bio c4 quiz
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
For historical reasons, compounds containing carbon are said to be organic, and their study is called __.
organic chemistry
Miller carried out a control experiment without discharging sparks and found no organic compounds. What might explain this result?
Since there were no sparks, organic compounds couldn't be produced because those sparks provided the energy needed to drive the chemical reactions that turned the inorganic compounds into organic ones.
The number of electrons required to fill the valence shell of an atom is generally equal to the atom’s _, the number of covalent bonds it can form.
valence
All of the molecules that are shown in Figures 4.3 and 4.5 are _, organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen.
hydrocarbons
Variation in the architecture of organic molecules can be seen in _, compounds that have the same numbers of atoms of the same elements but different structures and hence different properties.
isomers
differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms.
structural isomers
In ___ (also known as geometric isomers), carbons have covalent bonds to the same atoms, but these atoms differ in their spatial arrangements due to the inflexibility of double bonds.
cis-trans isomers
are isomers that are mirror images of each other and that differ in shape due to the presence of an asymmetric carbon, one that is attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms.
enantiomers
Draw a structural formula for C2H4. Draw the trans isomer of C2H2Cl2.
C2H4: double bonds btwn the Cs, single bonds between the C-H; C2H2Cl2: double bonds btwn the Cs but make the Hs and Cls on opposing sides
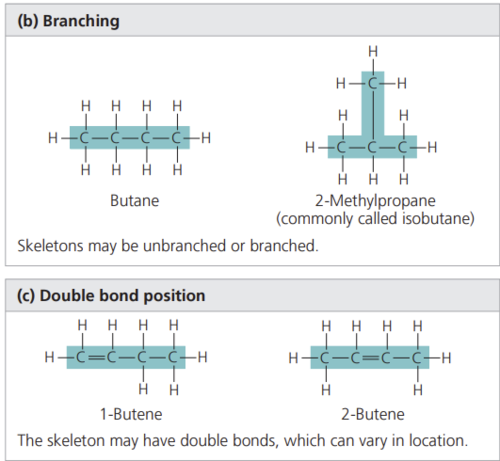
Which two pairs of molecules in Figure 4.5 are isomers? For each pair, identify the type of isomer.
in b and c they’re both structural isomers because they have the same number of each element but it's arranged differently
How are gasoline and fat chemically similar?
Both mostly consist of hydrocarbon chains and both provide fuel (gas for engines and fats for plant embryos and animals). Also, reactions with both of them release energy.
Can propane (C3H8) form isomers? Explain.
No. There is not enough diversity in propane’s atoms. It can’t form structural isomers because there is only one way for three carbons to attach to each other (in a line). There are no double bonds, so cis-trans isomers are not possible. Each carbon has at least two hydrogens attached to it, so the molecule is symmetrical and cannot have enantiomers.
In other cases, chemical groups are directly involved in chemical reactions; such groups are known as _.
functional groups
A more complicated organic phosphate, , or ATP, is worth mentioning here because its function in the cell is so important. ATP consists of an organic molecule called adenosine attached to a string of three phosphate groups.
adenosine triphosphate
What does the term amino acid signify about the structure of such a molecule?
that it has an amine group (NH2) making it an amine and a carboxyl group (COOH) making it an acid
What chemical change occurs to ATP when it reacts with water and releases energy?
it loses a phosphate and becomes ADP
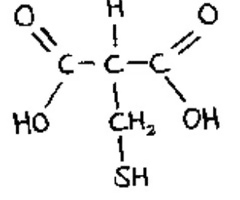
Suppose you had an organic molecule such as cysteine, and you chemically removed the —NH2 group and replaced it with —COOH. How would this change the chemical properties of the molecule? Is the central carbon asymmetric before the change? After?
Chemical properties: When you replace a chemical group that acts as a base (NH2) with a group that acts as an acid (COOH), the molecule becomes more acidic. The shape of the molecule also changes, which probably changes the molecules that it can interact with. Before the change, the cysteine molecule had an asymmetric central carbon, but after the change it became symmetric.