AP Physics C: Mechanics Ultimate Guide
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Circular Motion & Gravitation
AP Physics C: Mechanics
Kinematics
Kinematics: Motion in One Dimension
Kinematics: Motion in Two Dimensions
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Circular Motion
Newton's Third Law of Motion
Work, Energy, and Power
Forces and Potential Energ
Conservation of Energy
Power
Center of Mass
Impulse and Momentum
Torque and Rotational Statics
Rotational Kinematics
Rotational Dynamics and Energy
Angular Momentum
Simple Harmonic Motio
Gravitational Forces
Orbits of Planets and Satellies
University/Undergrad
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Kinematics
the study of motion without considering the forces causing the motion.
Displacement
the change in position of an object. It is a vector quantity.
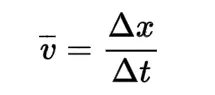
Velocity
the rate at which an object's displacement changes over time. It is a vector quantity. (Units: m.s-¹)
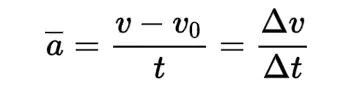
Acceleration
the rate at which an object's velocity changes over time. It is a vector quantity. (Units: m.s-²)
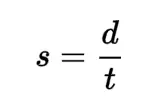
Speed
the rate at which an object travels over a distance. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and no direction. (Units: m.s-¹)
Scalar quantity
a quantity that has only magnitude and no direction, such as speed or mass.
Vector quantity
a quantity that has both magnitude and direction, such as velocity or force.
Position
the location of an object in space. It is often measured relative to a reference point.
Time
a dimension in which events occur in a sequence. It is often measured in seconds.
Distance
the total length traveled by an object, regardless of direction. It is a scalar quantity. It is measured in meters.
Displacement-time graph
a graph that shows the change in an object's displacement over time. Gradient of this graph represents velocity.
Velocity-time graph
a graph that shows the change in an object's velocity over time. Area under the graph represents the displacement.
Acceleration-time graph
a graph that shows the change in an object's acceleration over time. Area under the graph represents velocity
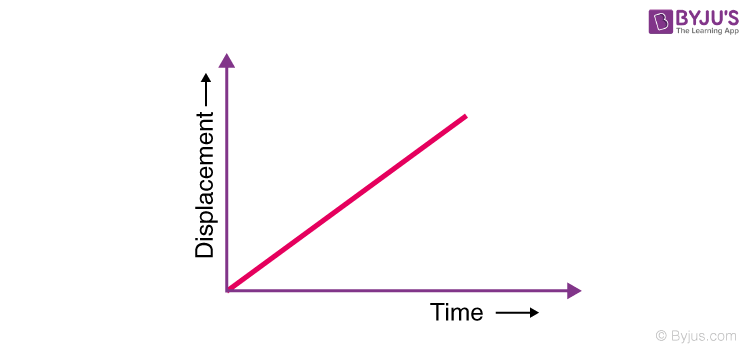
Uniform motion
when an object travels with a constant velocity (i.e. no acceleration).
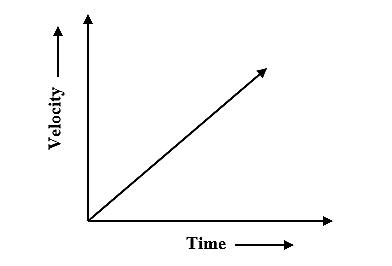
Uniformly accelerated motion
when an object accelerates at a constant rate.
Inertia
An object's tendency to resist changes in its state of motion.
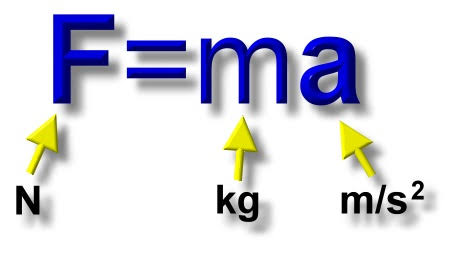
Force
A push or pull on an object that causes it to accelerate or change its state of motion.
Net force
The total force acting on an object, taking into account all the individual forces acting on it.
Mass
A measure of an object's resistance to acceleration, based on its amount of matter. SI Unit of mass is grams (g)
Circular motion
A type of motion in which an object moves in a circular path around a central point.
Centrifugal force
a fictitious force that appears to act on an object moving in a circular path. It is not a real force, but rather an apparent force that arises from the fact that the object is moving in a curved path.
Centripetal force
A force that is directed toward the center of a circular path and is responsible for keeping an object in circular motion.
Action and reaction
The concept that every force is part of a pair of forces that act on two different objects, and are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Newton's laws of motion
Three fundamental principles that describe how objects move and interact with each other, developed by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century.
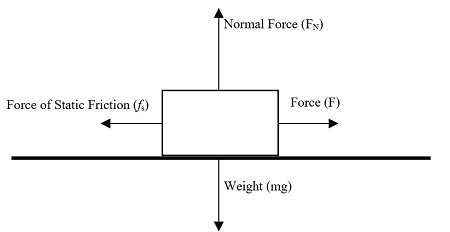
Static Friction
It is the friction that exists between two surfaces that are not moving relative to each other.
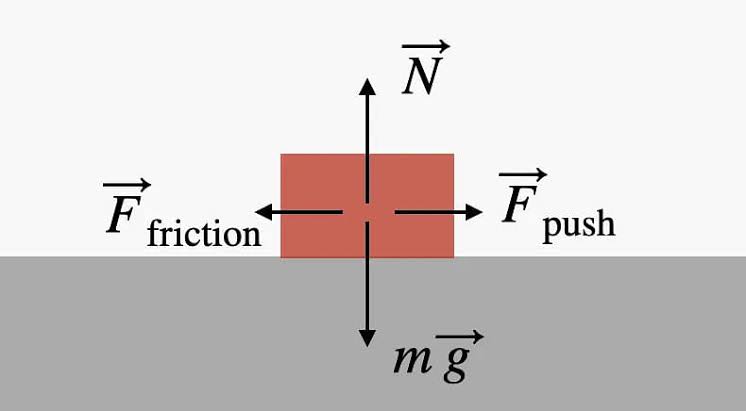
Kinetic Friction
It is the friction that exists between two surfaces that are moving relative to each other.
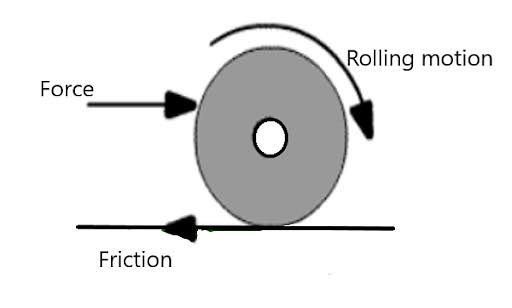
Rolling Friction
It is the friction that exists between a rolling object and the surface it is rolling on.
Uniform circular motion
the motion of an object moving in a circular path at a constant speed.
Newton's First Law of Motion/Law of Inertia
States that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force
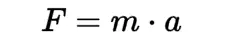
Newton's Second Law of Motion/Law of Acceleration
states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass.
Newton's Third Law of Motion
States that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
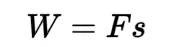
Work
The product of the force applied to an object and the distance over which that force is applied.
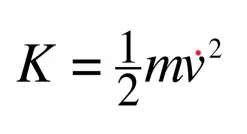
Kinetic energy
the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. It is a scalar quantity and is dependent on the mass and velocity of the object.
Work Energy Theorem
Formula that relates the work done on an object to the change in its kinetic energy. It states that the net work done is equal to the change in kinetic energy.
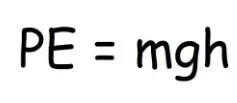
Potential energy
The energy possessed by an object due to its position or state. It is the energy that an object has stored within itself, which can be released when the object is allowed to move or change its state.
Gravitational Potential Energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to its position in a gravitational field. The higher an object is placed, the greater its gravitational potential energy.
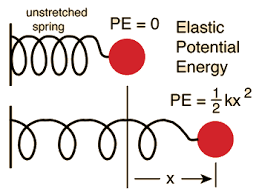
Elastic Potential Energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to its deformation or stretching. The more an object is stretched, the greater its elastic potential energy.
Chemical Potential Energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to the arrangement of its atoms or molecules. The more energy stored in the chemical bonds, the greater the chemical potential energy.
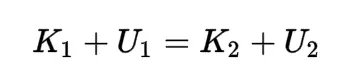
Conservation of Energy
Total energy in a closed system remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another.
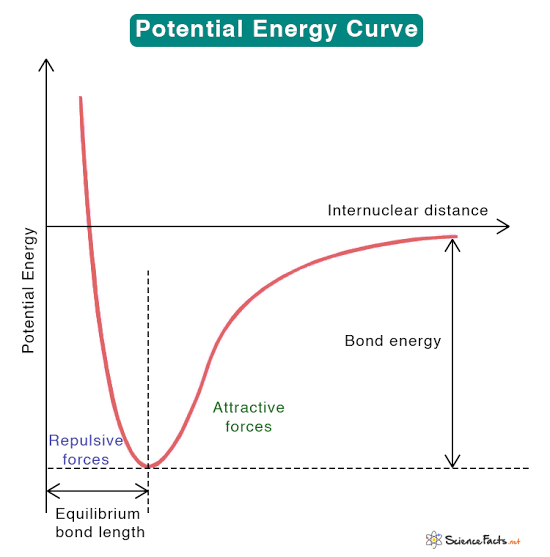
Potential energy curves
graphical representations of the potential energy of a system as a function of the distance between two or more particles.
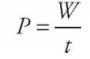
Power
the rate at which work gets done. Units: Watts
Center of Gravity
The point where the entire weight of an object can be considered to be concentrated
Center of Mass
The point where the mass of an object is concentrated, taking into account the distribution of its mass. It is the balance point where an object can be supported without any rotation.
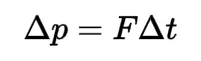
Impulse
A force that causes a change in an object's motion. It is equal to the change in momentum of the object over time.
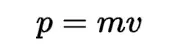
Momentum
The product of an object's mass and velocity. It describes the amount of motion an object has and is conserved in a closed system unless acted upon by an external force.
Linear momentum
The product of an object's mass and velocity, which determines the amount of motion it possesses in a straight line.
Conservation of Linear Momentum
The principle that states that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant unless acted upon by an external force.
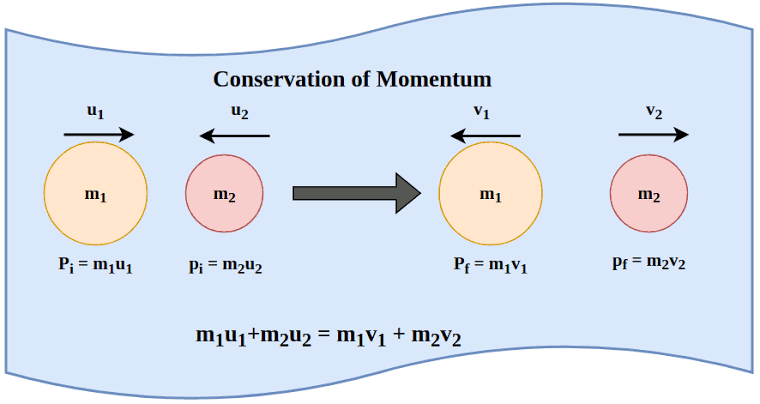
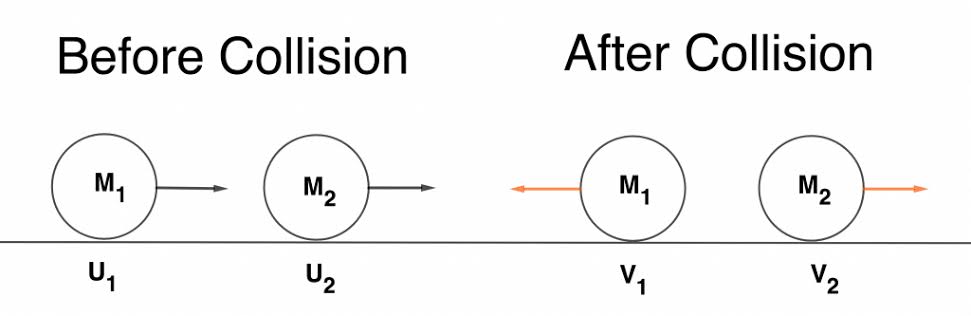
Collisions
It occurs when two or more objects come into contact with each other, resulting in a change in motion or deformation of the objects involved. It can be elastic or inelastic, and can be analyzed using the principles of conservation of momentum and energy.
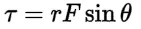
Torque
It is defined as the product of force and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force. Units: Nm
moment arm
The perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force and is an important factor in determining torque.
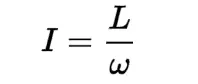
Rotational inertia
the property of an object that determines its resistance to rotational motion. It depends on the mass distribution of the object and the axis of rotation.
Parallel Axis Theorem
It states that the moment of inertia of a body about any axis parallel to its center of mass is equal to the moment of inertia about the center of mass plus the product of the mass of the body and the square of the distance between the two axes.
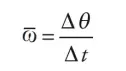
average angular velocity
Average angular velocity is simply the change in the objects angular position divided by the time it took for that change in position to take place.
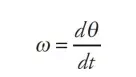
instantaneous angular velocity
the rate of change of angular displacement of a rotating body.
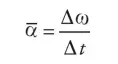
average angular acceleration
Average angular acceleration is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity.
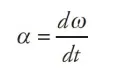
instantaneous angular acceleration
The instantaneous angular acceleration is defined as the limit of the average angular acceleration as the time goes to 0.
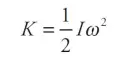
Rotational Kinetic Energy
Rotational energy or angular kinetic energy is kinetic energy due to the rotation of an object and is part of its total kinetic energy.
rolling motion
Where the total kinetic energy is the translational kinetic energy and the rotational kinetic energy
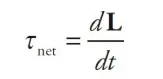
Conservation of Angular Momentum
Conservation of angular momentum is a physical property of a spinning system such that its spin remains constant unless it is acted upon by an external torque; put another way, the speed of rotation is constant as long as net torque is zero.
Equilibrium
occurs when an object is not rotating or is rotating at a constant angular velocity.
Static equilibrium
This occurs when an object is at rest and the net torque acting on it is zero.
Dynamic equilibrium
This occurs when an object is rotating at a constant angular velocity and the net torque acting on it is zero
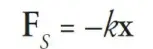
Simple harmonic motion
A type of periodic motion in which the restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium position and acts in the opposite direction to the displacement.

Hooke’s Law
The force required to extend or compress a spring is proportional to its displacement from its equilibrium position.
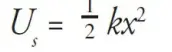
Elastic Potential energy
a spring with spring constant k, the elastic potential energy it possesses—relative to its equilibrium position
Oscillation
The back-and-forth motion of an object about its equilibrium position.
Amplitude
The maximum displacement of an oscillating object from its equilibrium position.
Period
The time taken by an oscillating object to complete one cycle of motion.
Frequency
The number of cycles per unit time of an oscillating object.
Spring constant (k)
The constant that relates the force exerted by a spring to its displacement from its equilibrium position.
Angular frequency
The rate at which an oscillating object completes one cycle of motion in radians per unit time.
Phase angle
The initial angle of an oscillating object at the start of its motion.
Resonance
A phenomenon in which an object is forced to vibrate at its natural frequency due to the application of an external force at the same frequency.
simple pendulum
Consists of a weight of mass m attached to a massless rod that swings, without friction, about the vertical equilibrium position.
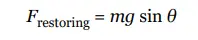
Restoring Force
the magnitude of the restoring force when the bob is θ to an angle to the vertical
Kepler’s First Law
Every planet moves in an elliptical orbit, with the Sun at one focus.
Kepler’s Second Law
As a planet moves in its orbit, a line drawn from the Sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals.
Kepler’s Third Law
If T is the period, the time required to make one revolution, and a is the length of the semimajor axis of a planet’s orbit, then the ratio T²/a³ is the same for all planets orbiting the same star.
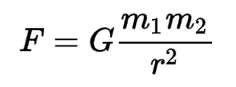
Newton's Law of Gravitation
States that every particle of matter in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
Gravitational Constant
a fundamental constant of nature and has a value of approximately 6.674 x 10-¹¹ N * m²/ kg²
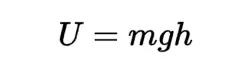
Gravitational potential energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to its position in a gravitational field. It is defined as the work done in moving an object from infinity to a point in the gravitational field.
eccentricity
The deviation of an ellipse from a perfect circle is measured by this parameter
barycenter
The focus is at the center of mass of the Sun-planet system, because when one body orbits another, both bodies orbit around their center of mass
Gravity
The force of attraction between two objects with mass.
Orbit
The path of an object as it revolves around another object in space.
Elliptical orbit
An orbit that is shaped like an ellipse, which is an elongated circle.
Orbital velocity
The speed at which an object must travel to maintain a stable orbit around another object.
Escape velocity
The minimum speed an object needs to escape the gravitational pull of a planet or other celestial body.