OB Exam 1 Chapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive Systems
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
ovaries develop around
10 wks gestation
testes develop between
7-8 wks gestation
differentiation of external genetalia is complete by?
12th wk of gestation (3rd month)
External Female Reproductive Organs (vulva...i.e. "covering") purpose
Protect urethral and vaginal openings
hymen (external repro)
-Tissue that partially (or sometimes completely) covers the vaginal orifice.
-May tear at first intercourse or during physical exertion, tampon use or injury
perineum
-Area between the vulva and the anus
-May become lacerated (tears) or incised (episiotomy) during childbirth and need to be repaired with sutures
cultural ritual of female repro organs
Female genital mutilation (cutting of the covering of the clitoris
(considered a human rights violation against women)
vagina (birth canal) description
internal reproductive structure, muscular, membranous, 3-4 inches in length
vagina functions
Allows for passage of: Menstruation, sperm, baby
the vagina contains
Rugae (allowing for stretching during intercourse and childbirth)
the vaginas pH
Acidic during reproductive years (pH = 4-5) to help prevent some infections
Factors that may upset the pH and place a woman at risk for infection include:
-antibiotics
-douching: liquid substance to cleanse vaginal area (disturbs normal flor increasing risk of infection)
-perineal hygiene sprays and deodorants
what should be used on the vagina
soap and water only
vaginal secretions and pregnancy
Vaginal secretions are increased in amount during pregnancy
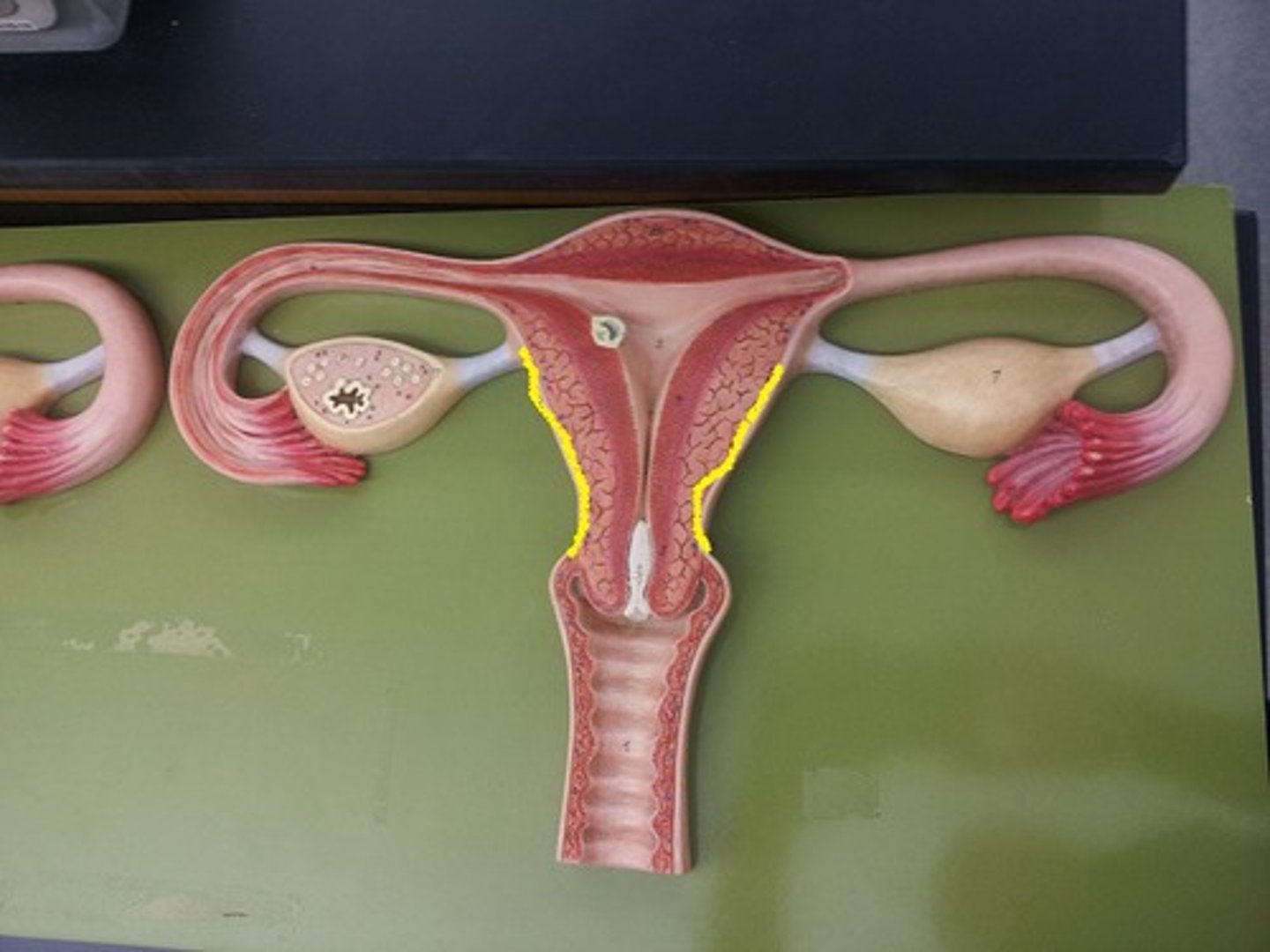
uterus (womb) description
-internal reproductive structure
-hollow, muscular, thick-walled
-body of the uterus is composed of primarily smooth muscle
uterus function
provide a safe environment for the developing fetus
uterus position
-anteverted (tilted forward) (ligaments help the uterus expand and be mobile)
-only the cervix is anchored*** NOT the uterus
structures of the uterus
-isthmus
-corpus*
-cervix*
-fundus
-carnua
isthmus
divides the uterus into 2 unequal parts
corpus
-the body of the uterus
-3 layers: perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium
perimetrium
outer layer of uterus
myometrium
-middle/muscle layer (contracts during labor)
** Uterine contractions: are responsible for cervical dilation
are the major force for passage of the baby through the pelvis and vagina
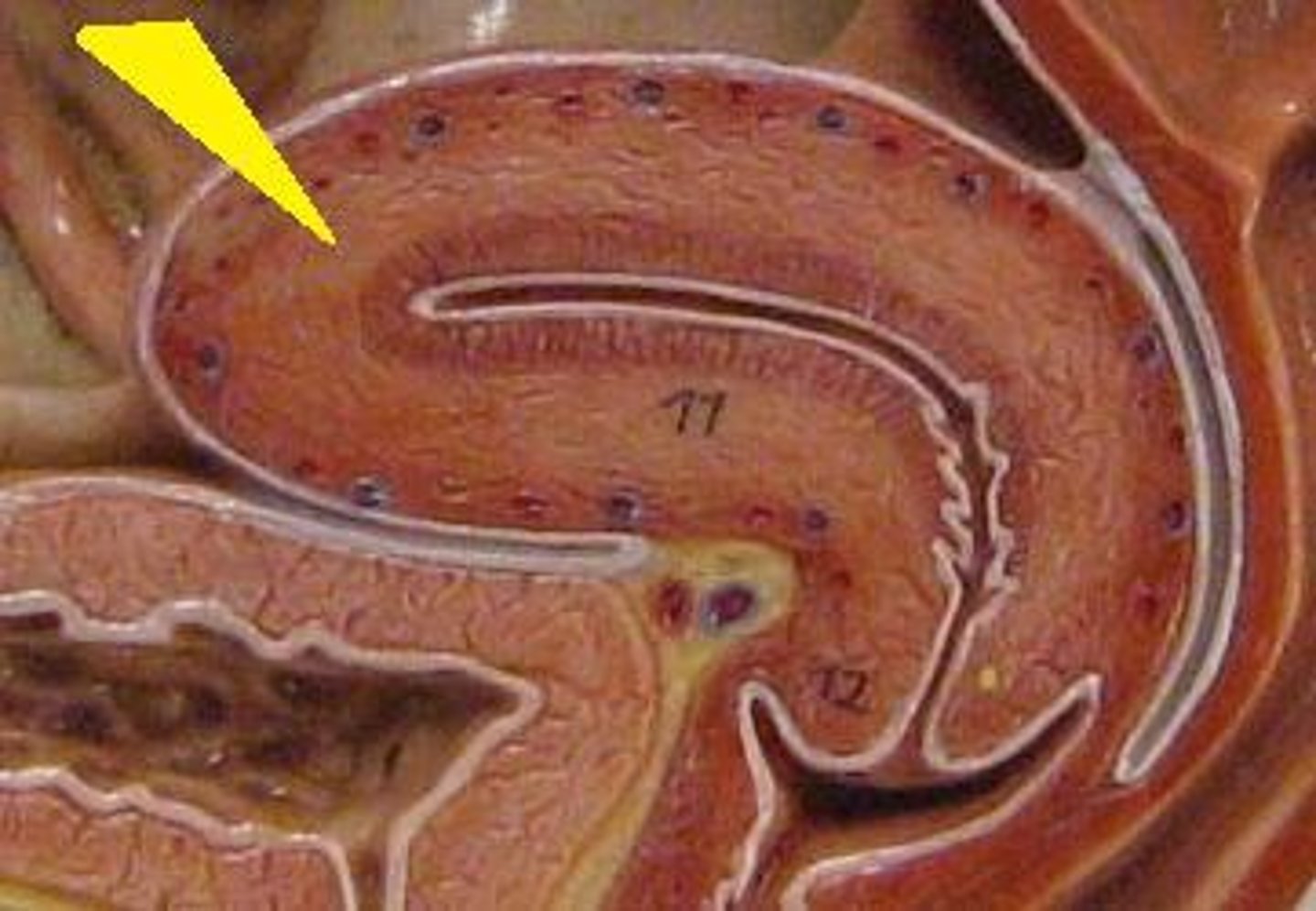
endometrium
- responds to hormonal cycle
- is thickest during the part of the menstrual cycle when a fertilized egg may enter the uterus
- is thinnest just after menstruation
the endometrium secretes endometrial milk which...
-keeps uterus moist
-facilitates sperm transport
-nourishes embryo prior to implantation
-is alkaline in nature
the endometrium contains 2 types of arteries which...
-provide a unique blood supply
-allow shedding of some tissue during menstruation
-prevent shedding of other tissue during menstruation
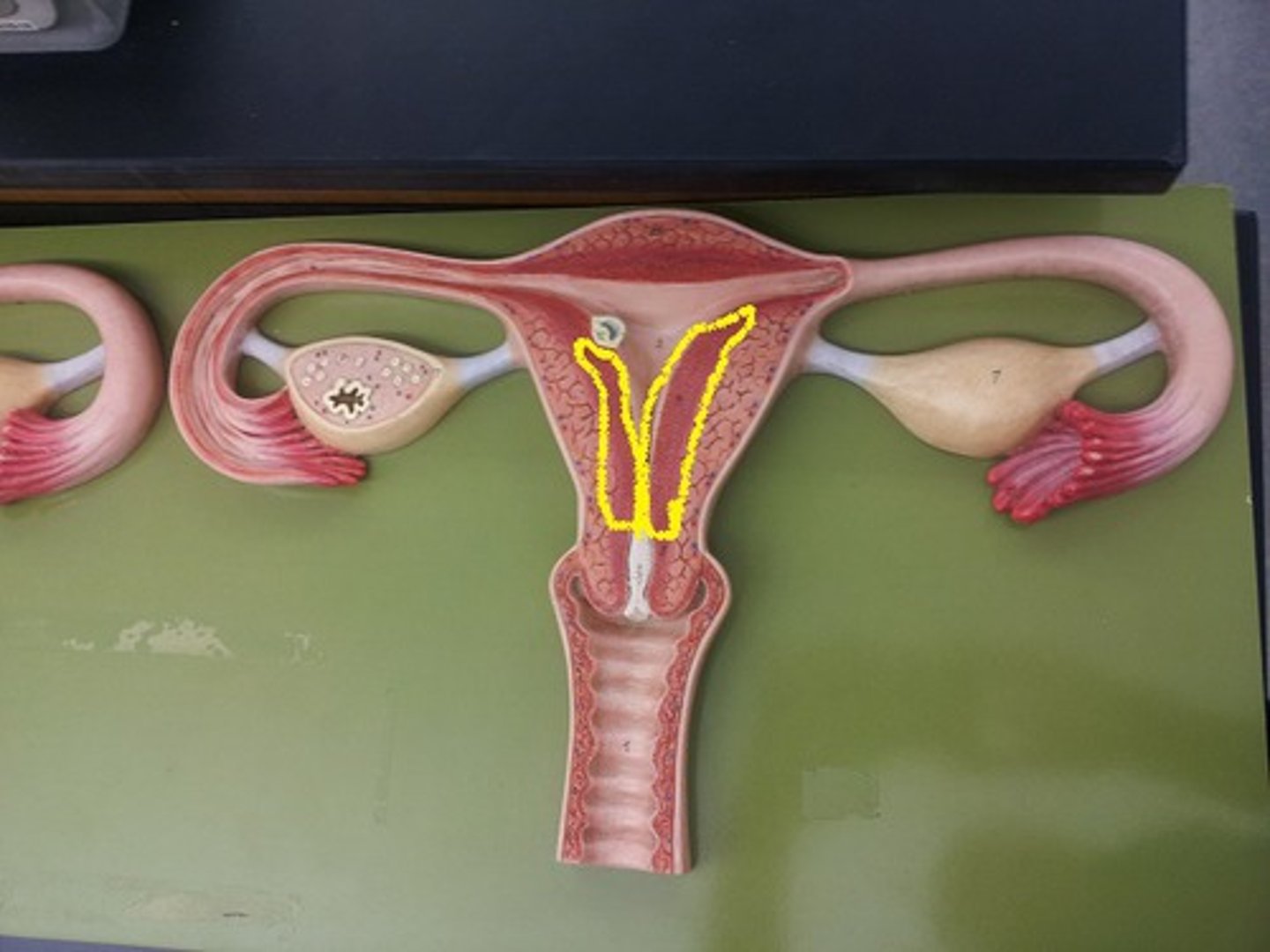
cervix
-the lower 1/3 of the uterus, opens into the vagina
-Elasticity/stretch-ability
-A protective portal
-Produces cervical mucous
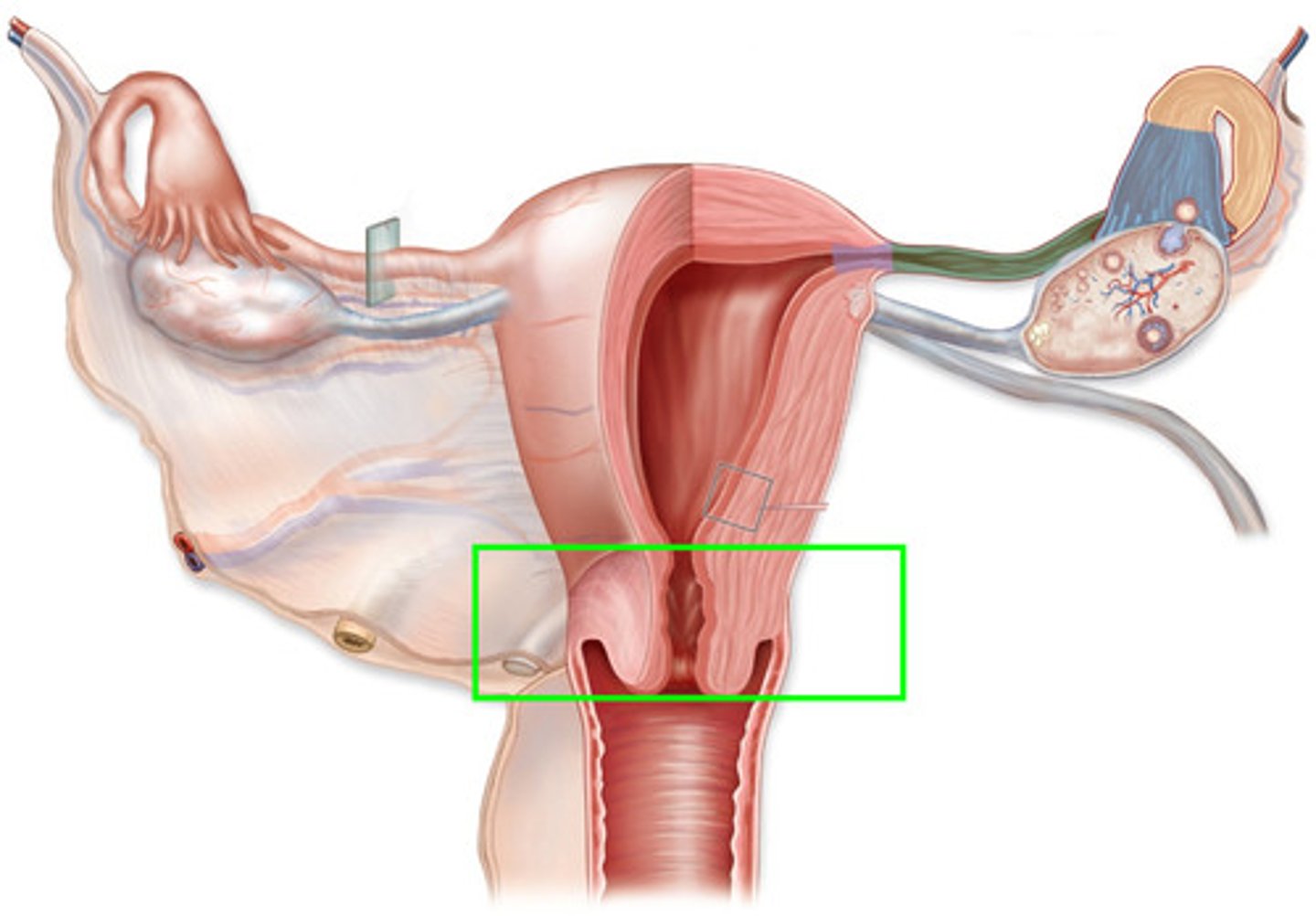
characteristics of cervical mucous
-Provides lubrication
-Acts as a bacteriostatic
-Alkaline pH (is more alkaline at ovulation/protects sperm from acidic vaginal secretions)
-Is thick and impenetrable to sperm until just prior to ovulation
-Thins at ovulation to allow sperm to access the uterus for potential fertilization
fundus
-the uppermost or top portion of the uterus
-measure from symphysis pubis to the top of the fundus when estimating how many wks someone is
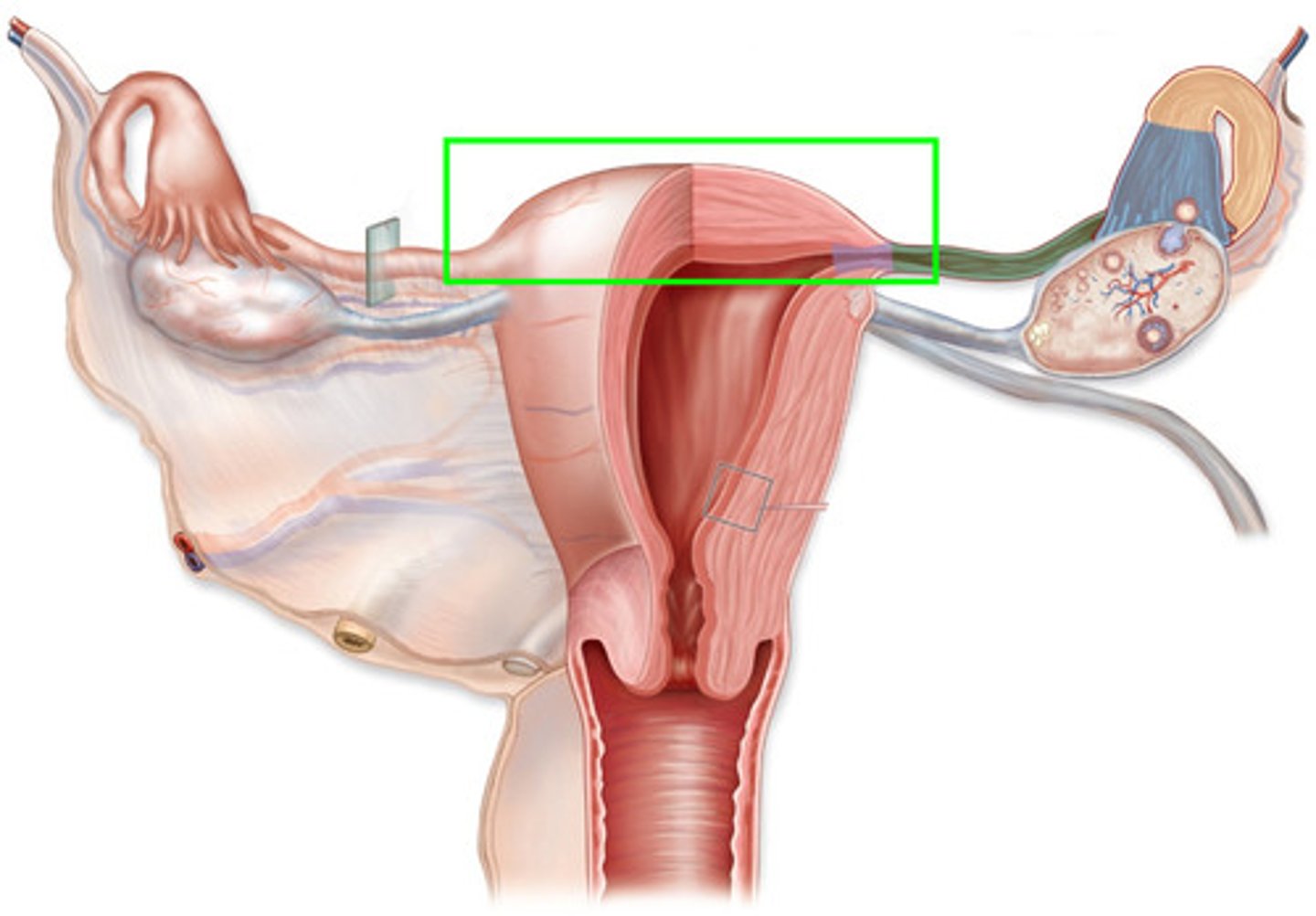
carnua
the narrowed area where the fallopian tubes enter the uterus
uterine ligaments
-Provide support
-Various ligaments support and suspend the uterus
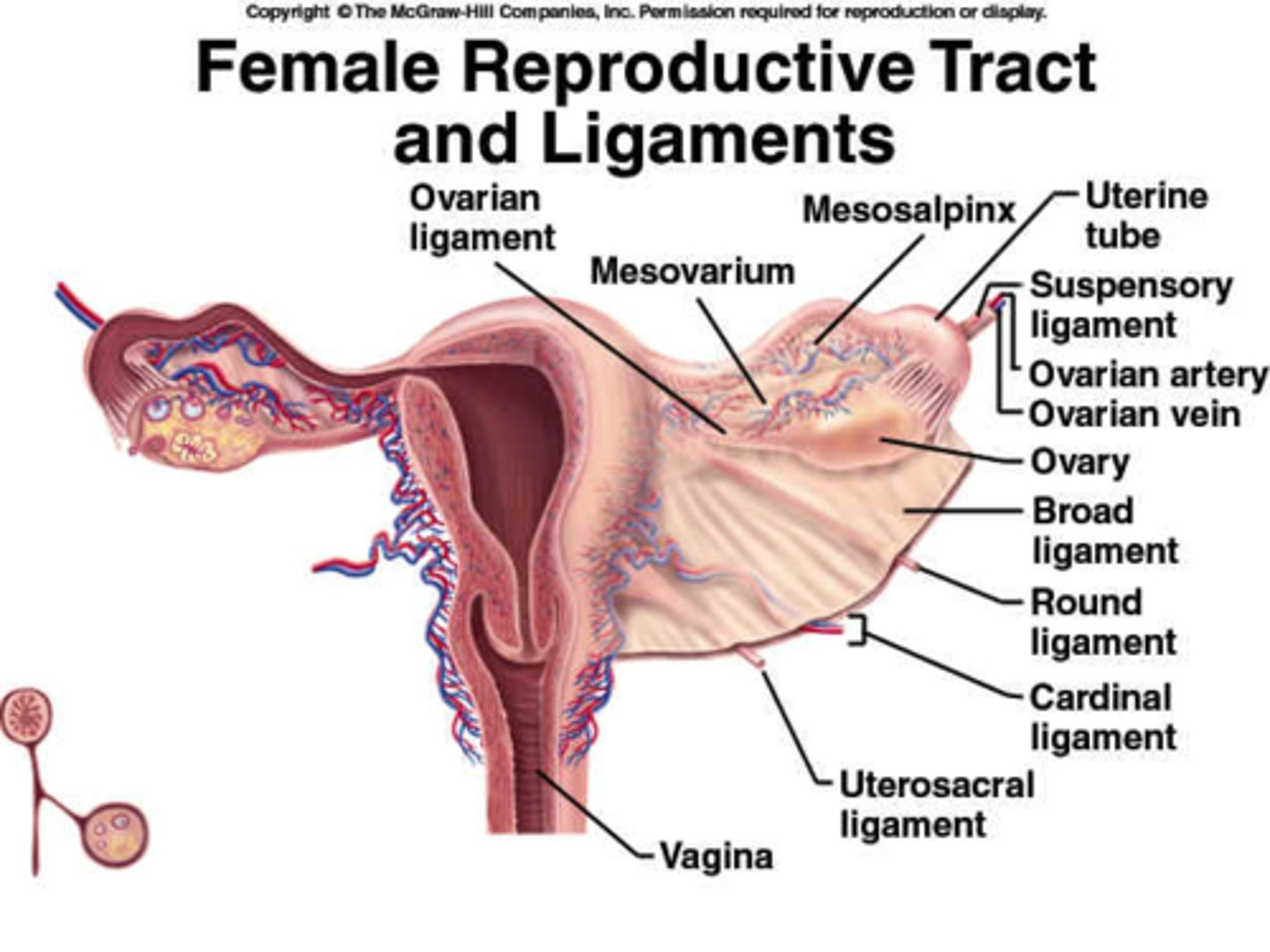
uterosacral ligaments
-contain sensory fibers that contribute to menstrual discomfort
-lower portion
-gives us back pain
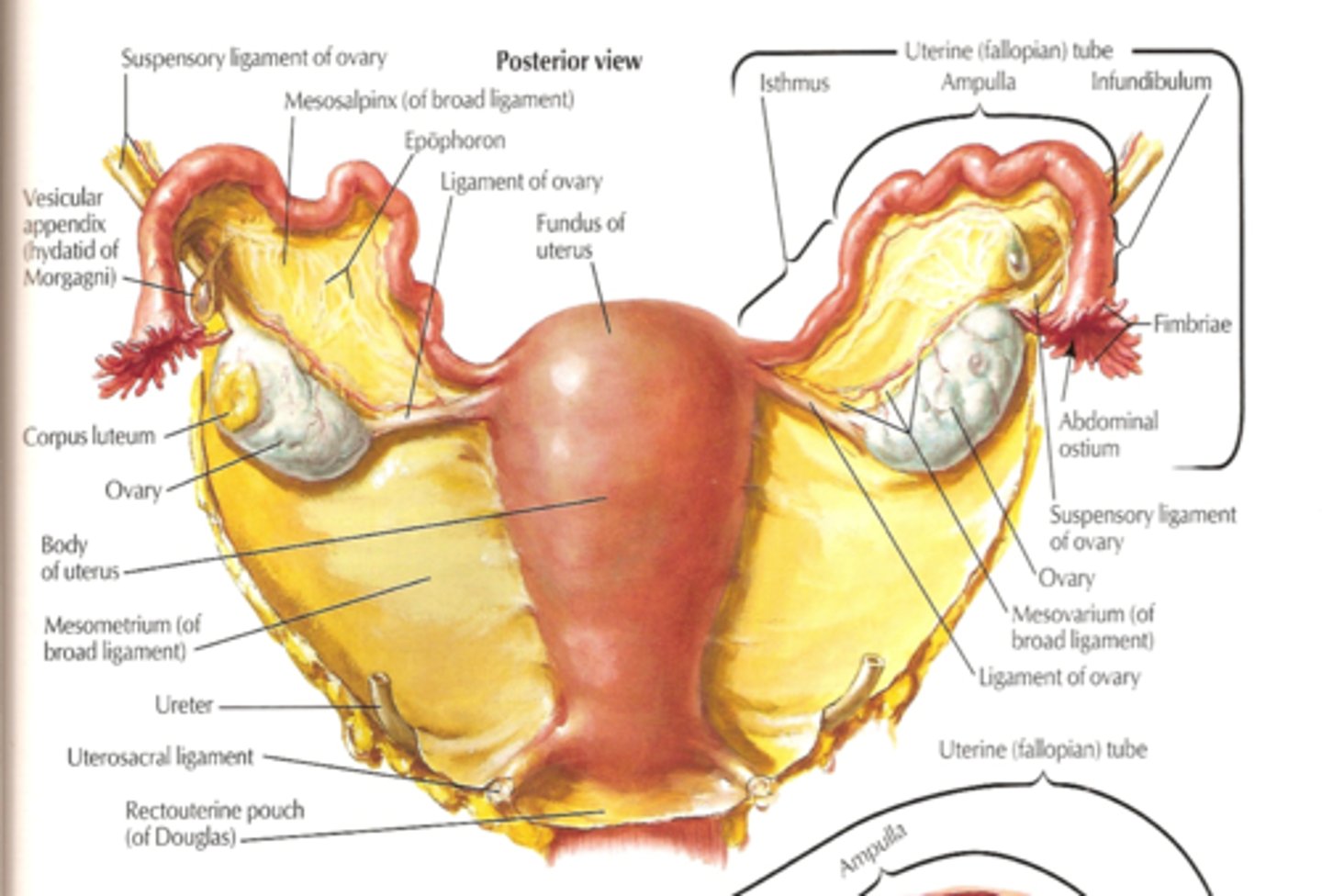
uterine innervation
-via ANS
-Sensory and motor innervation is separate
-Epidural anesthesia inhibits sensory fibers but maintains motor function
(eases pain/maintains contractions)
**doesn't stop uterine contractions, just eases the pain!!
fallopian tubes (oviducts)
-internal reproductive structure
-Approximately 4 inches in length
parts of the fallopian tube
-infundibulum with the fimbria: reach out and pick up the egg to bring it to the fallopian tube to be fertilized or not
-ampulla: site of fertilization (curved)
-isthmus: tubal ligations done here
fallopian tube cilia
-line the tubes, facilitate egg transport to the uterus
-estrogen also helps with this movement
hormones involved with the fallopian tubes
Prostaglandins: cause peristaltic movement of the tubes which propels the egg
functions of the fallopian tubes
-site of fertilization (ampulla)
-transport egg from ovary to uterus (3-4 days)
-warm, moist environment for the ovum or zygote (fertilized egg)
ovulation to implantation
7 to 10 days
smoking
nicotine paralyzes the cilia in the fallopian tubes causing a greater risk for ectopic pregnancy
ovaries
-internal reproductive structure
-Are NOT attached to the fallopian tubes but are supported by ligaments
ovaries numer and purpose
2, necessary for fertilization
hormones secreted from the ovaries
estrogen
progesterone
testosterone
hormones the ovaries are SENSITIVE to
-FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone)
-reproductive and endocrine systems are linked via hormone secretion
breasts (mammary glands)
Specialized sebaceous glands which secrete milk following pregnancy (colostrum)
colostrum
-sometimes called the "first breastmilk"
-produced the first few days after delivery
-Is rich in nutrients and antibodies
(IgA/immunoglobins A ...protects baby from enteric pathogens)
-Is higher in minerals and protein, lower in sugar and fat than mature milk (produced after the first few days)
the breasts are SENSITIVE to
placental hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
Effect of placental hormones on the breasts
-stimulate development of mammary glands during pregnancy
-may result in doubling of breast size (preparation for milk production)
effect of placental delivery on the breasts
-decreased levels of progesterone and lactogen (placental hormones)
-absence of inhibition of prolactin (stimulates milk production)
prolactin
stimulates milk production
female reproductive cycle characteristics
-Composed of 2 cycles:
Ovarian and Endometrial (Uterine)
-Cycles regulated by hormonal changes
-The breasts also experience cyclic changes
menarche
-Onset of menstruation in females
-Average age in U.S. is 12 (ranges between 8 - 18 years)
-Occurs about 2 years after onset of breast development
-Cycle regularity may take up to 2 years
most important factor in determining age of menarche
genetics
other factors determining menarche
geographic location, nutritional status, weight, general health, cultural and social practices
menstruation
-Monthly shedding of the endometrial lining of the uterus
-Marks the beginning and end of the monthly cycle
-Considered a normal, physiologic process in females
-Typically occurs on a monthly basis
menopause
Naturally occurring cessation of menstrual cycles
ovulation
Release of the ovum from the follicle
ovarian cycle
follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase
ovarian cycle phase 1: follicular phase
-Begins on day 1 of the menstrual cycle, continues until ovulation (usually on day 14 of a 28-day cycle)
-FSH is released
-Follicle maturation in the ovary and release of a mature egg
-Time variations in follicular development result in inconsistent duration of the follicular phase
-Menstrual cycle lengths vary in women due to variations in the length of the follicular phase
ovarian cycle phase 2: ovulation
-Release of a mature egg: Triggered by LH surge (Luetinizing hormone)
-Estrogen levels decrease
-Lifespan of the egg is typically 6 - 24 hours
-Spinnbarkheit
Spinnbarkheit
-thin, clear, stretchy, slippery cervical mucous produced by the cervix at ovulation
-captures and nourishes sperm
-enhances sperm transport through the cervix
hormones affect cervical mucous
-so if hormone levels are off, the cervical mucous may be thicker at the time of ovulation which impairs sperm from reaching the egg
-fertility issues
physical symptoms of ovulation
-Mittelschmerz: pain associated with ovulation (1-1.5 days)
-Increased discharge, mid-cycle spotting
-Increased temperature (0.5 - 1 degree F) 24 - 48 hours after ovulation until day before menstruation (d/t progesterone)
ovarian cycle phase 3: luteal phase
-release of LH (days 15-28 in a 28-day cycle)
-begins when egg leaves the follicle
-corpus luteum develops and secretes increased amounts of progesterone
**estrogen is still high to maintain the lining
main hormone during luteal phase
progesterone: is thermogenic
causes increased temp. (0.5 - 1 degree F) occurring 1-2 days after ovulation and lasting until approx. 3 days before onset of menstruation
fertilized ovum during luteal phase
secretes hCG (necessary to maintain the corpus luteum)
hCG
-human chorionic gonadotrophin hormone
-pregnancy test will be positive
-could be molar pregnancy or pheochromocytoma
unfertilized ovum during luteal phase (the period)
-corpus luteum degenerates
-estrogen and progesterone levels fall
-endometrial lining prepares to shed (ischemic phase)
uterine/endometrial cycle phase 1: menstrual phase
-Spiral arteries rupture
-Estrogen and progesterone levels fall
-Endometrial lining sloughs
-Menstrual bleeding occurs
uterine/endometrial cycle phase 2: proliferative phase
-Estrogen levels begin to rise and Endometrium thickens b/c estrogen makes things grow
-Cervical mucus is thin, clear, watery, more alkaline at the cervix with increased elasticity (increased favorability for sperm) (@ the time of ovulation, NOT before!)
-Begins near day 5 of the menstrual cycle
-Ends at ovulation
uterine/endometrial cycle phase 3: secretory phase
-Begins at ovulation
-Ends approx. 3 days before onset of next menstrual cycle
-Progesterone levels increase
-Endometrium thickens, vascularity increases (preparation for implantation)
if fertilization does not occur in the secretory phase
-corpus luteum degenerates
-estrogen and progesterone levels fall (so temp drops back down to baseline)
-endometrium involutes and sheds
uterine/endometrial cycle phase 4: ischemic phase
-Occurs 3 days prior to the onset of menstrual flow
-Sharp drop in estrogen and progesterone levels
-Endometrial vessels spasm
-Basal layer becomes ischemic
**prostaglandins (vasoconstrictor and smooth muscle contractions)
Irregular Menstrual Cycles may occur with:
-Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
-Stress/weather/disease/nutritional or social factors (affecting FSH!!)
-Thyroid disorders/hormone imbalance
GnRH
-menstrual cycle hormone
-Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone
-Induces release of FSH and LH for ovulation
FSH
-menstrual cycle hormone
-Follicle stimulating hormone
-Ovarian follicle maturation
LH
-menstrual cycle hormone
-Luteinizing hormone
-Necessary for final follicle maturation
-Surge occurs in the hours prior to ovulation
-Responsible for increased progesterone from the follicle (called "luteinizing")
estrogen
-menstrual cycle hormone
-Secreted by ovaries
-Crucial for follicle development and maturation
-Levels drop sharply after ovulation and progesterone dominates
-Causes uterus to increase in size and weight
uterus size before and after pregnancy
-not pregnant= 2 Oz
-pregnant= 2 lb (holding baby, amniotic fluid, and placenta)
progesterone
-menstrual cycle hormone
-Secreted by ovaries and corpus luteum
-Levels increase prior to ovulation
-Levels peak 5-7 days after ovulation
-Referred to as the "hormone of pregnancy"
-Has a "calming" effect on the uterus (reduces uterine contractions)
-Helps maintain pregnancy
-Thermogenic (increased temp. of 0.5 to 1.0 F with ovulation)
when you go into labor/right before labor
progesterone drops causing the release of oxytocin which allows for contractions of the uterus
Pictocin
synthetic oxytocin to induce labor
prostaglandins
-menstrual cycle "hormones"
-Oxygenated fatty acids (not hormones)
-Produced by the endometrium
-Large amounts are found in menstrual blood
prostaglandins on the cervix
to promote contractions
current research on prostaglandins
-Pathogenesis of menstrual cramps and pain is due to prostaglandin F2a (a powerful myometrial stimulant and vasoconstrictor)
-Elevated levels found in the endometrial fluid of women who experience dysmenorrhea
NSAIDS
-Primary choice of treatment for menstrual cramps
-ibuprofen
penis
-external male reproductive organ
-Outlet for both sperm and urine
-Composed mostly of erectile tissue
hypospadias
meatus is located on the under (dorsal) side
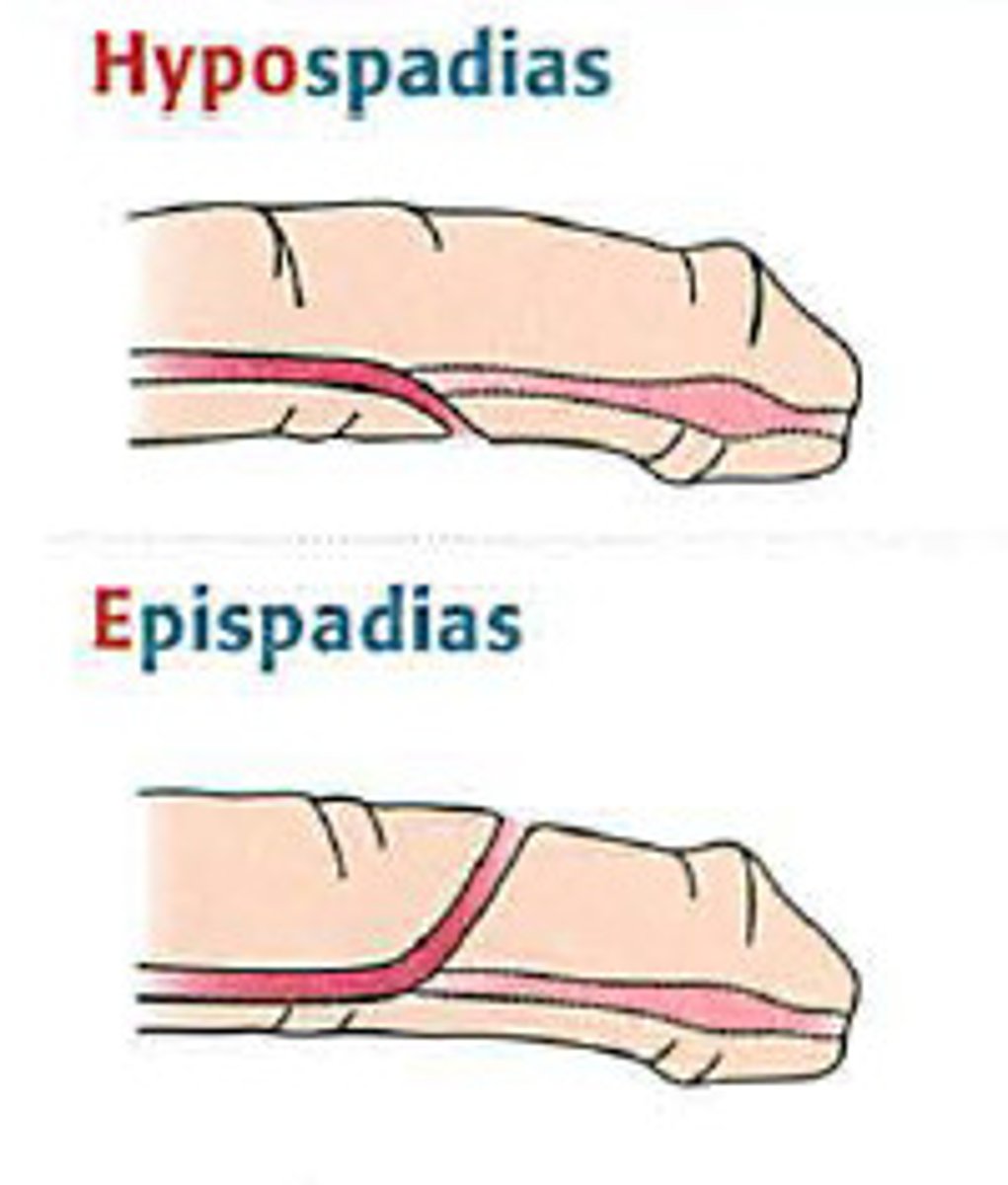
epispadias
meatus is located on the top (ventral) side
scrotum
-external male reproductive organ
-Contains the testes
-Maintains temperature slightly lower than body temp. to protect sperm development
testicular descension
-necessary for sperm formation
-place 2 fingers under scrotum and palpate
-if not palpable, could mean spermatic cord is twisted which would cause necrosis and affect the man the rest of his life
testes
-internal male reproductive organ
-site of sperm production
-site of testosterone production
ductal system: vas deferens
-Sperm travel through this structure to exit the body (severed during a vasectomy)
-after vasectomy the sperm are still formed they just can't exit the body
ductal system: epididymis
Holds maturing sperm
accessory glands: seminal vesicles
Provide nourishment for developing sperm
accessory glands: secrete prostaglandins
Promote receptivity of cervical mucous to sperm
accessory glands: prostate and bulbourethral glands
Secrete alkaline fluid (neutralizes acidic vaginal secretions)