3.3.5.1 alcohol production
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what are the two methods in which alcohols/ethanol can be produced industrially?
fermentation of glucose (for ethanol)
direct hydration of alkenes eg ethene in the presence of an acid catalyst
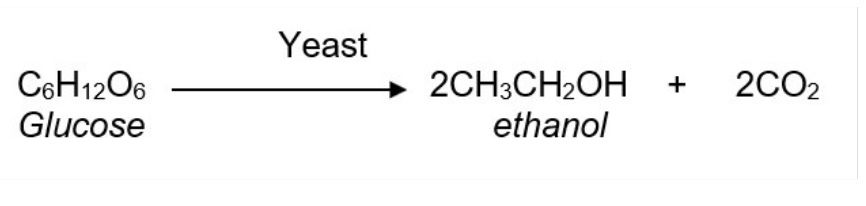
outline the method of fermenting glucose + give the equation
this process uses living yeast cells to convert sugars such as glucose into ethanol + carbon dioxide
describe + explain the conditions of the fermentation of glucose
yeast → provides enzymes which are the catalyst
37℃ so that the enzymes do not denature (optimum temp)
absence of O₂ (anaerobic respiration)
give 2 advantages of fermentation
low energy input is required
sugar cane is a renewable resource
the ethanol made from the fermentation of glucose is called a what?
a bio-fuel → derived from plants/animals
what is meant by carbon neutral?
no net emissions of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere
why is ethanol made from fermentation said to be carbon neutral?
the CO₂ released when it is burnt is balanced by the CO₂ taken in by the source plant during photosynthesis
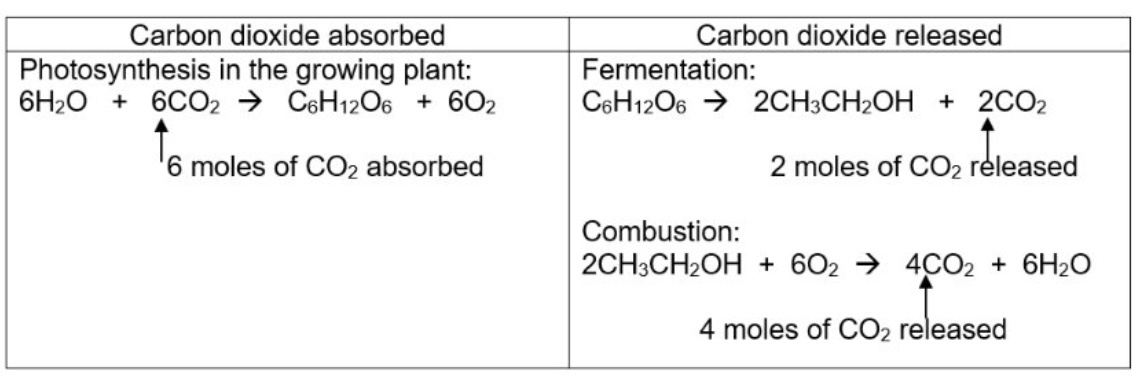
what are the 3 processes that show carbon neutrality?
photosynthesis (growing of the crops)
fermentation (process of producing ethanol)
combustion (burning/using of ethanol)
using the equations of the 3 processes, show how fermentation of glucose is carbon neutral
6 moles released = 6 moles absorbed
why is the process not actually carbon neutral in reality?
because additional carbon dioxide will be made from other processes including burning fossil fuels for transportation + harvesting the sugar cane crops
give 6 disadvantages of fermentation
low yield (15%)
the product is impure → further distillation is required
slow rate of reaction
this is a batch process
environmental issues with loss of habitats + deforestation to use land for producing crops
the land could be used for food production (instead of fuel production)
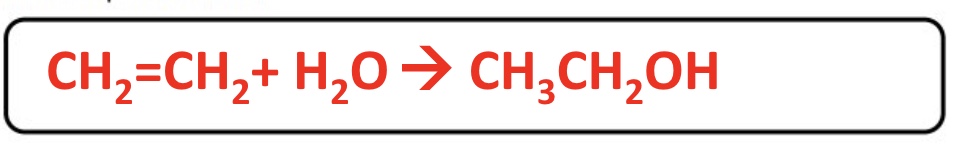
ethanol is also produced industrially by…
the direct hydration of ethene using steam
give the equation for the production of ethanol from ethene
give the conditions for the direct hydration of alkenes eg ethene
steam
heat
concentrated H₂SO₄
give 3 advantages of direct hydration of alkenes eg ethene
high yield + purity
fast rate of reaction
this is a continuous process
give 2 disadvantages of direct hydration of alkenes eg ethene
high energy input is required
ethene is obtained from crude oil which is a non-renewable resource
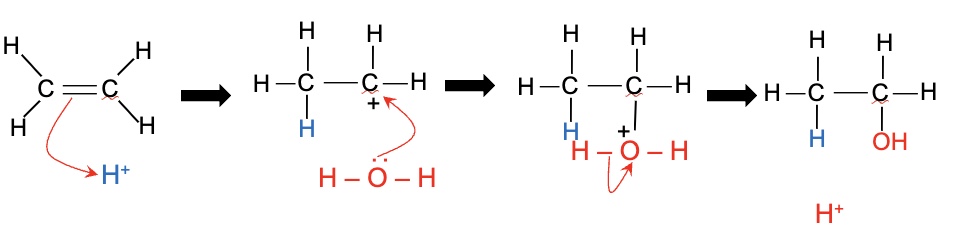
what is the mechanism of the direct hydration of ethene?
electrophilic addition
draw the mechanism of the direct hydration of ethene to form ethanol (electrophilic addition)