look at old problems in new ways; and they are able to excite, arouse, and inspire followers to put out extra effort to achieve group goals
idealized influence
Provide vision and sense of mission, instills pride, gains respect and trust
inspirational motivation
Communicate high expectations, uses symbols to focus efforts, expresses important purposes in simple ways
intellectual stimulation
promotes intelligence rationality and careful problem solving
individualized consideration
Gives personal attention, treats each employee individually, coaches, advises
Laissez-Faire
Hands off leadership
Trust Propensity
refers to how likely a particular employee is to trust a leader
Trustworthiness
ability, benevolence,integrity
Ability
skills, competencies, and areas of expertise that the individual possesses
Benevolence
the degree to which an authority wants to do good for the trustor, the desire to do nice things
Integrity
The degree to which an authority adheres to a set values and principles that the trustor finds acceptable. Honesty and truthfulness.
Feelings toward Trustee
•Affect-based trust is emotional – it is based on the feelings we have for people, not rational evaluations of their trustworthiness
Contrast leadership and power
Leaders use power as a means of attaining group goals
Power does not require goal compatibility, merely dependence.
power
the ability to influence the behavior of others and resist unwanted influence in return. Probably the most important aspect of power is that it is a function of dependence.
Explain the three bases of formal power and the two bases of personal power
organizational (Formal) power
legitimate, reward, and coercive
Legitimate power
shown in formal groups and organizations through one’s structural position. It represents the power a person receives as a result of his or her position in the formal hierarchy. Legitimate power is broader than the power to coerce and reward. It includes acceptance of the authority of a position by members of an organization.
Reward power
the opposite of coercive power. People comply because doing so produces positive benefits; therefore, one who can distribute rewards that others view as valuable will have power over those others. These rewards can be either financial—such as controlling pay rates, raises, and bonuses—or nonfinancial, including recognition, promotions, interesting work assignments, friendly colleagues, and preferred work shifts or sales territories.
Coercive power
depends on fear of negative results. It rests on the application, or the threat of application, of physical sanctions such as the infliction of pain, the generation of frustration through restriction of movement, or the controlling by force of basic physiological or safety needs.
Personal Power
Expert and referent
Expert Power
influence wielded as a result of expertise, special skill, or knowledge
Referent Power
identification with a person who has desirable resources or personal traits
Influence
The use of an actual behavior that causes behavioral or attitudinal changes in others
Downward influence
managers influencing employees
lateral influence
Peers influencing Peers
Upward influence
Employees influencing managers
Influence (power) tactics

Rational persuasion
presenting logical arguments and factual evidence to demonstrate a request is reasonable
Consultation
increasing the target’s support by involving him or her in deciding how you will accomplish your plan.
Inspirational appeals
developing emotional commitment by appealing to a target’s values, needs, hopes, and aspirations.
Collaboration
group working together
Ingratiation
using flattery, praise, or friendly behavior prior to making a request
Personal Appeals
asking for compliance based on friendship or loyalty
Exchange
rewarding the target with benefits or favors in exchange for following a request
Apprising
inform explaining
Pressure
using warnings, repeated demands, and threats
Coalitions
enlisting the aid or support of others to persuade the target to agree
Politics behavior
activities that are not required as part of one’s formal role in the organization, but that influence the distribution of advantages within the organization.
Impression management (IM)
The process by which individuals attempt to control the impression others form of them
Causes of politcal behavior
?
Consequences of political behavior
?
Ethics of Political behavior
?
Three Types of Conflict
task, relationship, process
Three loci of conflict
dyadic, intragroup, intergroup
conflict
a process that begins when one party perceives that another party has negatively affected, or is about to negatively affect, something that the first party cares about.
functional conflict
that supports the goals of the group and improves its performance
dysfunctional conflict
hinders group performance
task conflcit
relates to the content and goals of the work
relationship conflict
focuses on interpersonal relationships, always dysfunctional, most psychological exhausting to individuals
process conflict
is about how the work gets done
dyadic conflict
between 2 people
intragroup conflict
within a group or team
intergroup conflict
conflict between groups or teams
outline process
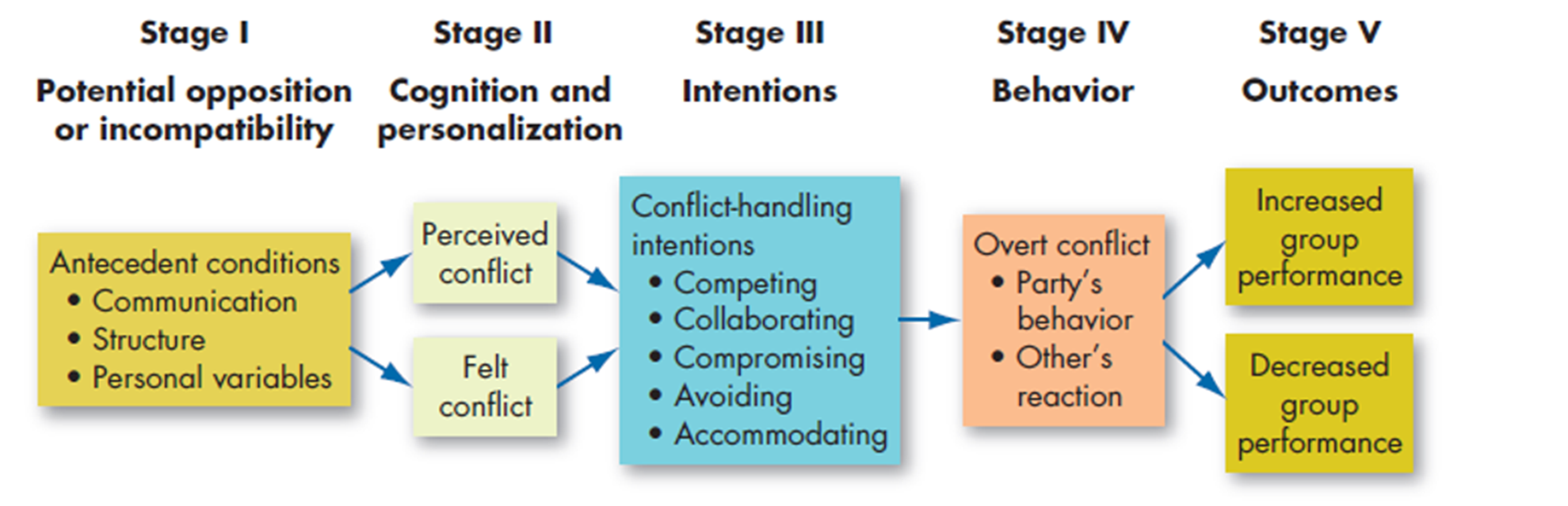
Five conflict-handling intentions
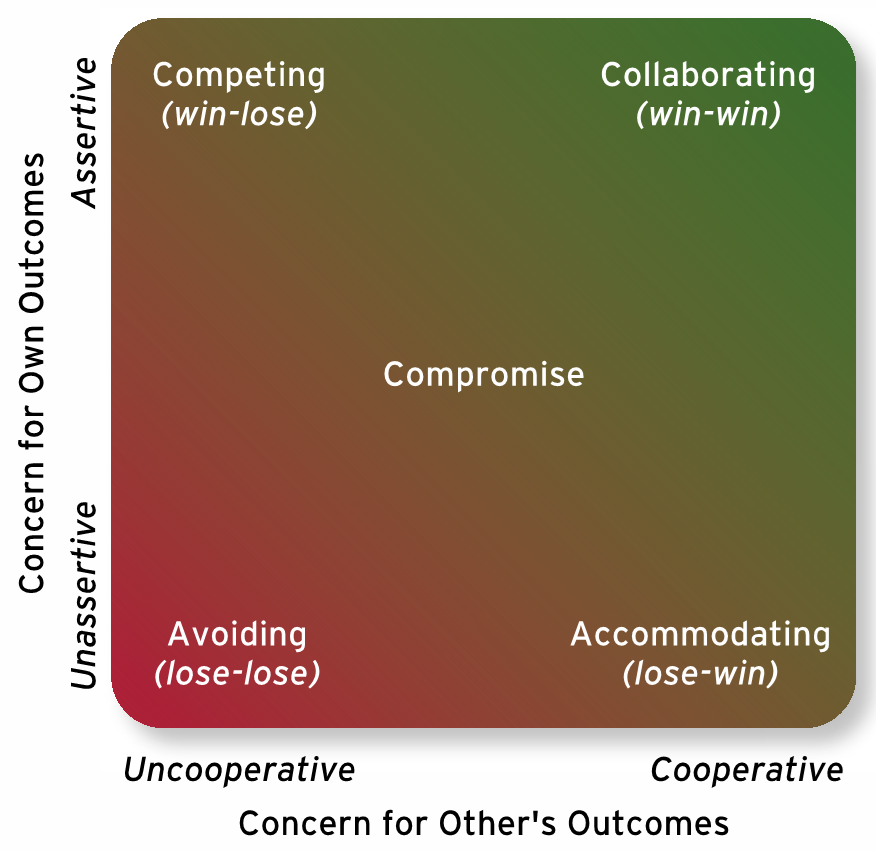
collaborating
both parties work together to maximize outcomes
accommodating
one party gives in and acts unselfishly
competing
one party attempts to get goal met without regard for the other party’s goals
compromise
each party losses are offsets by gains
avoiding
one party stays away from conflict
negotiating (baragaining)
is a process in which two or more parties exchange goods or services and attempt to agree upon the exchange rate for them.
distributive/integrative
get as much as the pie as possible, win-lose, low, short term/expand the pie so both parties are satisfied, win-win, high, long-term
Five steps of the negotiation process
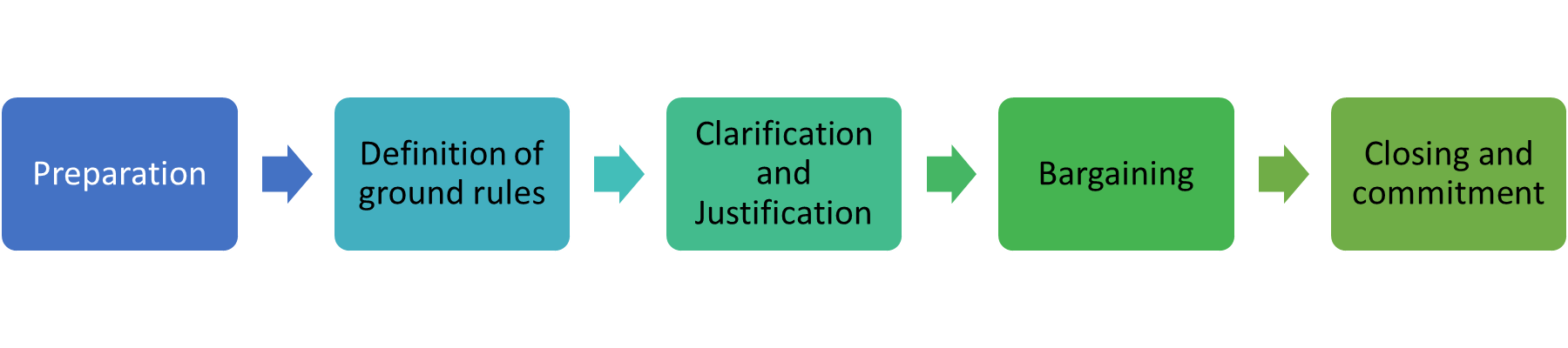
preparation
Each party determines its goals for the negotiation, including its best alternative to a negotiated agreement (BATNA)
definition of ground rules
Who will do the negotiating?
Where will it take place?
What time constraints, if any, will apply?
To what issues will negotiation be limited?
Will there be a specific procedure to follow if an impasse is reached?
clarification and justification
Explain, amplify, clarify and justify your original demands.
Each party makes a case for its position and put all favorable information on the table
bargaining
Each party uses distributive or integrated strategies to gain something of value
closing and commitment
An agreement is formalized
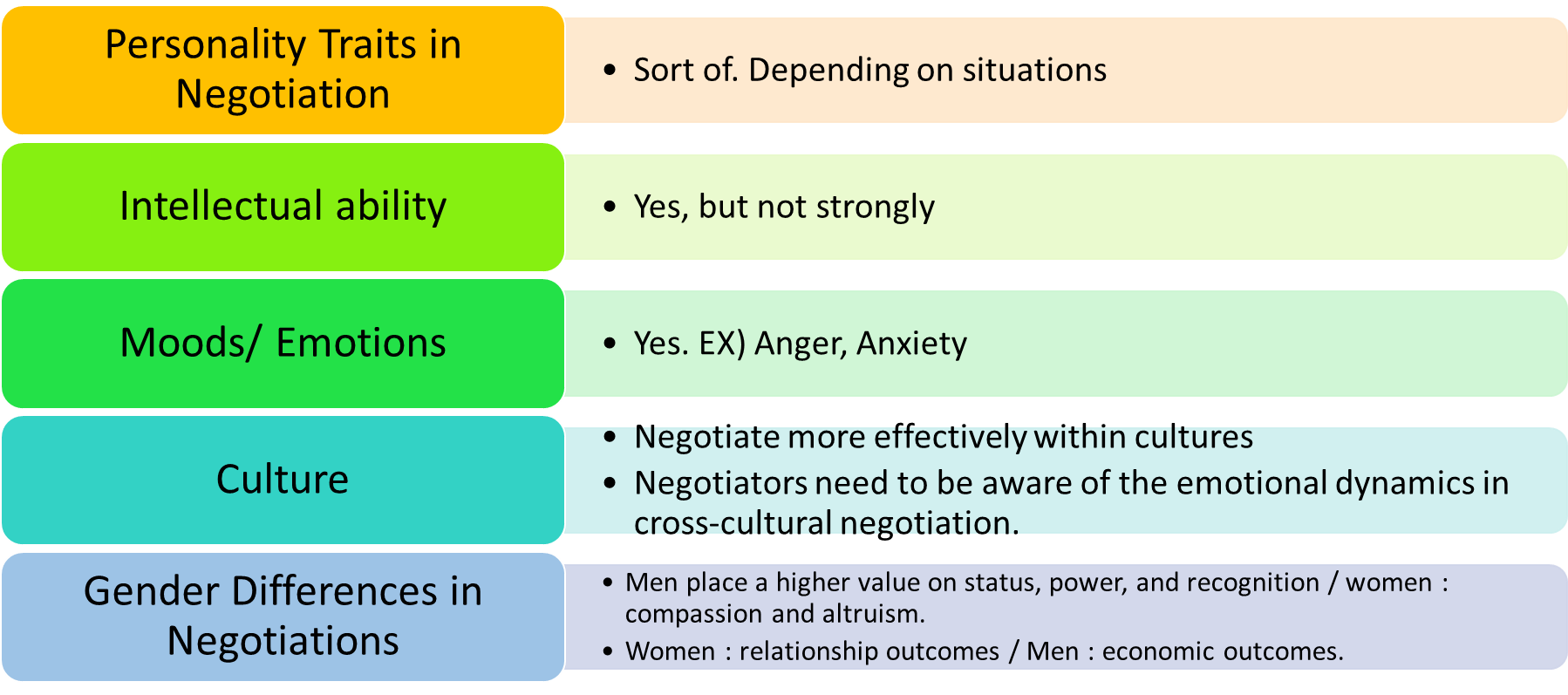
How individuals differences influence negotiations
organizational culture
a system of shared meaning held by members that distinguishes the organization from other organizations.
common characteristics of organizational culutre

innovation and risk taking
the degree to which employees are encouraged to be both innovative and take risks
attention to detail
the degree to which employees are expected to exhibit precision, analysis, and attention to detail
outcome orientation
the degree to which management focuses on results rather than on processes used to achieve them
people orientation
the degree to which management decisions consider the effect of outcomes on people within the organization
team orientation
the degree to which work activities are organized around teams rather than individuals
aggressiveness
the degree to which employees are aggressive and competitive
stability
the degree to which activities emphasize maintaining the status quo
functional of cultures
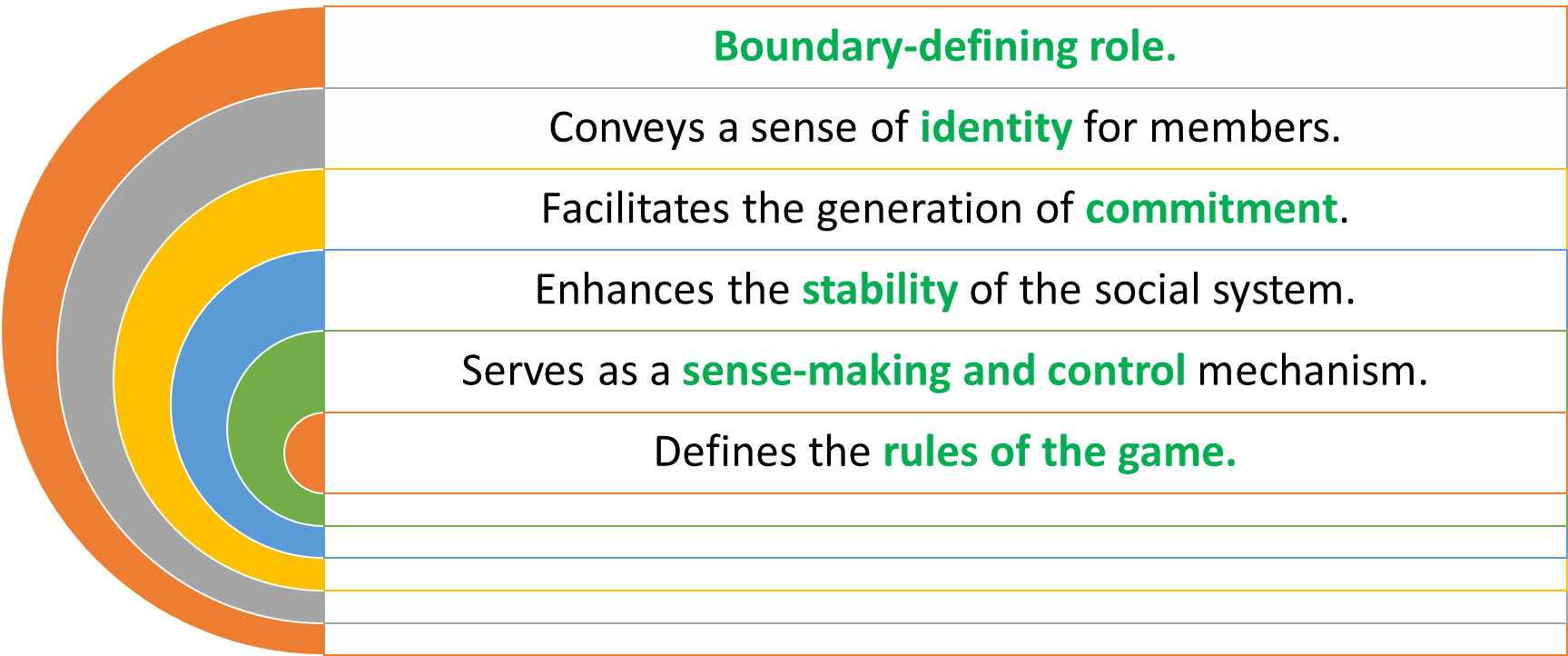
culture strength
the positive aspects and characteristics of a culture, often emphasizing its values, beliefs, traditions, and practices
consensus
a decision-making process where all parties involved agree to a course of action, not necessarily unanimity, but a level of acceptance and commitment to the outcome
intensity
the strategies and practices used to optimize and control the amount of effort, energy, and resources dedicated to achieving a specific goal or undertaking