A level further maths 6
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Modulus argument form of imaginary numbers
z= r(cos¥+isin¥)
Matrix multiplication for 2×2
First row x first column= top left
First row x second column = top right
Second row x first column = bottom left
Second row x second column = bottom right
Matrix size
Rows x columns
For multiplying, a (2×3)(3×2) will leave 2×2 as the inner two numbers cancel out
Identity matrix
1 0
0 1
I2 x any 2×2 matrix leaves it to be itself
Inverse matrix
1/determinant (top left and bottom right switch places, top right and bottom left switch signs)
Roots of polynomial facts
ą+ß= -b/a
ąß=c/a
and keeps increasing with increasing orders of polynomials
Singular matrix
Determinant= 0
If a matrix is singular, the inverse doesn’t exist
Invariant lines

Lines of invariant points

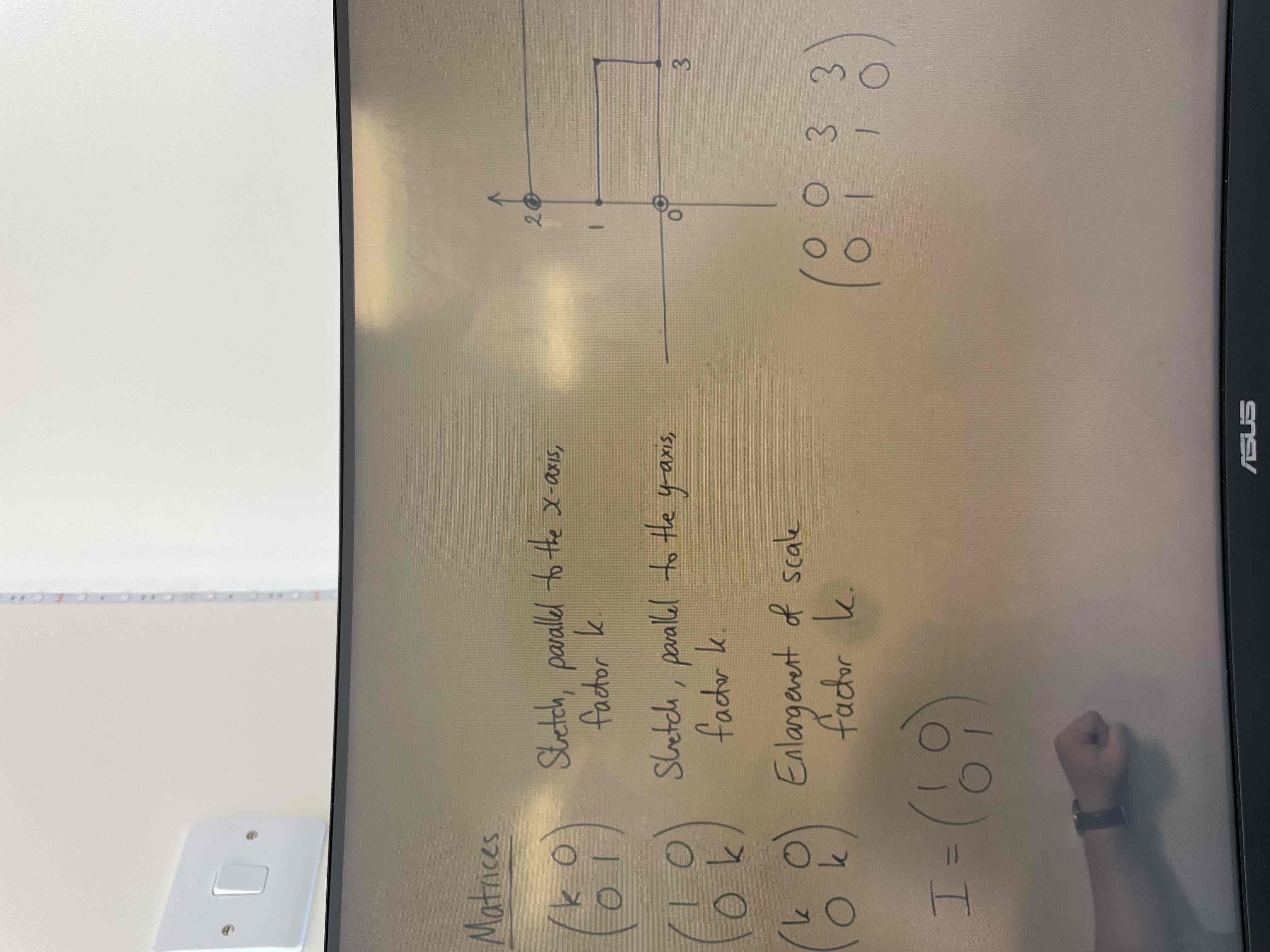
Matrix transformations
General formula for a reflection in the line y=(tan¥)x
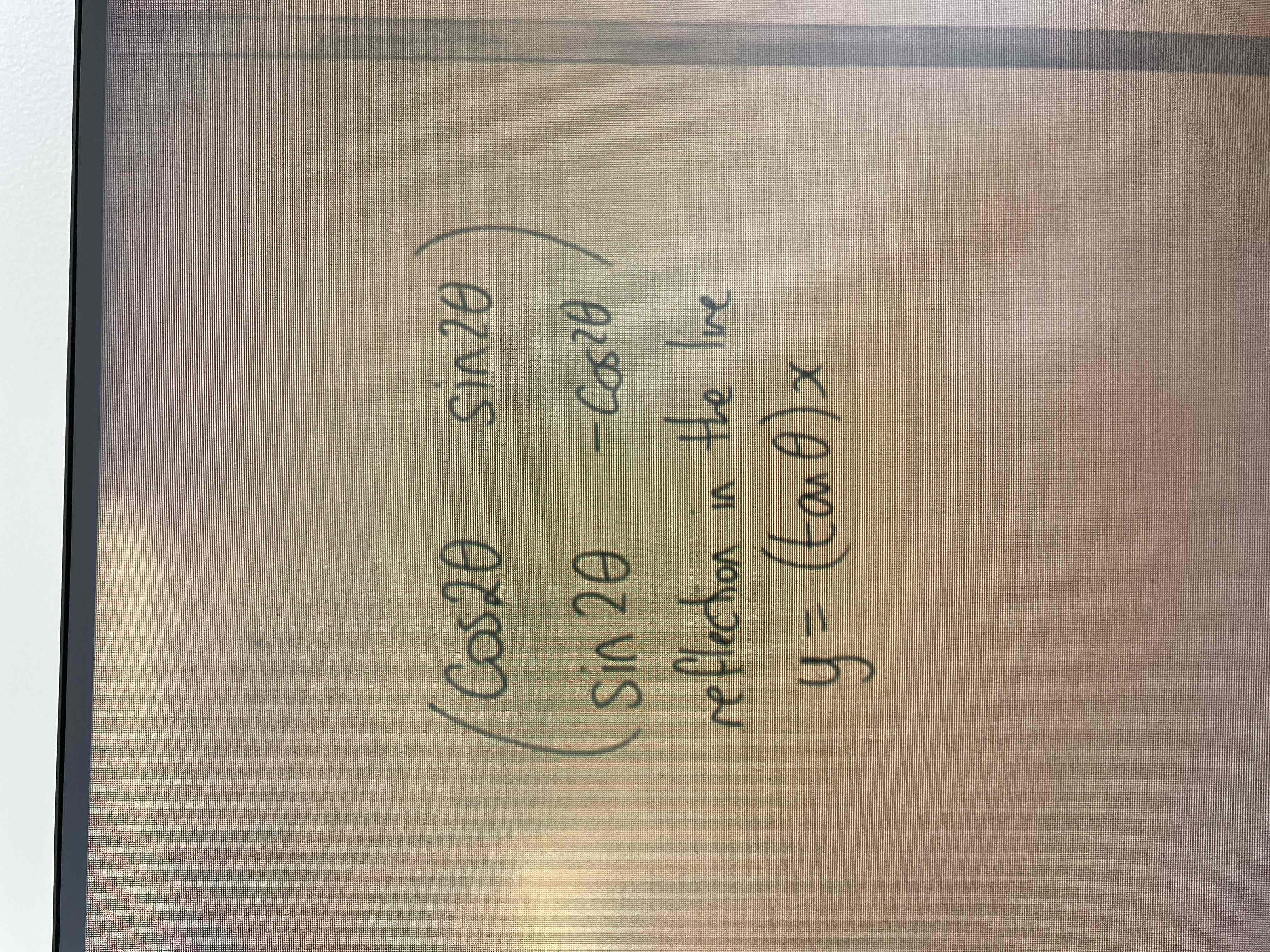
Reflective matrices

Rotational matrices

Rotation by certain angle
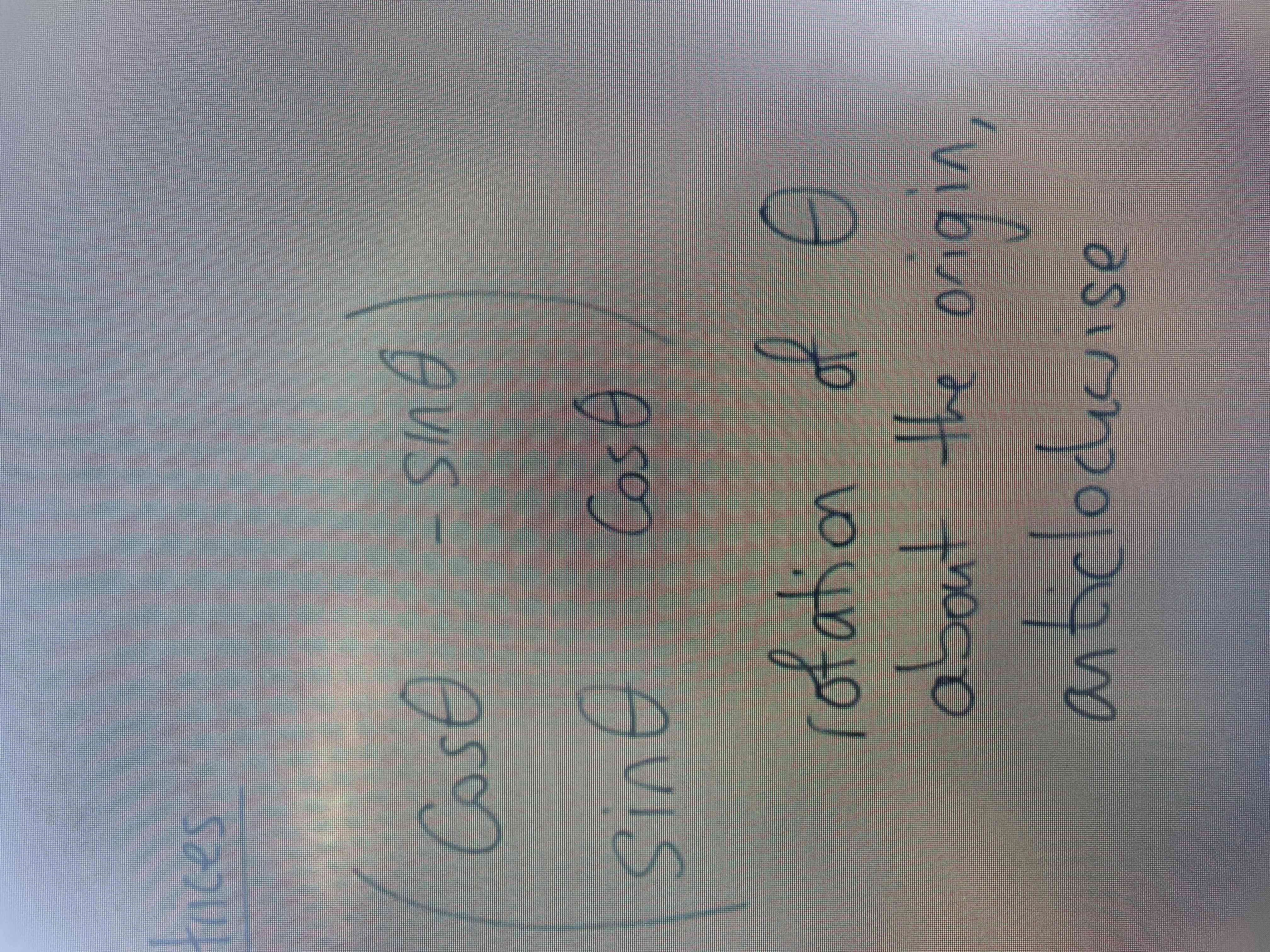
Shears
Points on the x axis remain fixed and all others move
Points below x axis move to the left, points above the x axis move to the right
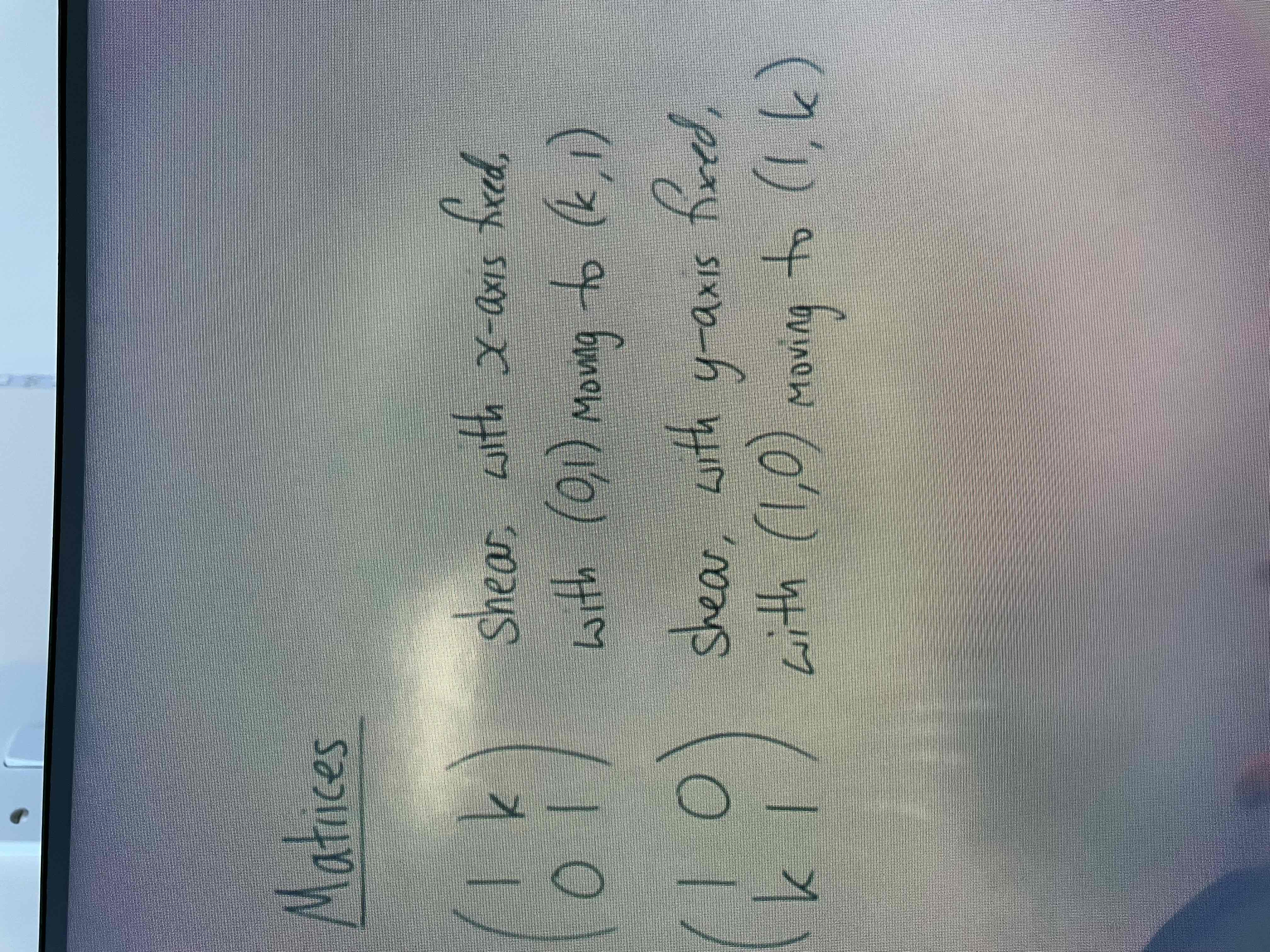
3D matrices for stretches and enlargement of certain axis

3D rotations about a given axis by an angle ¥

Solving simultaneous equations using matrices
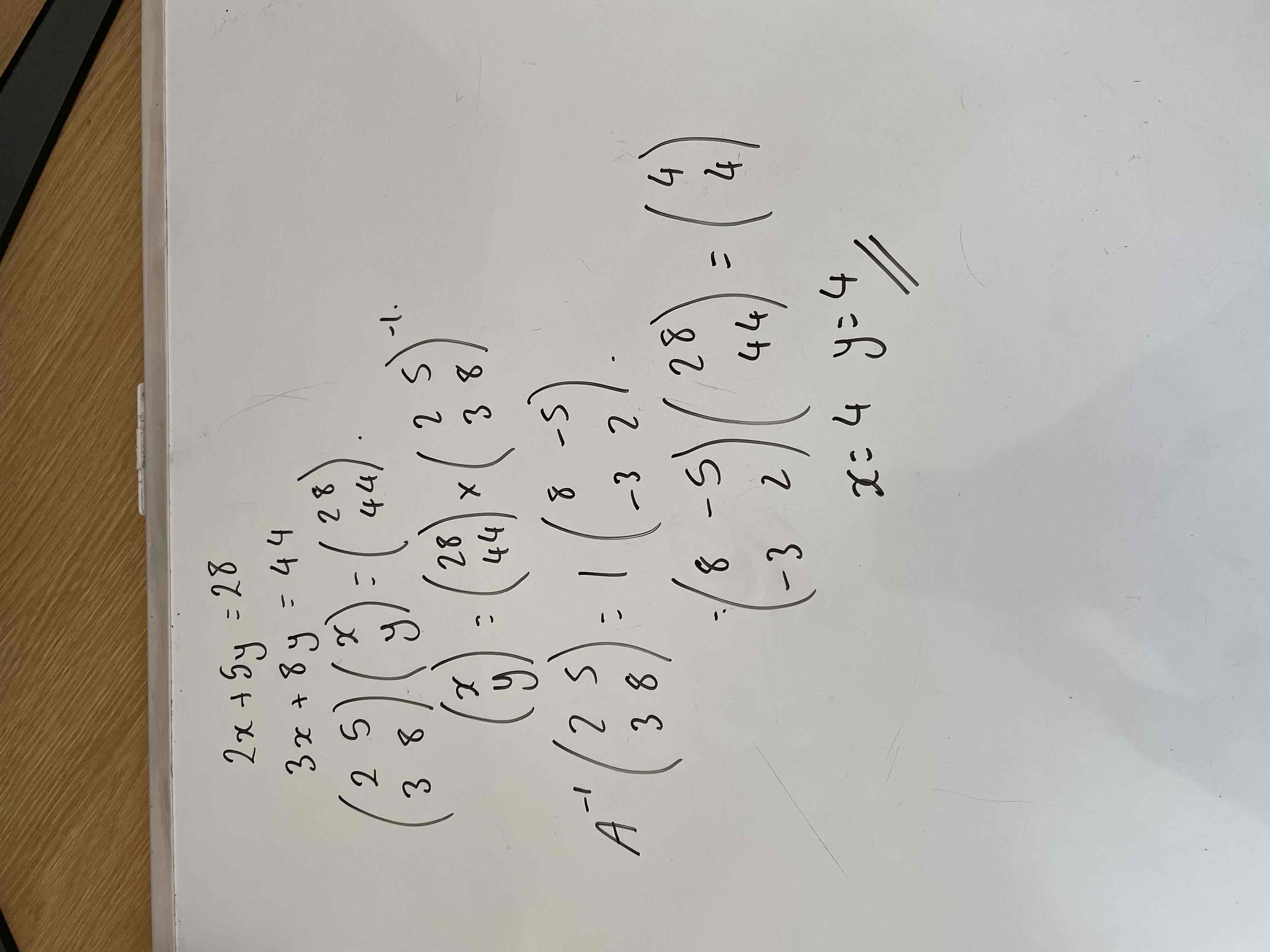
How to determine whether a simultaneous equation has a solution

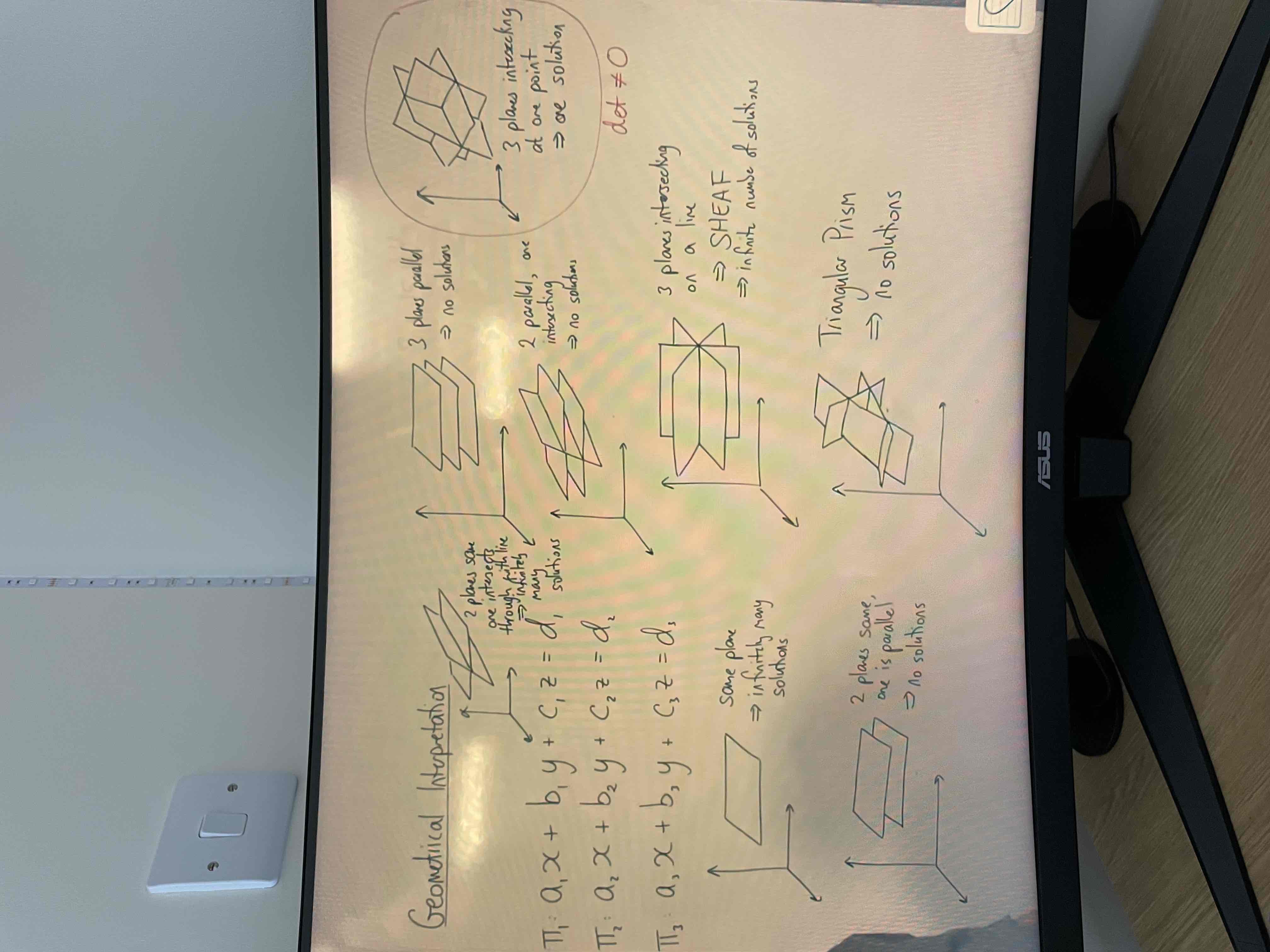
3D geometrical interpretations
General vector equation for 2D
OA + (lambda) AB

Vector: scalar product
Using cosine rule with the magnitude of the vectors
For 3D vectors, cos¥= a • b/ |a| • |b|
If perpendicular, dot product = 0
Inverse of 3×3 matrix 4 steps
DMFT

De moivres theorem
z=re^i¥

Finding the angle between a line and a plane
ALWAYS USE THE SCALAR PRODUCT

Intersecting vectors

Line and plane intersection
Split up into xyz and then sub in

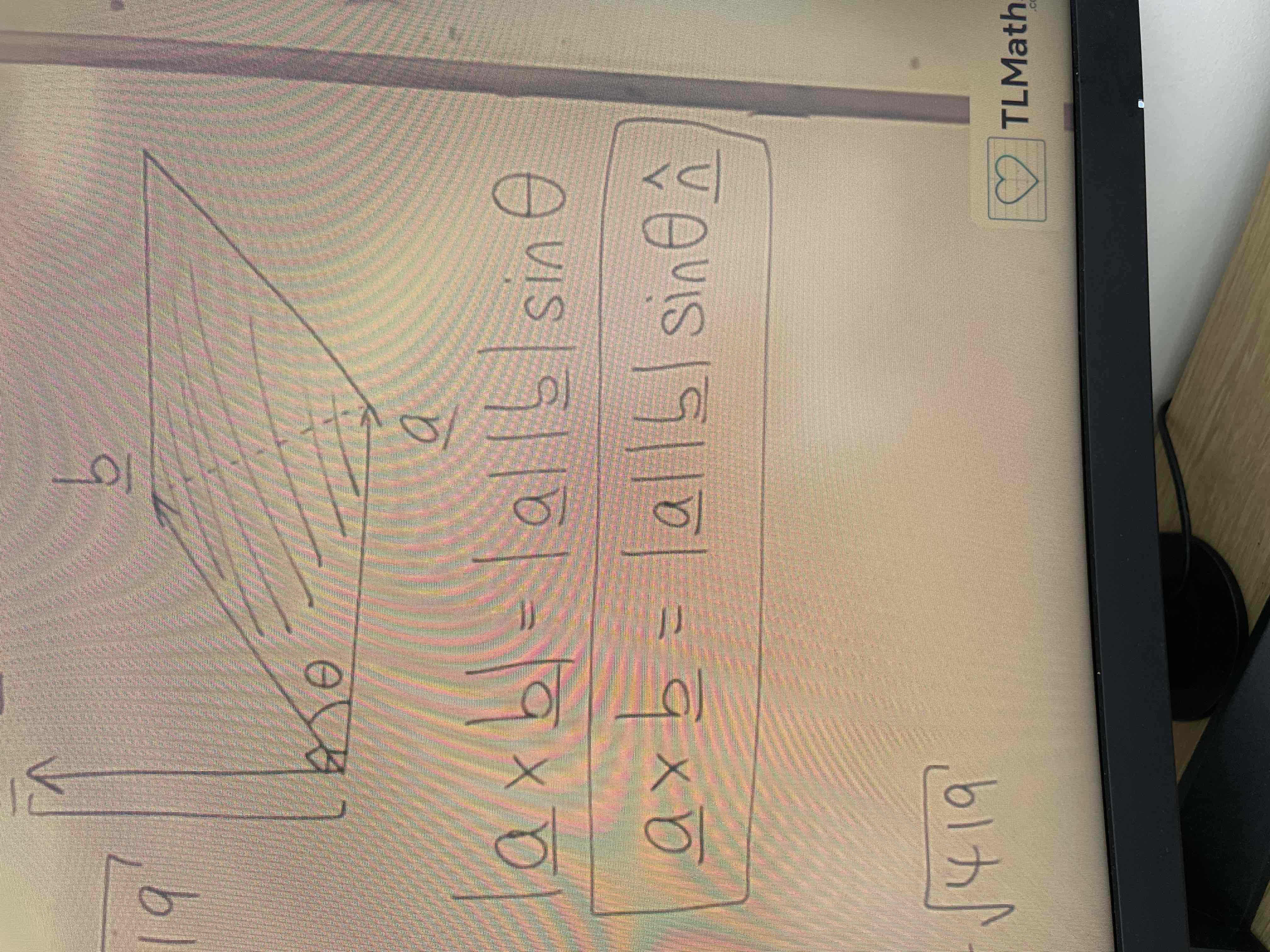
Vector product
Produces a vector that is perpendicular to the vectors that create it
Given formula in booklet

Vector cross product link to scalar product
Can be used to find the area of a parallelogram that connects vectors a and b
Shortest distance from a point to a line in 3d
Where P is the position vector and the line is of form r= a+¥d

Shortest distance from a line in 2D
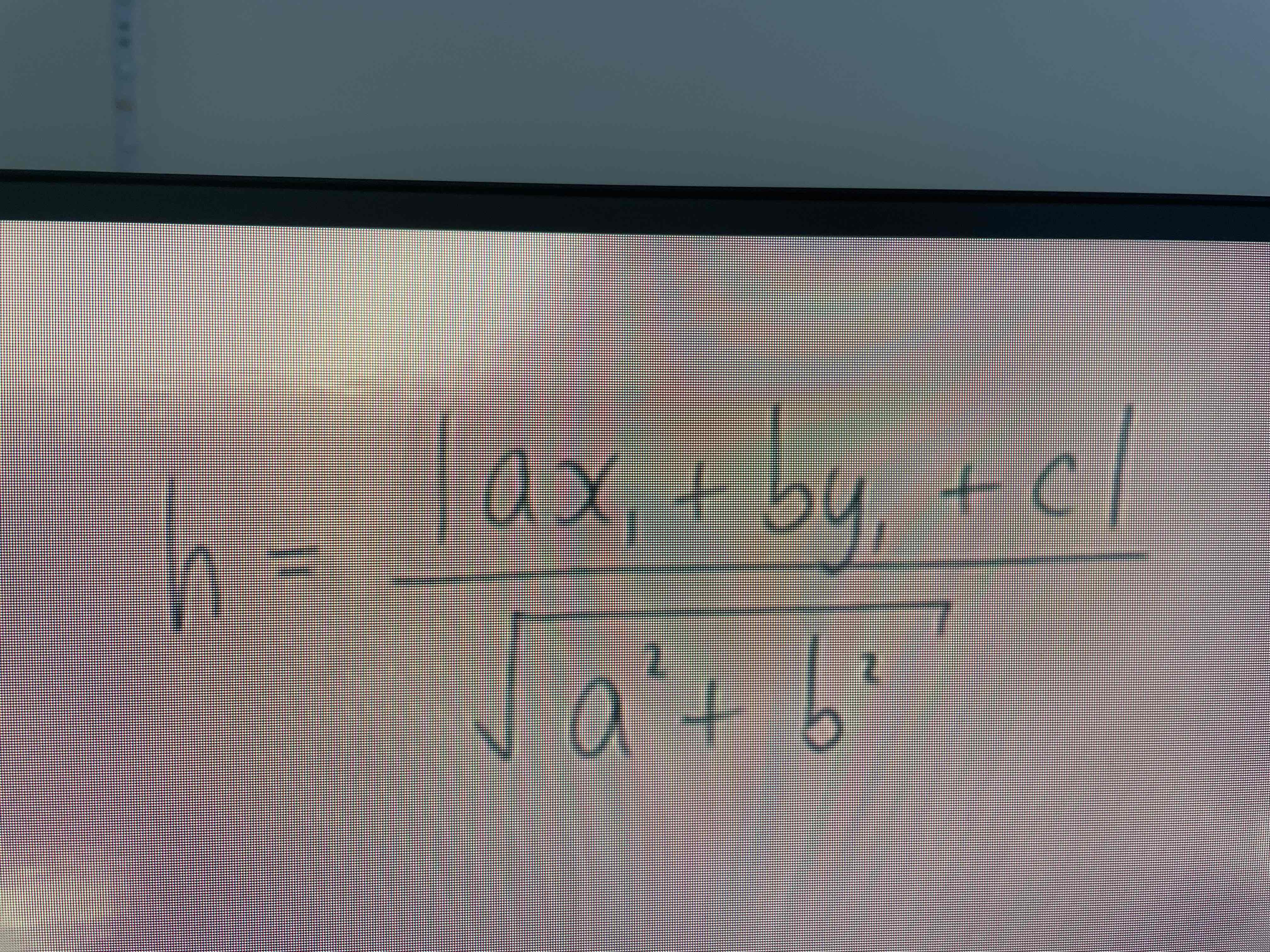
General vector equation of a 3D line
r = OA + ¥AB + (mew) AC
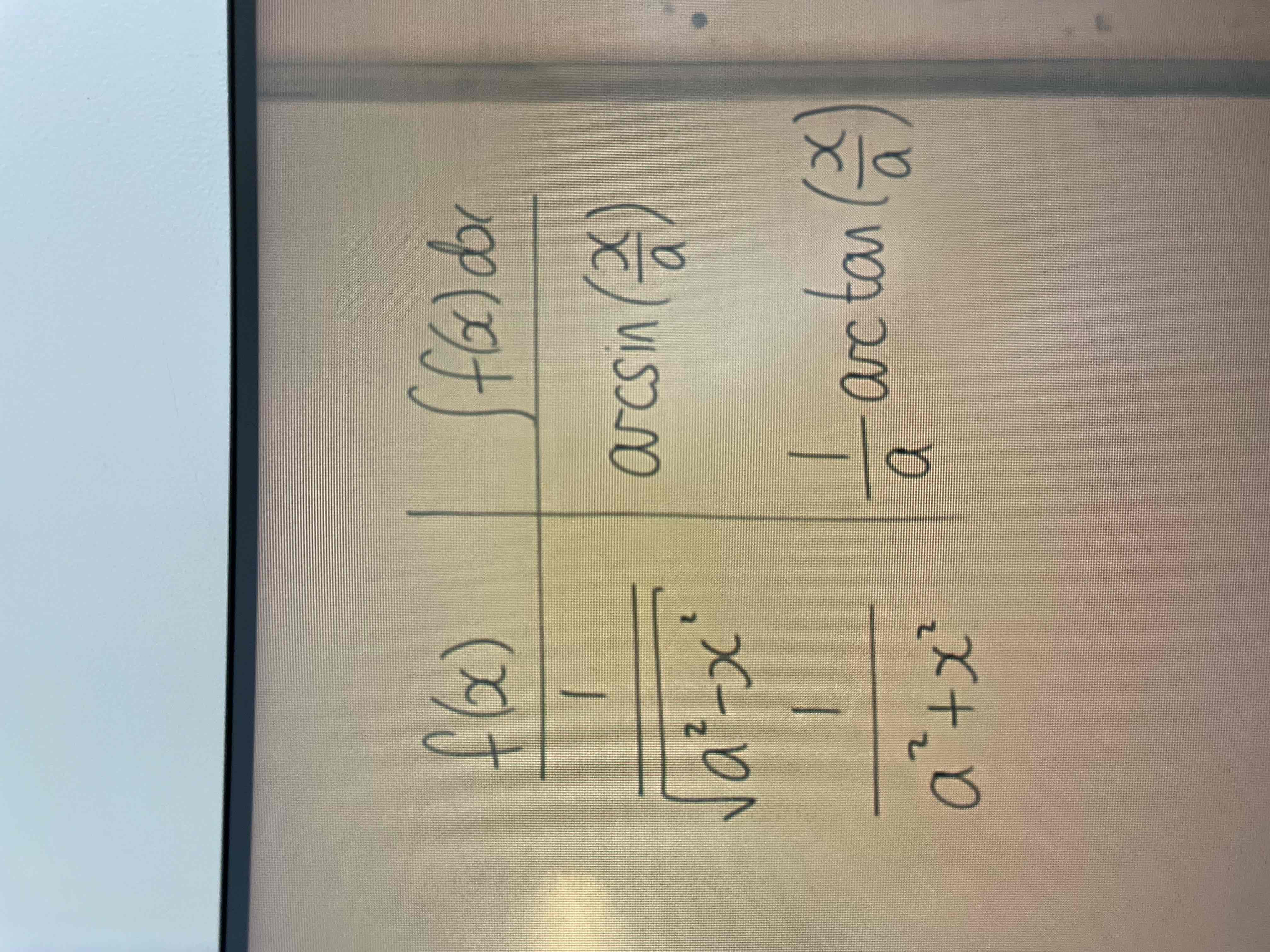
Differentiating arcsinx

Integrating to arcsinx
If a root is involved in the bottom of the fraction use substitution of x=sinu
Integrating arctanx
If there is not a root on denominator then use x=tanu
Integrating from 1/a²-x² to arctrig
Mean value formula
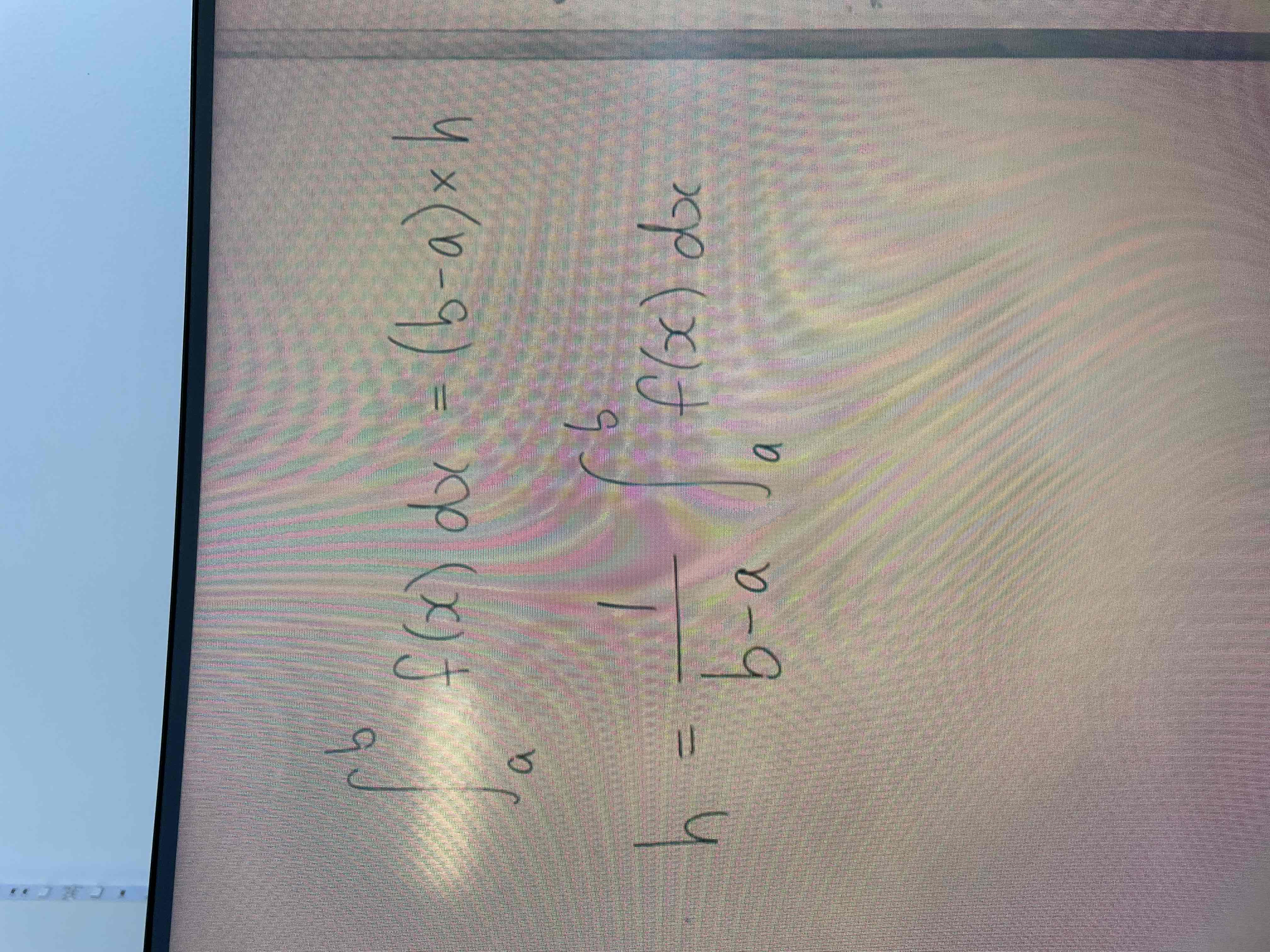
Partial fraction with quadratic factor

Hyperbolic functions in terms of e
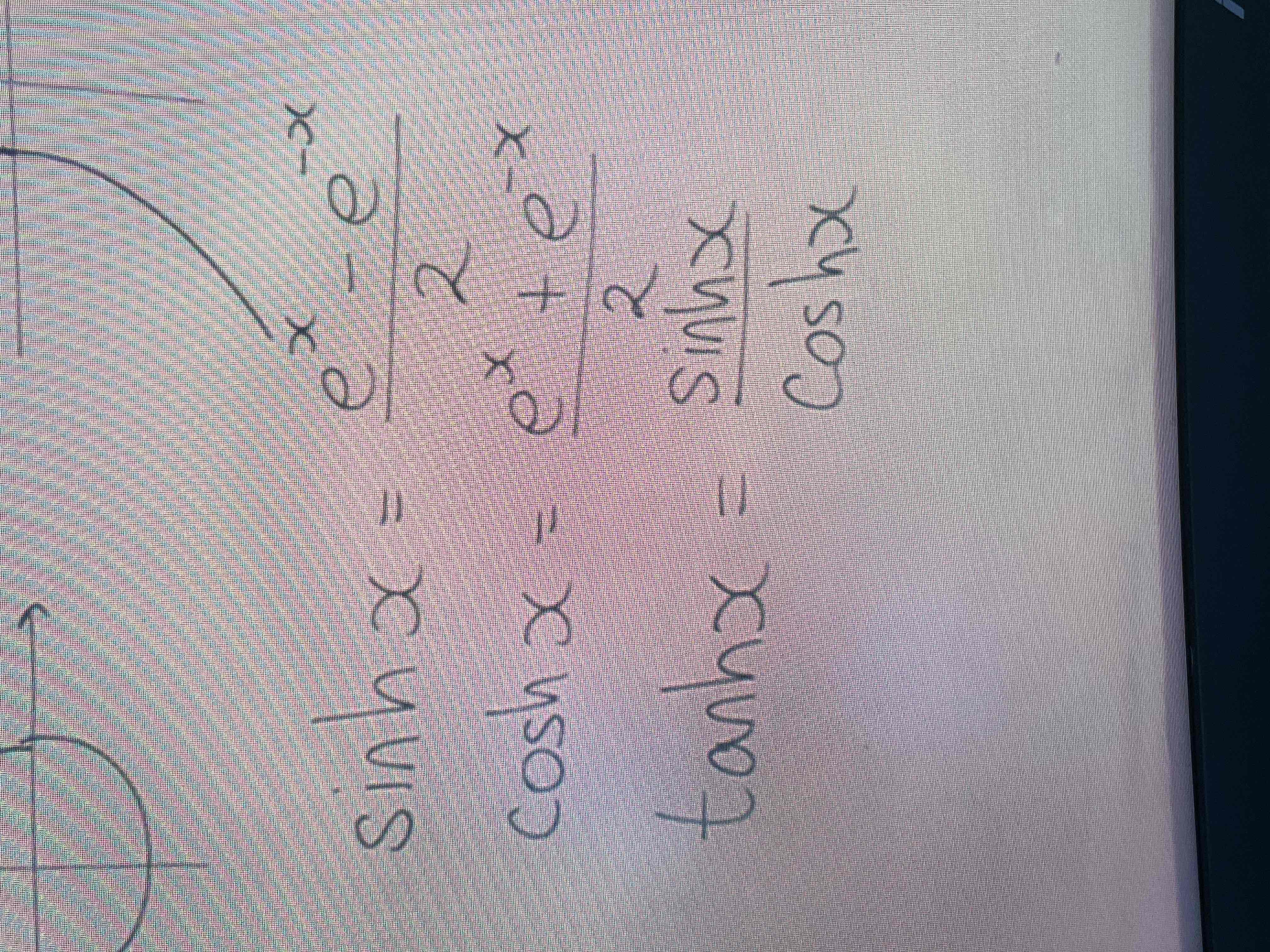
Sinhx domain range and graph

Derivatives of hyperbolic functions
sinh = cosh
cosh = sinh
tanh = sech²
coth = -csch²
Identities with hyperbolic functions
cosh² - sinh² = 1
1 - tanh² = sech²
coth² - 1 = csch²
Osbournes rule says they are identical to normal trig functions just put a negative in front every time sin²x appears
Inverse hyperbolic functions
To derive, use y= sinh^-1 then rearrange for y using quadratic formula

Differential equations forms for real and complex
Ae^(alpha)x+Be^(beta)x
Ae^(alpha)x+Bxe^(beta)x
Acos(alpha)x+Bsin(alpha)x
e^(alpha)x (Acos(beta)x + Bsin(beta)x) where complex numbers are of the form alpha+ or - beta i
System of differential equations
Solve for one variable in either x or y then sub into the other formula