Week 2: Intraoral Radiography Techniques
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What are some ways that movement occurs when taking radiographs?
1. radiation source movement: x ray tube is harder to control
2. patient/sensory movement: common as they may talk, have pain, or move their mouth
How should the occlusal plane be placed in patient position and preparation?
parallel to floor
How should the Ala-tragus line be placed in patient position and preparation?
parallel to floor
How should the head be positioned for mandibular periapicals in patient position and preparation?
incline the head backwards
How should the Tragus-corner of the mouth line be positioned for mandibular periapicals in patient position and preparation?
parallel to floor
Maxillary positioning
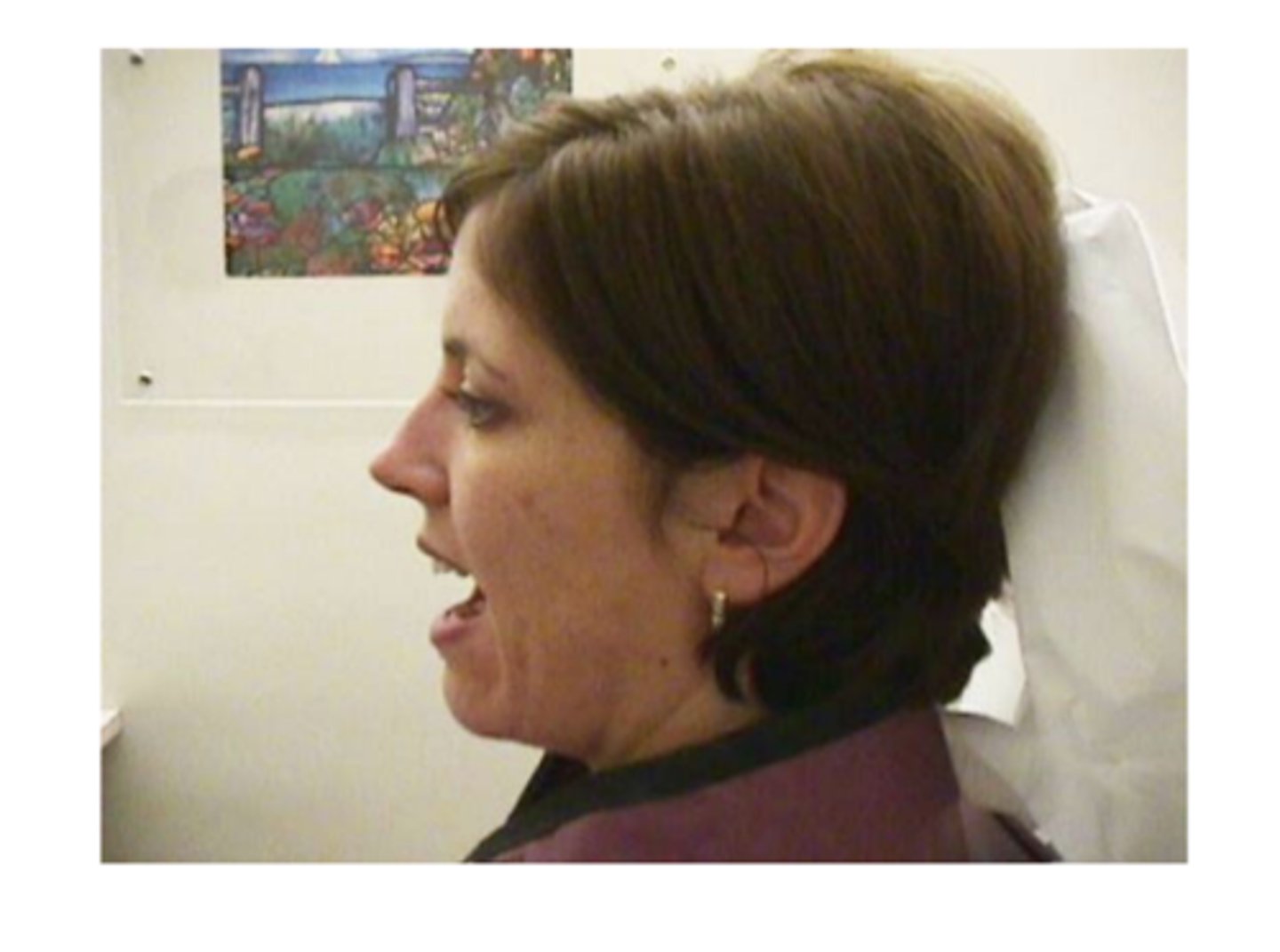
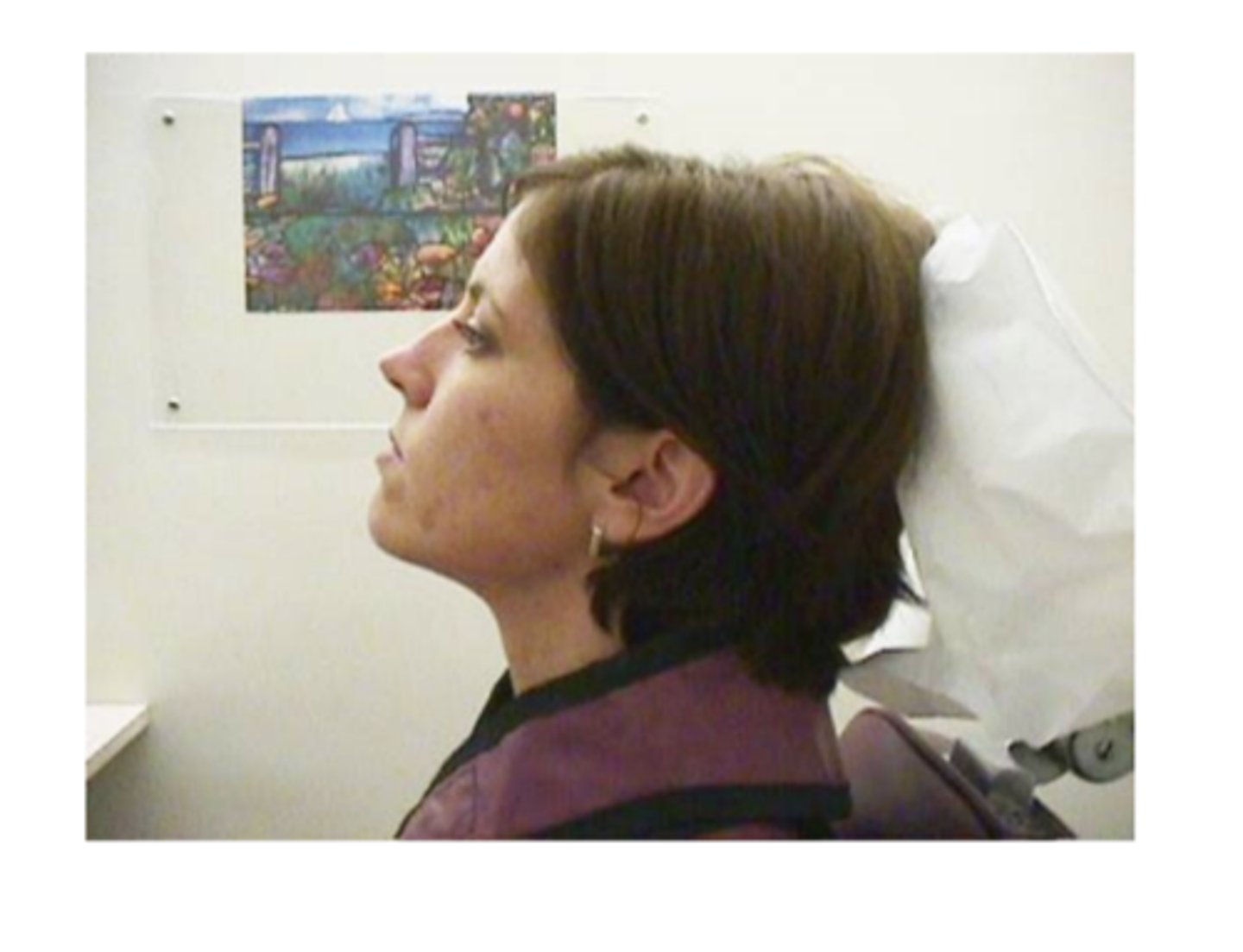
Mandibular positioning
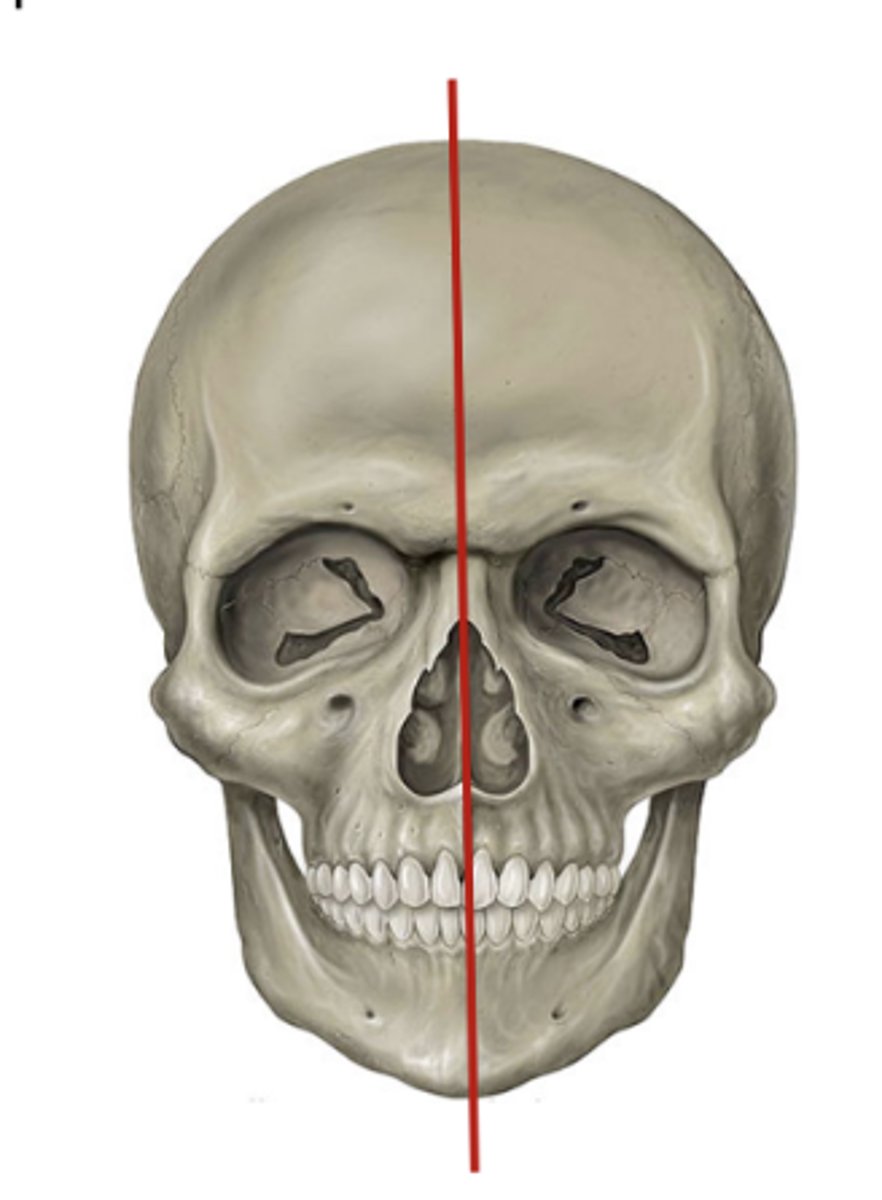
Where should the mid sagittal plane be in relationship to the floor in patient positioning and preparation?
perpendicular to floor
What should be removed if possible when taking radiographs?
glasses, prothesis (dentures), large earrings, nose rings
What is the axial orientation for posterior teeth?
long axis horizontal
What is the axial orientation for anterior teeth?
long axis vertical
Since we can't use our thumb to hold the sensor in place, what are some other options?
cotton rolls, metal, plastic, styrofoam
XCP (X-tension Cone Paralleling Instrument with plastic guiding
ring).
Masell Precision Instrument (with metal plate ring)
Snap-a-Ray
Hemostat (not really used)
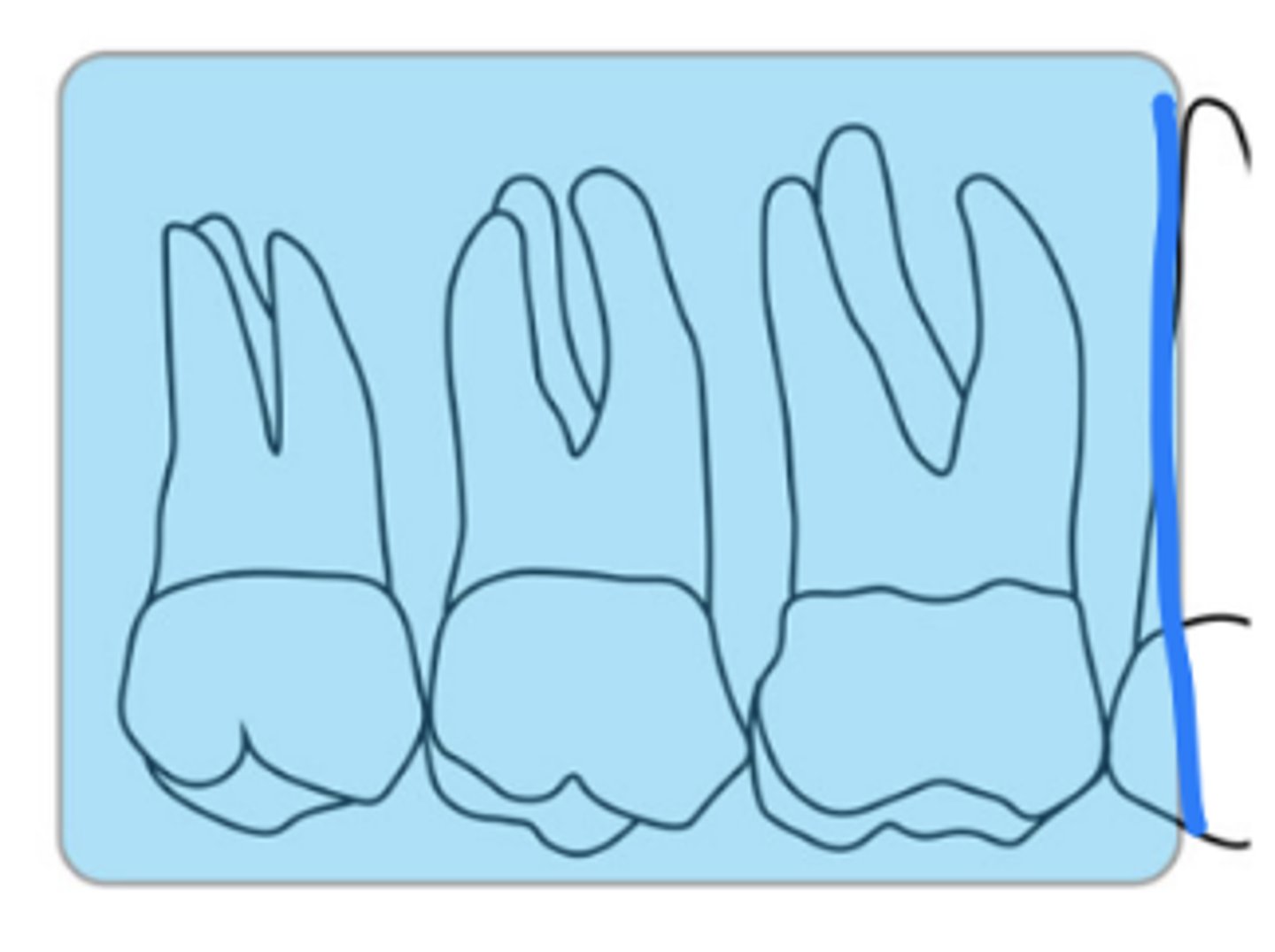
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for maxillary molar periapicals?
size 2
at least 4 mm distal of the 2nd molar
first molar is captured with premolars
What is the horizontal angulation for maxillary molar periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle of 80 degrees
What is the vertical angulation for maxillary molar periapicals?
A positive vertical angle of 30 degrees
approximately correct
central ray entry
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for maxillary premolar periapicals?
size 2
distal of canine, 1st and 2nd premolars, 1st molar
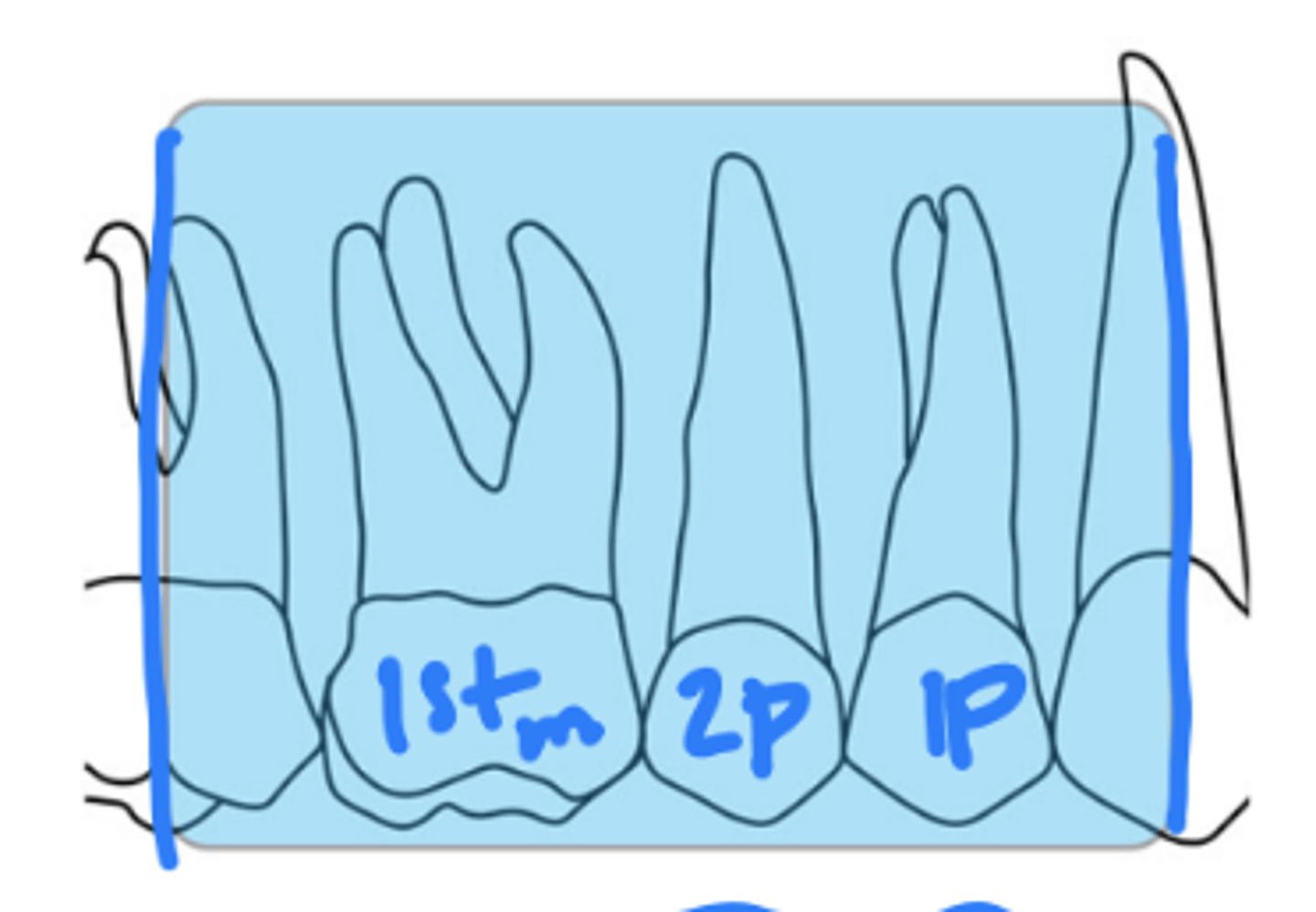
What is the horizontal angulation for maxillary premolar periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle directed perpendicularly to the facial surface of the first molar
What is the vertical angulation for maxillary premolar periapicals?
positive vertical angle of 25-35 degrees
approximately
correct central ray entry
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for maxillary canine periapicals?
size 1
mx canine
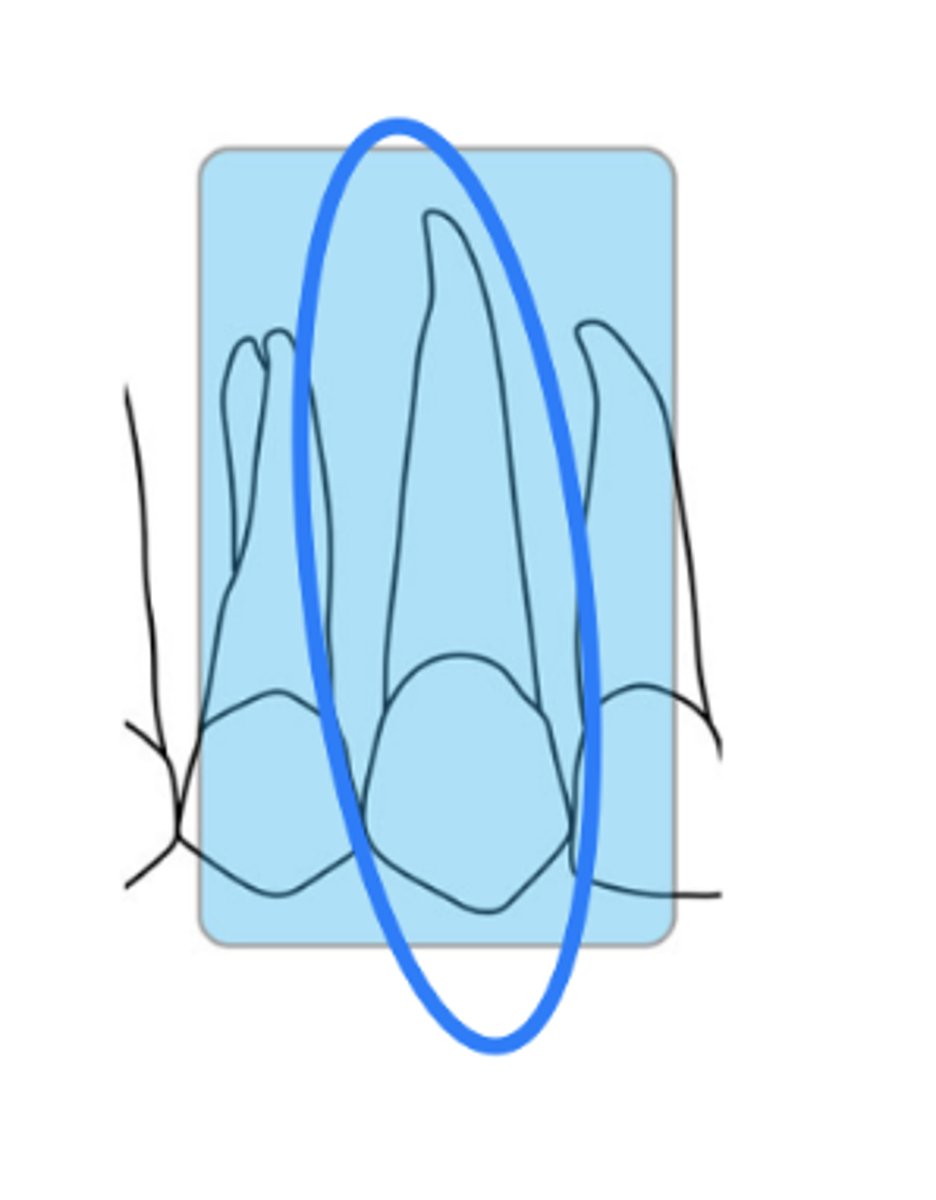
What is the horizontal angulation for maxillary canine periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle directed perpendicularly to the facial surface of the canine
What is the vertical angulation for maxillary canine periapicals?
positive vertical angle of 30 degrees
approximately correct central ray entry
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for maxillary lateral periapicals?
size 1
mx lateral incisor
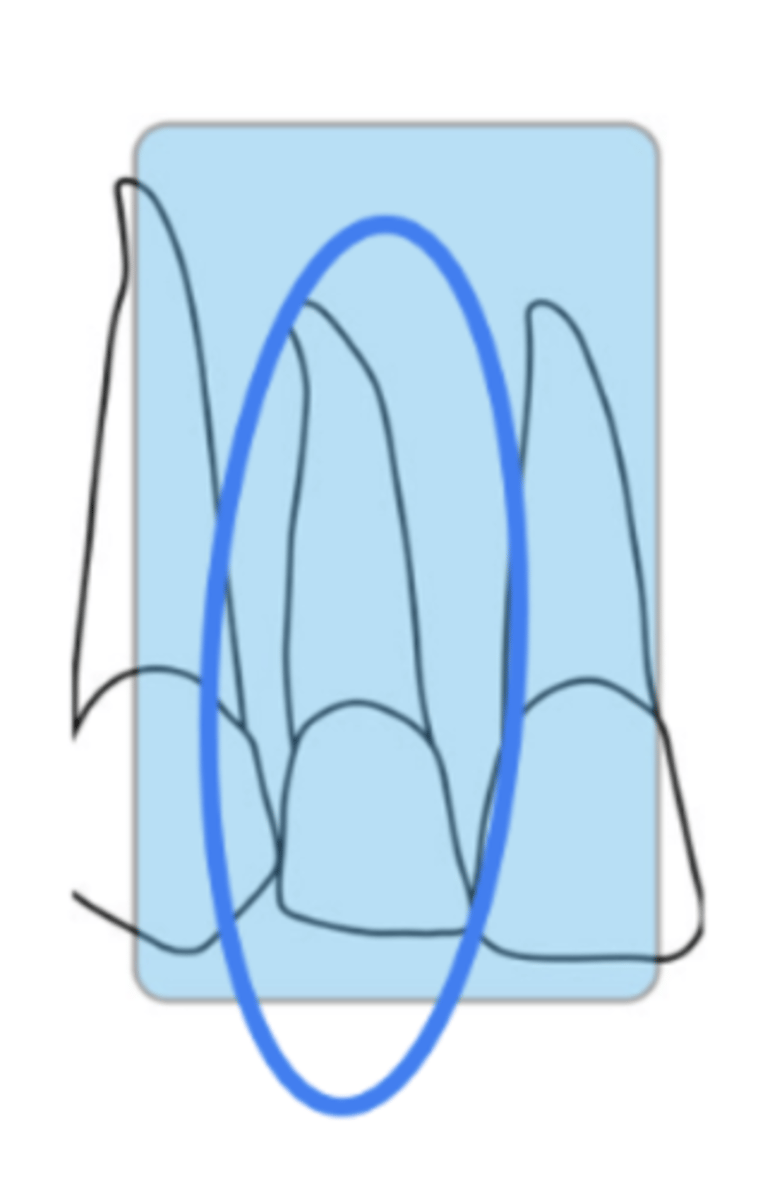
What is the horizontal angulation for maxillary lateral periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle directed perpendicularly to the facial surface of the lateral incisor
What is the vertical angulation for maxillary lateral periapicals?
positive vertical angle of 30 degrees
approximately correct central ray entry
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for maxillary central periapicals?
size 1
mx right and left central incisors
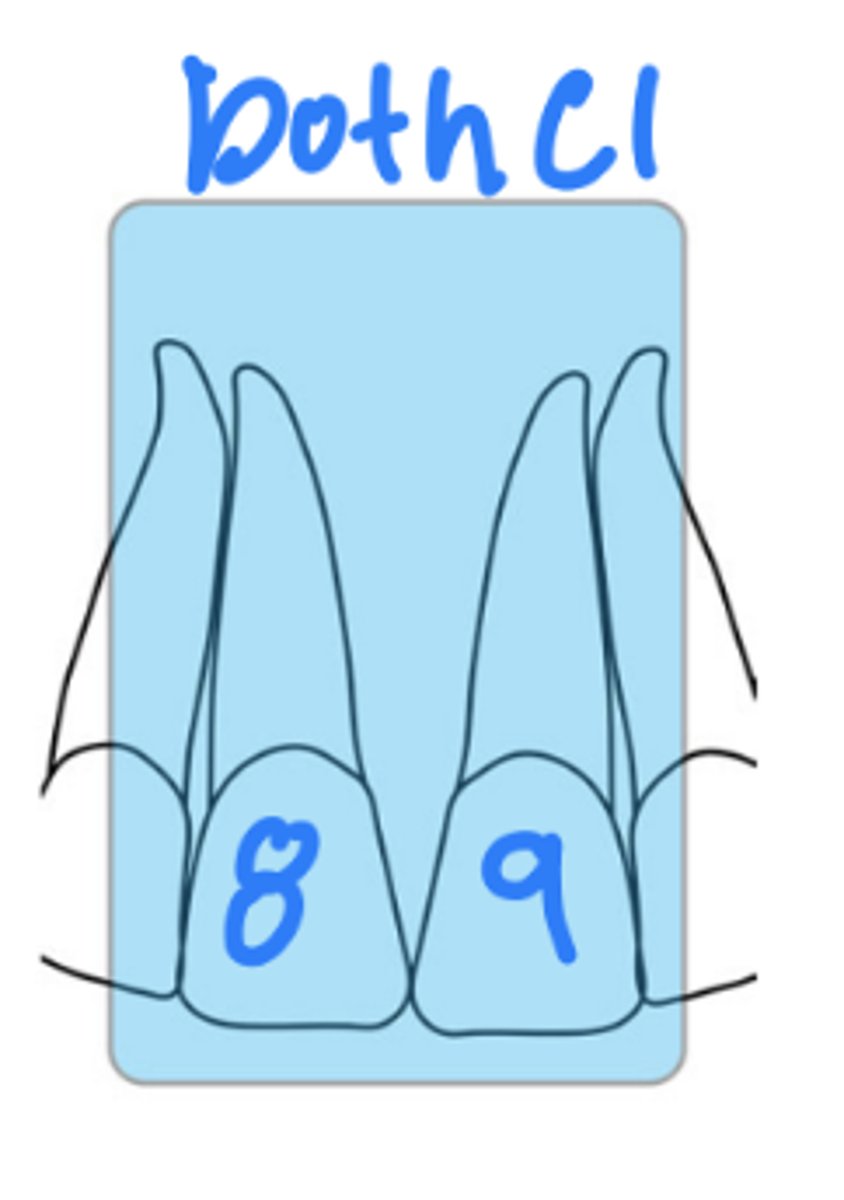
What is the horizontal angulation for maxillary central periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle of 0 degrees
What is the vertical angulation for maxillary cenral periapicals?
positive vertical angle of 30 degrees
approximately correct central ray entry
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for mandibular molar periapicals?
size 2
2 mm retromolar area, third molar, and second molar
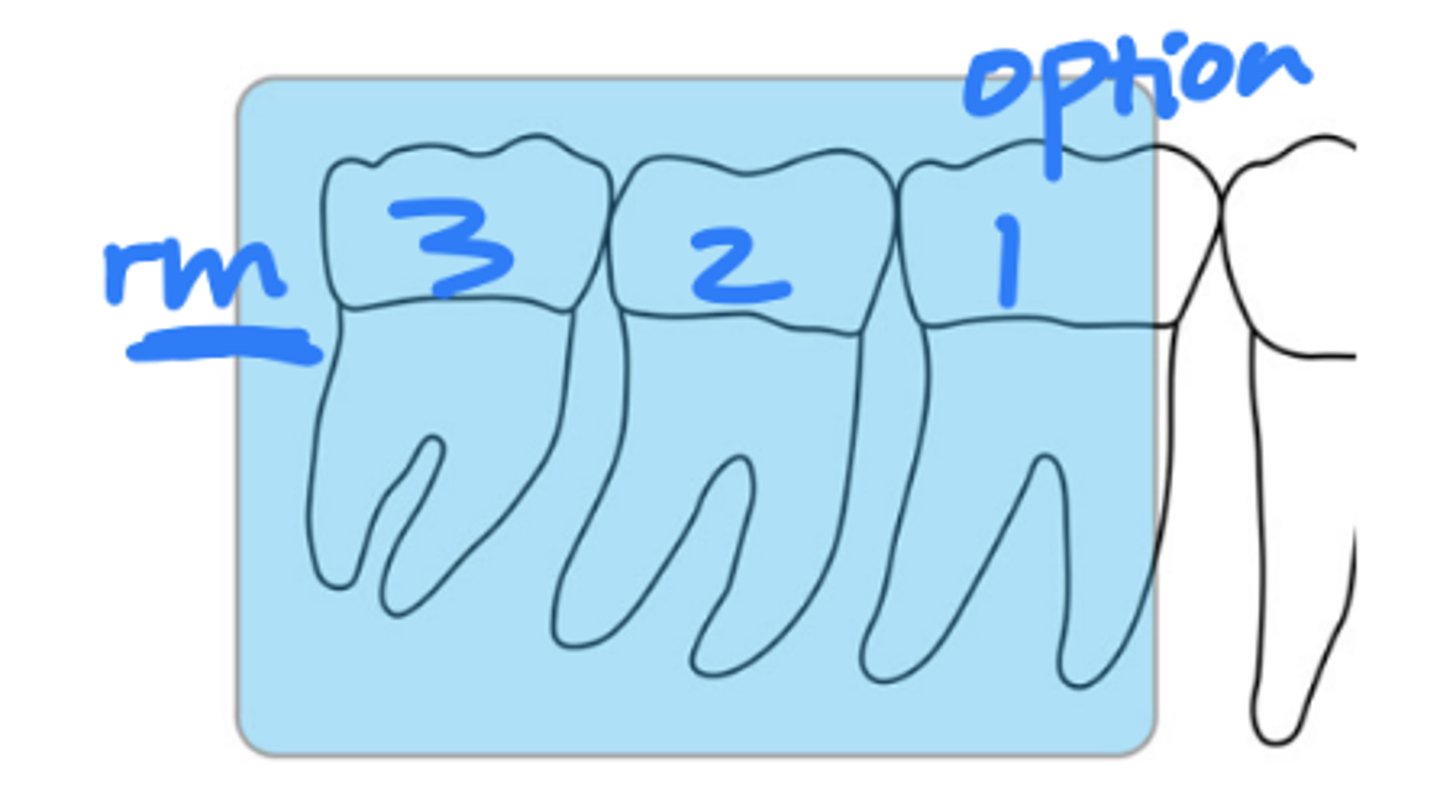
What is the horizontal angulation for mandibular molar periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle of 80 degrees
What is the vertical angulation for mandibular molar periapicals?
positive vertical angle of 0 - 5 degrees and approximately correct
central ray entry
(**all md periapicals will be neg VA, this is the EXCEPTION)
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for mandibular premolar periapicals?
size 2
distal of canine, 1st and 2nd premolars, and 1st molar
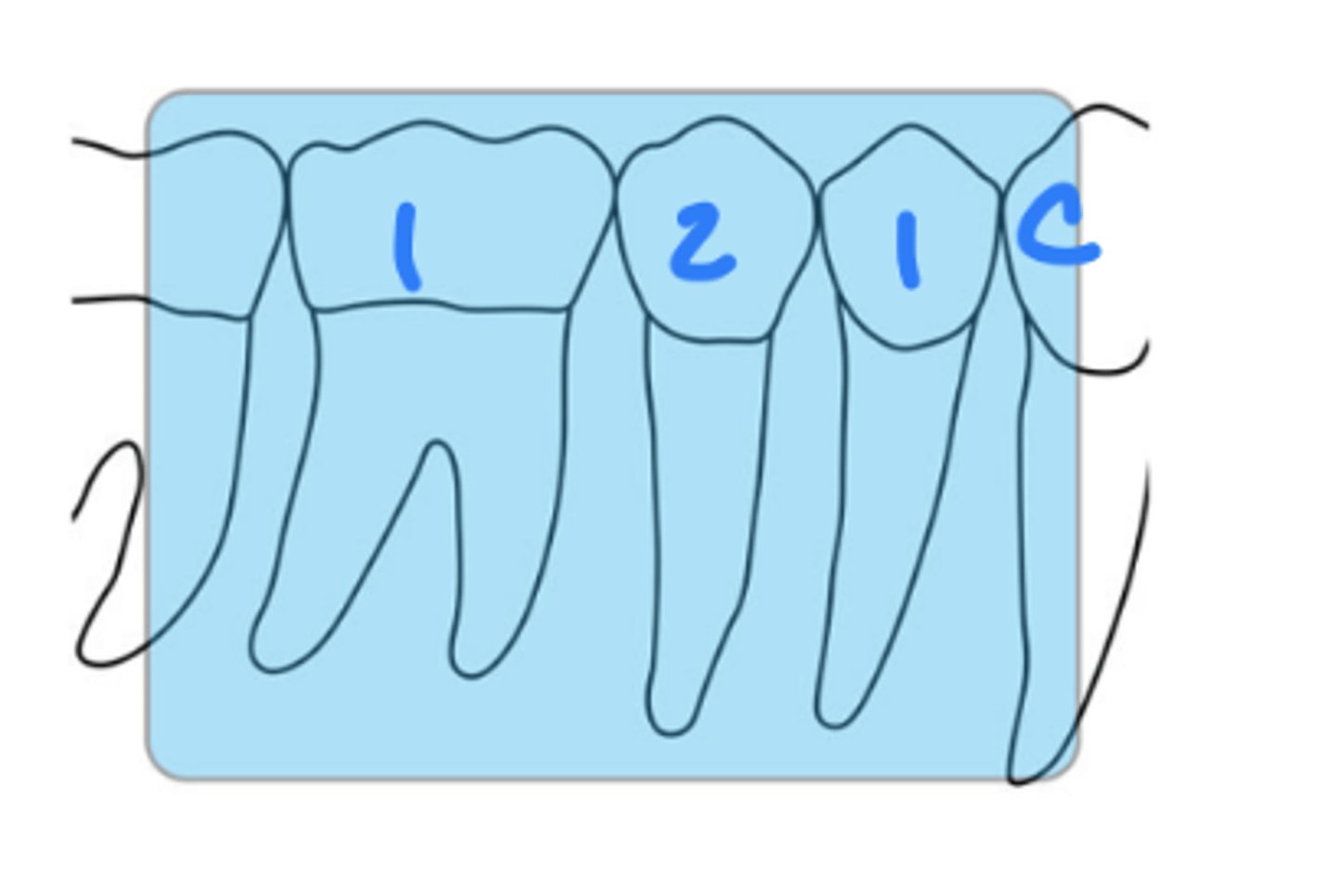
What is the horizontal angulation for mandibular premolar periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle directed perpendicularly to the facial surface of the first molar
What is the vertical angulation for mandibular premolar periapicals?
negative vertical angle of 15 degrees
approximately correct
central ray entry
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for mandibular canine periapicals?
size 1
canine and lateral incisor
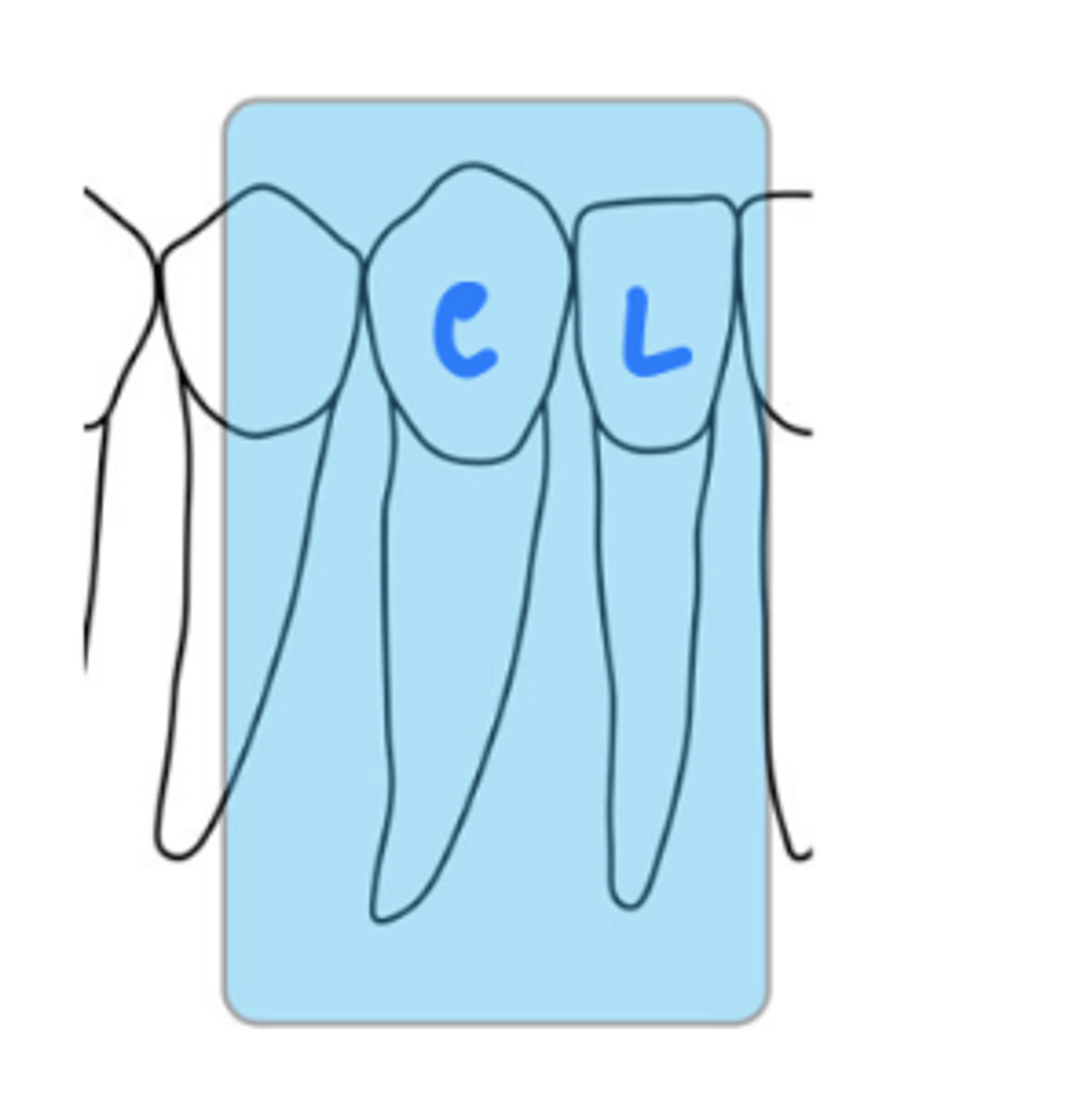
What is the horizontal angulation for mandibular canine periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle directed perpendicularly to the facial surface of canine
What is the vertical angulation for mandibular canine periapicals?
negative vertical angle of 15 degrees
approximately correct
central ray entry
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for mandibular incisor periapicals?
size 1
right and left central incisors
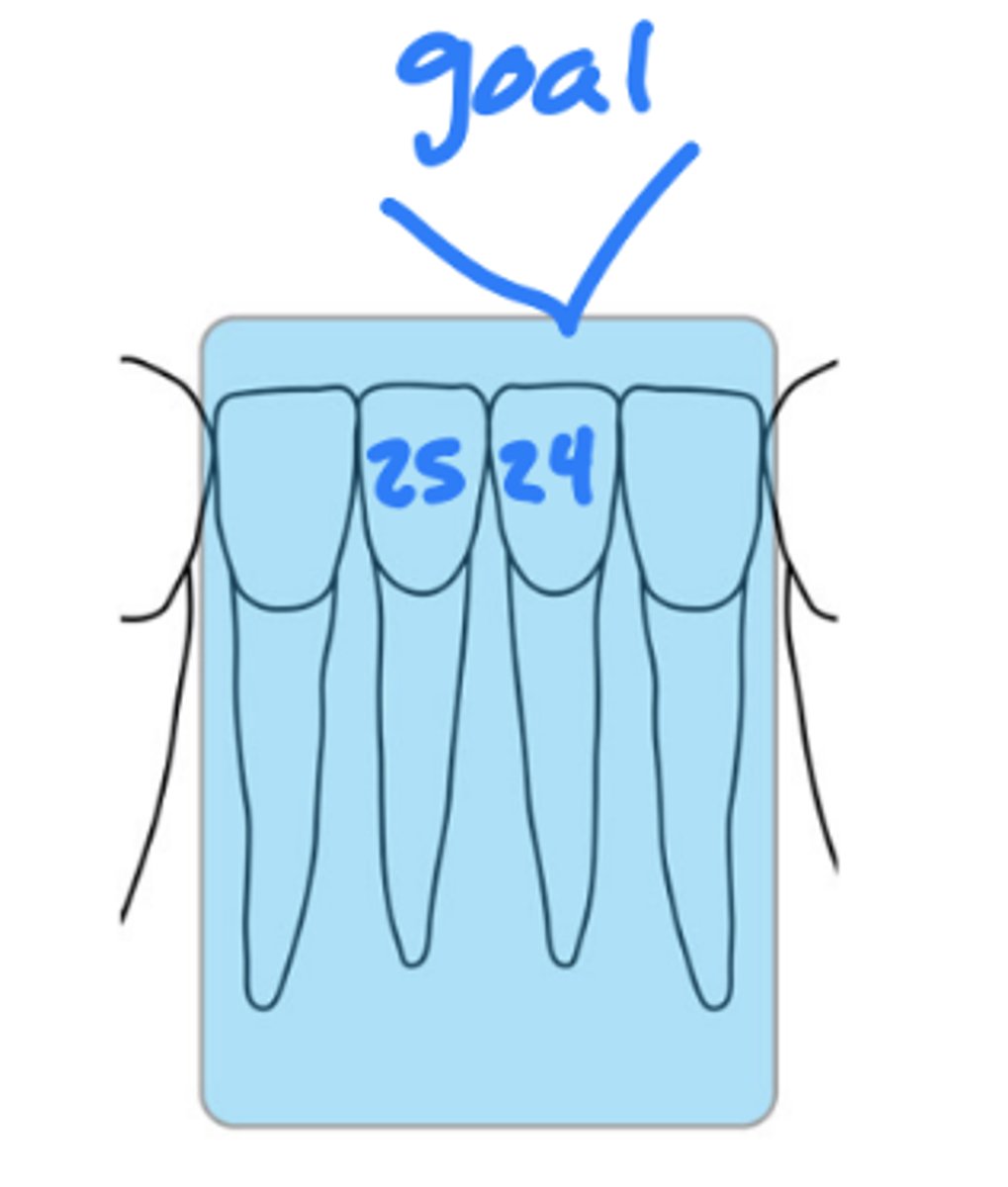
What is the horizontal angulation for mandibular incisor periapicals?
position the rectangular PID with a horizontal angle directed perpendicularly to the facial surface of central incisors (0 degree)
What is the vertical angulation for mandibular incisor periapicals?
negative vertical angle of 15 degrees
approximately correct
central ray entry
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for molar bitewings?
size 2
proximal surfaces of all
erupted molars and 2-3 mm of bone distal to the last erupted molar
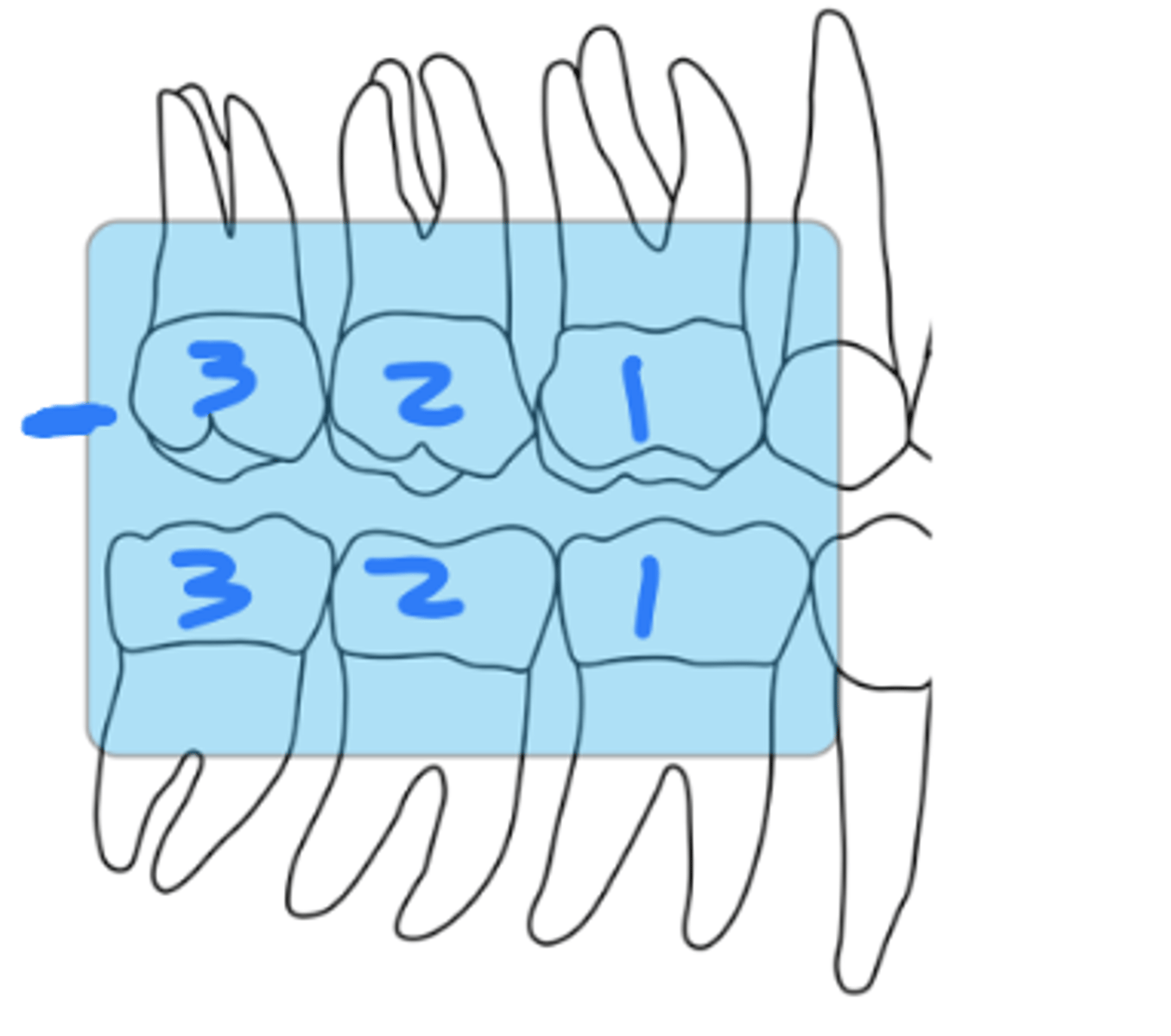
What is the horizontal angulation for molar bitewings?
horizontal angle is
determined by paralleling the central ray with the interproximal contact between the first and second maxillary molars
(In the case of erupted third molars, supplemental bitewings may need to be done to record all interproximal contacts)
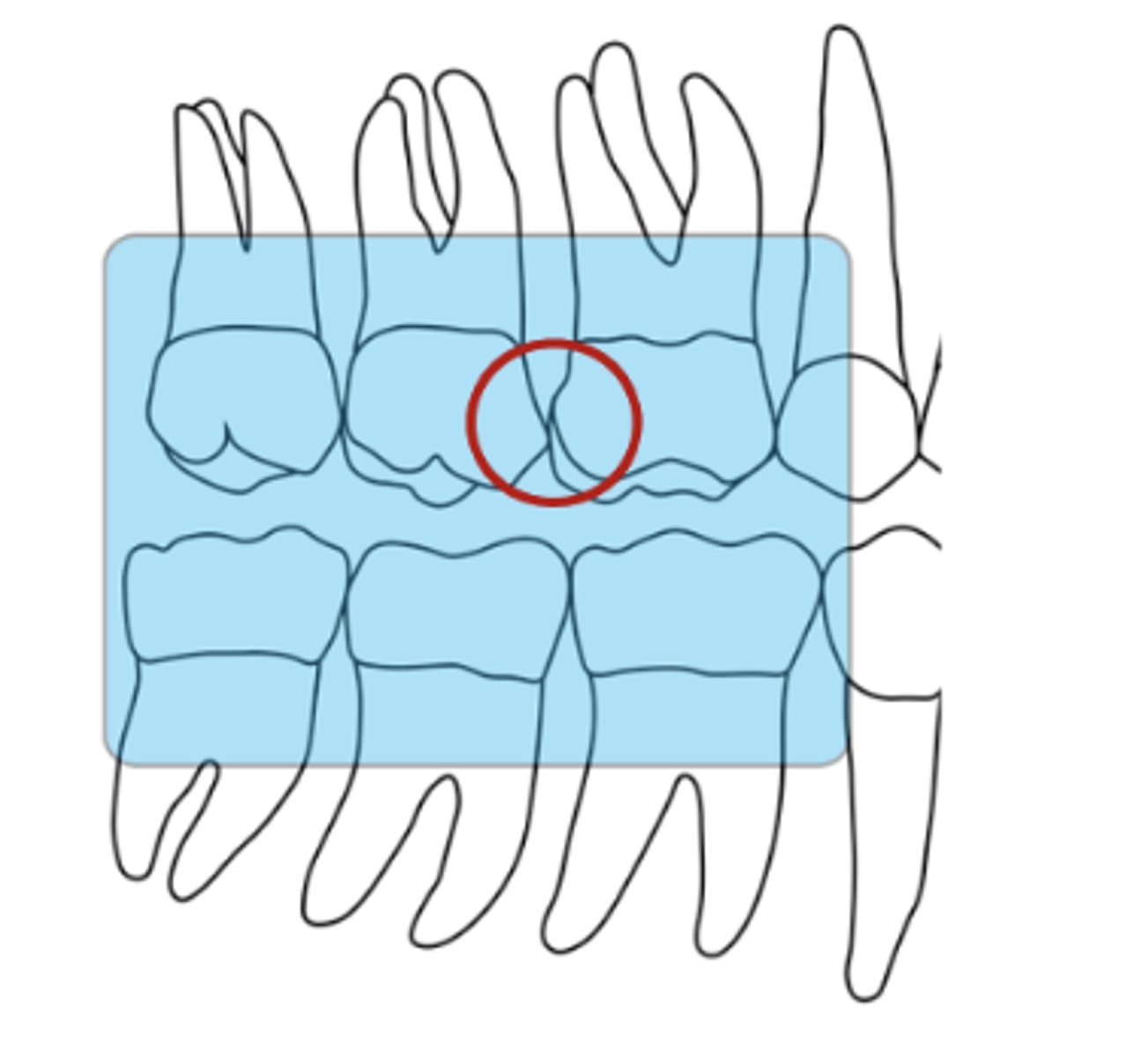
What is the vertical angulation for molar bitewings?
about +15-20 degrees and +30 is the max
determined by directing the central ray at right angles to the sensor
ensure that the vertical dimension of the rectangular PID (vertical diameter if round PID is used) is parallel to the vertical axis of sensor
What is the size of the sensor and recorded area for premolar bitewings?
size 2
distal of canine, proximal surfaces of 1st and 2nd premolars, and 1st molar
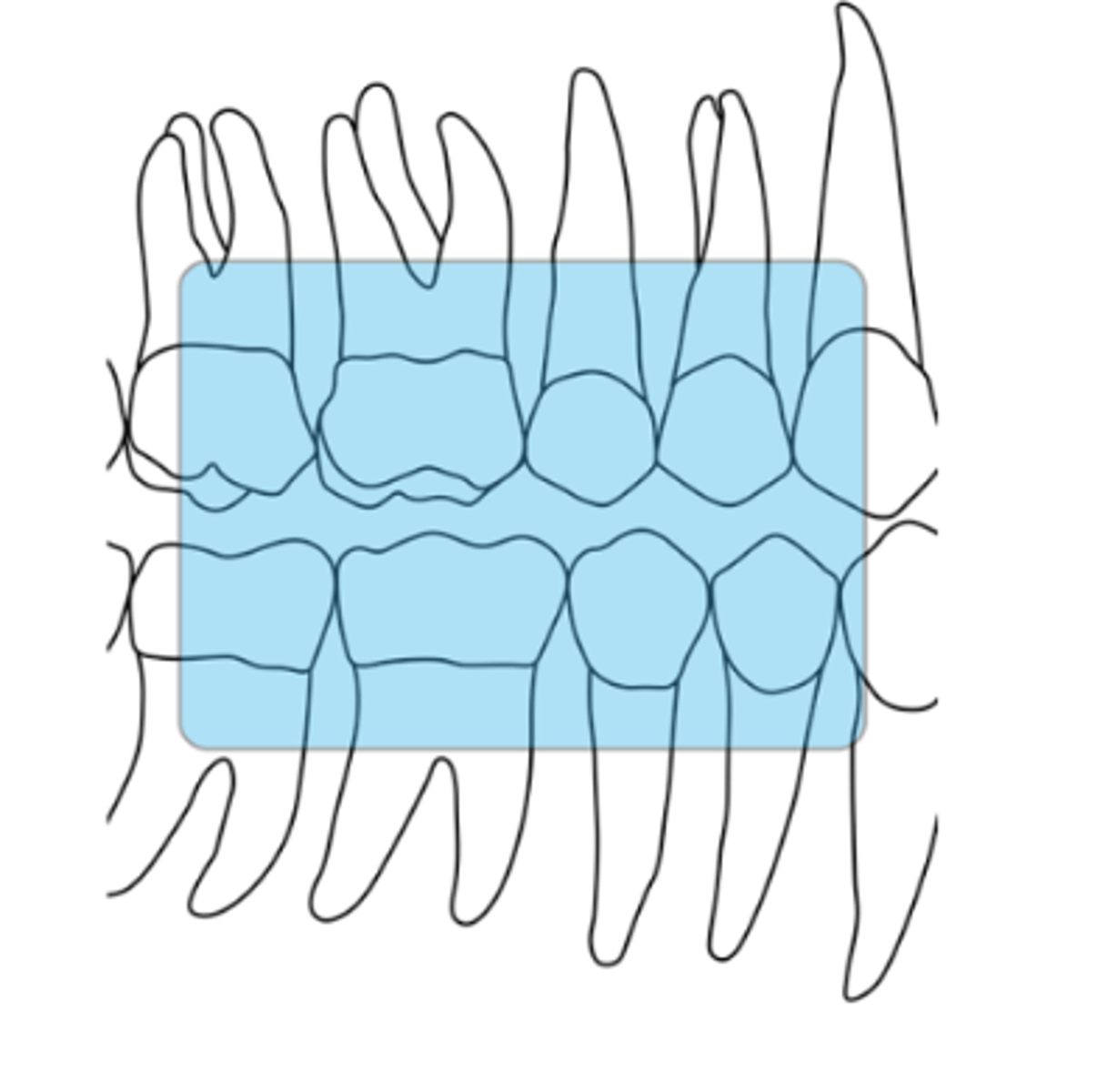
What is the horizontal angulation for premolar bitewings?
horizontal angle is determined by paralleling the central ray with the interproximal contact between the maxillary first molar and second premolar
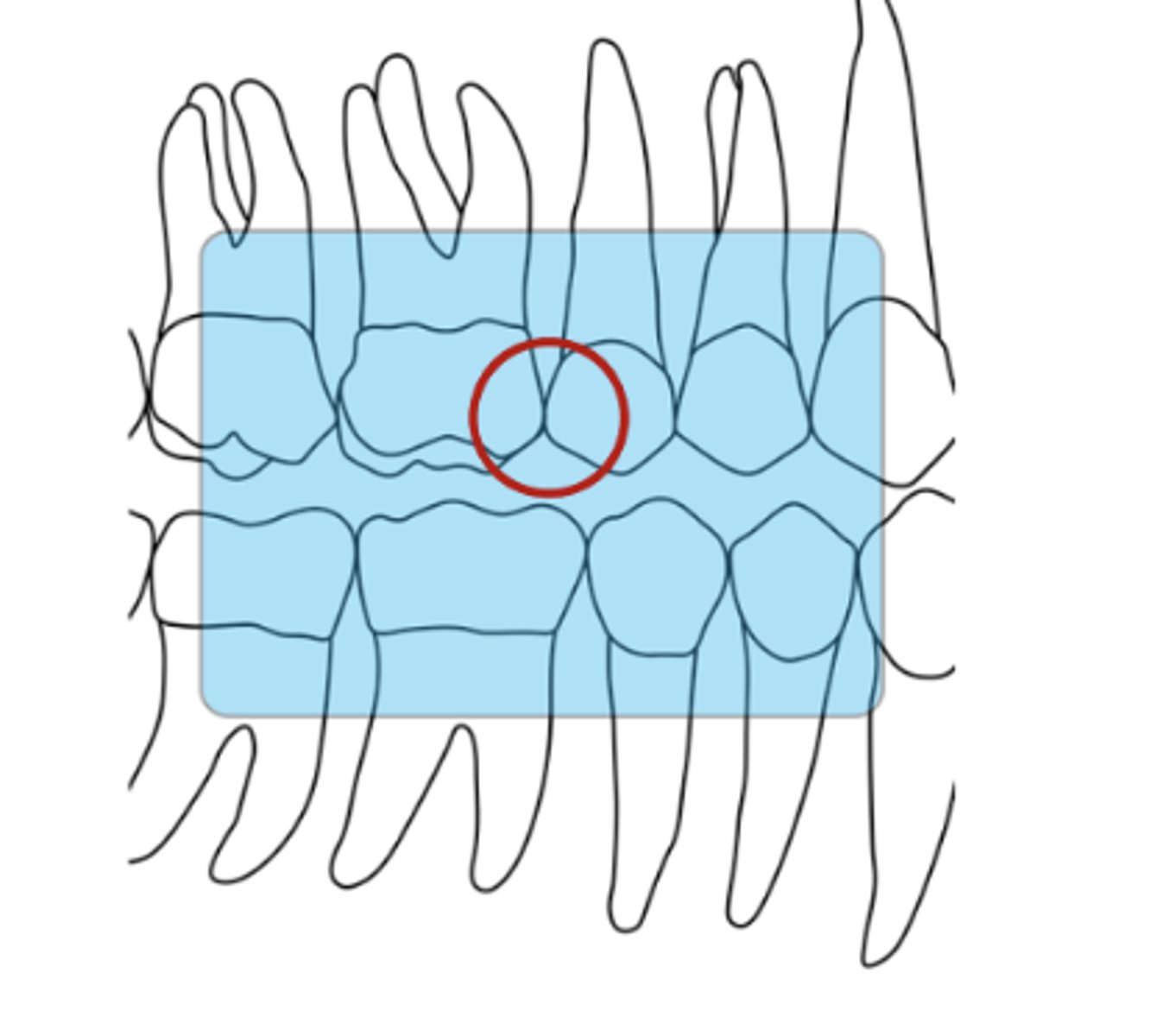
What is the vertical angulation for premolar bitewings?
about +10-15 degrees
determined by directing the central ray at right angles to the sensor
ensure that the vertical dimension of the rectangular PID (vertical diameter if round PID is used) is parallel to the vertical axis of sensor
Which radiographs use +VA?
all mx, BWXs, md molars
Which radiographs use -VA?
md PM, canine, incisor