stupid fucking evo bio fuck you
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
All living organisms posses
genotype
ability for mutations
relationship between genotype and phenotype
What happened during precambrian period
cyanobacteria produced oxygen and change the atmosphere
endosymbiosis resulted in aerobic organisms
multicellular organisms arose
What happened during the paleozoic era?
cambrian explosion (happened because of species interactions and diversification)
Land animals + plants, tetrapods, winged insects, seeded plants
end-permian mass extinction (THE LARGEST)
What happened during the mesozoic era?
dinosaurs
Cycads dominate plants
Angiosperm plants evolved
KT extinction (Birds survived)
What happened during the cenozoic era?
age of the mammals
galcial cycles
What causes speciation
barrier to reproduction
disruption in gene flow
Species concepts
Morphological- phenotypic differences, widely applicable but may not reflect evolutionary history, doesn’t define cryptic species, doesn’t distinguish varibale population of the same species and different species
Phylogenetic species concept - speices are defined as the smallest monophyletic group, widely applicable to fossils but leads to many more species and can disagree with molecular and morphological data
Biological-organisms in the same species can breed and organisms in different species can’t breed, evolutionarily meaningful but doesn’t apply to asexual species
allopatric, parapatric and simpatric speciation
allopatric- physical barriers
parapatric- range expansion but no physical barrier results in different conditions and speciation
sympatric- genetic differences result in reproductive isolation and then speciation
Allopatry is common in animals, sympatry is most common in plants
Biogeographic evidence of evolution
Even if there are similar climates, regions across globe contain unrelated species
Barriers to dispersal= difference in assemblage
What changes geographic range?
Dispersal
Extinction
vicariance
net diversification rate
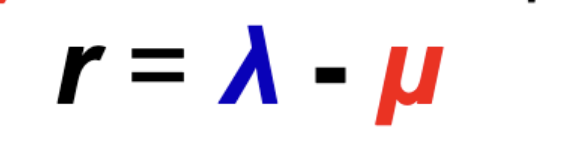
= seciation rate - extinction rate
Patterns of diversity over time
mass extinctions are common
Diversity rebounds after mass extinction
Types of competition and how diversification is affected by each
Direct- two species compete
Incumbent replacement- one species takes over due to anothers’ absence
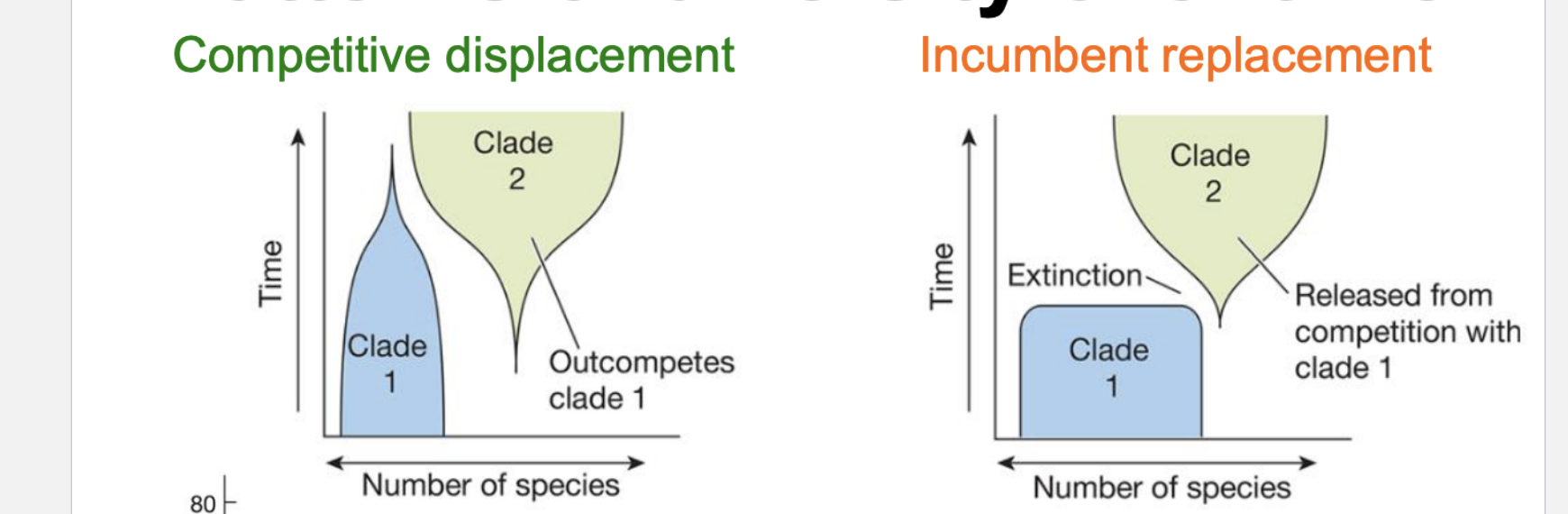
Difference between micro and macro evolution
microevolution occurws at the species level over a short period of time due to allele frequency changes while macroevlution occurs at or above species level over the longterm and results in speciation
How is phenotypic plasticity tested
Recipricol transplant experiments
two of the same species that live in different environments are put in each other’s environments
What does it mean for the genetic code to ber degenerate
Multiple codons code for the same amino acid
Which base changes result in amino acid changes? which don’t?
Most third base changes do not result in amino acid change
Second base change WILL RESult in an amino acid change
What are indels
single base pair insertions or deletions bc of replication mistakes
What is linkage equillibrium/ disequilibrium? How does it relate to recombination?
Linkage equilibrium= two alleles evolutions are independent of each other, recombination is high (>0.5 and prob on different chromosomes)
Disequilibrium= two alleles evolutions are not independent of each other, recombination is low (less than 0.5 and on same chromosome)
Disequilibrium decreases over time and D0 is above 0