Productivity and short run costs
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the short run?
The period of time when one or more FOP’s is fixed, usually capital or land.
What is the long run?
The period in which all FOP’s can be varied, within the confines of given technology.
What is the very long run?
The period of time in which all FOP’s and technology can be varied.
What is total product?
The total quantity of output produced by a given number of inputs within a particular time period.
What is average product?
the quantity of output per unit of input.
Total product/Quantity of inputs
What is marginal product?
The addition to output produced by an extra unit of input.
change in total product/ change in quantity of inputs
What is the law of diminishing returns?
When increasing quantities of a variable FOP are used in combination with a fixed FOP initially the average and marginal product increases but eventually decreases.
What causes the initial increase in productivity?
Due to the use of Specialisation and the eventual decline in productivity occurs due to overcrowding of the fixed FOP.
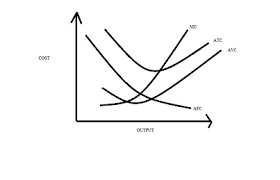
Diagram showing total, marginal and average product.
The MP reaches a maximum point first, then AP and finally TP. (MAT)
MP intersects the AP at the maximum point
TP,AP and MP all decline eventually (law of diminishing returns)
MP becomes negative as total product falls; if output is falling then the extra workers are reducing output
What is a fixed cost?
costs that do not vary with output.
What is a varied cost?
Costs that vary directly with output
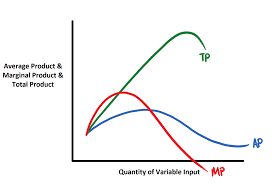
What are total costs?
FC+VC
Diagram representing costs.
Costs will never be zero.
What are semi-variable costs?
Costs that vary non-proportionately or indirectly with output. They have a variable and fixed element.
What is an example of semi-variable costs?
Labour- some labour costs rise when output rises such as the wage bill as production line workers are paid by the hour.
however some labour costs do not vary with output- such as the salaries of the admin staff.
What are average variable costs (AVC)?
VC/Quantity produced.
What are average fixed costs (AFC)?
FC/Quantity produced, will always decline as output rises.
What are average total costs (AC)?
TC/Quantity produced
What is a marginal cost?
The amount of one extra unit of output adds to total costs.
change in TC/change in Q or change in VC/change in Q
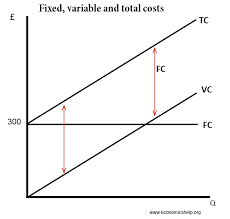
Diagram of AFC, AVC, ATC and MC.
AFC falls as output rises
the vertical distance between the ATC and the AVC curves is the AFC
ATC, AVC and MC are u-shaped because costs fall initially as output rises and then after reaching a minimum they begin to rise (law of diminishing returns)