Year 9 Ecosystems & Diseases
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are some abiotic factors that affect organisms in an ecosystem?
Temperature, water availability, light, soil type, and nutrients.
What are some biotic factors that affect organisms in an ecosystem?
Predation, competition, symbiosis, and disease.
What is the primary source of energy for most ecosystems?
The Sun.
What is biomass?
The total mass of all living organisms in a given area.
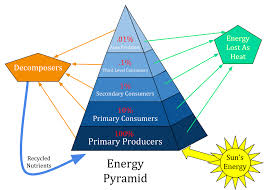
Describe the concept of an energy pyramid.
An energy pyramid shows the distribution of energy among trophic levels; energy decreases as you move up the pyramid.
What is biodiversity?
The variety of life in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Why is biodiversity important?
It ensures ecosystem stability, productivity, and resilience.
What is the basic equation for photosynthesis?
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂.
Where does photosynthesis occur in plant cells?
In the chloroplasts.
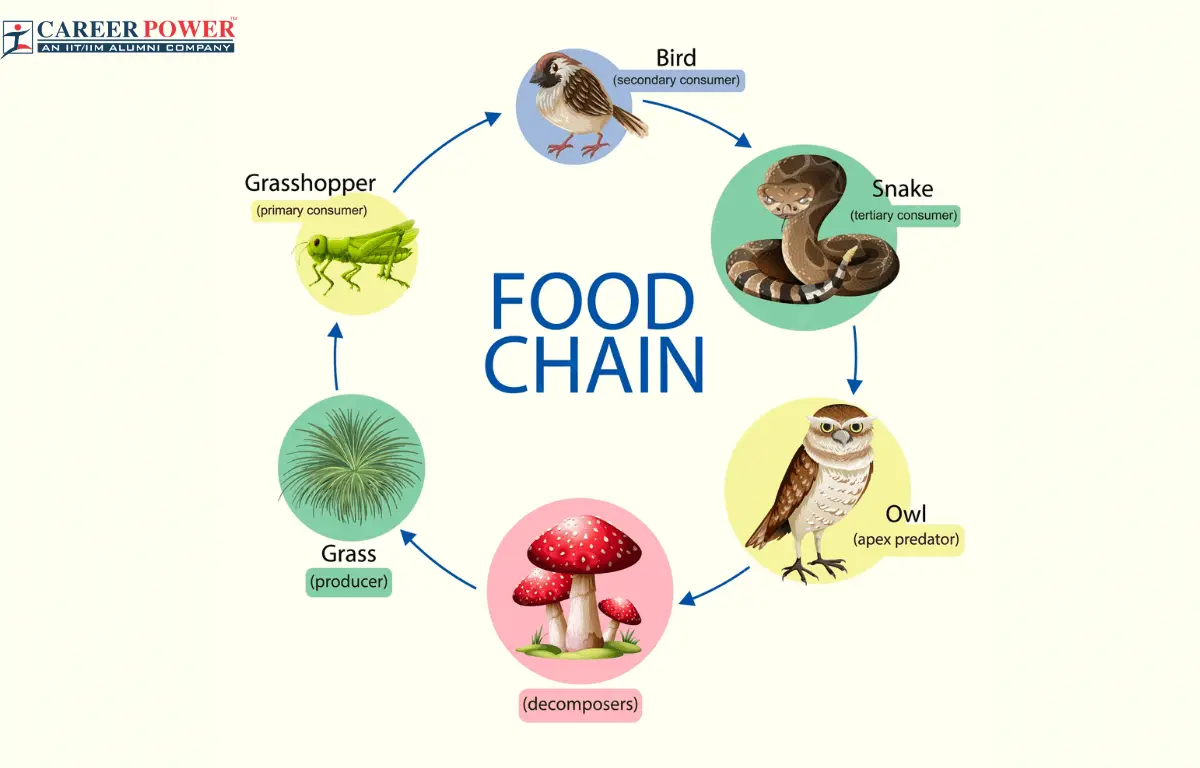
What is a food chain?
A linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; energy flow.
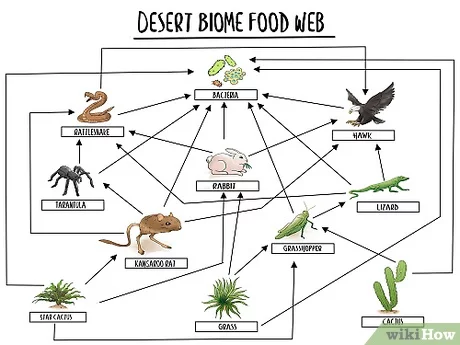
What is a food web?
A complex network of interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
Name a major human activity that affects ecosystems.
Deforestation, pollution, urbanization, and climate change.
What is the difference between seasonal changes and extreme weather events that affect population sizes?
Seasonal changes: Short-term weather changes that may increase or decrease population size. (e.g. monsoons, droughts, etc)
Extreme weather events- sporadic natural disasters that can greatly decrease population size. (e.g. hurricanes, wildfires, etc.)
What is mutualism?
A relationship where two organisms live close together and both benefit. (e.g. pollination)
What is competition?
The interaction of individuals that vie for a common resource that is in limited supply. (e.g. two birds fight for food)
What is predation?
An interaction in which one organism, the predator, eats all or part of the body of another organism, the prey. (e.g. a lion chasing a gazelle)
What is parasitism?
A relationship between the two living species in which one organism is benefitted at the expense of the other. (e.g. a mosquito and a person)
What is the order if a food chain showing the cycling of matter?
Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Tertiary consumers → Apex predators [(all) → decomposers]
![<p>Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Tertiary consumers → Apex predators [(all) → decomposers]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e4326e3b-d744-42ca-9b2b-2eb20b0b2141.png)
What are the 2 main reasons introduced species flourish in a new ecosystems?
They have no natural predators in the new environment
There are no diseases that affect them in the new environment
What is the role of decomposers?
To break down deceased organisms to provide nutrients to be reused in the food chain. (e.g. mushrooms, worms, termites and millipedes)
What is an ecosysten?
Non-living and living, co-existing.
What is the difference between an ecosystem and an environment?
Ecosystem- All interactions between non-living and living factors in an area.
Environment- Is all the living and non living factors in an area.
What is a population?
A group of organisms living in an area.
What is a community?
Different populations living in the same area.
What are different types of ecosystems?
Ocean, river, etc
Desert
Forest
Grassland
Mountains
Tundra
What does an ecosystem do?
Transforms energy and processors of matter and has to be self-sustaining: Capture energy, transfer energy, cycle nutrients.
What is the different levels of organisation?
Individual → Population → Community → Ecosystem → Biome → Biosphere
What is a biosphere?
A sphere where things survive.
What are biotic factors?
The living part of an ecosystem, (e.g. animals, plants)
What are abiotic factors?
The physical non-living part of an ecosystem, (e.g. oxygen, water, rocks)
What is the simplified photosynthesis formula?
Carbon dioxide + water —(sunlight)→ water → oxygen
(it is reversed at night)
What is an energy flow in an ecosystem?
It only flows in one direction and shows relationships between producers, consumers and decomposers.
What can the energy flow be shown as?
Nuclear energy (from the sun) → Light energy (from the sun) → Chemical energy (made by producers) → Chemical energy (eaten by consumers)
What are producers/autotrophs?
Plants. They gain their energy from the sun; photosynthesis.
What are primary consumers/heterotrophs?
Herbivores. (all consumers gain nutrition by eating other organisms)
What are secondary consumers?
Carnivores.
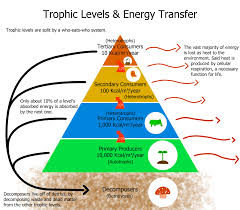
What are the trophic levels?
→(Decomposers/ bacteria/ fungi)←→ Level 1: producer (autotrophs) → Level 2: primary consumer (heterotrophs, herbivore) → Level 3: secondary consumers (carnivore) → Level 4: tertiary consumer (top carnivore)
What is symbiosis?
Two organisms live together in a close relationship that is beneficial to at least one of those relationships. (e.g. a crocodile and plover)
What is commensalism?
A relationship which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected. (e.g. barnacles on the outside of whales)
What are threats to biodiversity?
Overhunting
Invasion of non-native species
Habitat loss/ deforestation
Pollution
Climate change
What is a pathogen?
Any organism or infective agent that lives in or on another living organism and causes a disease.
How do pathogens multiply?
Need to be in the right conditions.
What are different types of pathogens?
Bacteria
Viruses
Protozoans
Fungi
Macro-parasites
How do pathogens spread?
Direct contact- being in contact with an infected person.
Indirect contact- sharing an infected item from that person.
Contact with contamination- undercooked foods or water.
Contact with animals/insects- tick bites that spread Lyme disease.
What is a disease?
Any condition that interferes with the proper functioning of the body or mind.
What is an infectious disease?
A disease that can be spread to a person from another person, an animal or object via pathogen. (e.g. common cold, influenza, mononucleosis, etc)
What is an non-infectious disease?
A disease that can NOT be spread from person to person. (e.g. cancer, heart disease, asthma, ect)
Why is it important to locate the source of infection?
Prevents more people from getting sick.
What are measures for preventing/treating the spread of disease?
Quarantine
Isolation
Vaccination
Proper hygiene
Ways the community can stay healthy.
Clean water supply
Effective plumbing
Clean surfaces
Personal hygiene
Treating wounds
Safe food preparation
Safe sex practices
Facts about bacteria.
Single-celled organisms (prokaryotes)
No nucleus or mitochondria but have a single strand of DNA
Living cells
Produce toxins that damage cells and tissues
e.g. Lactobacillus, Salmonella, Staphylococcus
Can multiply quickly under the right conditions
Can remain inactive and can be active again
Many different bacteria can be killed using penicillin and other antibiotics.
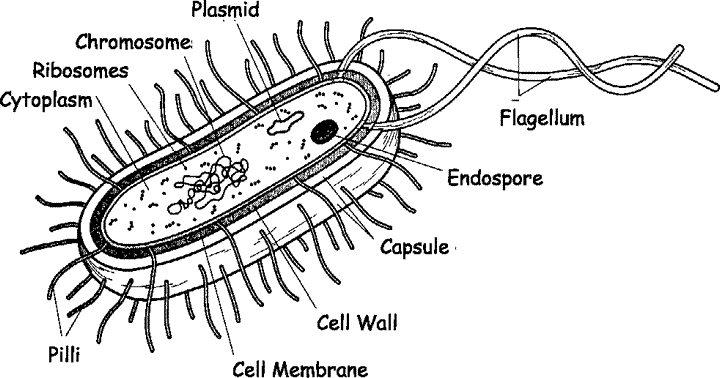
What are the different shapes of bacteria?
Coccus- round/spherical (e.g. Staphylococcus)
Bacillus- rod-like (e.g. Diphtheria)
Spirillum- spiral form (e.g. Syphilis)
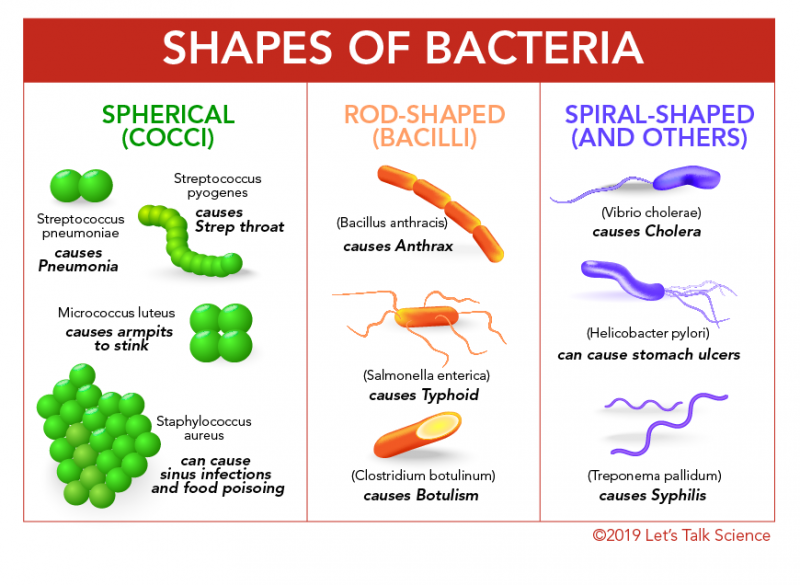
What is bacteria reproduction?
Reproduce by asexual reproduction using the process of binary fission (dividing in two)
Thousands of bacteria can be produced in a very short time.
What happened before antibiotics?
Bacteria could kill 80% of people with infective wounds.
Who discovered antibiotics?
Alexander Fleming in 1928 was growing mould on the agar plate, where bacteria couldn’t grow near it. He discovered that the mould had antibacterial properties which is now called ‘penicillin’.
What do antibiotics do?
They kill and inhibit the growth of the bacteria. A bacterium consists of one single cell and antibiotics and disturb their cell functions.
Why don’t antibiotics not work against viruses?
Viruses consists of a DNA/RNA fragment instead of a cell
What is antibiotic resistance?
Random mutations in bacterias’ DNA causes them to be resistant against antibiotics (some).
You can pass on the mutation to others.
You can develop a resistance from having so much antibiotics.
What are viruses?
Non-cellular pathogens that have both living and non-living characteristics.
They contain genetic material and are able to pass on hereditary information.
They are smaller than bacteria (can only seen under microscope)
They are unable to reproduce on their own and replicate only side host cells.
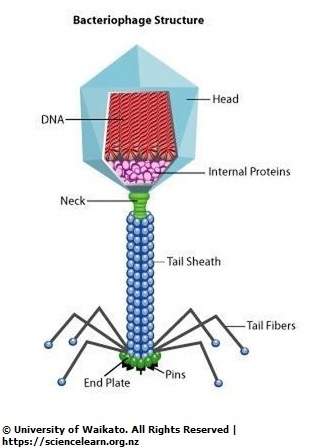
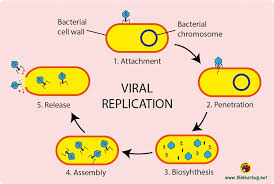
What is the virus reproduction cycle?
Virus attaches to host cell, injects nucleic acid.
Cell makes copies of DNA.
Cell makes proteins, structures and assemble new viruses.
Cell bursts and releases new viruses.
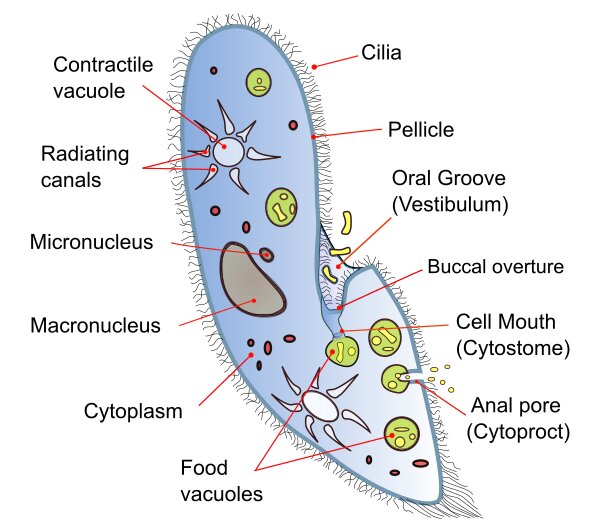
What are protazoans?
Protozoa are single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. (e.g. Malaria)
What are fungi?
Eukaryotic organisms that do not contain chlorophyll and can’t make their own food. The cell is different to a regular plant cell (no cell wall). They can be unicellular or multicellular. (e.g. Athletes food/Tinea)
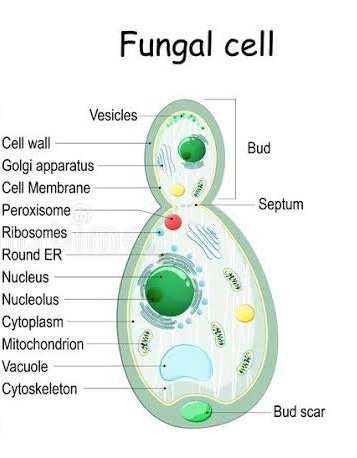
How do fungi reproduce?
either asexually or sexually.
What are vaccines?
Contain inactive parts or whole pathogen that has been either killed or weakened.
They trigger a specific immune response, to immunise individual, protecting them from the pathogen in the future.
How do vaccines work?
Small or whole parts of inactive pathogen are put into the body by injection.
Antigen in the vaccine stimulate the white blood cells into making antibodies.
Antibodies stick to antigens on the surface of the pathogen, causing them to clump together.
Another white blood cell engulfs/destroys pathogen.
Memory cells are retained, immune to future infections by the pathogen.
What are two different types of macro-parasites?
Endoparasites and Ectoparasites
What are Endoparasites?
Live inside the host’s body and include flat worms (tapeworms and flukes) and round worms. (e.g. Taeniasis)
What are Ectoparasites?
Parasites that live on the outside of the body, usually sucking blood. (e.g. mosquitos, flea, ticks, leeches, mites and lice)
What can these macro-parasites do?
Inject toxins while feeding, causing inflammation, allergic reactions, partial paralysis.
What are examples of non-specific defences (innate/natural immunity) in the first line of defense?
Skin mucous
Membranes
Secretions of skin and mucous membranes (e.g. ear wax, nasal hair/sneezing, tears, saliva, coughing/mucous, skin, stomach acid)
What are examples of non-specific defences (innate/natural immunity) in the second line of defence?
Phagocytic leukocytes
Antimicrobial proteins
Inflammatory response
Fever
What are examples of specific defences (adaptive immunity/gain as you get exposed to pathogen) in the third line of defence?
Lymphocytes
Antibodies
Memory cells
What are minerals?
Growth and repair of skin, bones, teeth and production of tissues, muscle fibres.
Assist in chemical reactions.
What are nutrients?
Substances that are essential for healthy growth and maintenance of your body.
What is protein?
Used for growth and repair, absorbed into the bloodstream for growth and repair by white blood cells.
Comes from meat, fish and dairy.
What are carbohydrates?
Main source of energy.
Excess sugar is stored in the liver (fat)
Liver store will be used for energy when exercising for short period but fat will be used for energy when exercising for long periods.
Comes from starches, sugar, grains, fruits and vegetables.
What are fats?
Body stores energy as fat.
Provides 2x the amount of energy as carbs.
Major source of energy- broken down and used in muscle for fuel.
Are essential for insulation, protecting vital organs.
Found in oils, meat and dairy products.
What is hypoglycaemic?
Low blood sugar.
What is hyperglycaemic?
High blood sugar.
What are the signs of diabetes?
C- Cardiovascular (heart) disease and high lipids
H- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
A- Adult onset diabetes
O- Obesity
S- Stroke
What is type 1 diabetes?
Cannot be prevented or cured.
The body doesn’t create enough insulin.
Causes are unknown, genetics play a role.
Requires insulin injections for life.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Can be prevented through lifestyles modifications.
The body doesn’t create enough insulin or develops an insulin resistance.
Causes include genetics, aging, inactivity, obesity, etc.
Requires insulin as needed.
How is the third line of defence different from the second line of defence?
Third line of defence- specific to certain pathogens and builds over time.
Second line of defence- general response and can happen during any infection.
Name three methods of disease transmission.
Direct contact, airborne transmission, and vector-borne transmission.
What are the two main parts of the immune system?
The innate immune system and the adaptive immune system.
What does Cows Moo Softly stand for?
Change one thing (independent variable)
Measure something (dependent variable)
Keep everything else the same (controlled variable
What does S.A.L.T. stand for when studying graphs?
Scale
Axis
Label
Title