Grade 8 Science End of Term 1 Revision
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and facts from the Grade 8 Science end of term 1 revision material.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
__ is the transfer of energy by the flow of gases or liquids.
Convection
When fast-moving warm air molecules rise and spread out from Earth’s surface, a ______ forms
low pressure system
___ causes by the Coriolis effect.
Earth’s rotation
When a warm air mass slides over a cold air mass, a ______forms.
warm front
A __________ causes rain or snow since many clouds form when air rises.
low pressure system
Trade winds are located in parts _3 and 4_.
3 and 4
What might be one reason for two cities at the same latitude to have different Climates?
One City is located near a large body of water, while the other is further inland.
The tropical zone is the area located between ——- north of the equator and __ south of the equator.
23.5º
The result of having moist air on the windward side and dry air on the leeward side of a mountain is called__________.
rain shadow
The ________is the source of energy needed for the water cycle on Earth.
sun
The climate on the leeward side of a mountain tends to be_________.
dry and warm
What factors affect the motion of surface ocean currents?
Convection patterns, the Coriolis, and winds.
Much of the chemical energy that organisms need and use is stored in the bonds of ______.
glucose
Atoms are made of smaller particles called _________.
subatomic particles
To find the number of neutrons in an atom.
formula: number of neutrons = mass number – number of protons.
A substance that results from a chemical reaction is called a _______.
product
When methane gas burns in the presence of oxygen, a blue flame is produced. What does the flame indicate?
The reaction gives off energy in the form of light.
A shorthand to describe a chemical reaction is a _________.
chemical equation
The chemical equation for the formation of ammonia gas is represented as N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g)_.
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g)
In the equation, what does the number 2 preceding O2 represent? CH4 + 2O2 → 2H2O + CO
coefficient
The flame in a fireplace indicates that____________.
energy is released
After adding baking soda to a flask containing vinegar, bubbles form and the temperature of the flask decreases slightly. a. What are the products of the reaction taking place? b. What do the bubbles produced during this reaction indicate?
A. liquid water, carbon dioxide, and dissolved sodium acetate
B.A gas is being produced.
Mike decided to do a couple of experiments at home in order to describe the different processes of the water cycle. In his first experiment, he placed a plate filled with water on a sunny window. After a few days he noticed that the plate was completely empty. In his second experiment, he brought a cold can of soda from the fridge and placed it in direct sunlight. After a few minutes, he noticed that water began to collect on the outside of the can. a. In the first experiment, Mike showed the process of ______________. b. In the second experiment, Mike showed the process of ____________.
A. evaporation
B. Condensation

This is a leaf. What do the leaf’s dots represent? What roles does it play?
The dots on the leaf are the stomata, and they play a role in gas exchange.
What cells have a cell wall? - ROOT Cells -Bacteria Cells- Fungal Cells- Leaf Cells- Animals Cells?
Root Cells
Bacteria Cells
Fungal Cells
Leaf Cells.
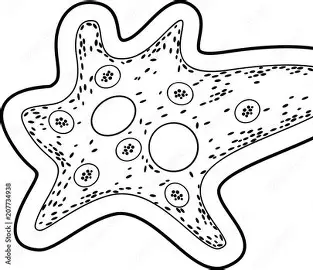
This picture shows Amoeba proteus, a unicellular protozoan, with several leg-like extensions. Amoebae use the leg-like extension to_________?
Move and get energy.
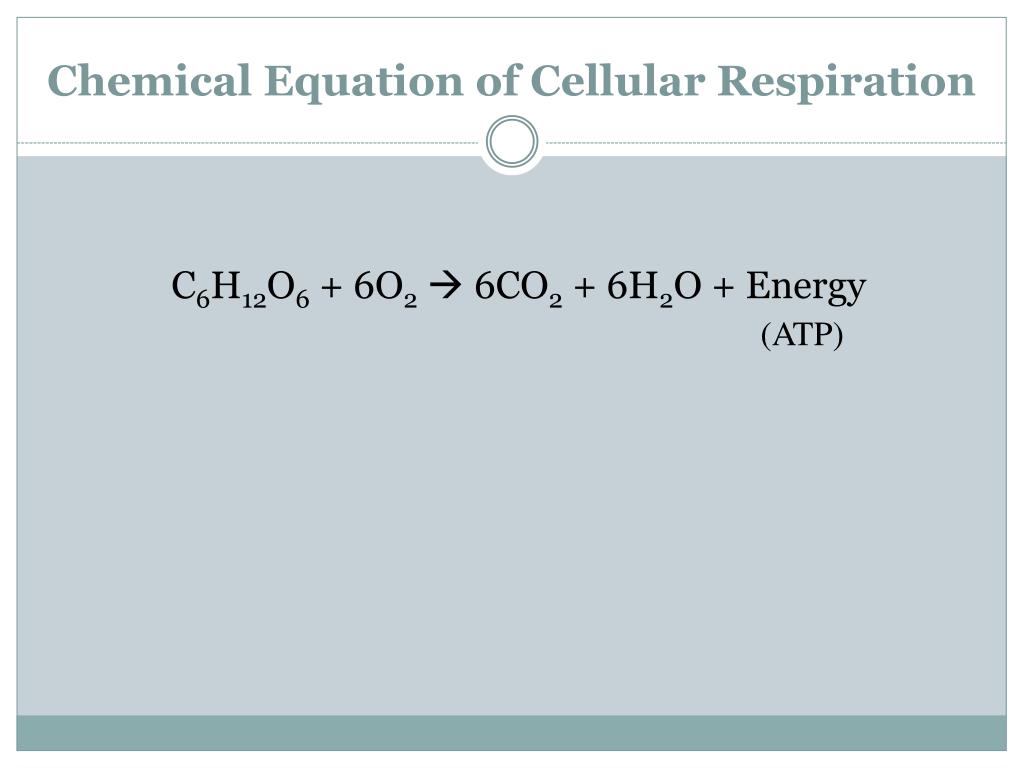
Write the equation for Cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
The parts of the cell theory include:
The cell is the basic unit of life,
Cells carry out the functions needed to support life,
And cells come only from pre-existing cells__.
List four factors that affect weather and name the instrument used to measure each of them.
Temperature measured by a thermometer
Air pressure measured by a barometer
Wind direction measured by a wind vane
Wind speed measured by an anemometer.
Give one difference between a severe weather watch and a severe WEATHER WARNING.
A severe weather watch means that weather conditions are right for severe weather to develop; a severe weather warning is issued if a severe weather watch already exists, and the severity of the weather is increasing
Silver nitrate reacts with sodium chloride yielding silver chloride and sodium nitrate. AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq).
Write the word equation of the reaction.
b. Write the ionic equation of this reaction, having
Ag+, NO3-, Na+, and Cl- Ag+ (aq) + NO3 - (aq) + Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)→ AgCl (s) + Na+ (aq) + NO3 - (aq
A. silver nitrate + sodium chloride → sodium nitrate + silver chloride
B. silver, nitrate, sodium, and chloride respectively.
What are the numbers of electrons, protons, and neutrons in carbon-14? Show your work.
the carbon-14 atom has 6 protons, 6 electrons, and 8 neutrons. Isotopes have the same atomic number, so the atomic number of carbon-14 is 6 which is the number of protons in an atom, and the number of protons and electrons is the same, so the carbon-14 has 6 protons and 6 electrons. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom, so the atom has 14 – 6 = 8 neutrons.