Rad Positioning
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Which of the following best describes the correct patient position for a lateral forearm?
Humerus and forearm 90 degrees, but it does not matter if they are in the same plane.
Humerus and forearm 90 degrees, in the same plane
Humerus and forearm 45 degrees, in the same plane
Humerus and forearm 45 degrees, but it does not matter if they are in the same plane.
Humerus and forearm 90 degrees, in the same plane
The hand should be pronated for the AP projection of the forearm.
False
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the ulna?
Styloid process
Ulnar notch
Coronoid tubercle
Radial notch
Ulnar Notch
The joint found between the base of the third metacarpal and carpal bones is the:
intercarpal
proximal metacarpophalangeal
carpometacarpal
interphalangeal
proximal metacarpophalangeal
For the lateral projection of the wrist, which surface of the wrist should be in contact with the IR?
Medial
Lateral
Anterior
Posterior
Lateral
The CR should be directed perpendicular to the forearm for the AP projection.
True
False
True
Which is the most commonly fractured carpal bone?
Scaphoid
Trapezium
Hamate
Lunate
Scaphoid
The hand is pronated for the lateral forearm position.
True
False
False
How much CR angulation to the long axis of the hand is required for the tangential projection to demonstrate the carpal sulcus (Gaynot Hart)?
10 degree to 15 degrees
25 degrees to 30 degrees
35 degrees to 45 degrees
5 degrees to 10 degrees
25 degrees to 30 degrees
The bending or forcing of the hand outward with the hand pronated in a posteroanterior (PA) projection is known as:
radial deviation
ulnar extension
ulnar deviation
radial abduction
Ulnar
Deviation
What two bony landmarks are palpated for positioning of the AP elbow?
Humeral epicondyles
Trochlea adn capitulum
Humeral condyles
Ulnar and radial heads
Humeral Epicondyles
The PIP joint is formed by the articulation of the ____.
Base of the proximal phalanx and the base of the middle phalanx.
Head if the proximal phalanx and the base of the middle phalanx.
Base of the proximal phalanx and the head of the middle phalanx.
All answers are true.
Head of proximal phalanx, base of the middle phalanx
What is the distance between the x-ray tube and the image receptor (IR) for a lateral forearm?
42"
39"
40"
30"
40"
Which of the following descibes correct IR/CR positioning for the Stetcher?
IR flat, perpendicular CR
IR flat, CR angled 15 degrees
IR angled 20 degrees, CR angled 15 degrees
IR angled 20 degrees, perpendicular CR
IR angled 20 degrees, perpendicular CR
Which of the following carpals articulates with the radius?
Trapezium
Capitate
Scaphoid
Pisiform
Scaphoid
A general positioning rule is to place the long axis of the ____ part to the long axis of the image receptor.
Perpendicular
axial
adjacent
parallel
Axial
Where is the CR center for a PA projection of the hand?
At the third distal interphalangeal joint
At the third metacarpophalngeal joint
At the base of the third metacarpal
At the third proximal interphalangeal joint
At the third metacarpophalngeal joint
Which of the following is not one of the evaluation criteria applied in the evaluation of images?
Anatomy Demonstrated
Patient Condition
Exposure Criteria
Collimation and CR
Patient condition
The anterior portion of the hand is referred to as the ____ side.
Palmer
Plantar
Distal
Dorsal
Palmer
Which of the following bones are classified as a long bone?
Cranium
Scapula
Carpal Bone
Humerus
Humerus
A radiograph of a PA oblique of the hand reveals that the mid-shaft of the fourth and fifth metacarpals are superimposed. What specific positioning error has been committed?
Excessive rotation of the hand and/or wrist laterally
Fingers of the hand are not parallel to IR
Insufficient rotation of the hand and/or wrist laterally
Incorrect CR angulation
Excessive rotation of the hand and/or wrist laterally
How many separate bones are found in the adult human body?
236
206
215
181
206
Which specific anatomy is better visualized with a fan lateral as compared with the other lateral projections of the hand?
Phalanges
Carpals
Sesamoid Bones
Carpometacarpal joints
Phalanges
Why is it important to keep the phalanges parallel to the image receptor (IR) for a PA oblique projection of the hand?
Prevents foreshortening of radio carpal joint
Prevents foreshortening of phalanges and obscuring of interphalangeal joints
Opens up the carpometacarpal joints
Demonstrates the sesamoid bones near the first interphalangeal joint
Prevents foreshortening of phalanges and obscuring of interphalangeal joints
Where is the central ray (CR) placed for a PA projection of the third digit?
At the head of the third metacarpal
At the metacarpophalngeal joint
At the distal interphalangeal joint
At the proximal interphalangeal joint
At the proximal interphalangeal joint
For the lateral projection of the elbow, how should the hand be adjusted?
Lateral with the thumb side up
Pronated
Lateral with thumb side down
supinated
Lateral with the thumb side up
A patient with a history of carpal tunnel syndrome comes to radiology. The physician wants to rule out abnormal calcifications in the carpal sulcus. Which of the following projections would best demonstrate this region?
Gaynor-Hart Method
Coyle Method
Carpal Bridge
Jones Method
Gaynor-Hart Method
Which of the following projections of the wrist will best demonstrate the wrist joint and intercarpal spaces?
Gaynor-Hart
PA Oblique
PA
Stecher
PA
A radiograph of the elbow demonstrates the radius directly superimposed over the ulna and the coronoid process in profile. Which projection of the elbow has been performed?
AP
External (lateral) rotation oblique
Lateral
Internal (medial) rotation oblique
Internal (medial) rotation oblique
How much rotation of the humeral epicondyles is required for the AP medial oblique projection of the elbow?
90 degrees
30 degrees
45 degrees
20 degrees
45 degrees
Which of the following structures is considered to be the most proximal?
Olecranon Process
Radial Tuberosity
Head of the Ulna
Radial Styloid process
Olecranon Process
The hand is pronated for the medial (internal) oblique projection of the elbow.
True or False
True
Which routine projection of the elbow best demonstrates the radial head and tuberosity free of superimposition?
Lateral
AP oblique with external rotation
AP
AP oblique with internal rotation
AP oblique with EXTERNAL rotation
Which routine projection of the elbow best demonstrates the olecranon process in profile?
AP
Lateral
Medial rotation oblique
Lateral rotation oblique
Lateral
For the AP projection of the forearm, how should the elbow be positioned?
Flexed 45 degrees
Fully Extended
Flexed 90 degrees
Fully extended
What is the name of the joint found between the proximal and distal phalanges of the first digit?
Proximal Interphalangeal
Interphalangeal
Distal Interphalngeal
Metacarpophalangeal
Interphalangeal
How many degrees of flexion of the elbow are necessary for the lateral projection?
90 degrees
20 degrees
40 degrees
45 degrees
90 degrees
Which of the following actions will lead to the proximal radius crossing over the ulna?
Placing epicondyles parallel to the image receptor
Pronation of the hand
Supination of the hand
External rotation of the elbow
Pronation of the hand
Which of the following bony structures is found on the distal aspect of the ulna?
Coronoid process
all of the above
Head
Olecranon process
Head
For the AP projection of the elbow, how should the CR (central ray) be directed?
Perpendicular
Angled cephalically
Angled Caudally
Perpendicular
How should the humeral epicondyles be aligned for a lateral projection of the elbow?
Parallel to the image receptor
Perpendicular to the image receptor
30 degrees to the image receptor
45 degrees to the image receptor
Perpendicular to the image receptor
For the medial (internal) oblique of the elbow projection, how should the coronal plane through the humeral epicondyles be placed with reference to the IR (image receptor)?
Rotated medially 45 degrees
Parallel
Perpendicular
Rotated 45 degrees laterally
Rotated medially 45 degrees
When positioning the AP forearm projection, select and IR long enough to include the entire forearm from the _____ of the ulna, to the ______ of the radius.
head; styloid process.
olecranon process; styloid process
olecranon process; head
head; head
olecranon process, styloid process
Which projection of the elbow best demonstrates the trochlear notch in profile?
Lateral rotation oblique
Medial rotation oblique
AP
Lateral
Lateral
A patient arrives radiology with a metal foreign body in the palm of the hand. Which of the following hand routines should be performed to confirm the location of the foreign body?
PA and fan lateral projections
PA and flexion lateral projections
PA and extension lateral projections
PA and Gaynor-Hart Projections
PA and extension lateral projections
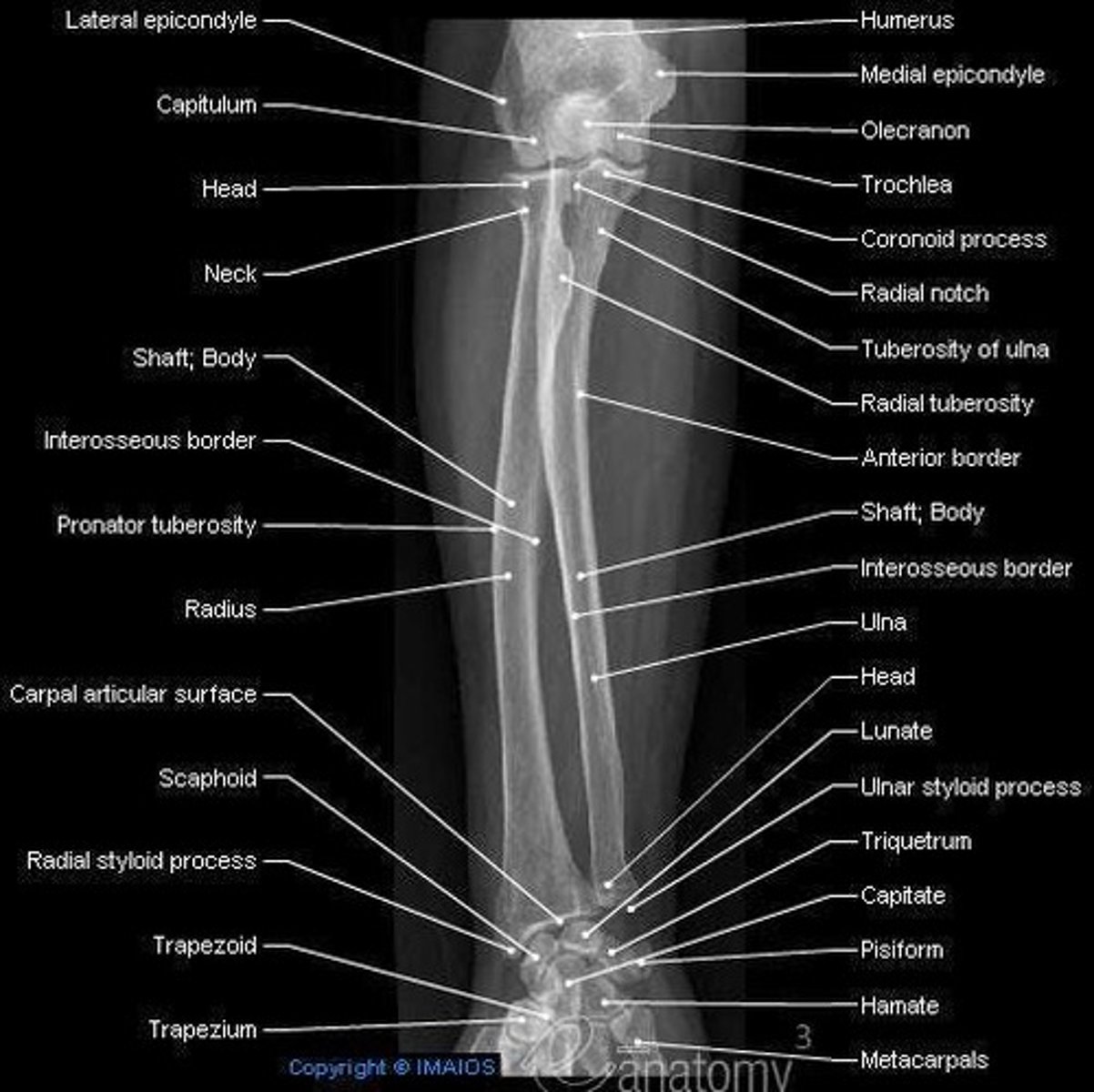
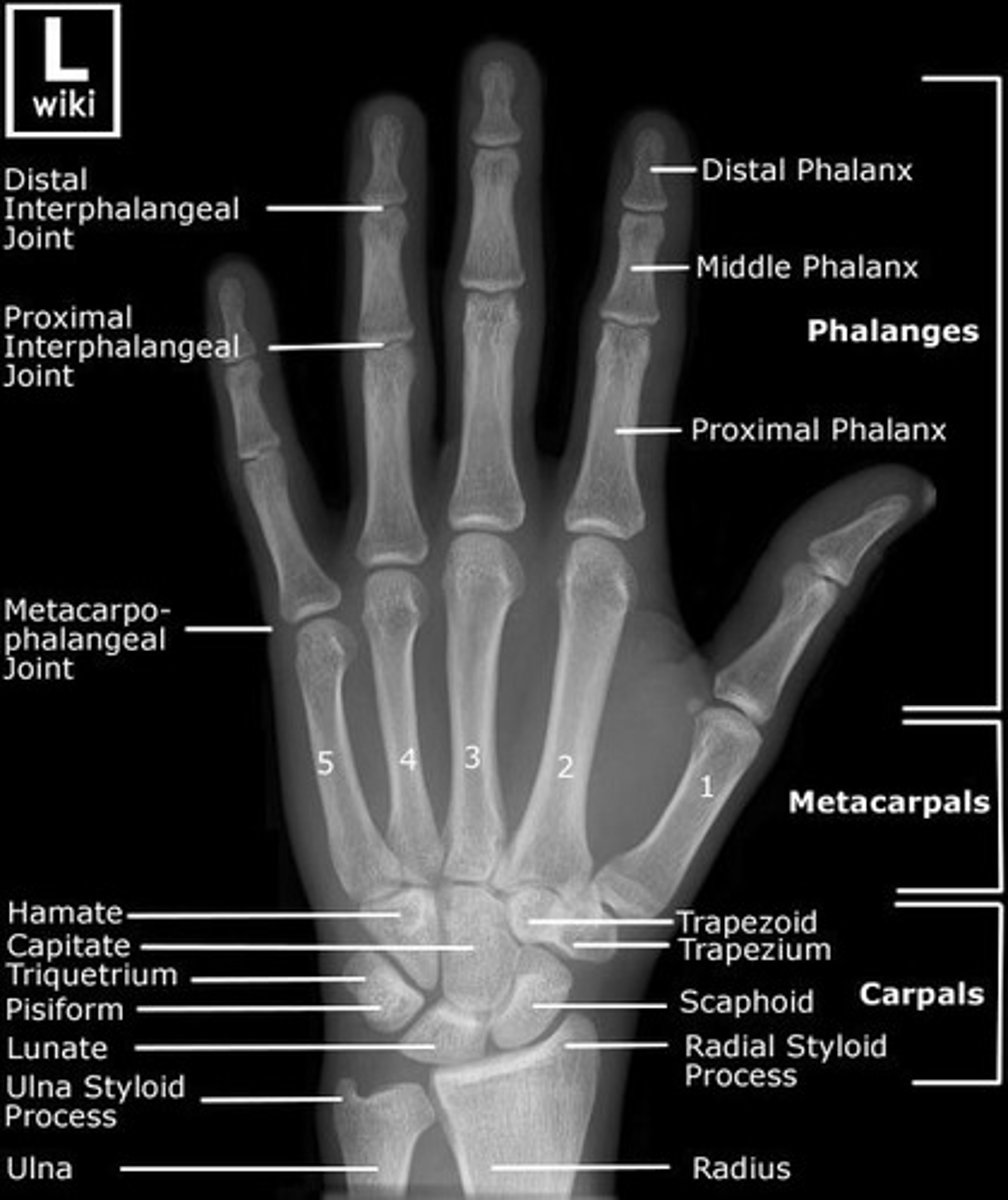
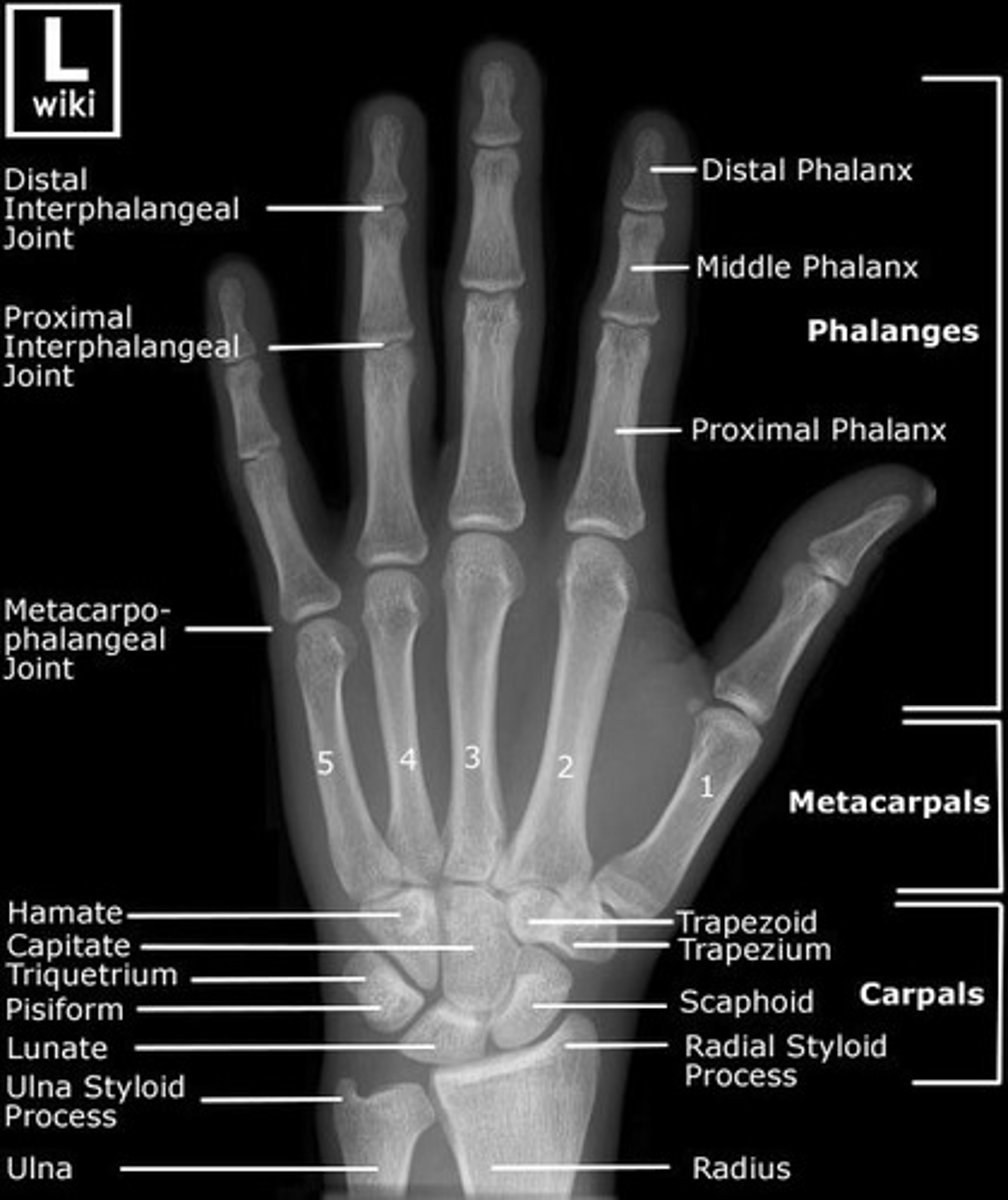
HAND
WRIST
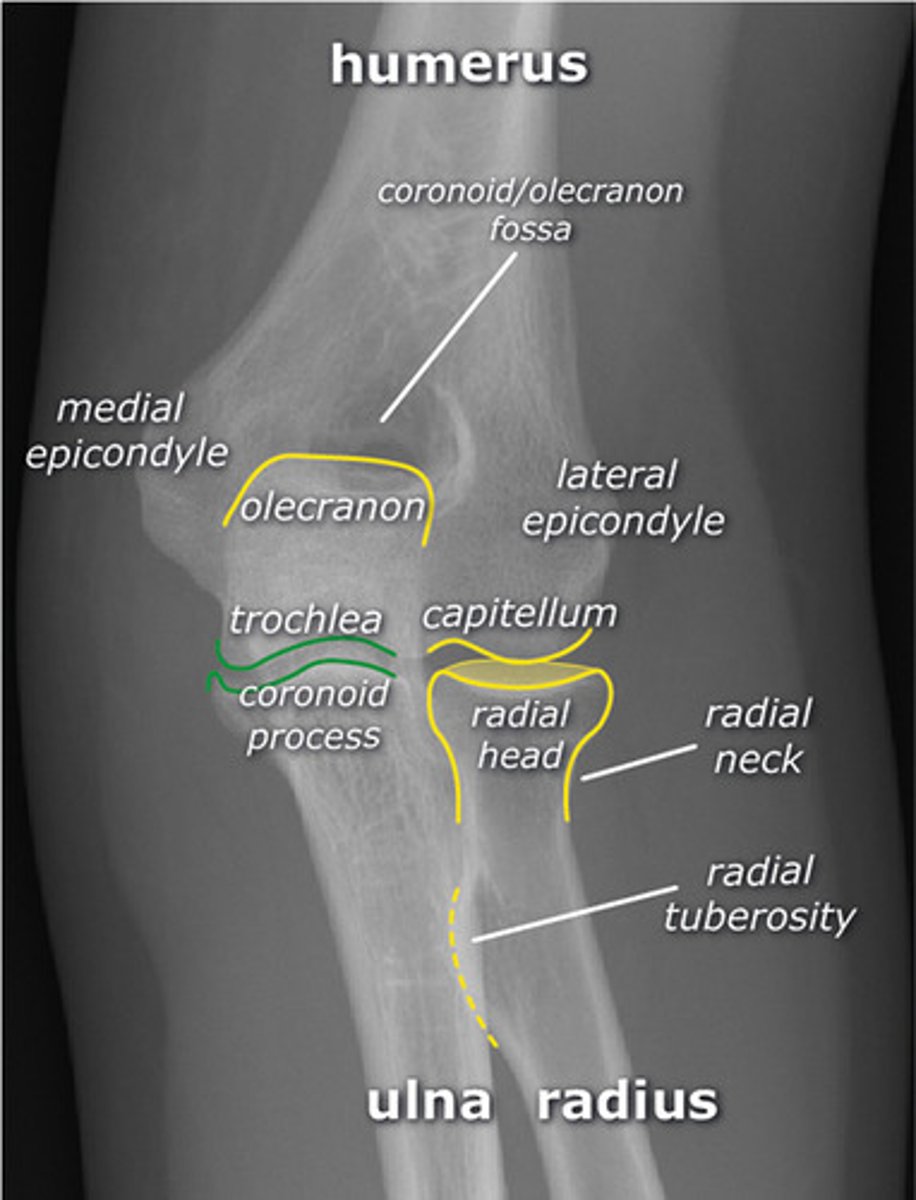
ELBOW
FOREARM