Health Final 2025
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
what are the three parts of the health triangle
mental, physical, and social health
what is the first step of the Decide Process
define the problem
second step of decide process
explore the choices
Third step of decide process
consider the consequences (risks and benefits)
4th step of decide process
identify your values
5th step of decide process
decide and act
last step of decide process
evaluate your results
what is heredity
traits passed down biologically from parent to child
lifestyle choice
actions a person takes on a daily basis
lifestyle disease
Can be caused by choices we make in our life (ex: smoking causes cancer)
top three causes of death for teens
Accidents, 2. Homicide, 3. Sucide
top three causes of death for adults
Heart disease, 2. Cancer, 3. Accidents
What is the most important factor to consider when making a healthy decision?
Is this legal and is it consistent with my values
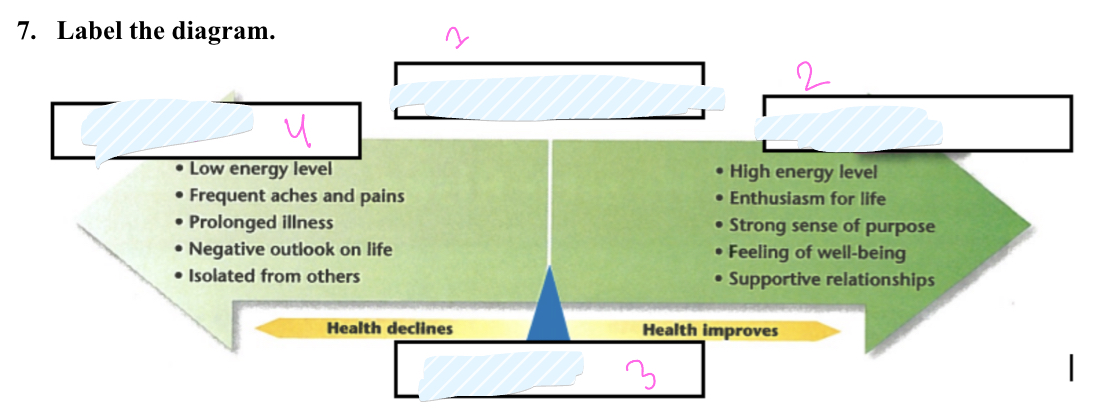
What is 1
health continuum
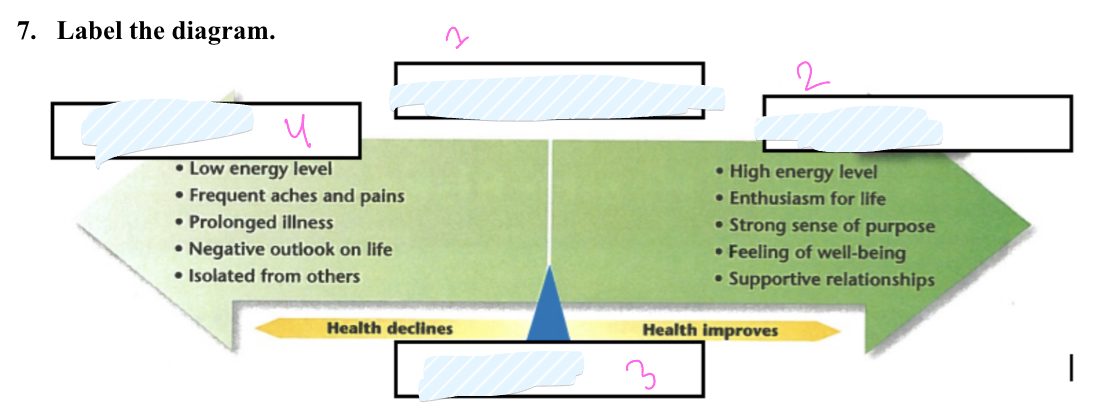
what is 2
wellness
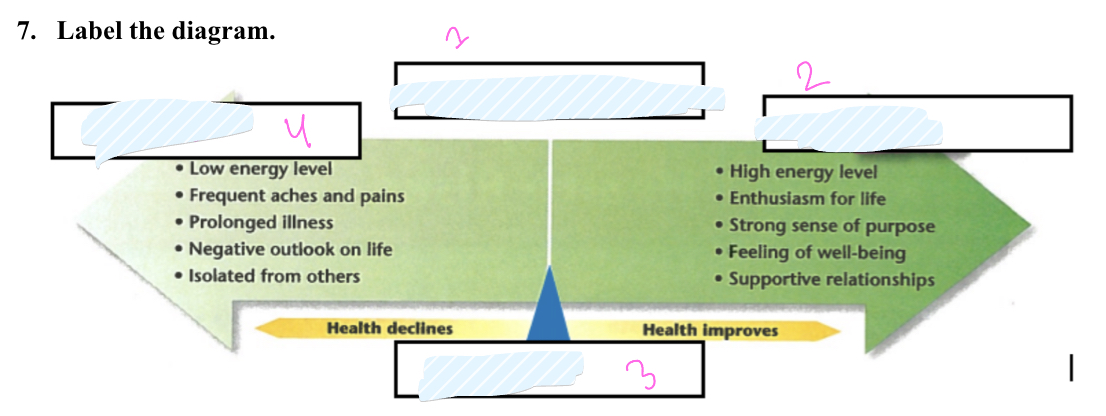
What is 3
Midpoint
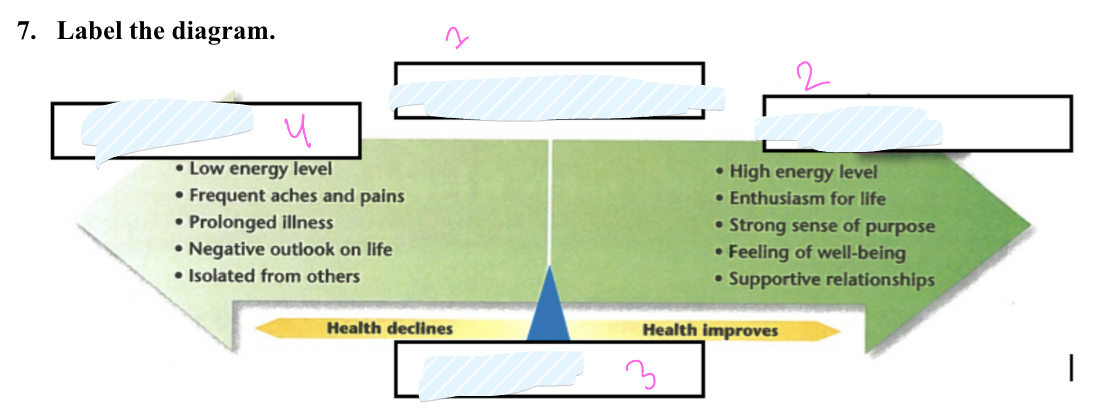
What is 4
illness
what is self esteem
self-esteem refers to how much you respect and like yourself
what is wellness
State of high level of health
stress
response of your mind and body to being challenged or threatened
Eustress
positive stress
distress
negative stress
What is ARE
what happens in each stage of stress
what is the A in the stages of stress
alarm stage
What is R in the stages of stress
resistance stage
What is the E in the stages of stress
exhaustion stage
what illnesses are related to stress
stomach aches, asthma, headaches, more likely to develop heart disease
What is mental illness
an illness that affects the mind and reduces a person’s ability to function
what causes a mental illness
physical factors, heredity, early experiences, and recent experiences
what is the most important thing you can do to help someone showing signs of a mental disorder?
Get them help
what is ACT
the steps to help a friend who is depressed and suicidal
what is the A in ACT
acknowledge
what is C in ACT
care
what is T in ACT
treatment
What is the number one cause of suicide
untreated depression
What are the signs of suicide
giving things away and saying “I would be better off dead”
what are the signs of depression
changes in weight, loss of energy, drop in grades, sadness
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fat
saturated is solid at room temp and unsaturated is liquid at room temp (veg oil)
main function of carbohydrates
to provide the body with energy. This nutrient is the body’s preferred energy source.
Good sources of carbohydrates
rice, cereals, wheats, tortillas, whole-wheat rolls
what is the main function of fats
supply your body with energy, form your cells, maintain body temp and protect your nerves
good sources of fats
olive oil, peanuts, and butter
main functions of protein
help with growth and repair of your body’s tissues
good sources of protein
meat, eggs, poultry, milk, and milk products
main function of vitamins
help the body with various processes including the use of their nutrients. This nutrients plays a key role in various chemical reactions in the body.
What are good sources of vitamins
A,D,E, K
main function of minerals
maintain healthy skin, bones, and teeth
good sources of minerals
phosphorus, sodium, iron, and zinc
maintain function of water
help with all life processes, including the production of energy
good sources of water
vegetable juice and fruit juice
calorie
measure of energy availed in food
nutrition
science that studies food and how it benefits the body
nutrient dense food
contains a lot of vitamins and minerals relative to the number of calories. At the same time, nutrient dense foods are low in saturated fat, added sugar, and salt
nutrient
food essentials needed by body
anti-nutrient
a substance that interferes with the utilization of one or more nutrients by the body
basal metabolic rate
the rate at which you use energy at rest
Follow a healthy eating____ at every life stage
pattern
customize and enjoy nutrient-dense food and _____ choices to reflect personal preferences, cultural traditions, and_______ considerations
beverage and budgetary
focus on meeting food group needs with nutrient-dense foods and beverages, and stay within_____limit
calorie
limit foods and beverages higher in added sugars, _______ fat and ______, and limit alcoholic beverages
saturated, sodium
what is my plate and what does it help us balance
my plate is the current government eating plan, it helps balance our food intake
which mineral is important for bone strength
calcium
which anti-nutrient is the most harmful to your health? It also takes a healthy fat and turns it into an unhealthy fat?
Trans-fat
signs of eating disorder
rapid weight loss or gain
Three common eating disorders
anorexia nervosa, bulimia, and binge eating disorder
how are ingredients listed
most to least by weight
how are food labels titled
nutrition facts
what is high for vitamins and minerals
20% or more
what is low for vitamins and minerals
5% or less
what is the percent daily value based on
2,000 calorie diet
what is the most effective form of birth control and STD protection
absintence
what is the safe haven law
law that allows a person to legally surrender an unharmed, newborn baby at specific location - up to 30 days old
where can a baby be dropped off
hospital, staffed fire station, staffed police station, emergency care facilities
what is the cycle of violence
violent episode → calm→tension building
what is consent and how do if you have consent
if they say yes
what is abstinence
no sex
what are some qualities of a good relationship
trust-respect-honesty
what is sexual harassment
unwelcome sexual remarks or advancement
what is the most important thing we can tell a victim of sexual violence? Erins law
It is NOT your fault
what is the most effective form of birth control
abstinence
when should men get screened for prostate cancer
after 50 years old
how often should woman get her reproductive system checked
once per year
what part of the male reproductive system produces sperm
testes
what tubes connect the epididymis to the seminal vesicles
vas deferens
What is the name of the tube that serves at a passageway for both semen and urine?
urethra
what is the mixture of sperm cells and other fluids called
semen
what is the purpose of the prostate gland
neutralize the acid in the vagina
which part of the female reproductive system produces hormones and releases eggs?
Ovaries
where is the egg fertilized
fallopian tubes
where does the fertilized egg grow
uterus
what is the birth canal
vagina
what day does ovulation occur
on day 14 or day 15
why is the women’s vagina acidic
to protect her from infections
how do hormonal birth control methods work
prevents ovulation, thickens cervical mucous, makes it difficult for the fertilized egg to implant in the uterus
what are the four risks of sexual intimacy
pregnancy, STDs, emotional changes, relationship changes
what is the difference between communicable and non-communicable diseases
communicable diseases can be passed from person to person. Non communicable diseases cannot be passed and are not infectious
what is a pathogen
something that causes disease
how are STDs/STIs passed
bodily fluids and sex
What are the six links in the chain of infection
pathogen, host/reservoir, port of exit, method of transmission, port of entry, and susceptible host
pathogen
virus/bacteria