AP Biology: Cell Organelles Pt 1
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
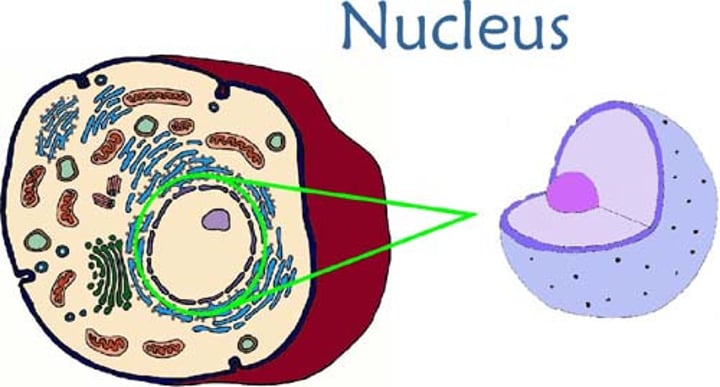
Nucleus
(Brain / Control Center)
Structure:
- filled with nucleic acids, DNA & mRNA
- surrounded by nuclear membrane
Function:
- provides genetic information to the cell
- controls cell process & reproduction
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Network of canals used to transport and store substances. It is a pathway between the nucleus and cell membrane
ER (emergency room- ambulance transports you to the ER)
Smooth ER
Structure:
- NOT covered in Ribosomes
- series of membrane tubes
Function: (highway for materials)
- creates lipid-based molecules like hormones and steroids
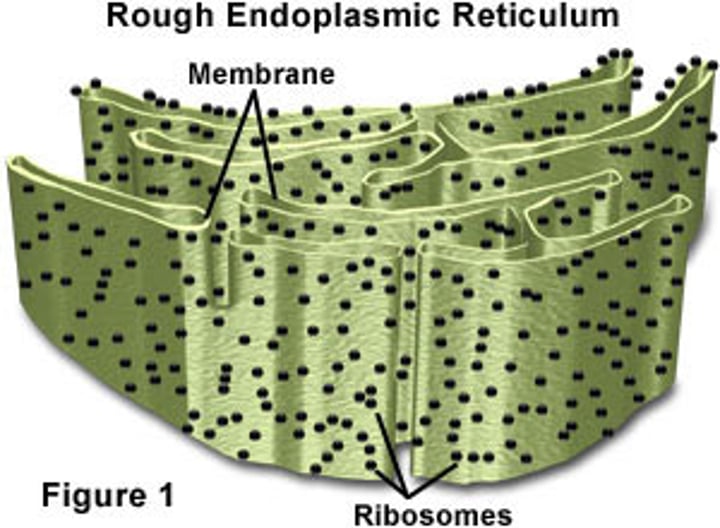
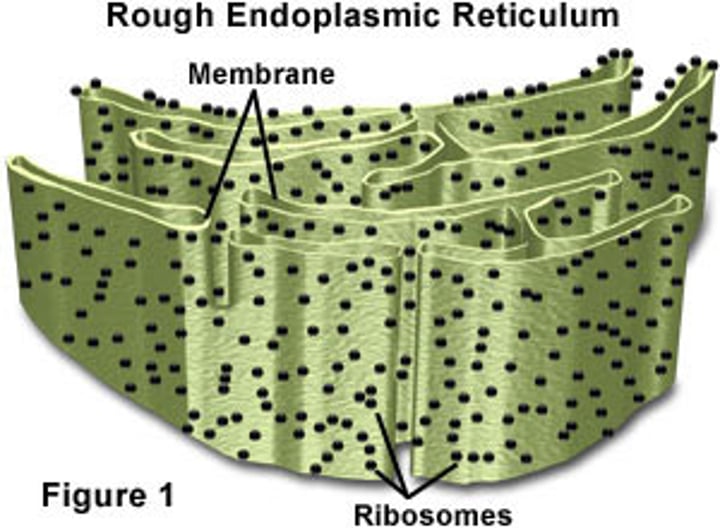
Rough ER
Structure:
- covered in Ribosomes
- series of membrane tubes
(usually found near nucleus)
Function:
- creates proteins and transports them to the Golgi body.
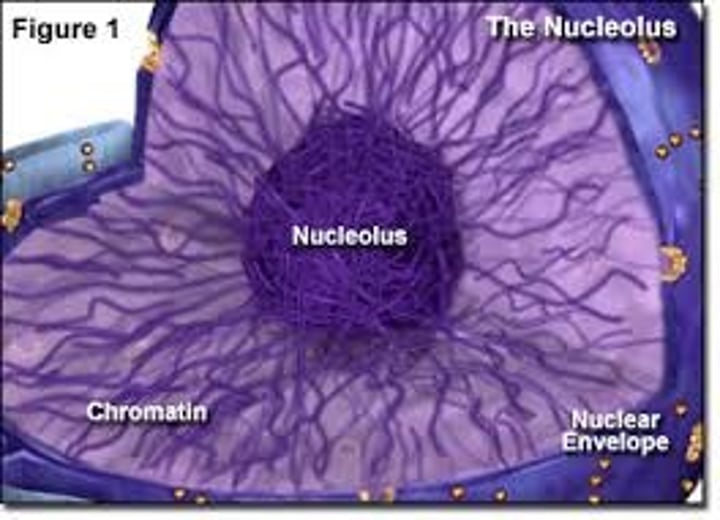
Nucleolus
(Meatballs found in the nucleus)
Structure:
- filled with RNA (cheap copies of DNA)
- found in nucleus
- no membranes
Function:
- creates ribosomes (which produces proteins)
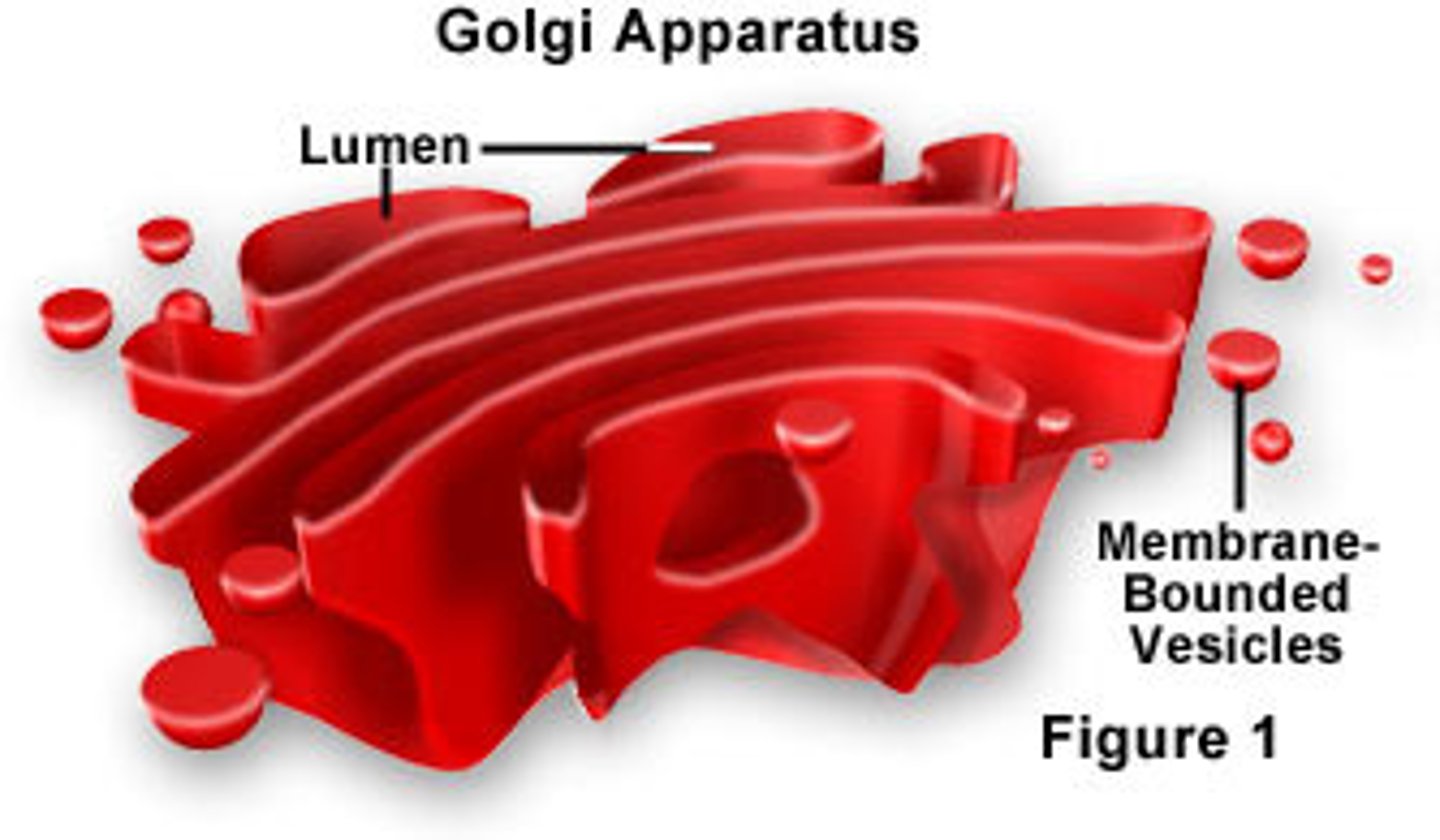
Golgi
(packaging plant/post-office)
-stacks of flattened membrane sacks that...
- modifies, and packages proteins and lipids for the cell
- puts products in membrane sacks called vesicles
- produces lysosomes
Extras:
- major player in exocytosis
- releases them into the cytoplasm
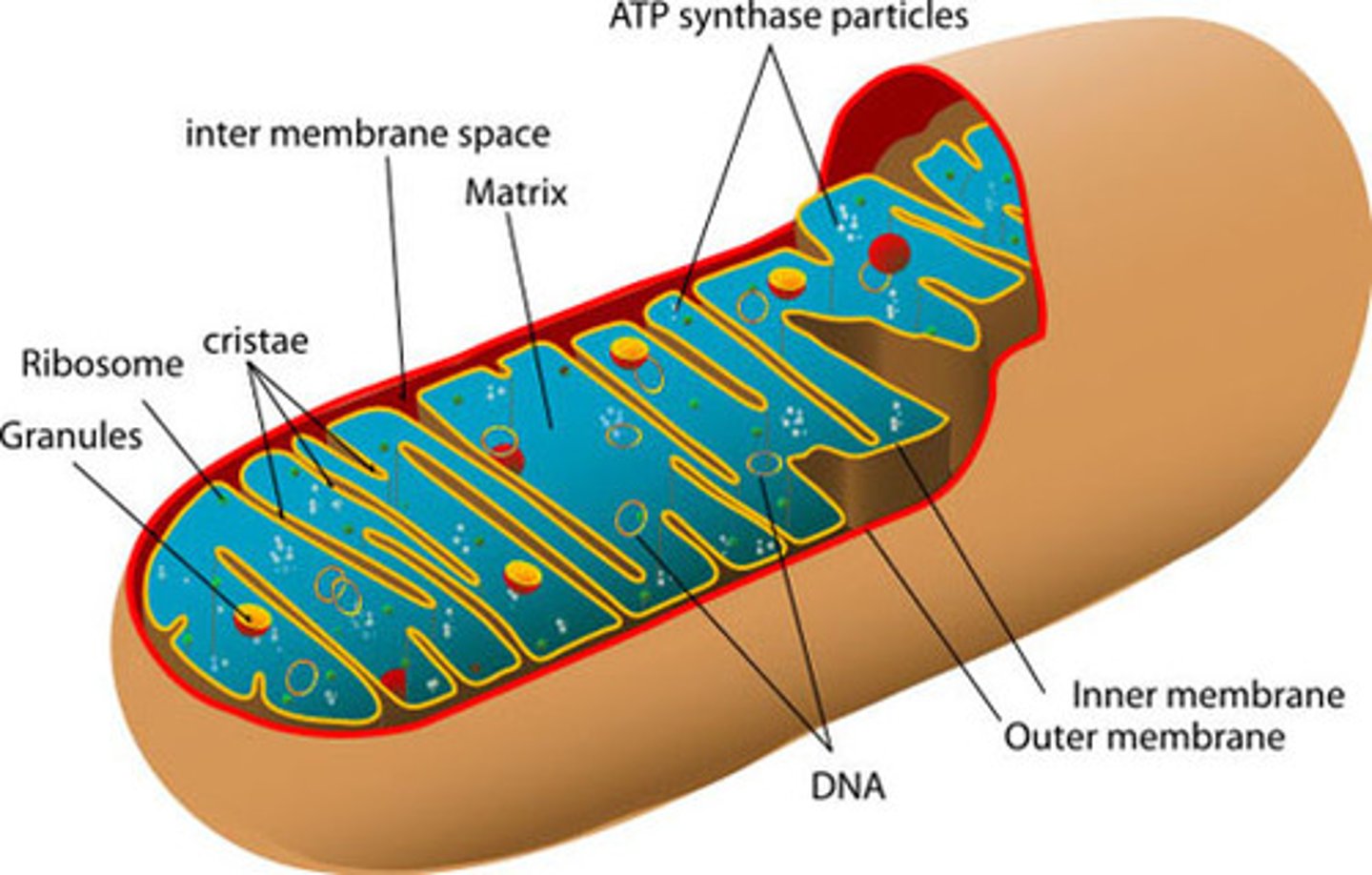
Mitochrondia
(powerhouse of the cell)
-has 2 membrane and its own DNA that produces ATP (which is broken down to produce energy)
- ATP is produced on the inner membrane of the mitochondria
- has folds on the inner membrane because the more surface area the inner membrane has, the more surface area the membrane has, the more area there is to produce ATP
Extra Note:
You only get Mitochondrial DNA from your mother.
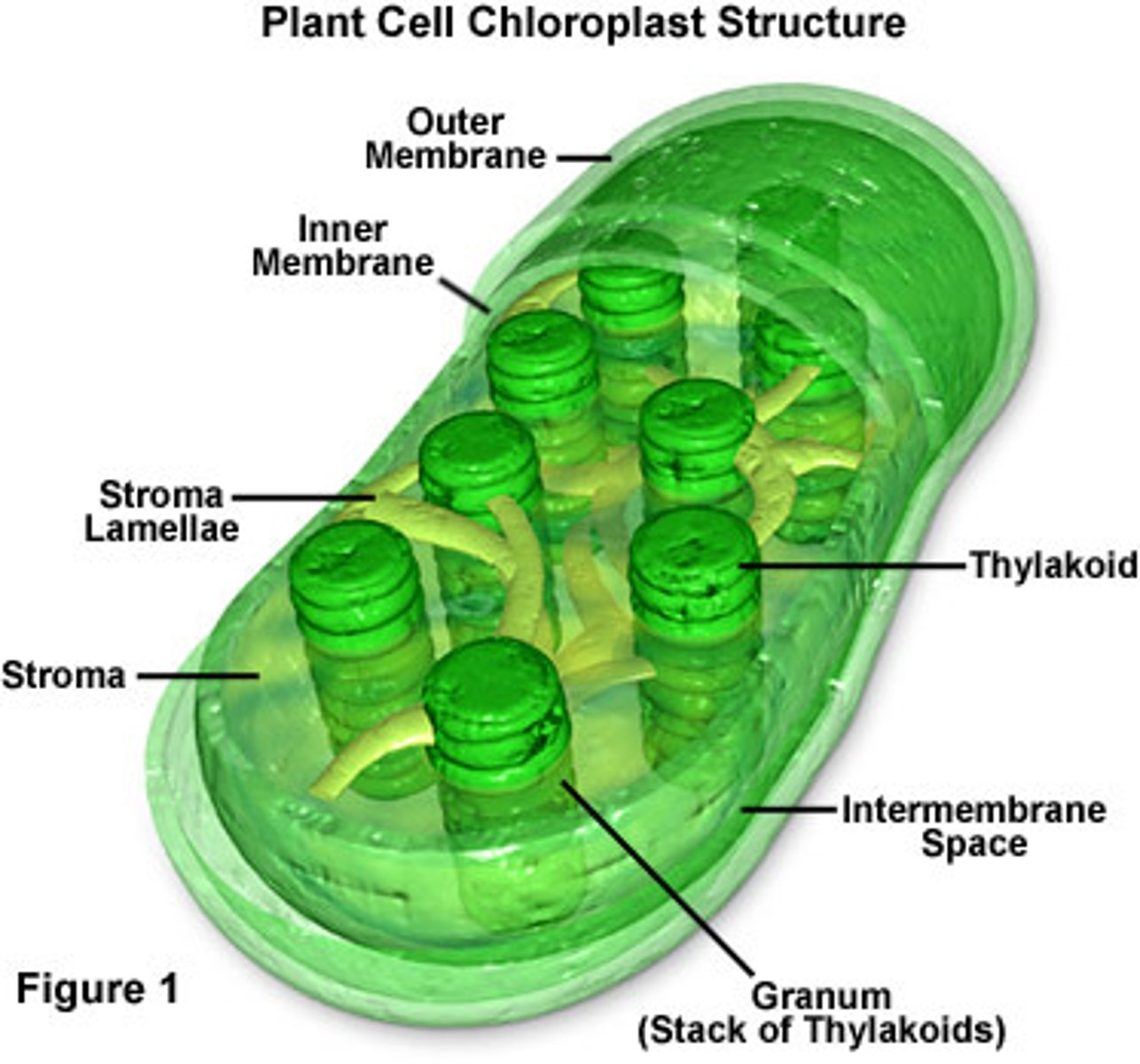
Chloroplast
Structure:
- membrane-bound organelle
- appears green from a molecule called "chlorophyll" which captures light
Function:
- performs photosynthesis to make food for the cell
- found only in plants
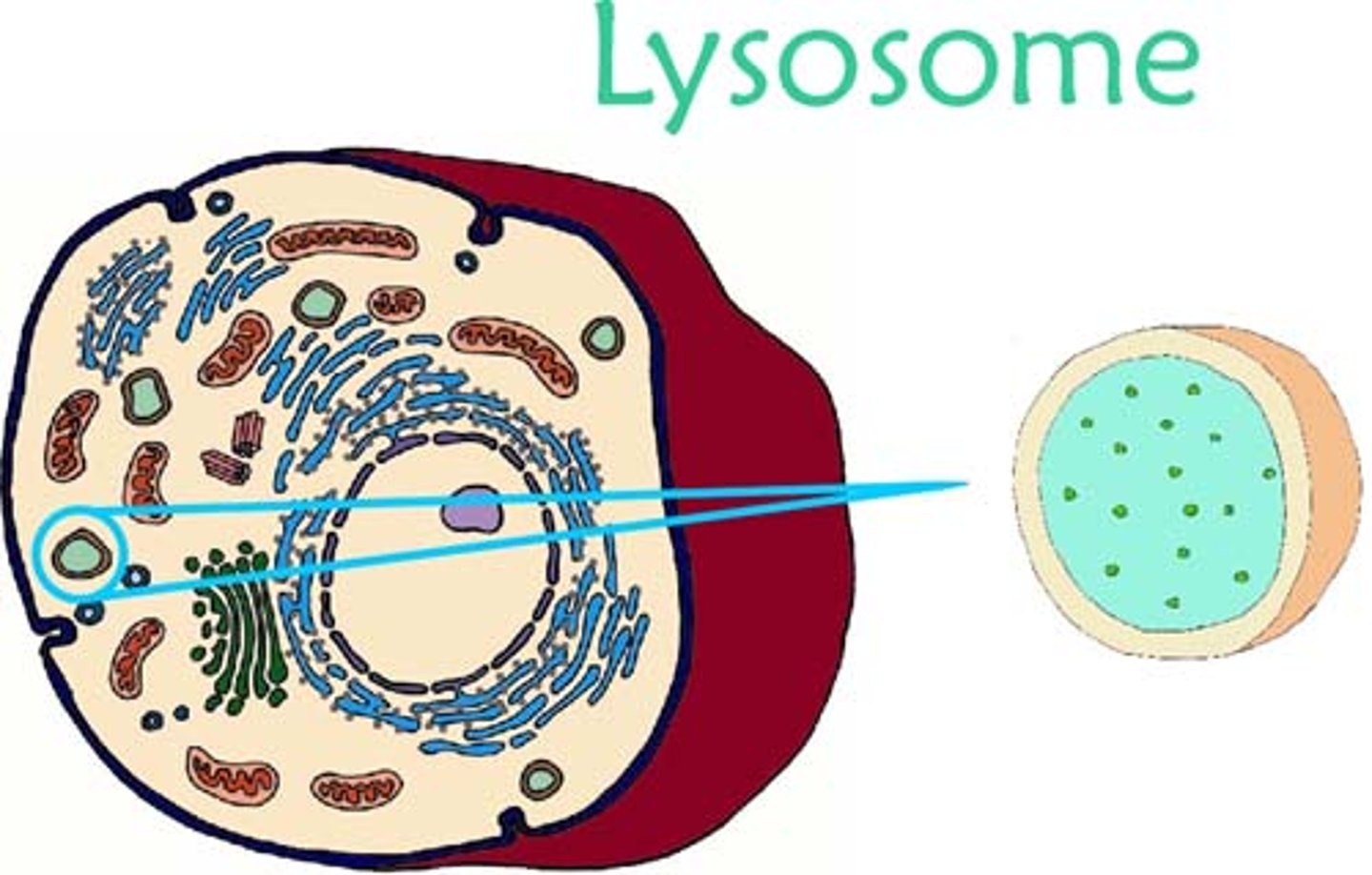
Lysosomes
(Lysol cleaner)
- membrane bound sacks (called a vesicle)
Function:
- contains enzymes (lysozyme)
- destroy bacteria and old cells
- breaks down food
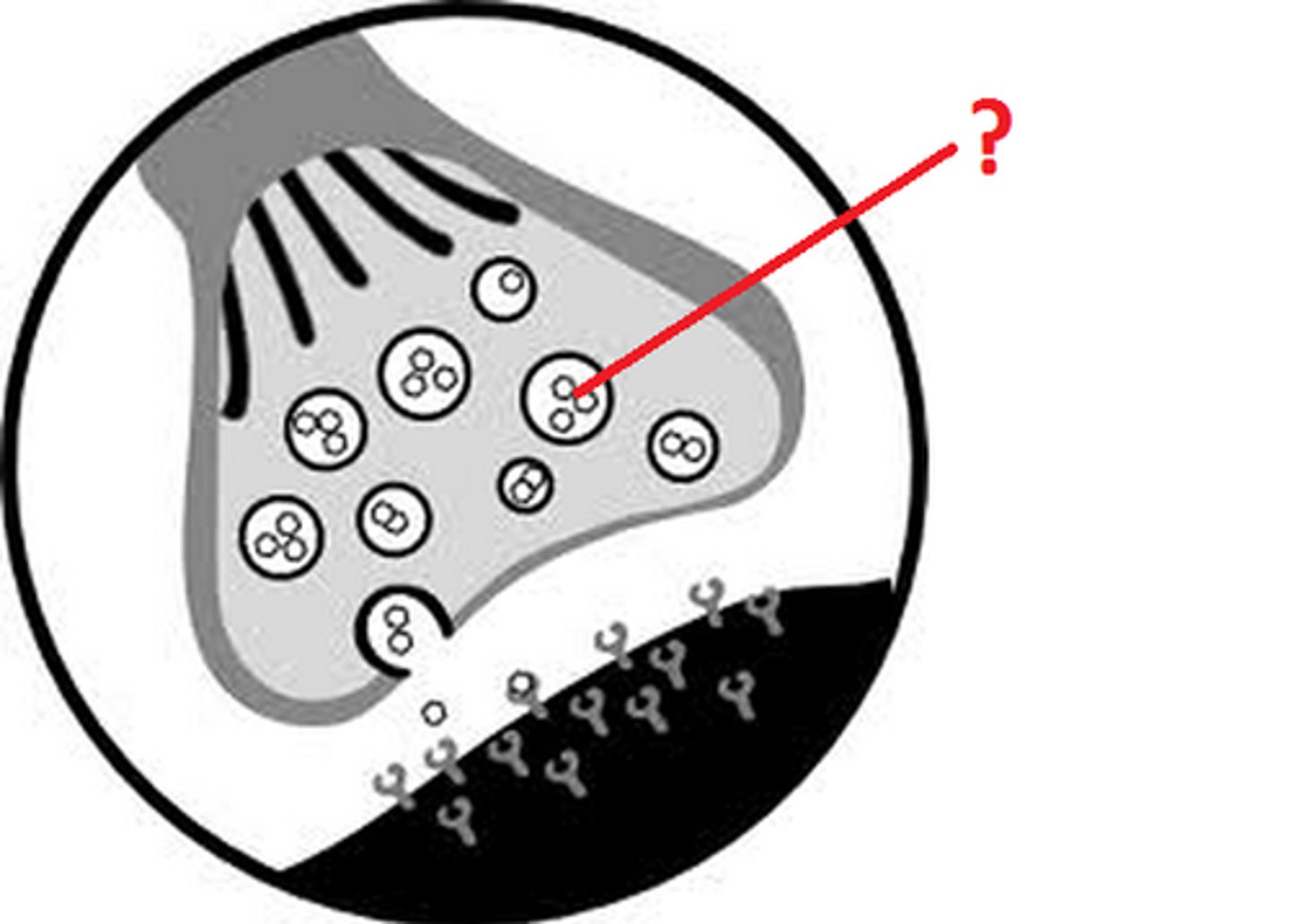
Vesicle
sacs that proteins are placed in by the golgi body before being shipped away
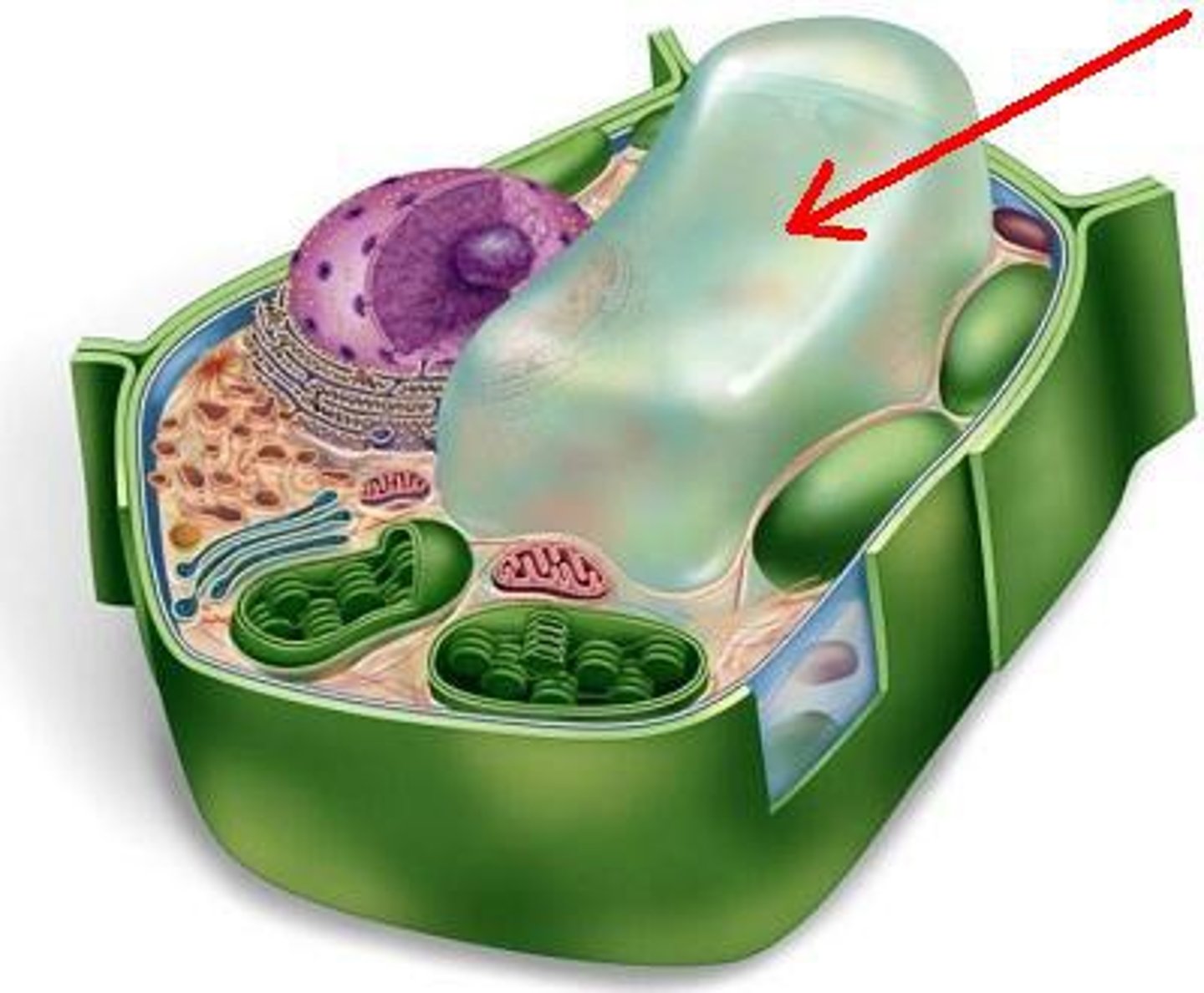
Vacuole
(Vaccuum up the dirt. Vaccuum holds/stores the dirt in a bag/ food containers)
Structure:
-large membrane-bound sacks
Function:
-stores materials
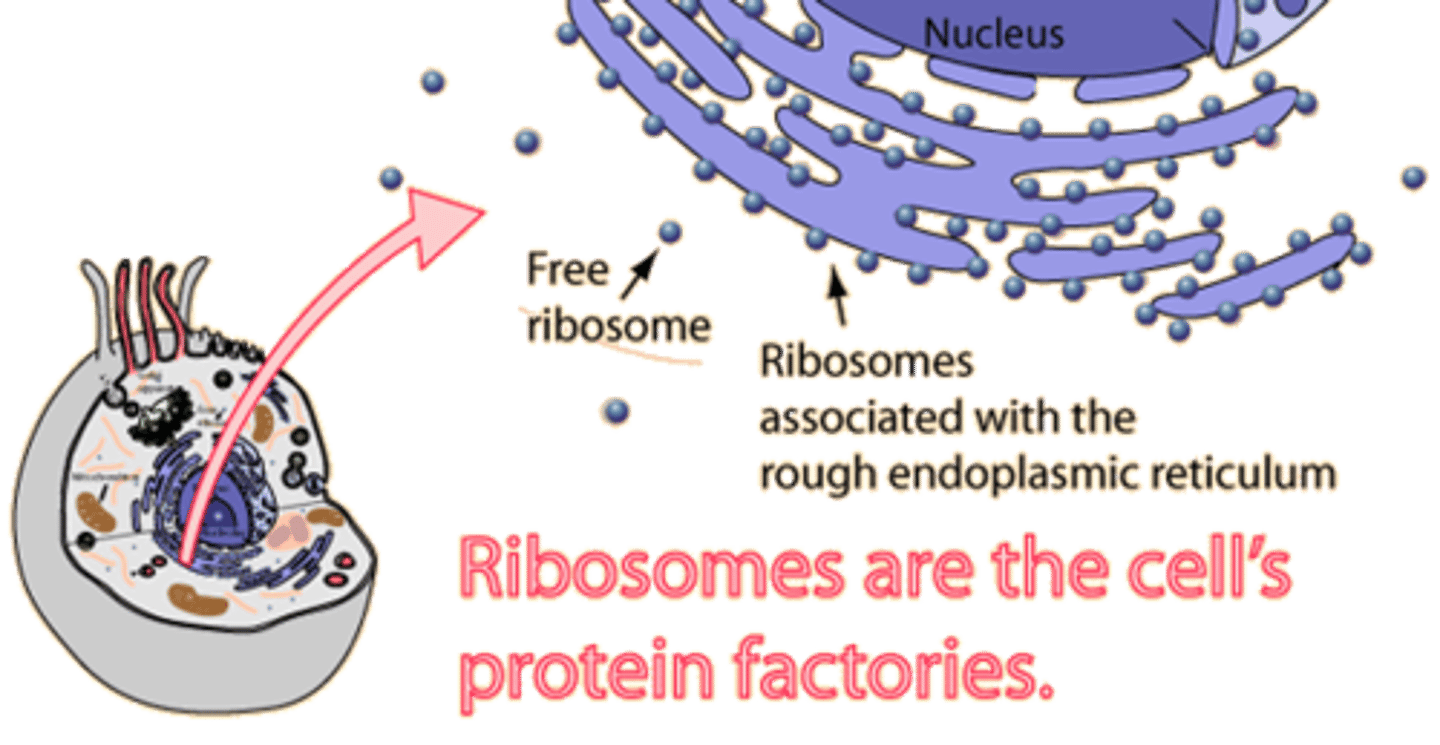
Ribosome
2 pieces of proteins that read RNA to make proteins
Cell Wall (tree bark)
A large chain of carbohydrates that gives the cell rigid structure
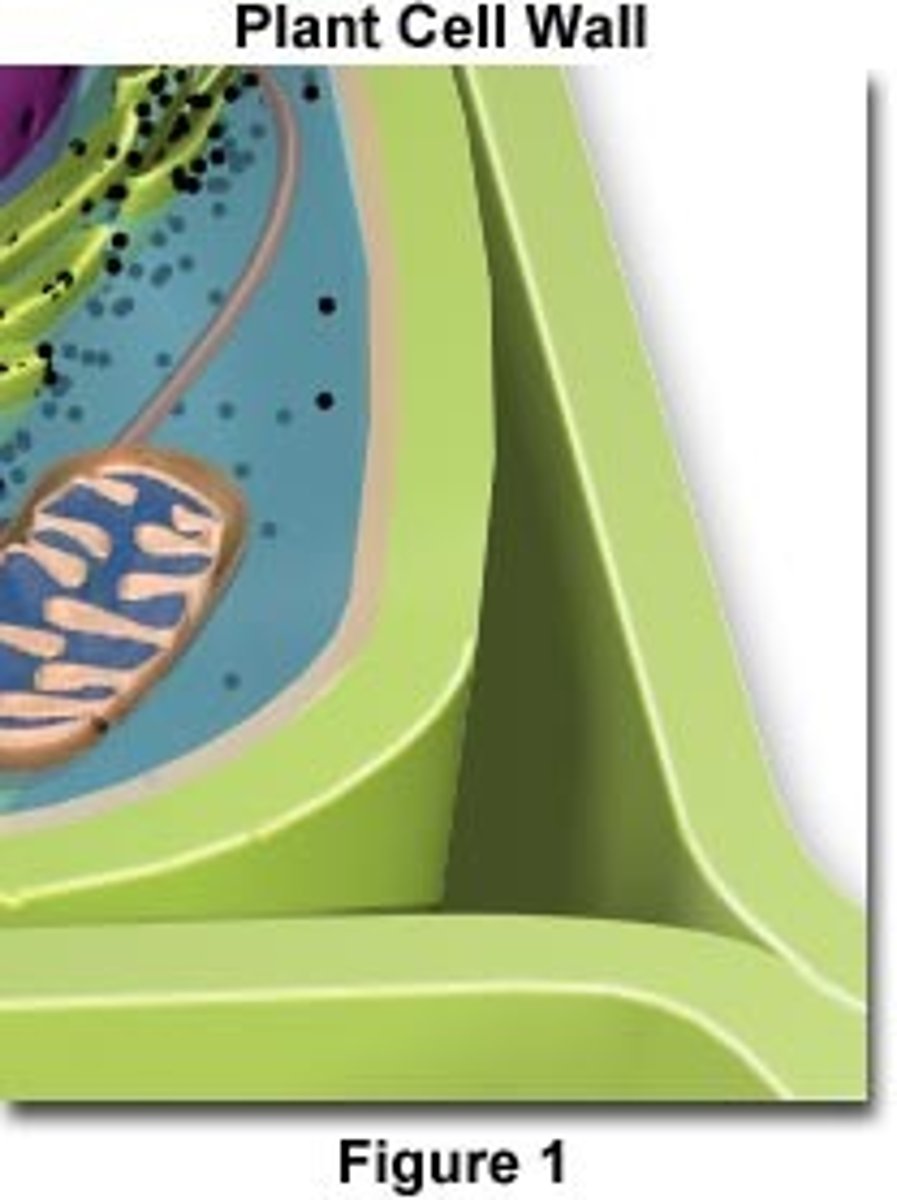
Cytoplasm
Structure:
-jelly-like material that is 80% water
-contains Proteins, Lipids, and Carbohydrates
Function:
- gives shape to the cell
- holds organelles
-gives shape &structure to cells
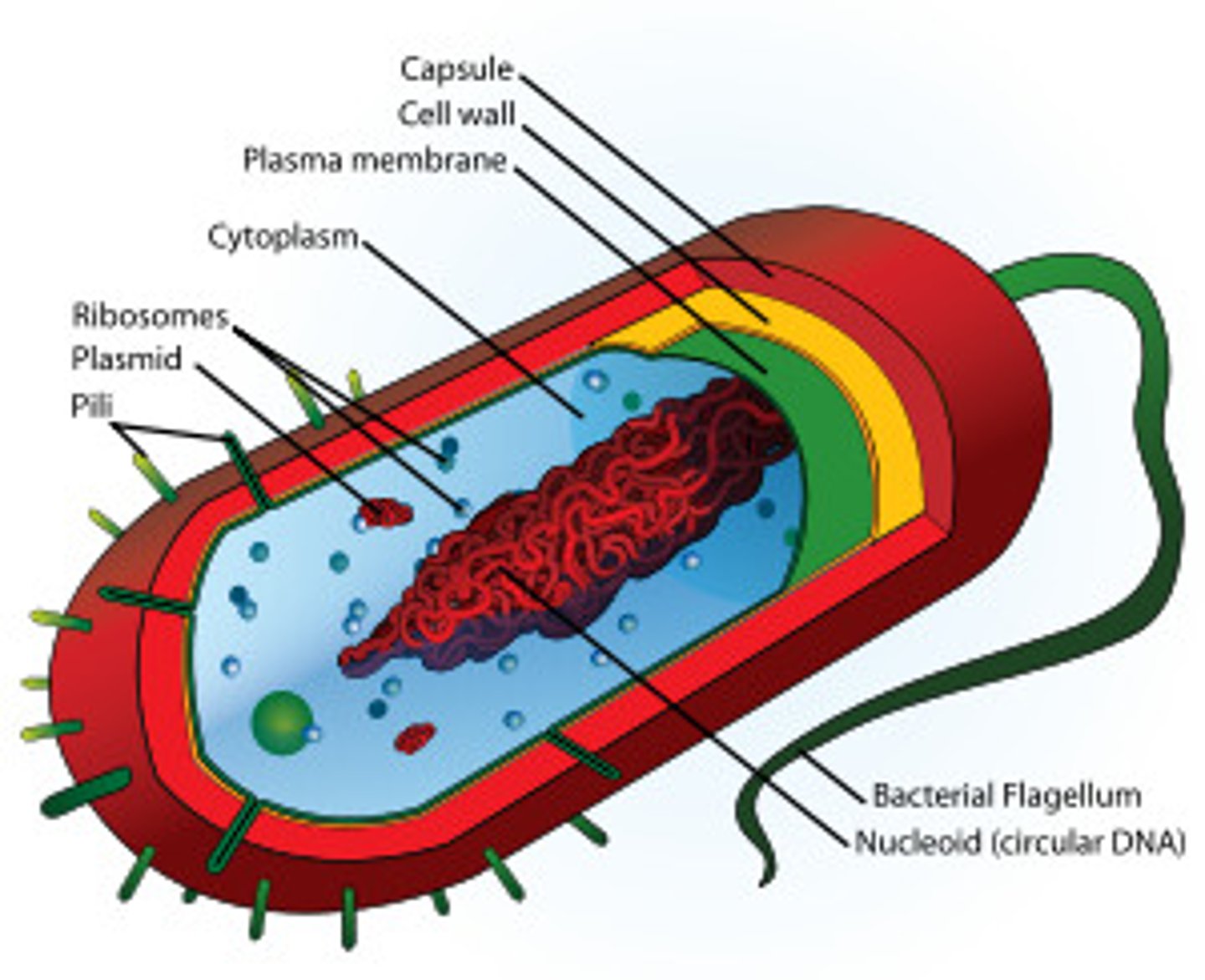
Prokaryotes
cells without nucleus & other membrane-bound organelles.
Ex:
Bacteria; first cell life on earth
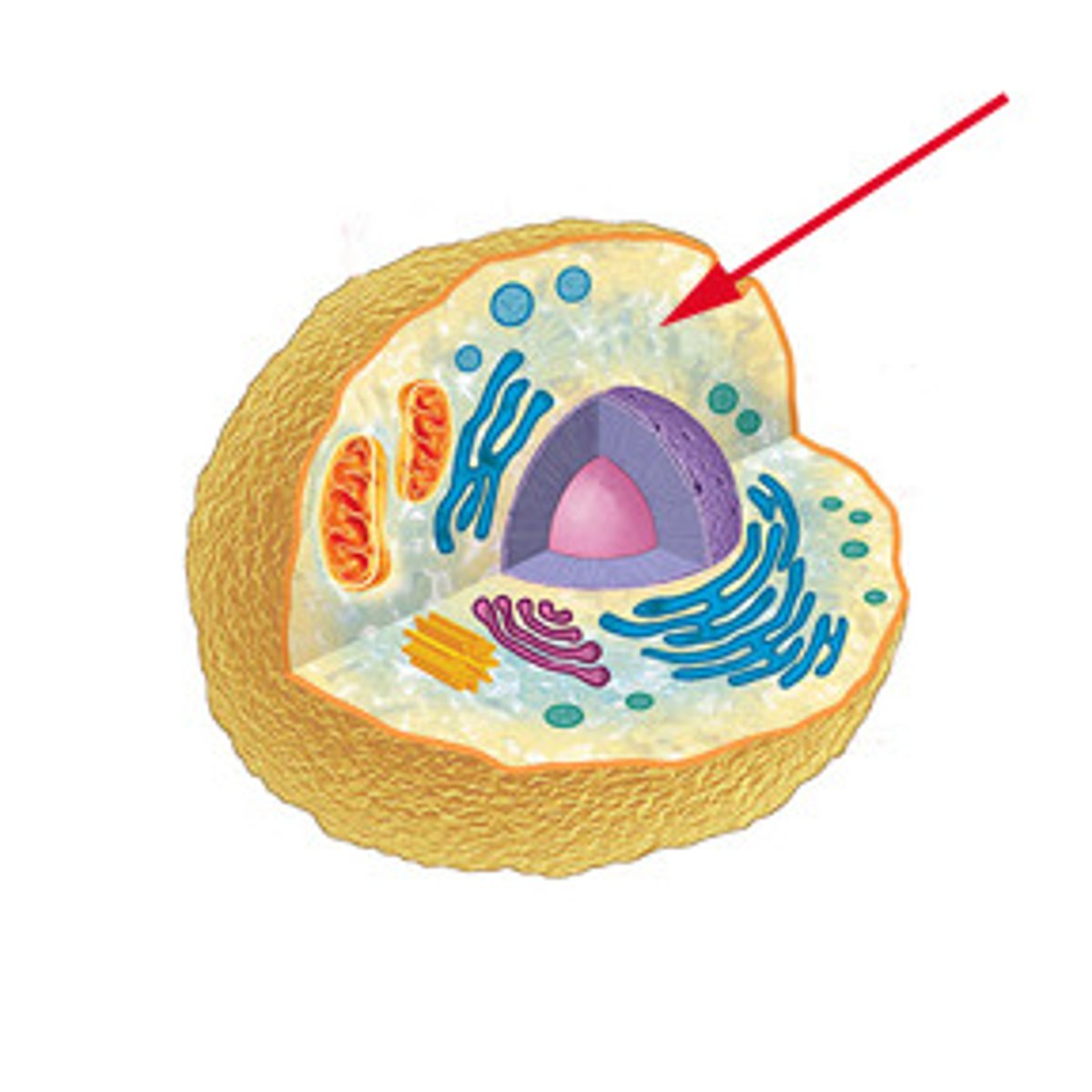
Eukaryotes
cell with nucleus & membrane bound organelles
evolved from prokaryotes, and thus are more complex.
Ex:
Protists, fungi, plants, animals
