NURS 308- Exam 3
1/213
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
214 Terms
what do you inspect on the female external genitalia?
-skin color
-hair distribution
-lesions
-perineum
-anus
speculum exam
internal exam to observe for female internal organ normalcy; obtain specimens
pap smear
Test for early detection of cervical cancer; scraping of cells removed from cervix for examination under microscope.
cytobrush
use this to collect endocervical cell samples; goes into os
STI screening
done if patient has complaints or abnormal discharge (GC or chlamydia culture is done with a sterile cotton applicator)
bimanual examination done with...
cervix, uterus, adnexa (ovaries)
HPV vaccination
requires a series of 3 shots; give at ages from 9-26 to prevent cervical cancer; recommended at 11 & 12
urinary incontinence
inability to control urination
Urgency Urinary Incontinence
loss of urine with sudden compelling desire to urinate that is difficult to defer
stress urinary incontinence
involuntary discharge of urine during coughing, straining, or sudden movements
cystocele
bulge of the bladder into the vagina
rectocele
bulge of the rectum into the vagina
uterine prolapse
downward displacement of the uterus into the vagina
menopause
when estrogen and progesterone decrease and stop producing
vagina becomes shorter and narrower, decreases secretions; typically lasts 1-2 years
pediculosis pubis
also known as crab lice; an infestation with lice in the pubic hair and pubic region; transmission through sexual contact, bedding, towels, etc; causes severe itching and erythematous
genital herpes
pain, fever, dysuria, or asymptomatic
shallow vesicles with erythema on inner thighs and genital area
no cure, just suppression
syphilis
papule that is red, round, oval, yellowish serous discharge
treat with antibiotics, damage can't be undone
human papillomavirus
has a high correlation with cervical cancer
chlamydia
minimal or no symptoms, urinary frequency, dysuria, vaginal discharge
can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease
can be cured with meds
gonorrhea
women have NO symptoms and can eventually cause infertility
contagious until cured, need antibiotics
bacterial vaginosis
constant discharge of thin creamy white
foul fishy odor
trichomoniasis
an infection caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis; also known as trich
pruritis, urinary frequency, red raised papules and petechiae, yellow-green discharge
living organism
candidiasis
yeast infection
itching, thick white discharge in the vulva and vagina
predisposing causes of vulvovaginal inflammation
oral contraceptives, antibiotics
puberty for boys
9-10 years old
enlargement of testes, pubic hair appears, penis size increases
40 years
when does sperm production decrease?
older male adult genitalia changes
hair decreases
penis size decreases
scrotum hangs lower
testes size decrease
urinary frequency
the need to urinate often
urinary urgency
sudden, compelling urge to urinate
nocturia
excessive urination during the night
dysuria
painful or difficult urination
urination hesitancy
inability to start and/or maintain urination
phimosis
stenosis or narrowing of foreskin so that it cannot be retracted over the glans penis
hypospadius
a congenital condition in males in which the opening of the urethra is on the underside of the penis
epispadius
congenital abnormality where urethral opening is located on upper surface of penis
cryptorchidism
undescended testicles
hydrocele
scrotal swelling caused by a collection of fluid
hernia
bulge at the inguinal ring or femoral canal
testicular cancer risk factors
Cryptochordism, prior testicular cancer or family hx; race (Caucasian 5X greater risk than African American)
TSE
testicular self-examination
T: timing (once a month)
S: shower (warm water relaxes scrotal sac)
E: examine (check for and report changes immediately)
Inspection for the vascular system
arms: skin, profile sign, capillary refill, symmetry, pulses
legs: skin & hair, symmetry, temperature, calf muscle, inguinal lymph node, pulses, pretibial edema, and leg veins
normal pulse grade
2+
doppler
used when unable to palpate a pedal pulse
pretibial edema
depress skin over tibia or medial malleolus for 5 sec; +1 slight
1+ edema
mild pitting, slight indentation, no perceptible swelling of the leg
2+ edema
moderate pitting, indentation subsides rapidly
3+ edema
deep pitting, indentation remains for a short time, leg looks swollen
4+ edema
very deep pitting, indentation lasts a long time, leg is very swollen
Raynaud's syndrome
diminished blood supply to extremities resulting in discoloration (due to extreme temperatures or stress)
lymphedema
swelling due to an abnormal accumulation of lymph fluid within the tissues
arterial ulcer
An open wound on the lower legs and feet caused by poor arterial blood flow
venous ulcer
wound that results from inadequate return of blood from an extremity
superficial varicose veins
normal leg veins have dilated as a result of chronic increased venous pressure and incompetent valves that permit reflux of blood back toward leg instead of forward toward heart
DVT (deep vein thrombus)
blood Clot usually deep in veins. Usually legs or pelvis can move
acute swelling
warmth and redness
use a doppler to find a pulse
occlusions
blockages in blood vessels
atherosclerosis with the build up of fat
aneurysms
sac formed by dilation in artery wall
arteriosclerosis
hardening of the arteries, commonly seen with old age
atherosclerosis
fatty deposits (plaque) build up in the arteries
chronic arterial symptoms
deep muscle pain
cool, pale skin
numbness and tingling
onset is gradual after exertion
aggravated by activity and elevation
relieved by rest
chronic venous symptoms
chronic pain increases at the end of the day
aching, tiredness, fullness feeling
aggravated by prolonged standing, sitting
relieved by elevation, lying, walking
edema, weeping ulcers at ankles
arterial ulcer
due to plaque buildup
cool, pale skin
pain, numbness
venous stasis
due to incompetent valves, poor circulation
brownish discoloration
hemosiderin (RBC breakdown, iron deposits)
C1
atlas
C2
axis
thyroid gland
secretes hormones that stimulate cellular metabolism (T3 and T4)
lymphatic
major part of the immune system with a separate vessel system; conserves fluid and plasma protein, major part of the immune system; absorbs lipids from the intestinal tract
preauricular
in front of ear
posterior auricular
mastoid process
occipital
base of the skull
submental
midline behind tip of mandible
submandibular
halfway between the angle and the tip of the mandible
jugulodigastric
under the angle of the mandible
superficial cervical
overlying the sternomastoid muscle
deep cervical
deep under the sternomastoid muscle
posterior cervical
edge of trapezius muscle
supraclavicular
just above and behind the clavicle, at the sternomastoid muscle
lymph nodes
cervical, axillary, epitrochlear, inguinal
spleen
upper left quadrant
destroys old RBC, filters microorganisms, produces antibodies, store RBC
tonsils
entrance to the respiratory tract
protects against local infection
thymus
gland above mediastinum in front of the aorta
no function in adults
atrophies after puberty
migraine
severe, recurring, unilateral, vascular headache
tension headache
pain is like a band squeezing the head
cluster headache
Unilateral, severe periorbital headache with tearing and conjunctival erythema.
how to palpate lymph nodes
Use a gentle circular motion of fingerpads
Palpate bilaterally with both hands to compare the two sides for symmetry
Begin with pre-auricular lymph nodes, palpate the 10 groups of lymph nodes in routine order
Many lymph nodes are close together: be thorough and consistent
acute lymph infection
onset is less than 14 days
enlarged bilaterally, warm, tender, firm, freely moveable
chronic lymph infection
clumped together
lymph malignancy
hard, nontender, matted, fixed, unilateral, greater than 3 cm
goiter
enlargement of the thyroid gland
torticollis
head tilt due to shortening or spasm of one sternomastoid muscle
pilar cyst (wen)
Smooth, firm, fluctuant swelling on scalp; pressure of contents causes overlying skin to be shiny and taut
Benign growth
parotid gland enlargement
Rapid painful inflammation of the parotid occurs with mumps. swelling anterior to lower ear lob
hyperthyroidism
excessive activity of the thyroid gland
results in a goiter and protruded eyes
hypothyroidism
condition of hyposecretion of the thyroid gland causing low thyroid levels in the blood that result in sluggishness, slow pulse, and often obesity
bell's palsy
CN VII LMN lesion - both upper and lower facial weakness on same side of lesion
cannot wrinkle forehead or blink
stroke
paralysis only in lower facial region, unilaterally
isolated head tremors (aging adult)
unknown causes
benign, head nodding, tongue protrusions
tooth loss (older adult)
may cause lower jaw to appear smaller
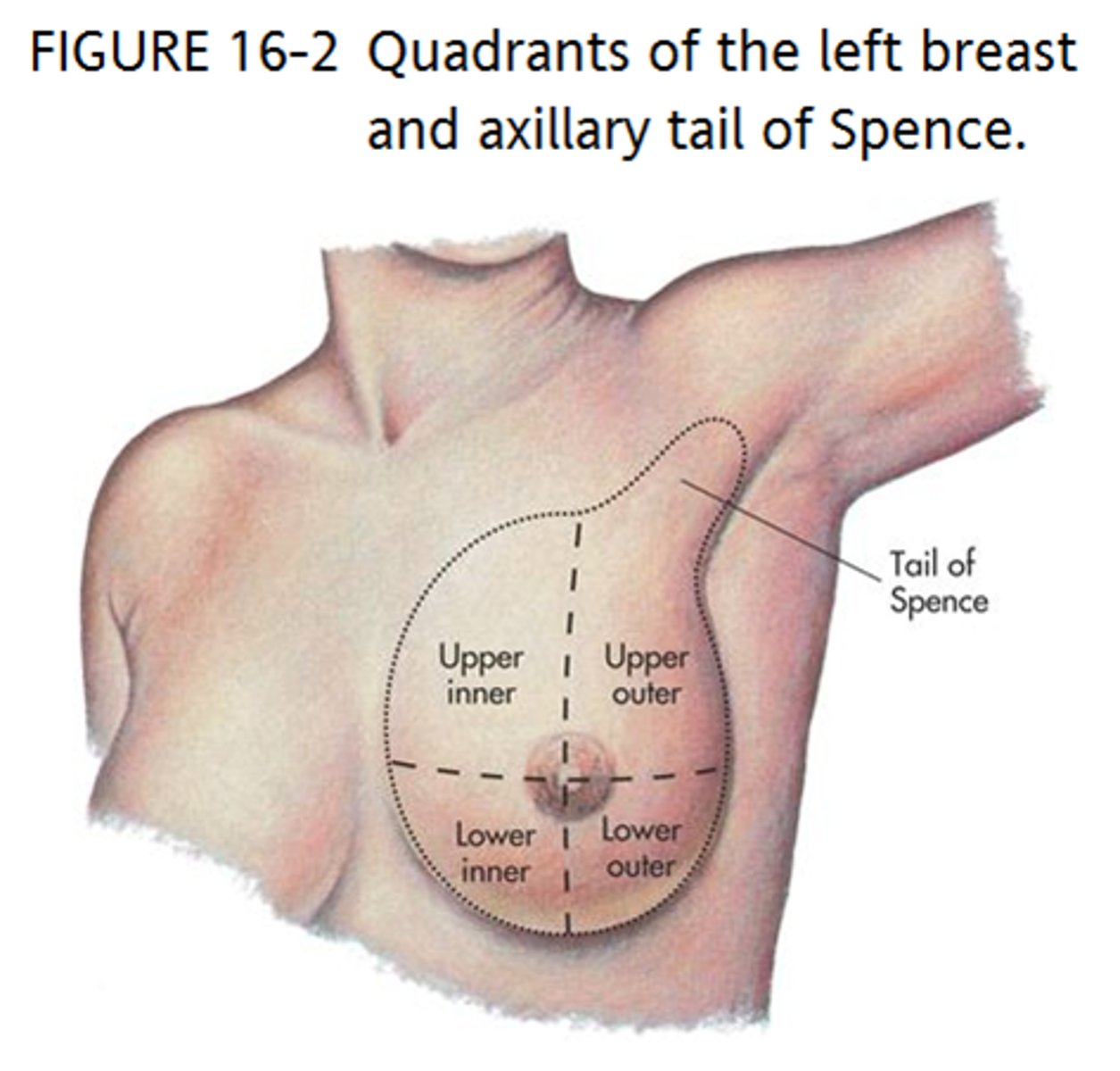
tail of spence
extension of breast tissue into the axilla
MEN
besides women, who can get breast cancer and should also do breast exams?
days 4-7 of your cycle
when is the best time to do a breast self exam