Anatomy Lecture Exam 2
1/261
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 5 - 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
262 Terms
skeletal system
contains
skeleton: axial and appendicular
cartilage
ligaments
axial skeleton
bones of the head, trunk, vertebral column and thorax
appendicular skeleton
limbs, pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle
skeletal system functions
support: framework for attachment of other organs
movement/locomotion
storage of minerals: calcium and phosphate ions
blood cell production
protection
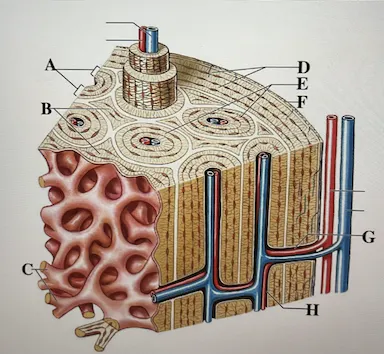
osseous tissue
matrix of bone consists of:
hydroxyapatite crystals
calcium phosphate make up 2/3 of bone mass
collagen fibers
make up 1/3 of bone mass
contribute to tensile strength of bones
bone cells (2%)
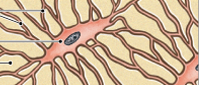
osteocytes
maintains matrix; mature not actively producing matrix
matian protein and mineral content of matrix
resides in lacunae
controls release and deposition of Ca2+ in/out of bone
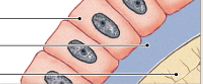
osteoblasts
produce matrix; immature, active bone cells
found on inner & outer surfaces of bones
produce osteoid
osteogenesis
osteoprogenitor cells
produce osteoblasts (bone stem cells)
innermost layer of periosteum and inner lining of endosteum
involved in repair of bones after a fracture
osteoclasts
break down matrix
multinucleated cells
maintain calcium ions in actual blood stream
osteolysis
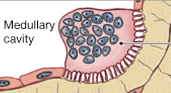
osseous tissue types
compact bone and spongy bone
compact bone
dense bone
dense and solid
forms walls of boen
parallel compression
spongy bone
trabecular bone
open network of platelets
multidirectional or light strain
surround medullary cavity
epiphysis
heads of long bone; houses red marrow for RBC formation
diaphysis
shaft of long bones; houses yellow-marrow
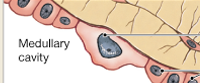
medullary cavity
inner cavity of diaphysis
epiphyseal line
“growth line”
periosteum
membrane on outer surface of bone
fibrous layer & osteogenic layer
isolates and protects bone from surrounding tissue
attachment for circulatory and nervous supply
attachment site for tendons and ligaments
endosteum
membrane on inner surface of bone; single, incomplete cell layer
lines medullary cavity, perforating canals and central canals
appositional growth
osteoblasts in periosteum add bone matrix to surface
forming circumferential lamellae on outer surface
osteons are formed
osteoclasts break down layer below endosteum to enlarge medullary cavity
bone age is set by age 25
factors regulating bone growth
minerals: magnesium, calcium, phosphate, citrate, carbonate
vitamins
A: stimulates osteoblasts
C: collagen formation and osteoblast differentiation
D3: used for calcitriol by kidneys
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
stimulates osteoclasts
increases circulating Ca2+
influence production of calcitriol in kidney
calcitonin
produced by thyroid gland
inhibits osteoclasts
decreases circulating Ca2+
thyroxine
growth hormone
influence basal metabolic rate of bone cells
maintain activity in epiphyseal region for growth
estrogen & testosterone
important for maintaining osteoblasts
stimulate osteoblast activity causing growth spurts during puberty
maintain bone density in adults
sutural bones
attached by sutures
small, flat, oddly shaped bones
found between flat bone of the skull along sutures
pneumatized bones
hollow or contain lots of air pockets
ex: ethmoid bone
sesamoid bones
found in joints
ex: patella
small, round, flat
most often found near joints at knee, hands, and feet
embedded in tendons
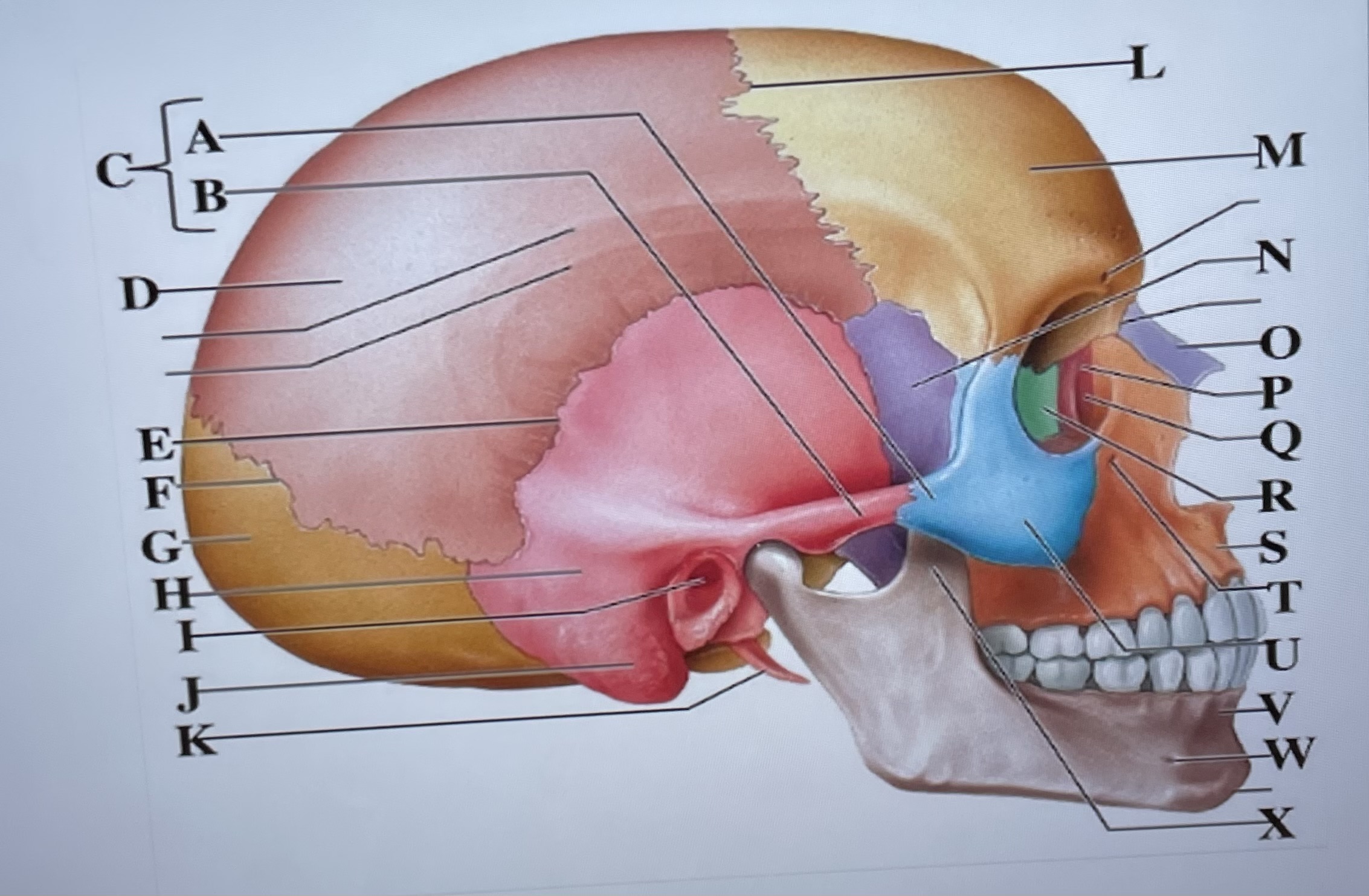
temporal process of zygomatic bone
A
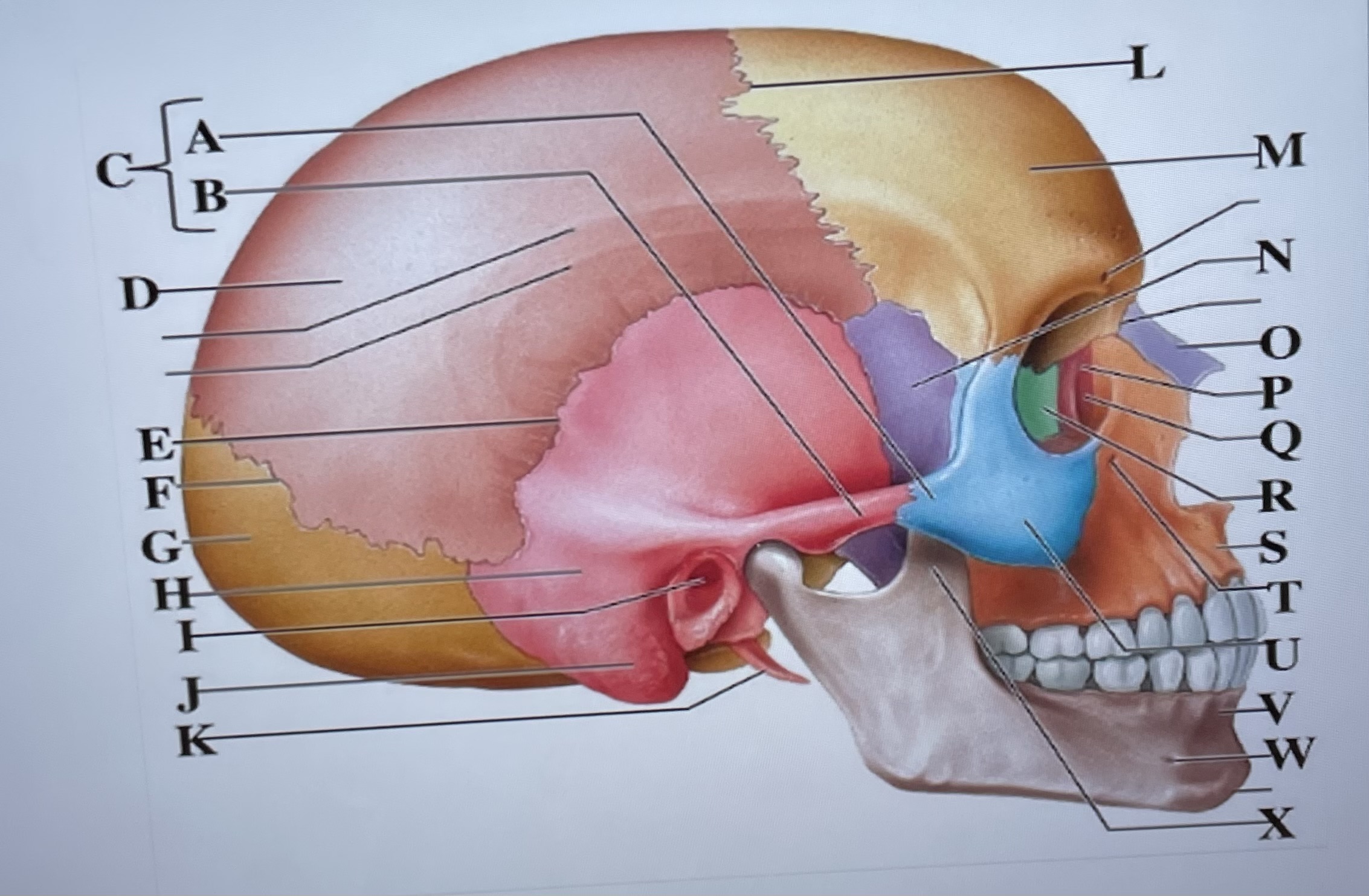
zygomatic process of temporal bone
B
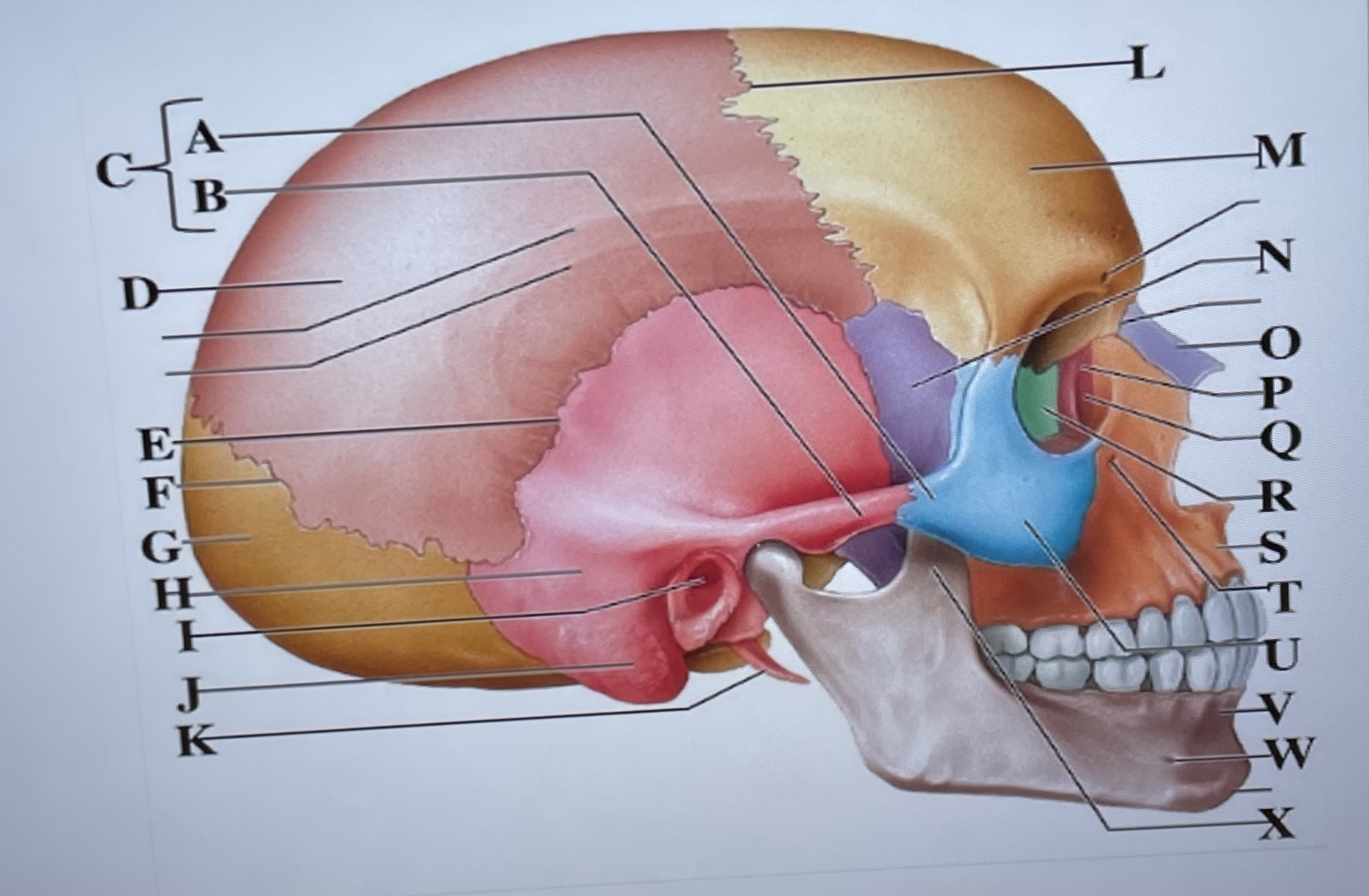
zygomatic arch
C
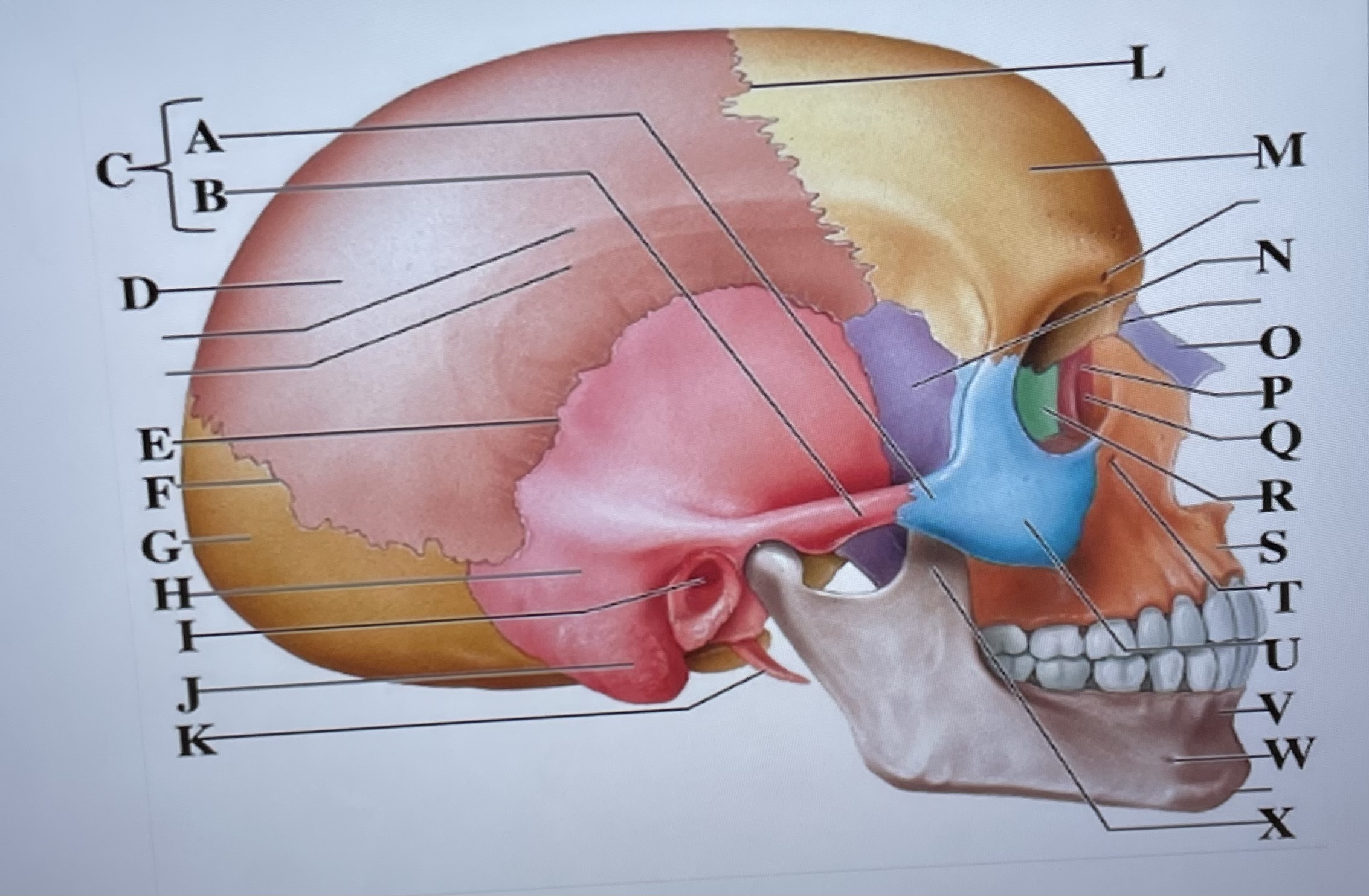
parietal bone
D
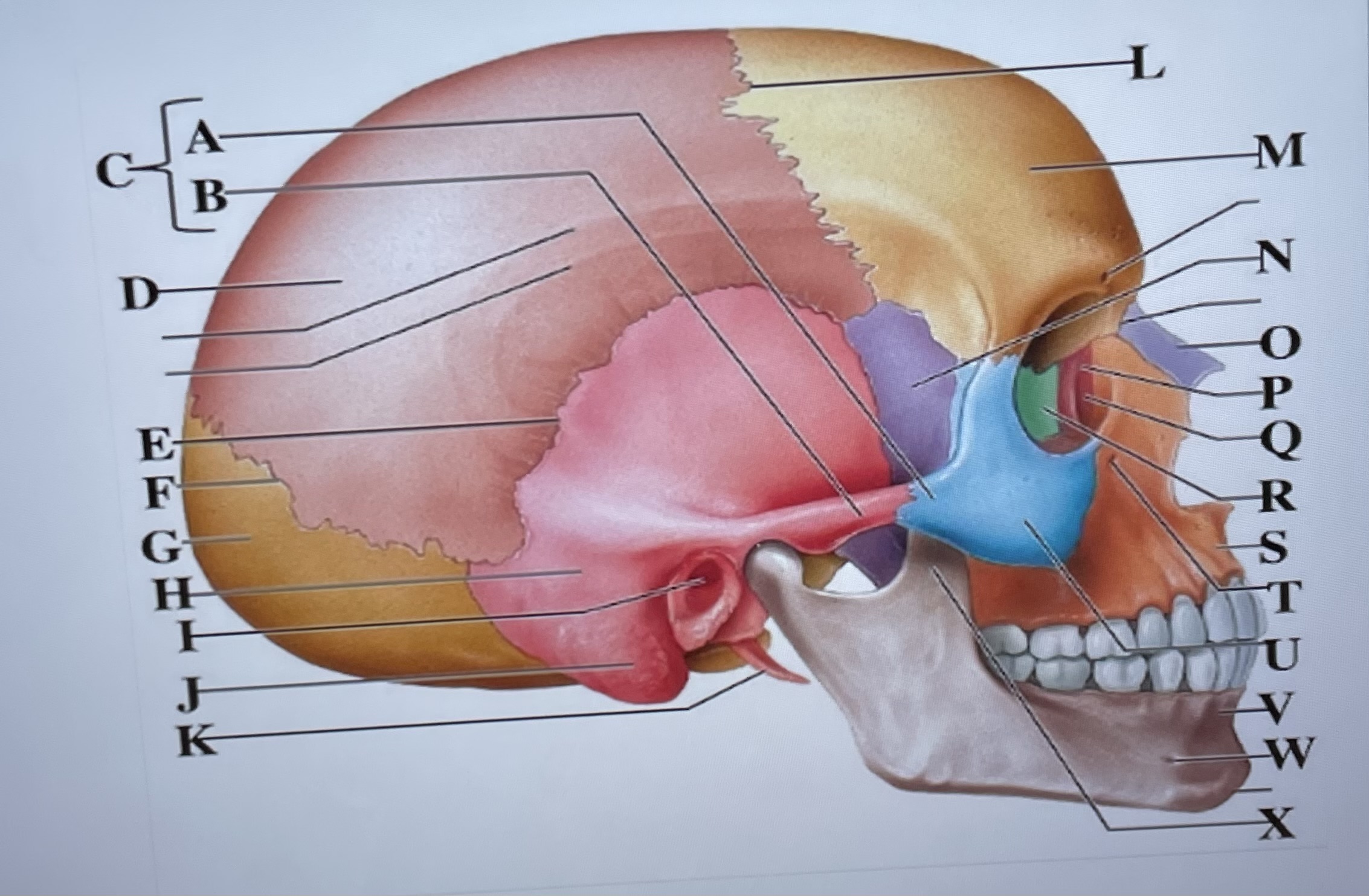
squamous suture
E
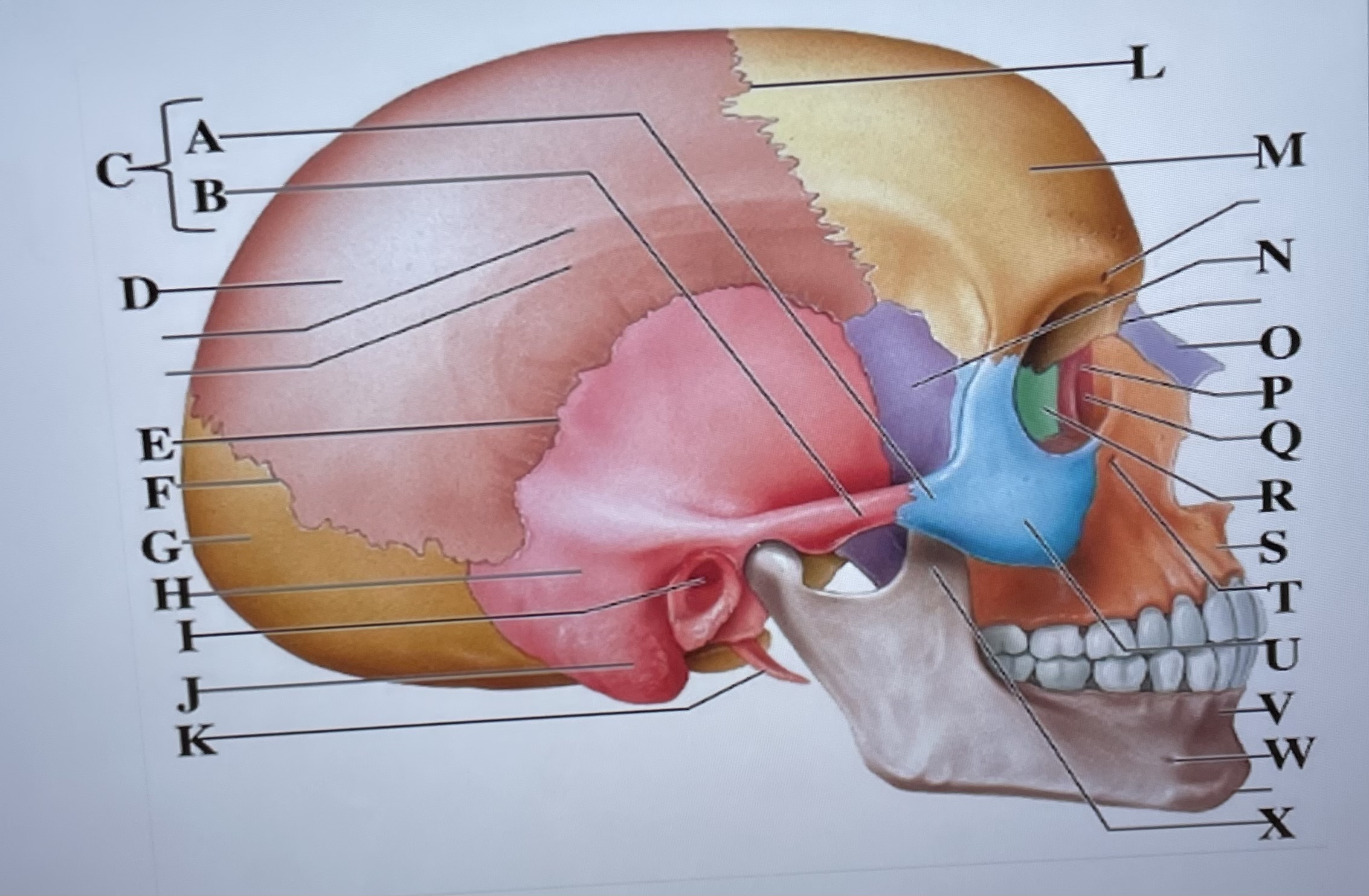
lambdoid suture
F
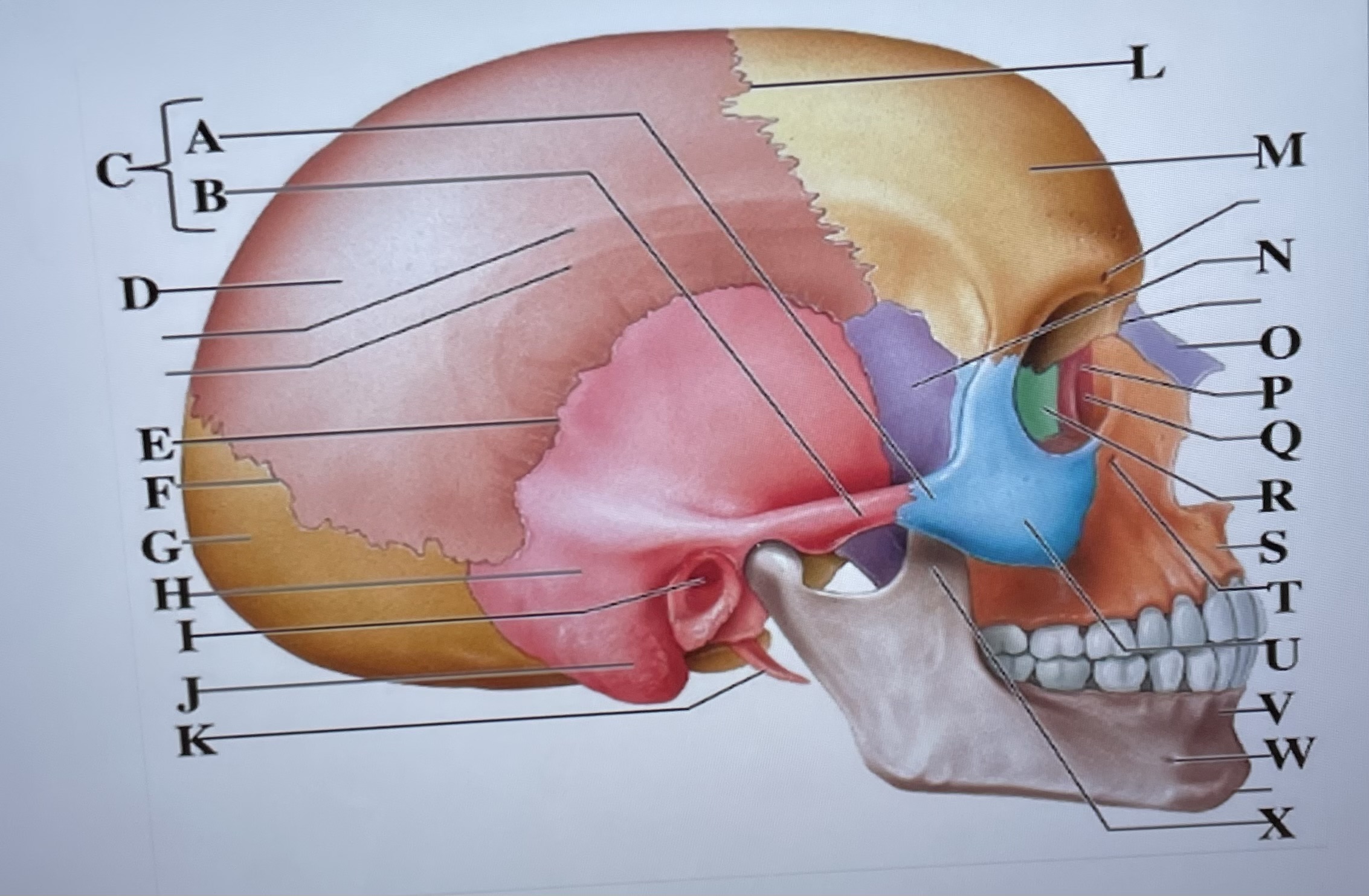
occipital bone
G
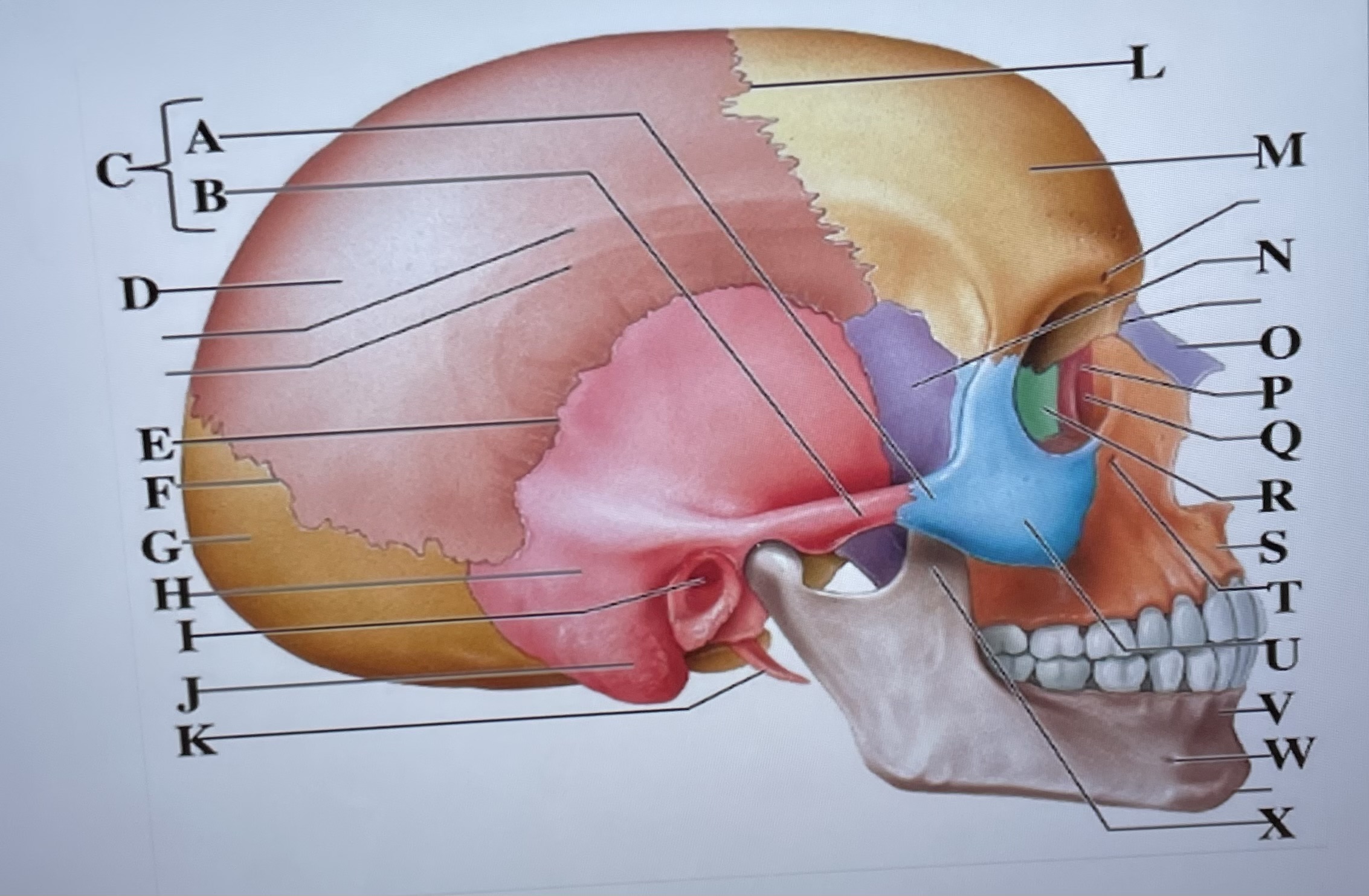
temporal bone
H
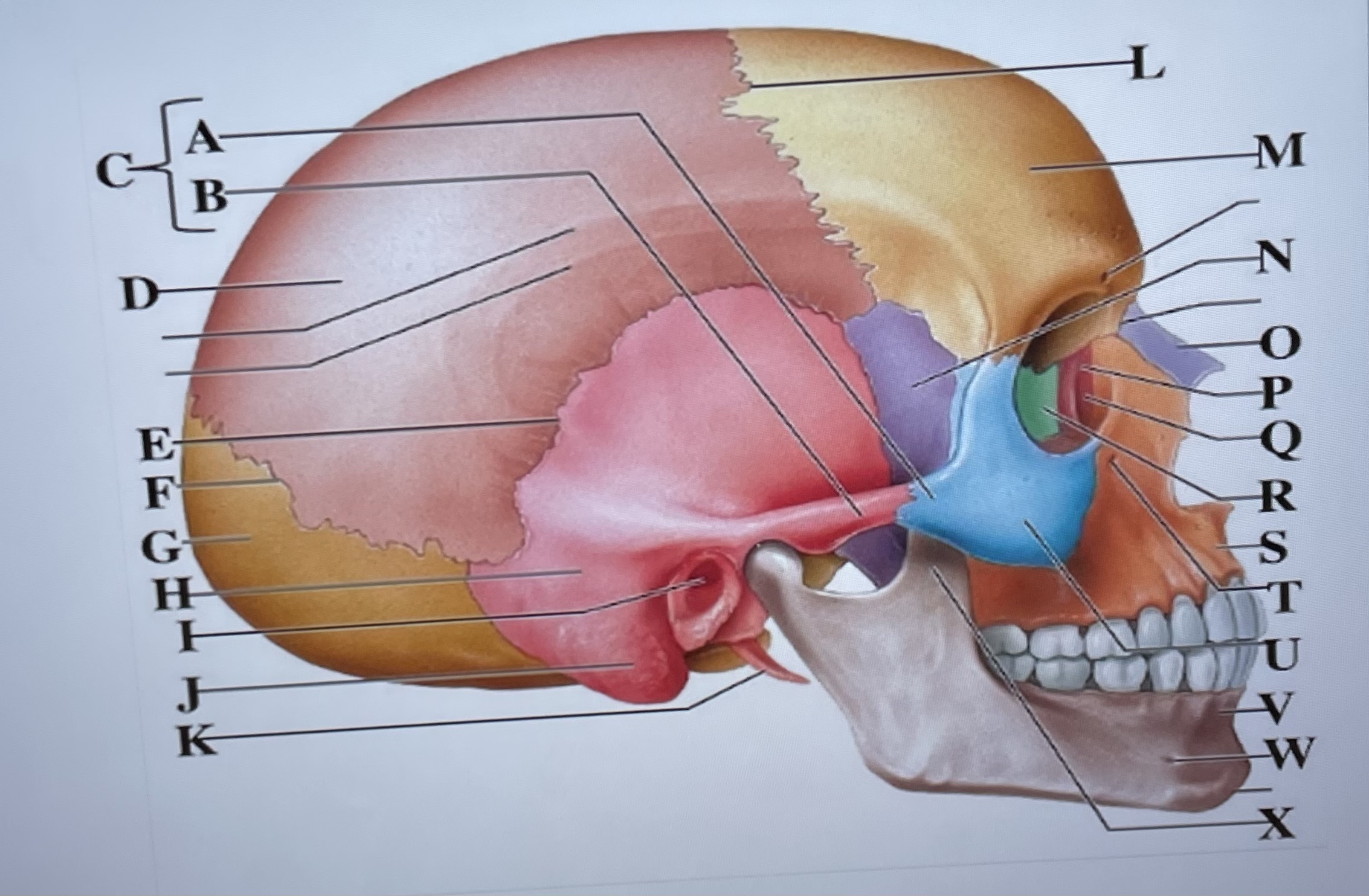
external acoustic meatus
I
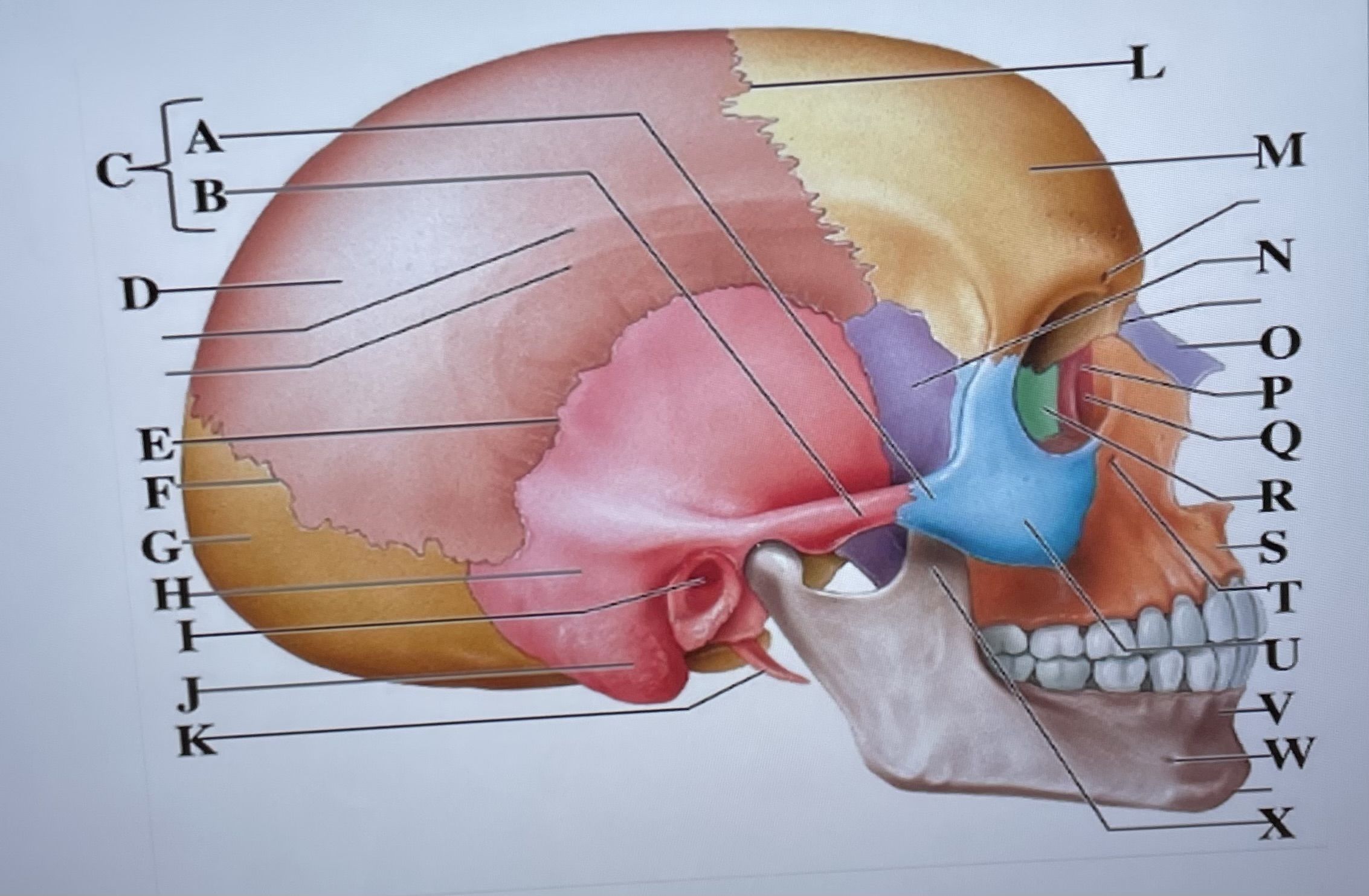
Mastoid process
J
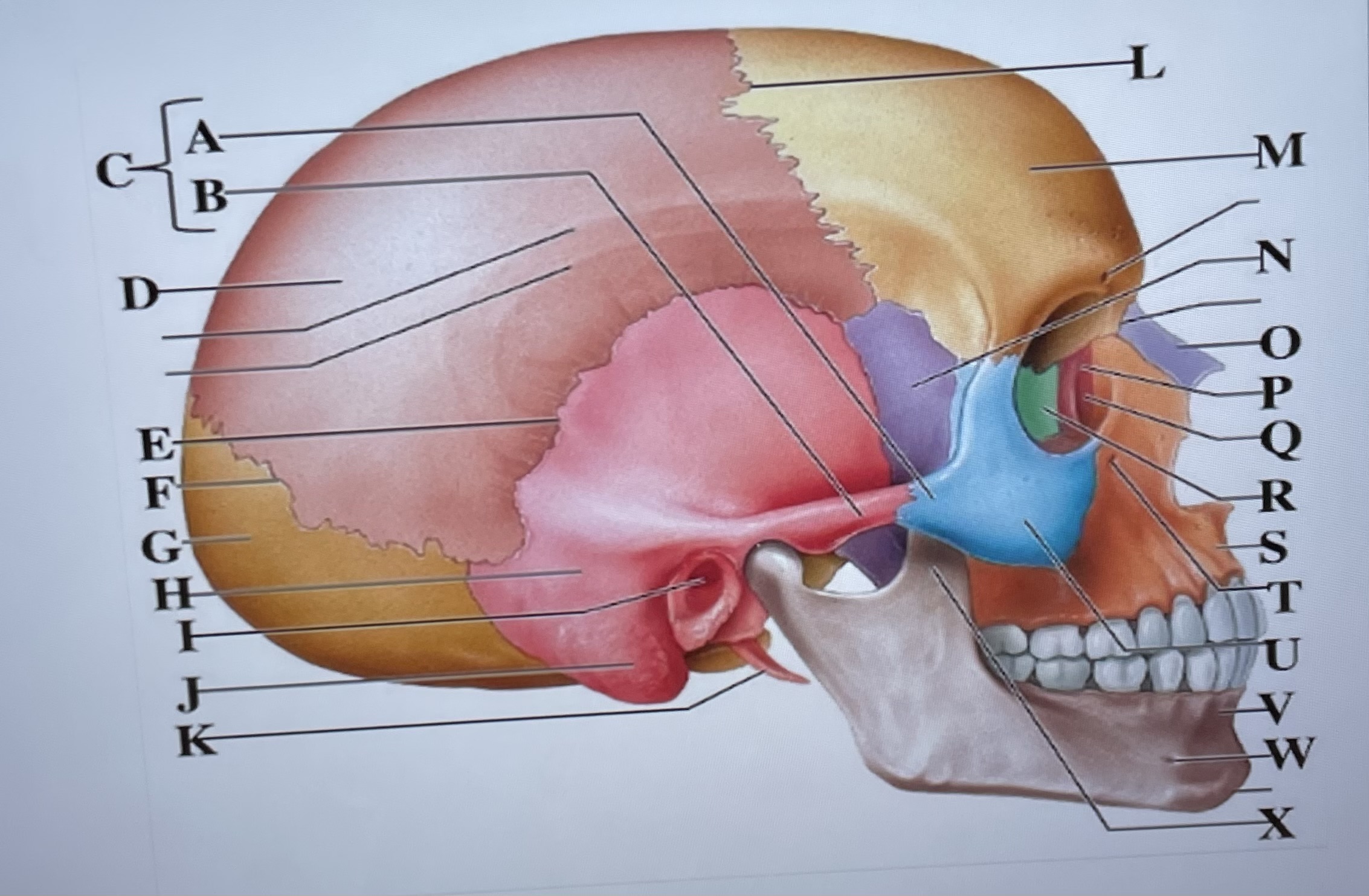
styloid process
K
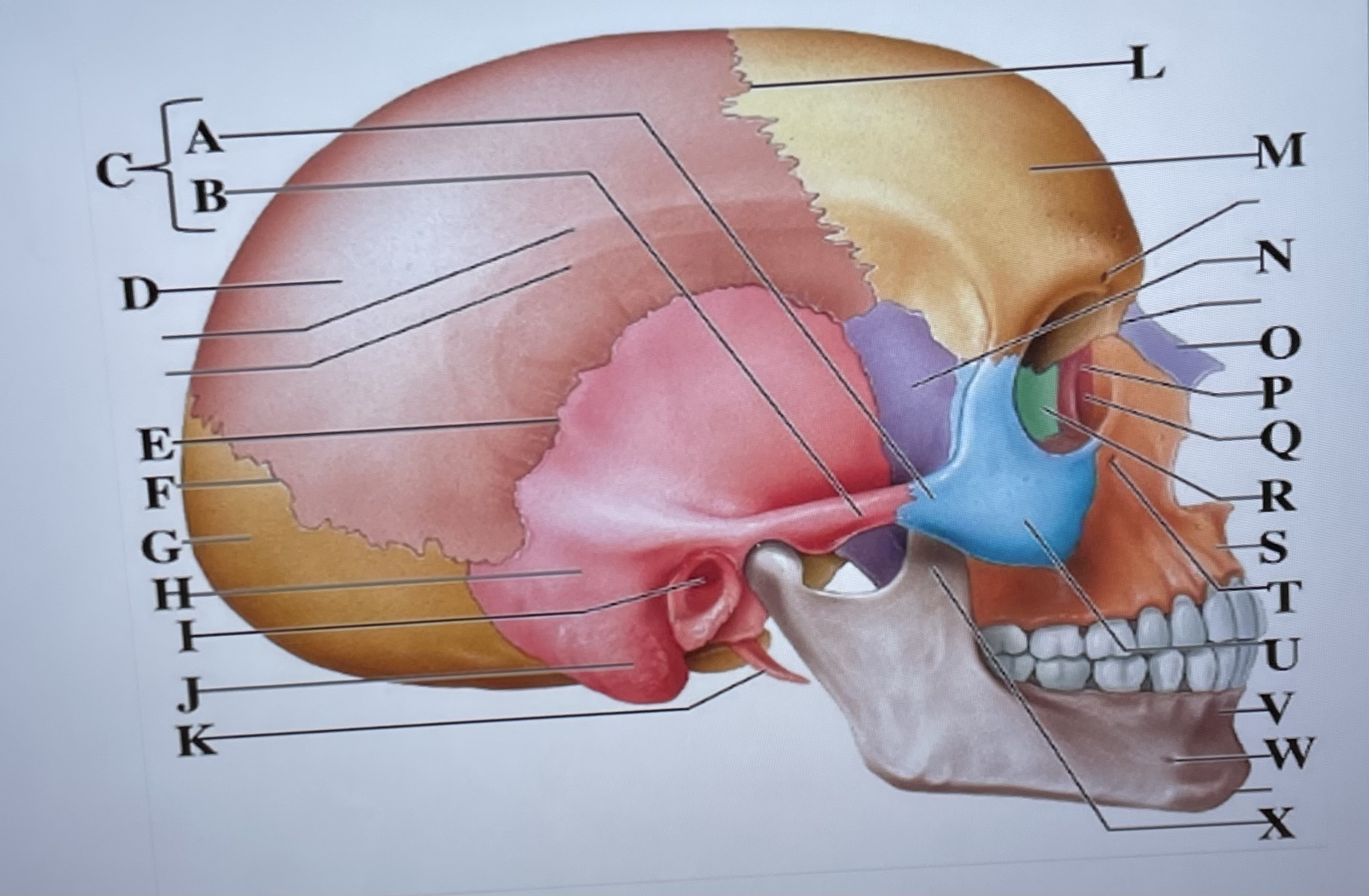
coronal suture
L
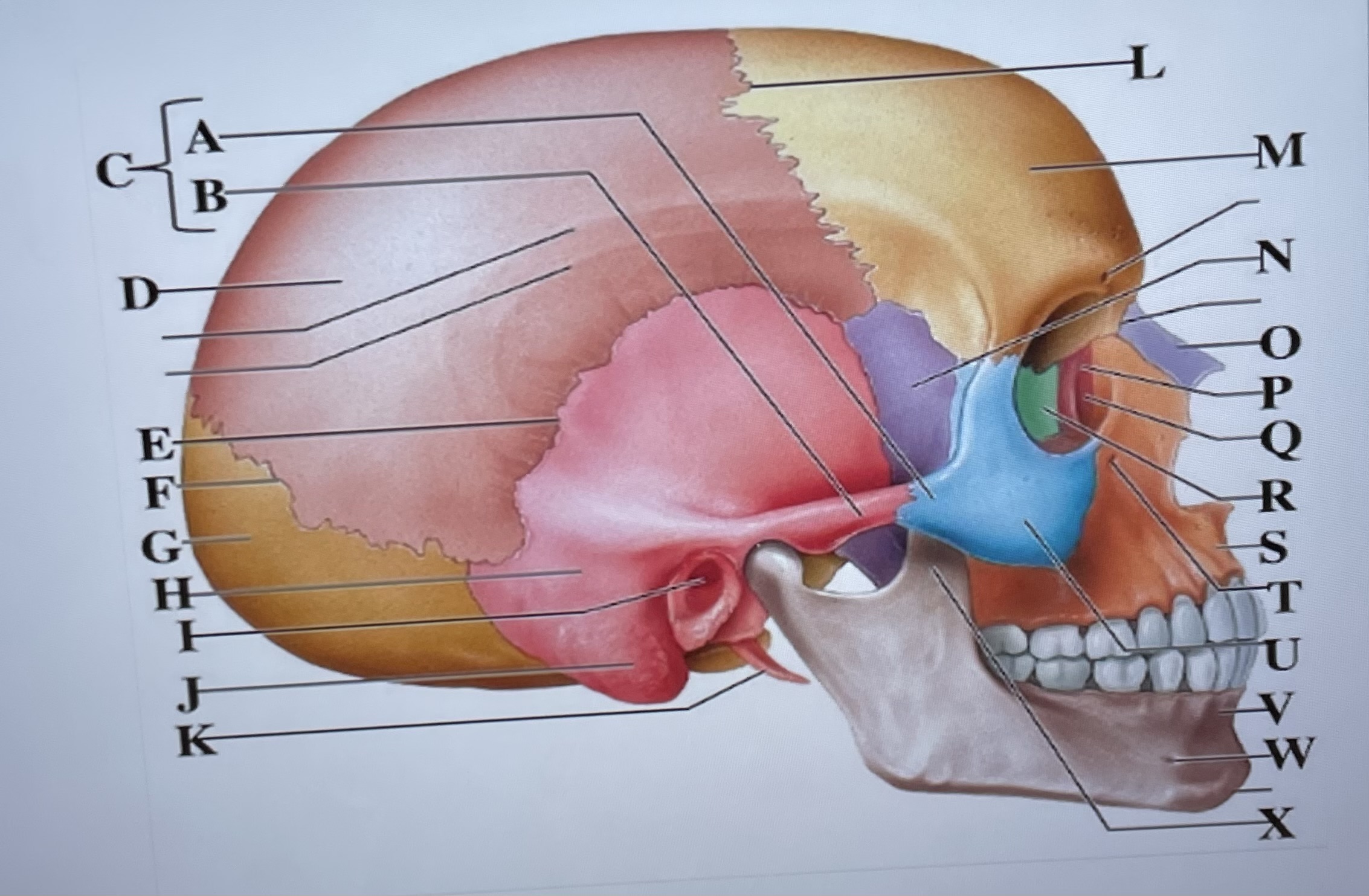
frontal bone
M
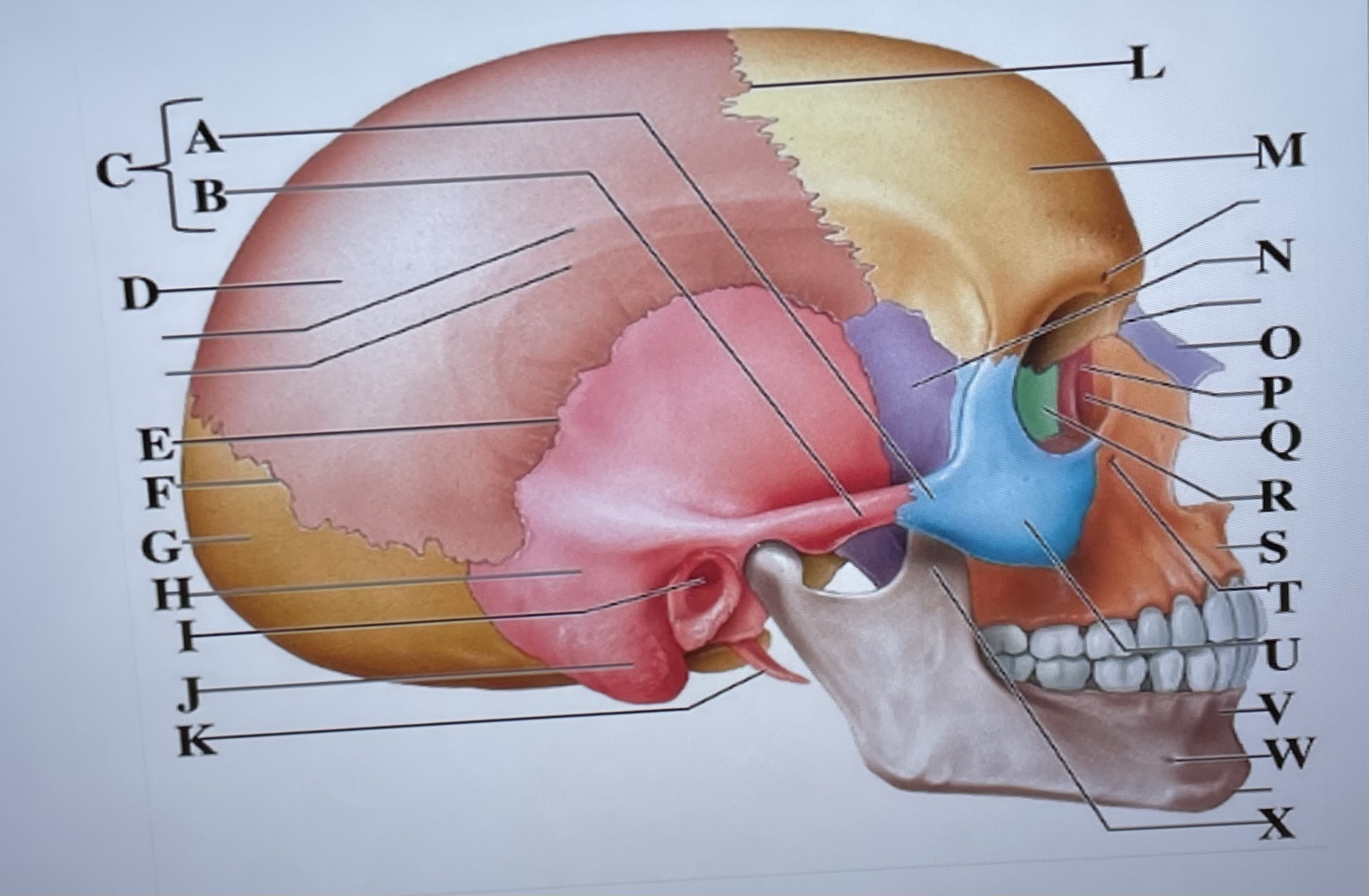
sphenoid
N
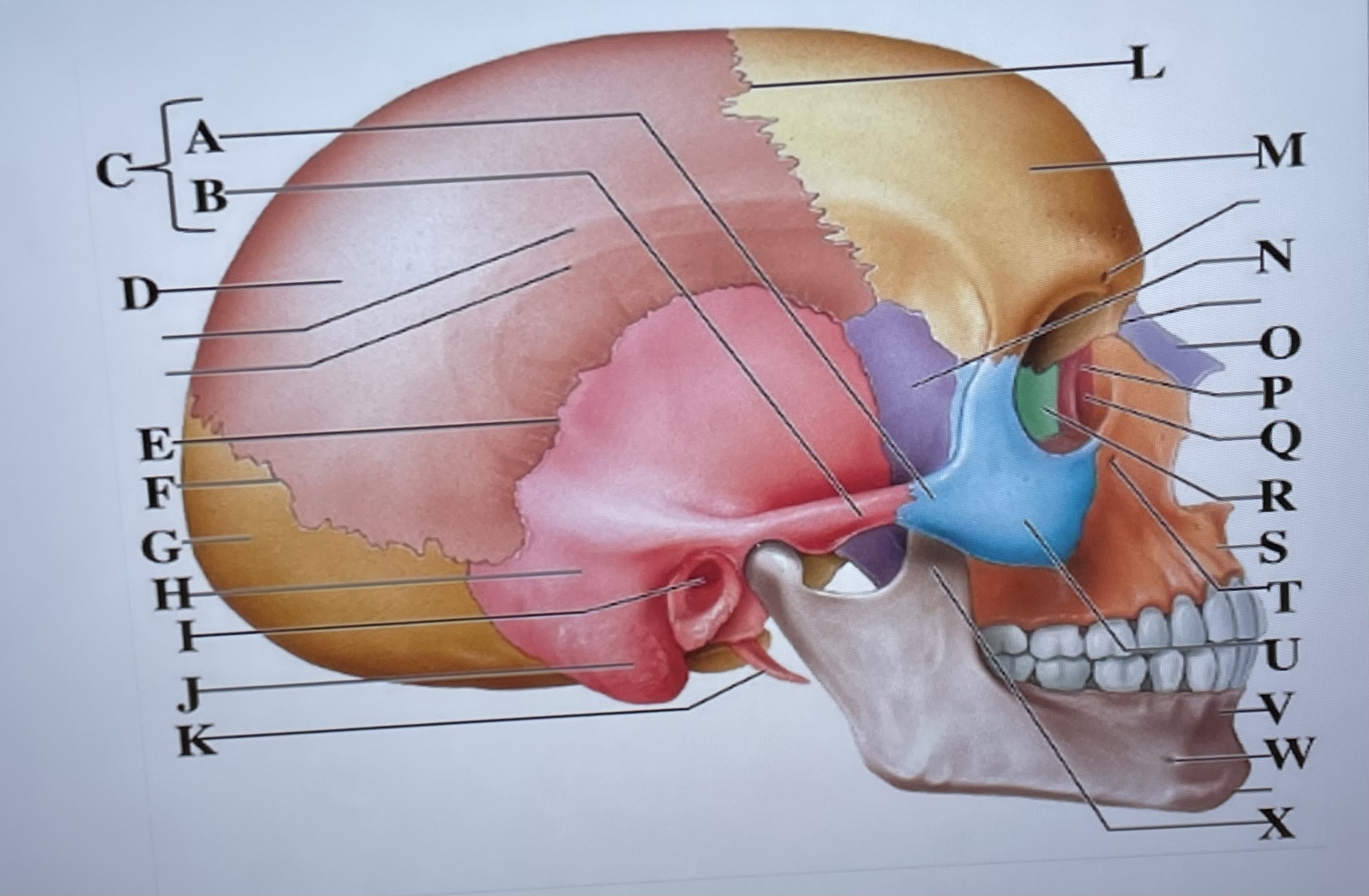
Nasal bone
O
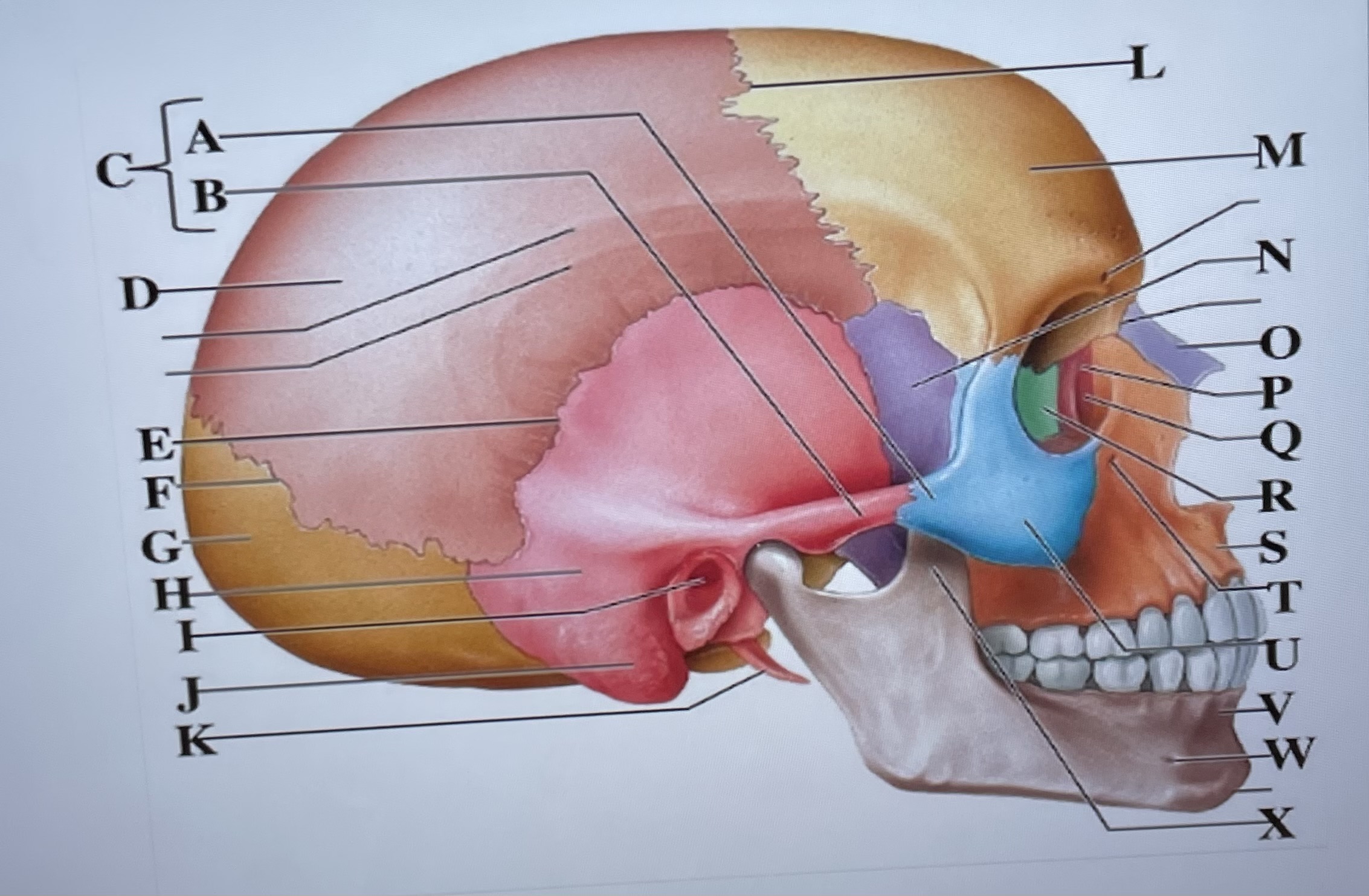
lacrimal bone
P
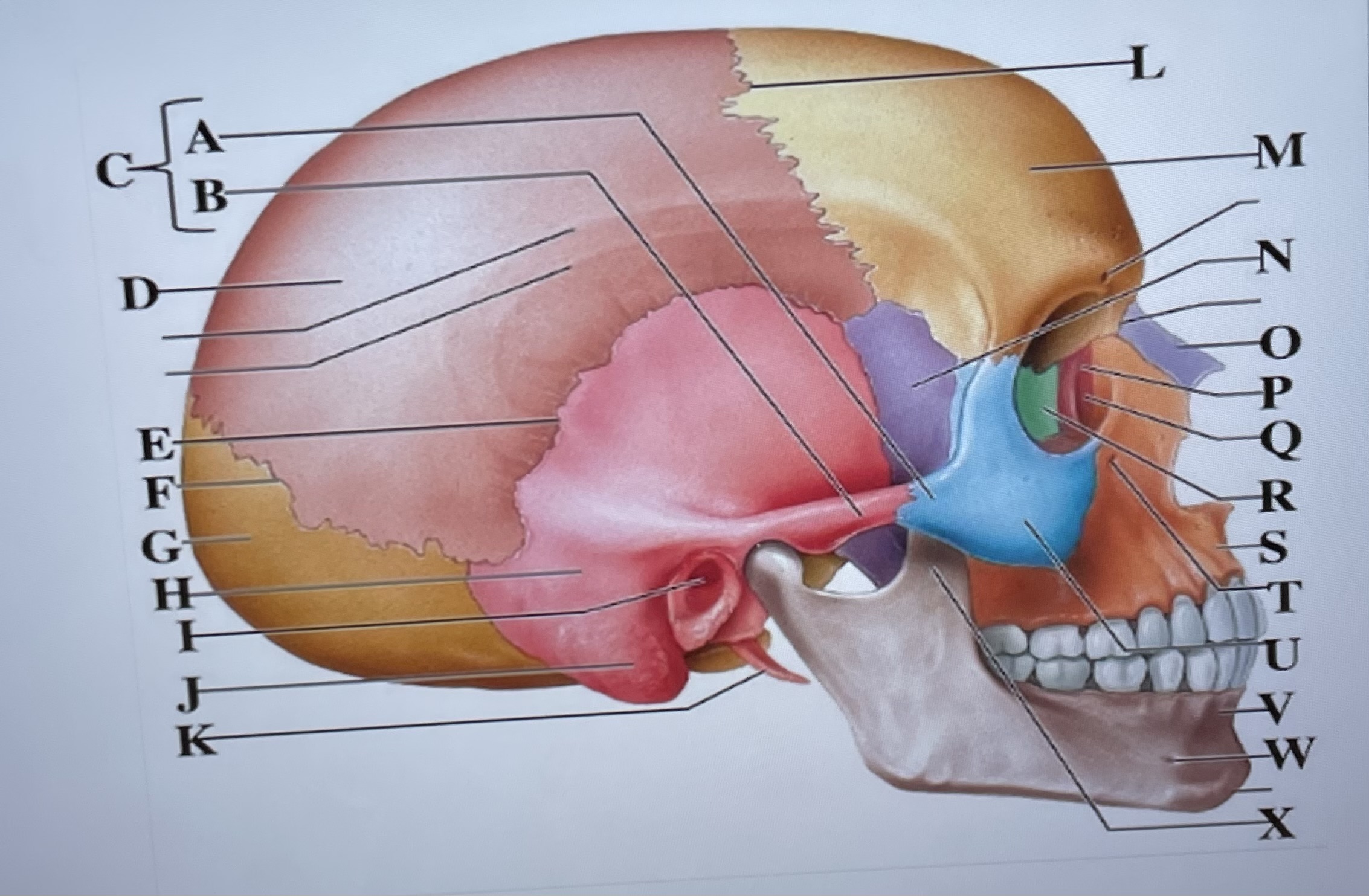
lacrimal groove
Q
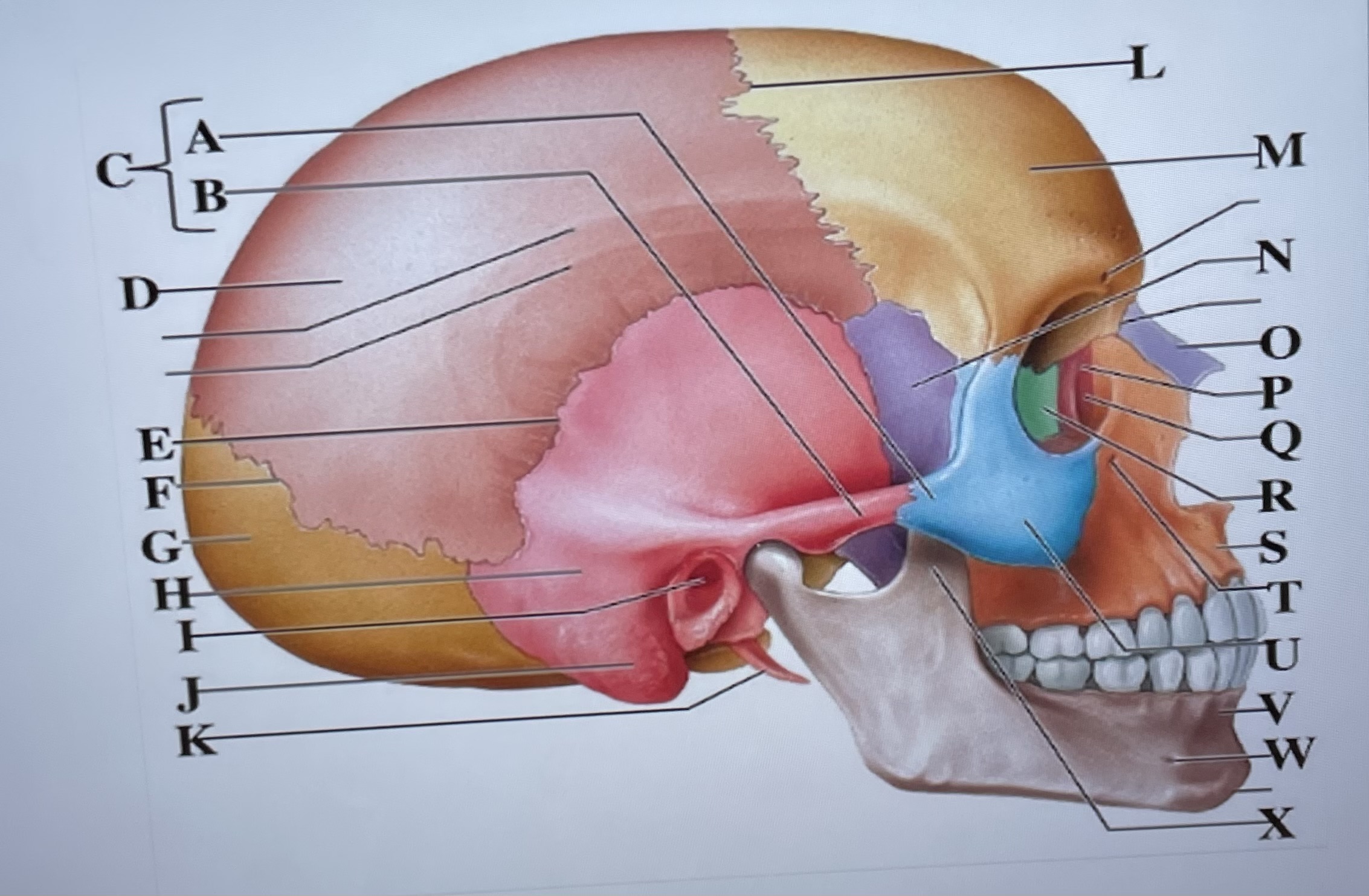
ethmoid
R
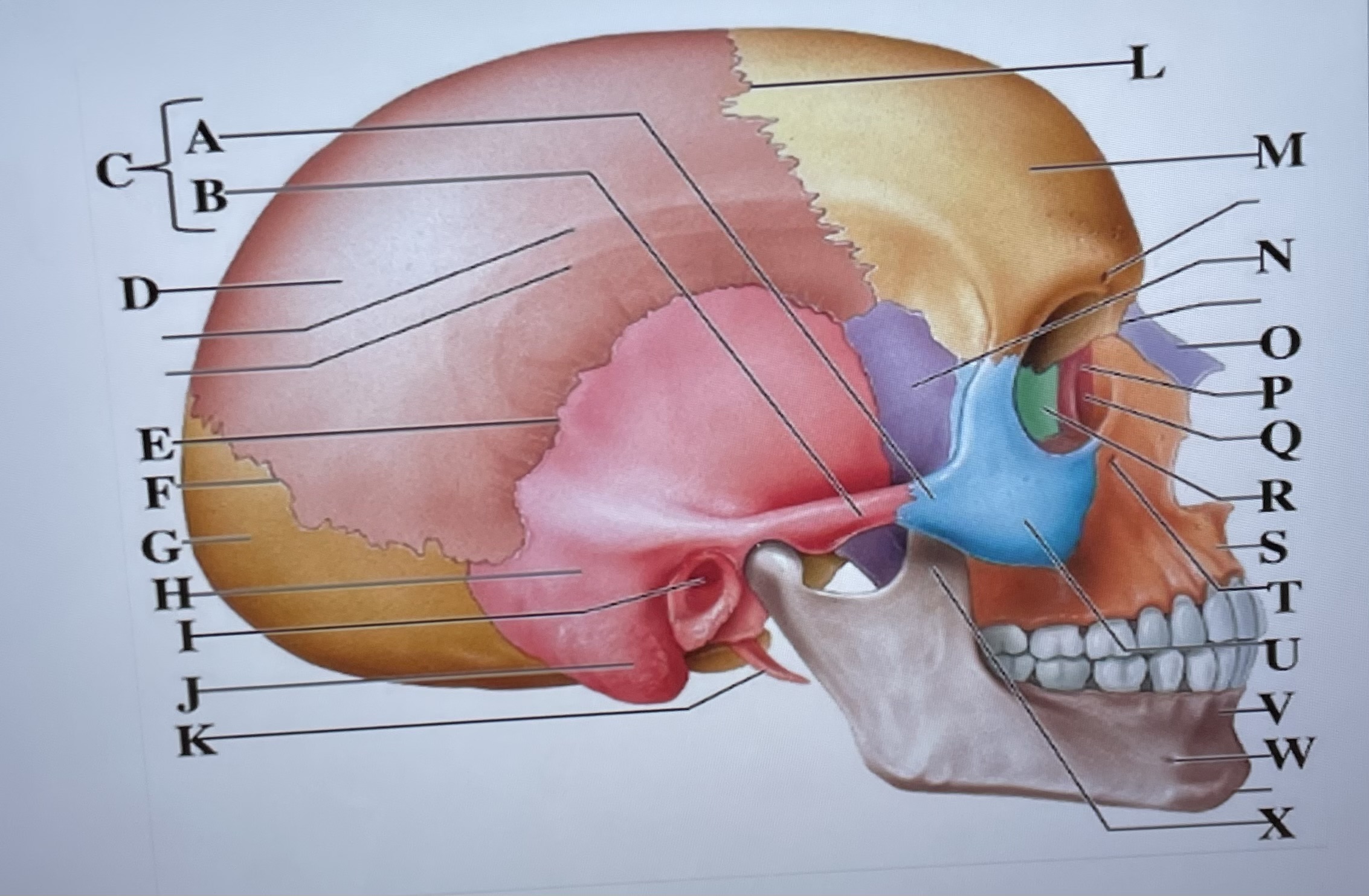
maxilla
S
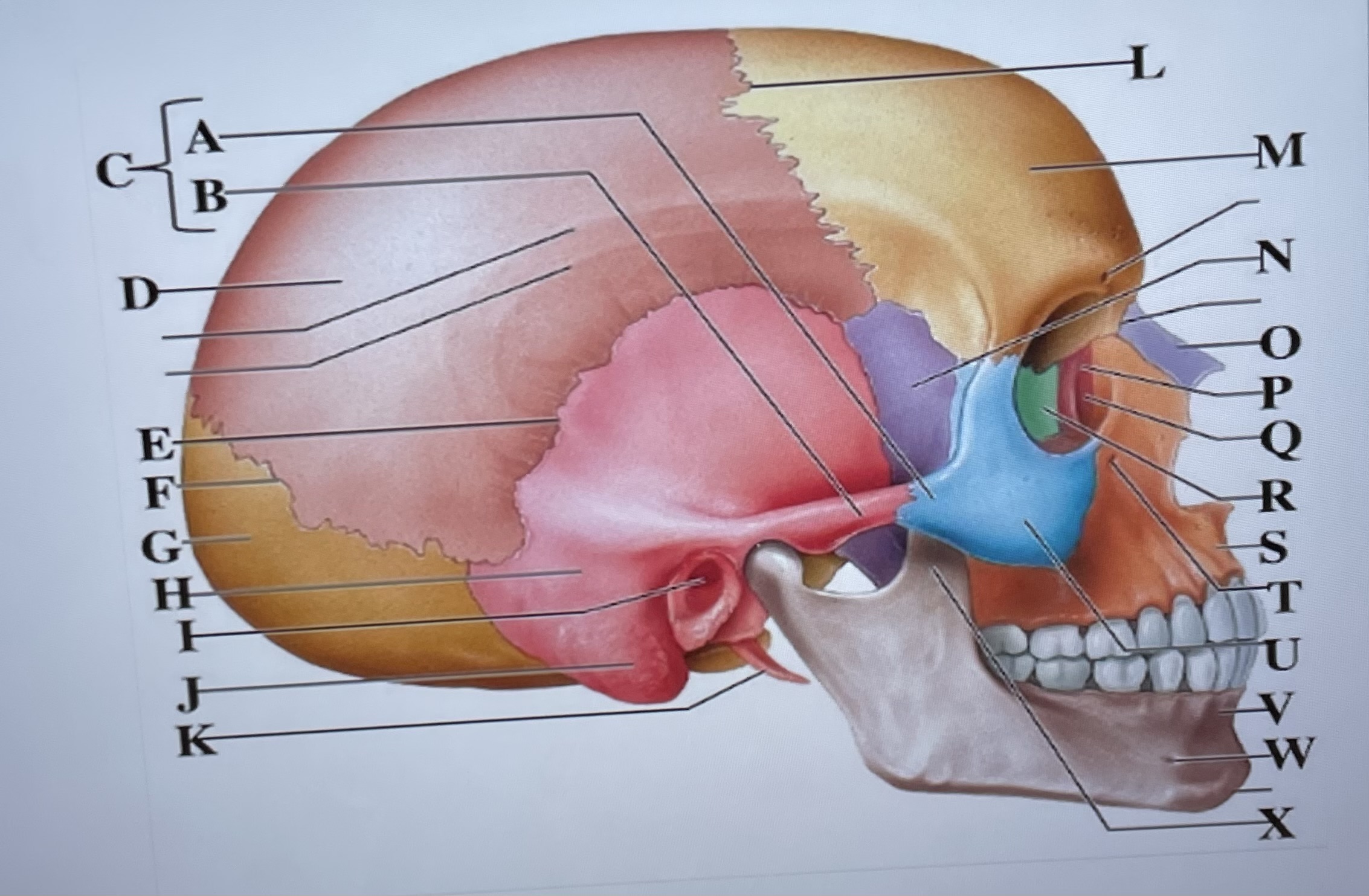
infraorbital foramen
T
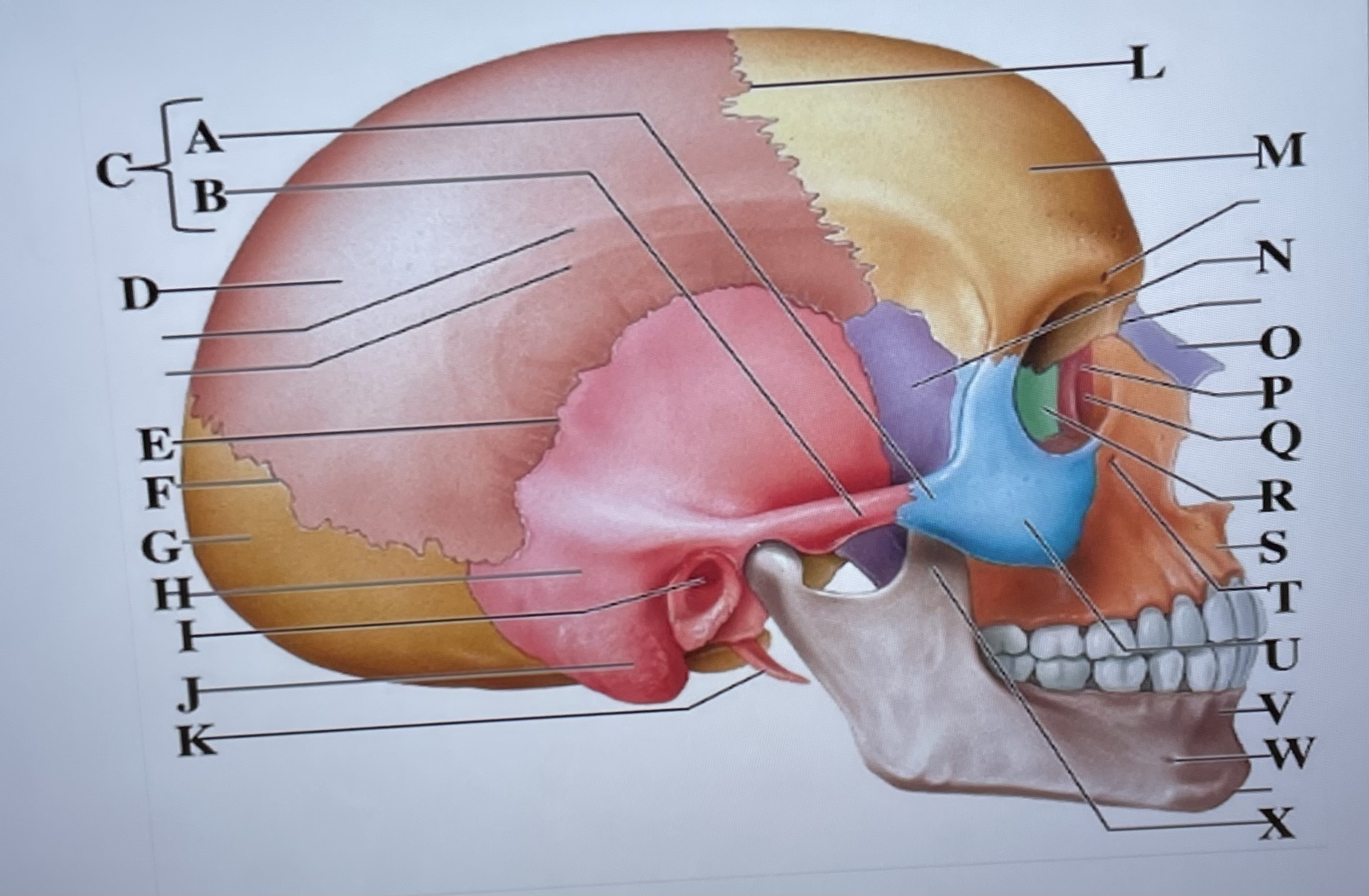
zygomatic bone
U
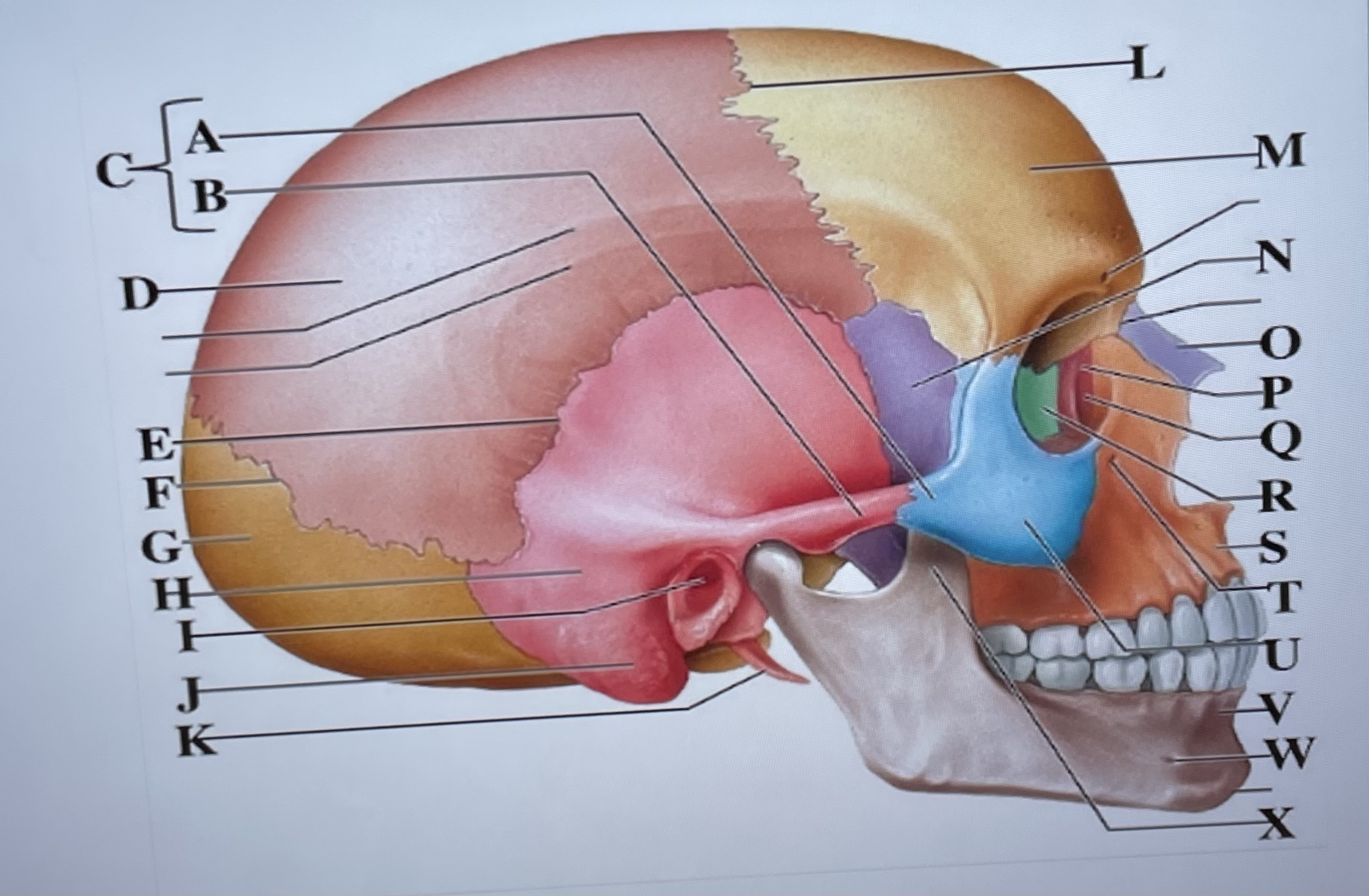
mandible
V
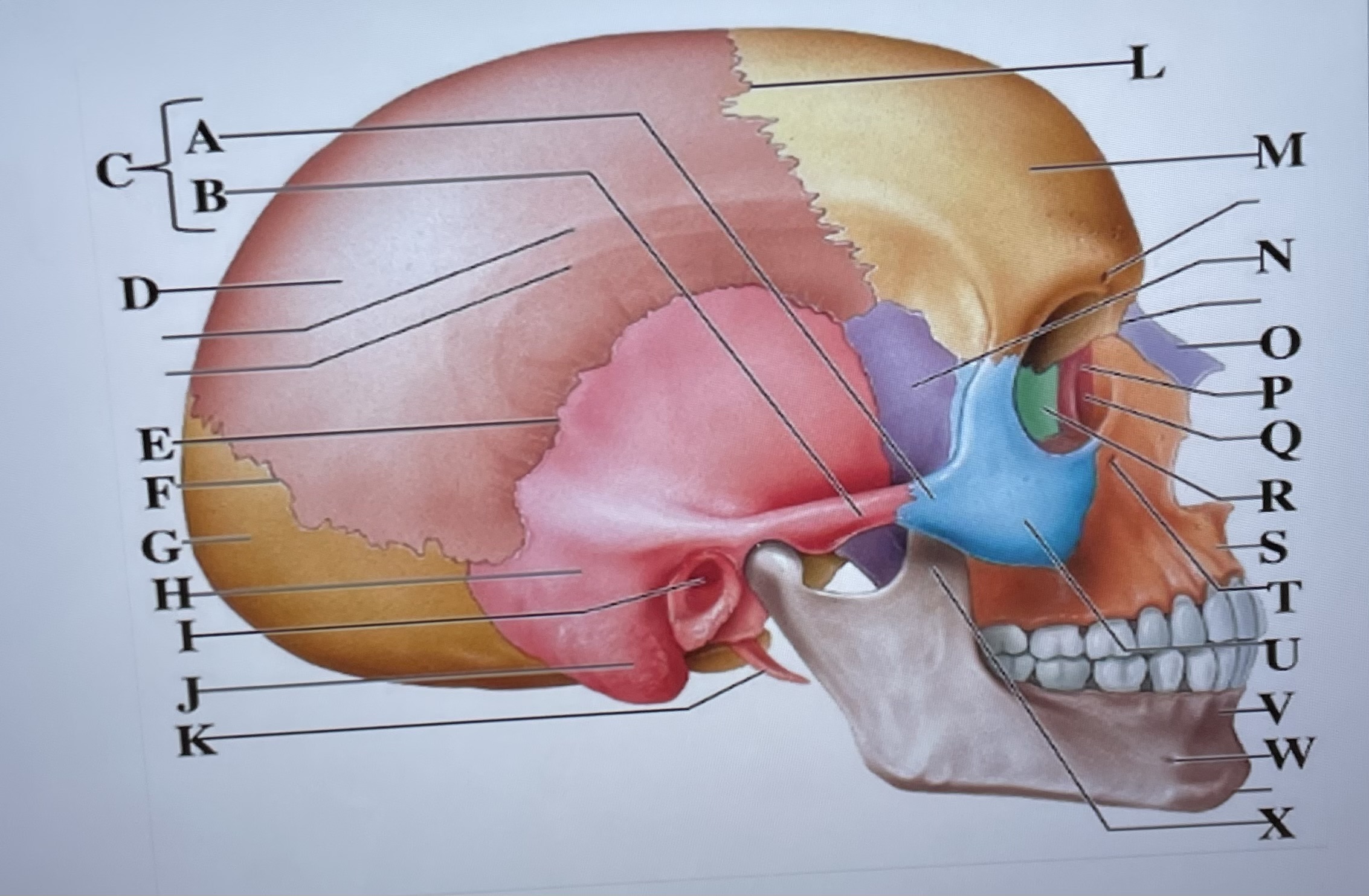
mental foramen
W
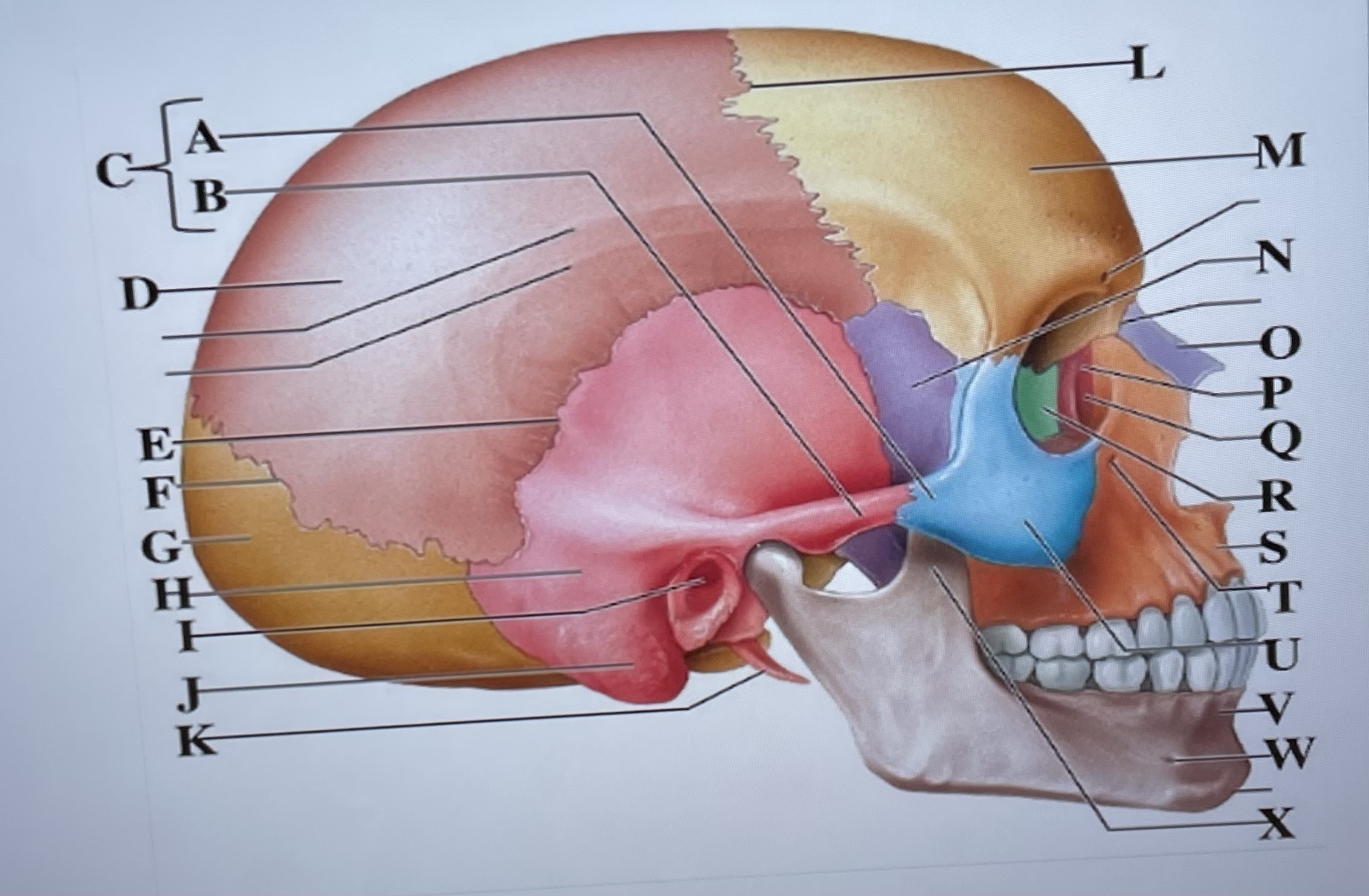
coronoid process
X
sternum
A
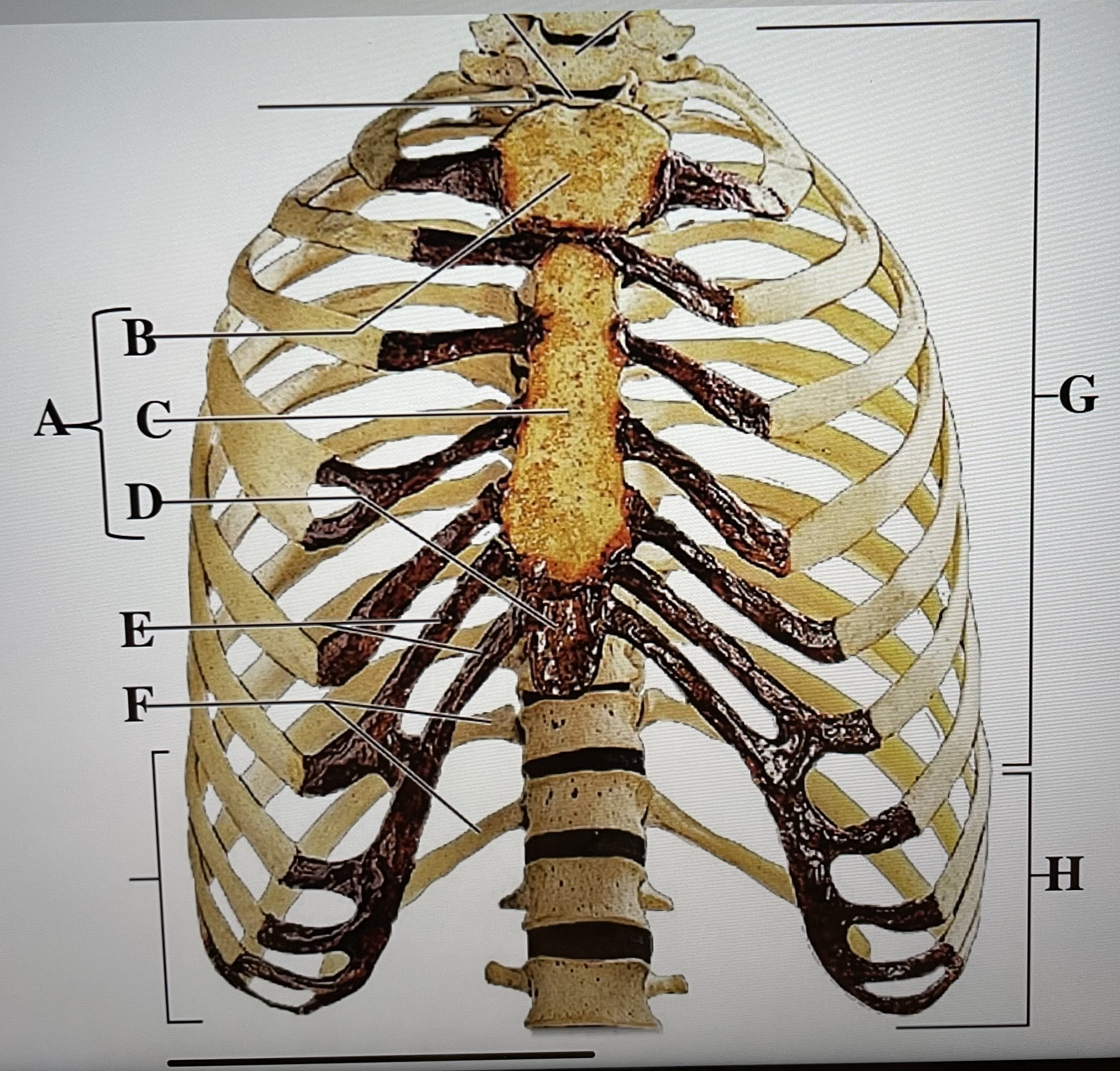
manubrium
B
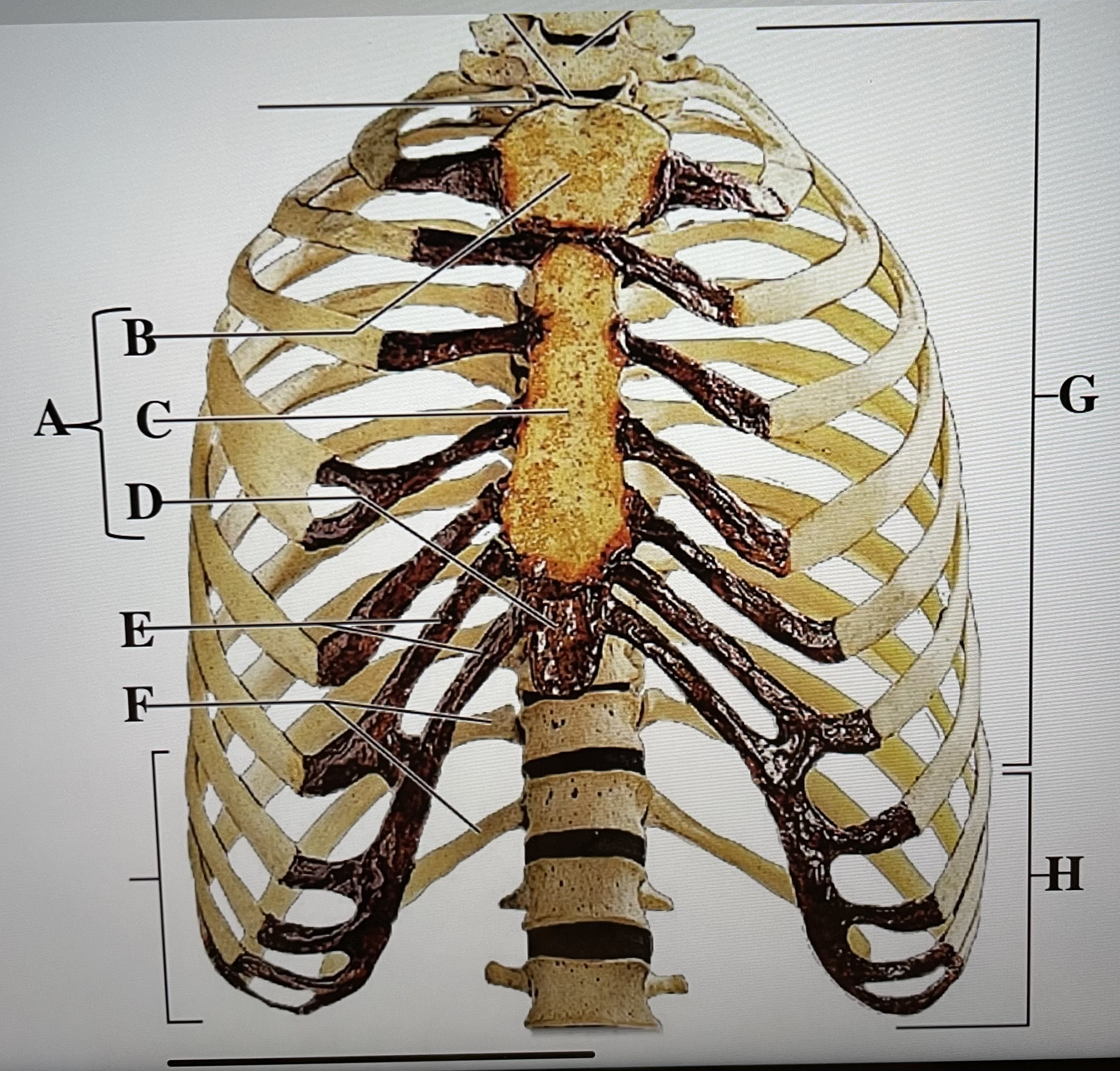
body of sternum
C
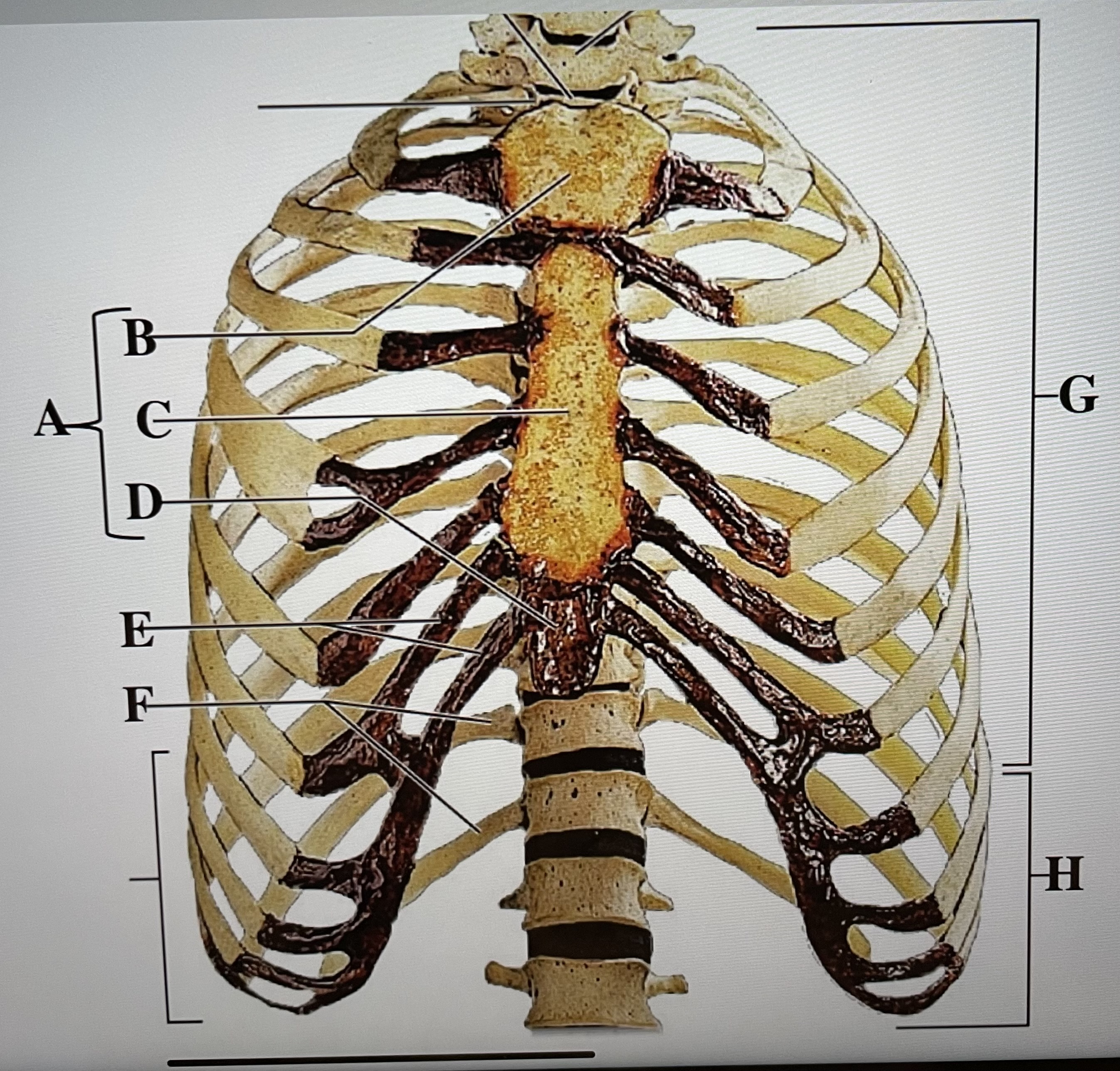
xiphoid process
D
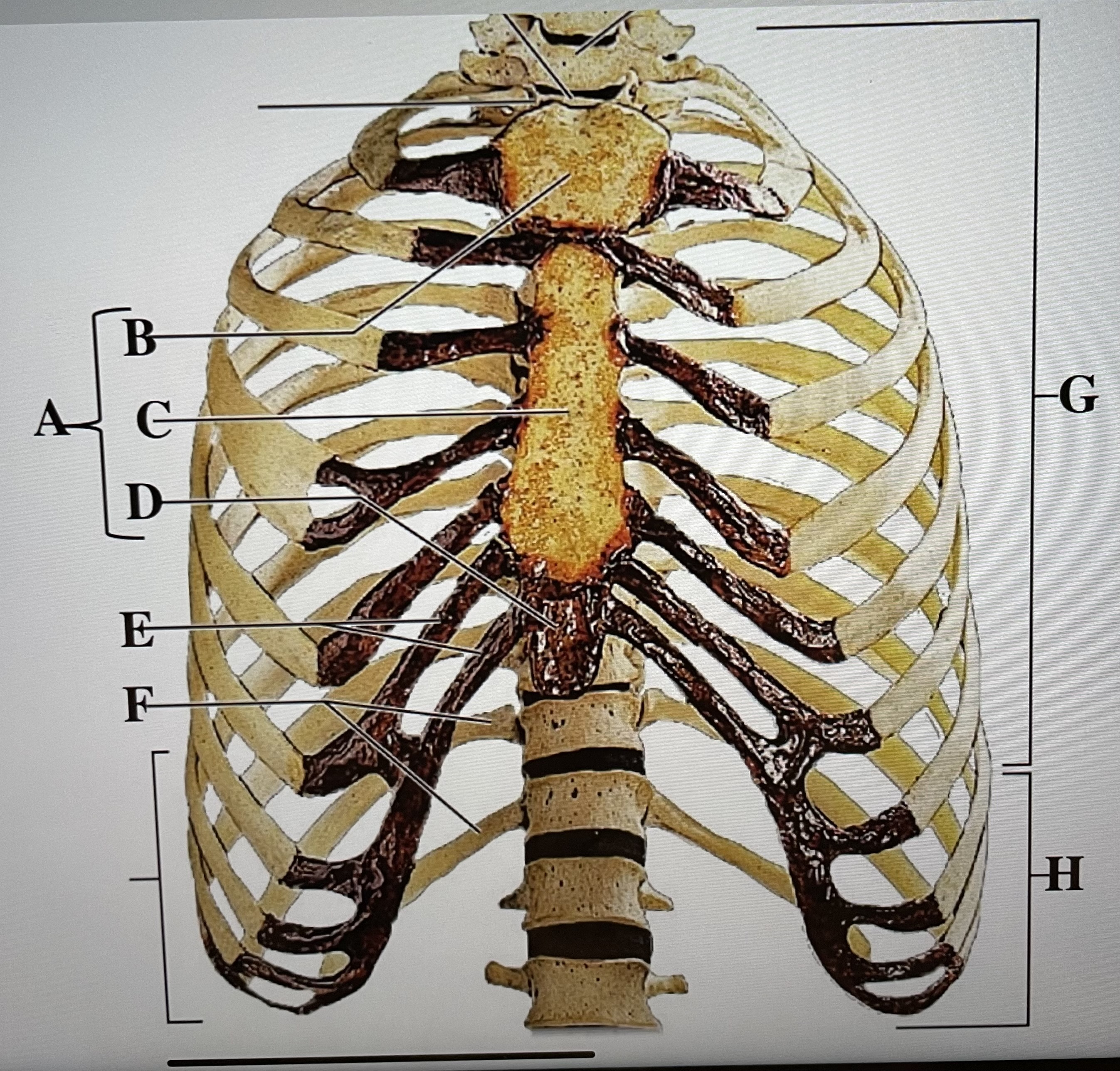
costal cartilages
E
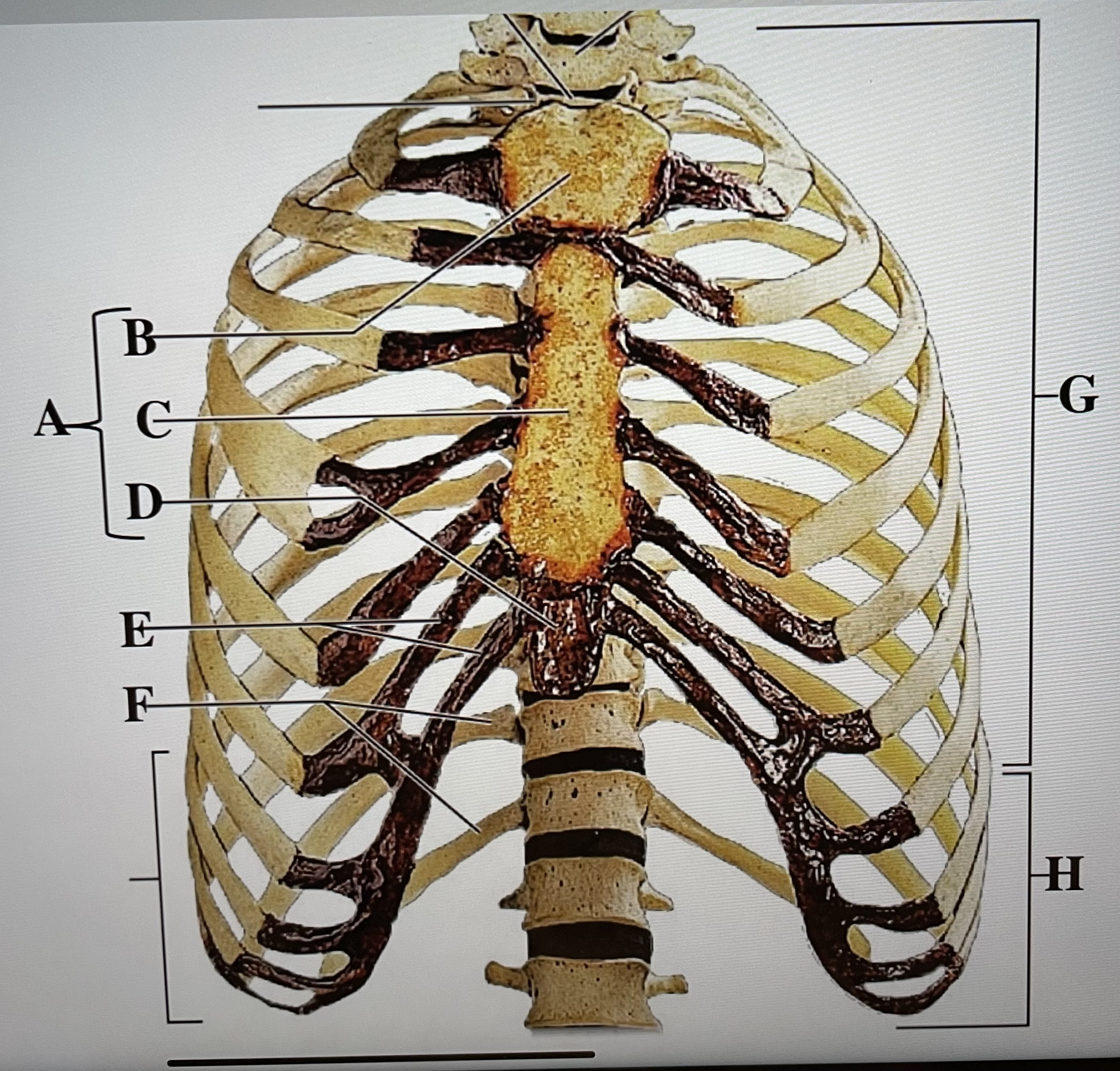
floating ribs (11-12)
F
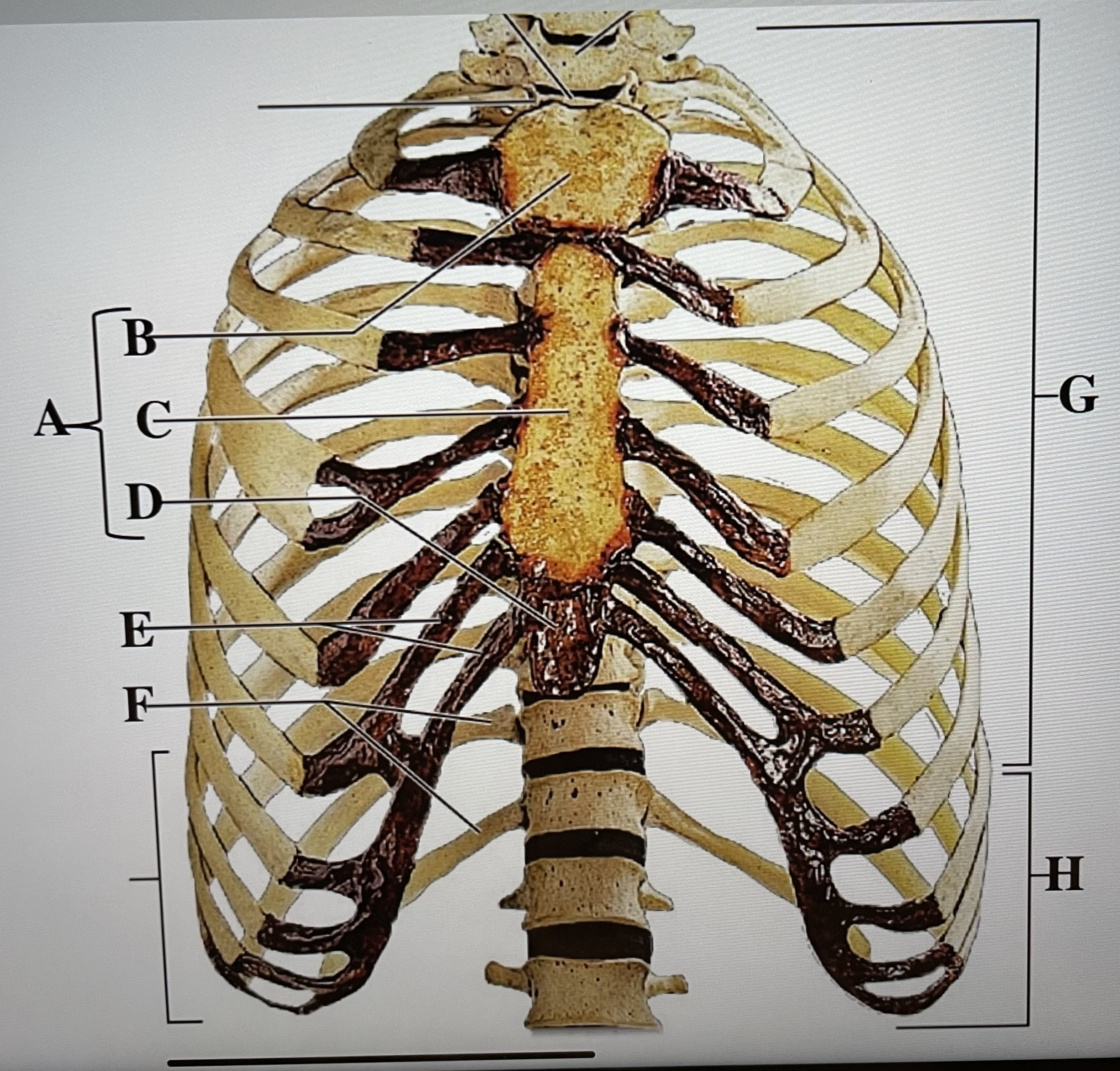
true ribs (1-7)
G
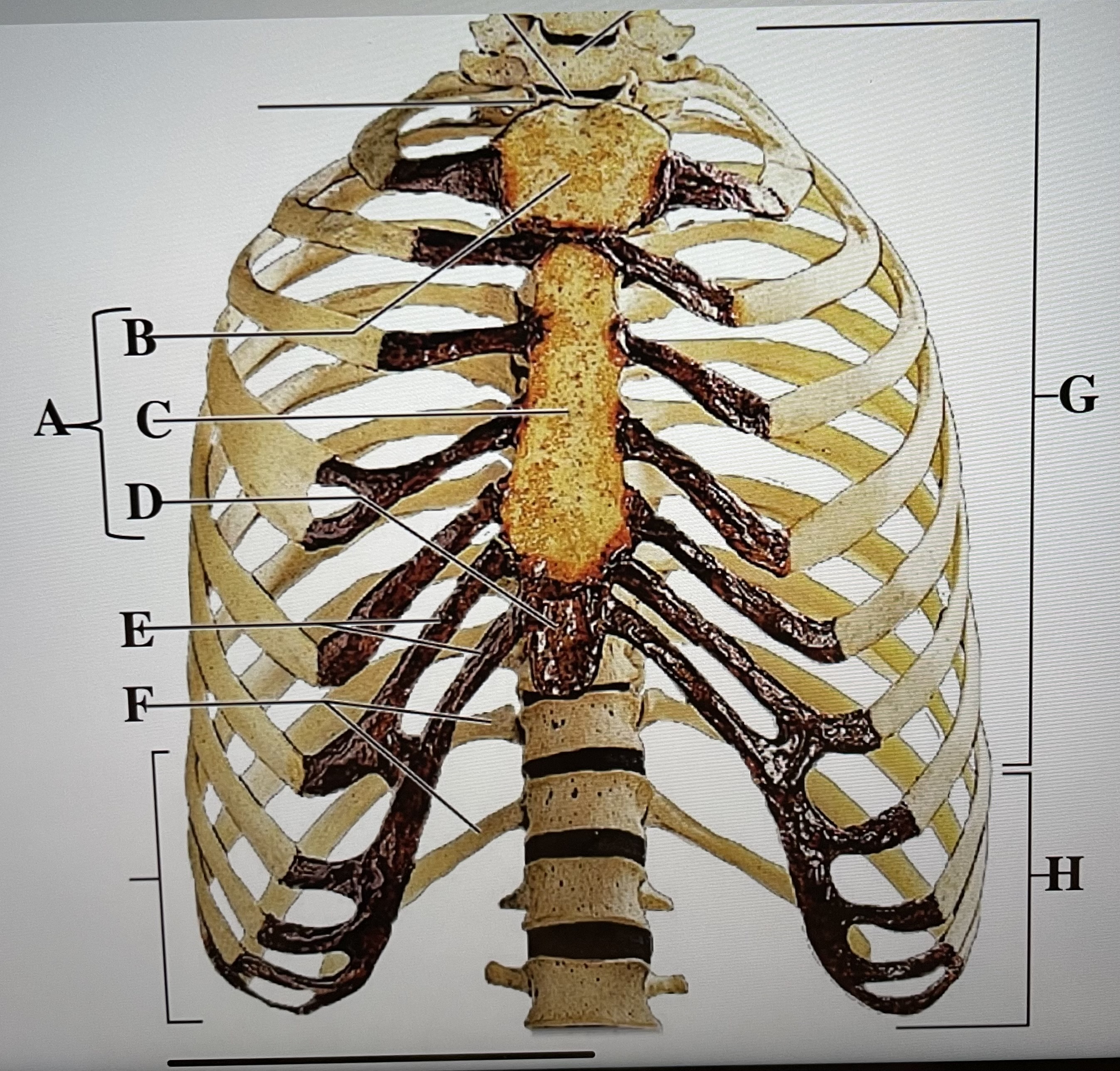
false ribs (8-12)
H
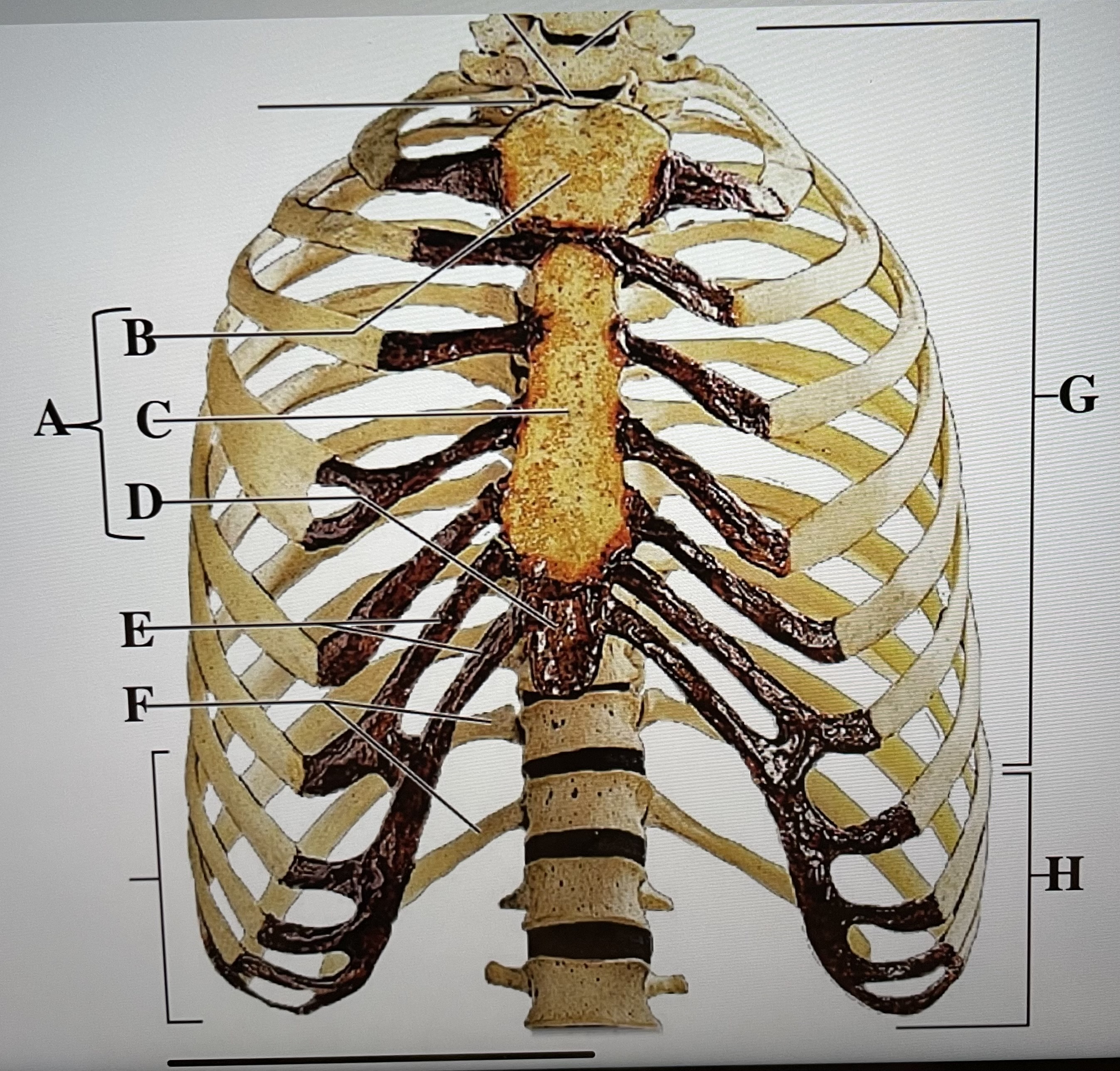
hyoid
A
frontal
B
coccyx
C
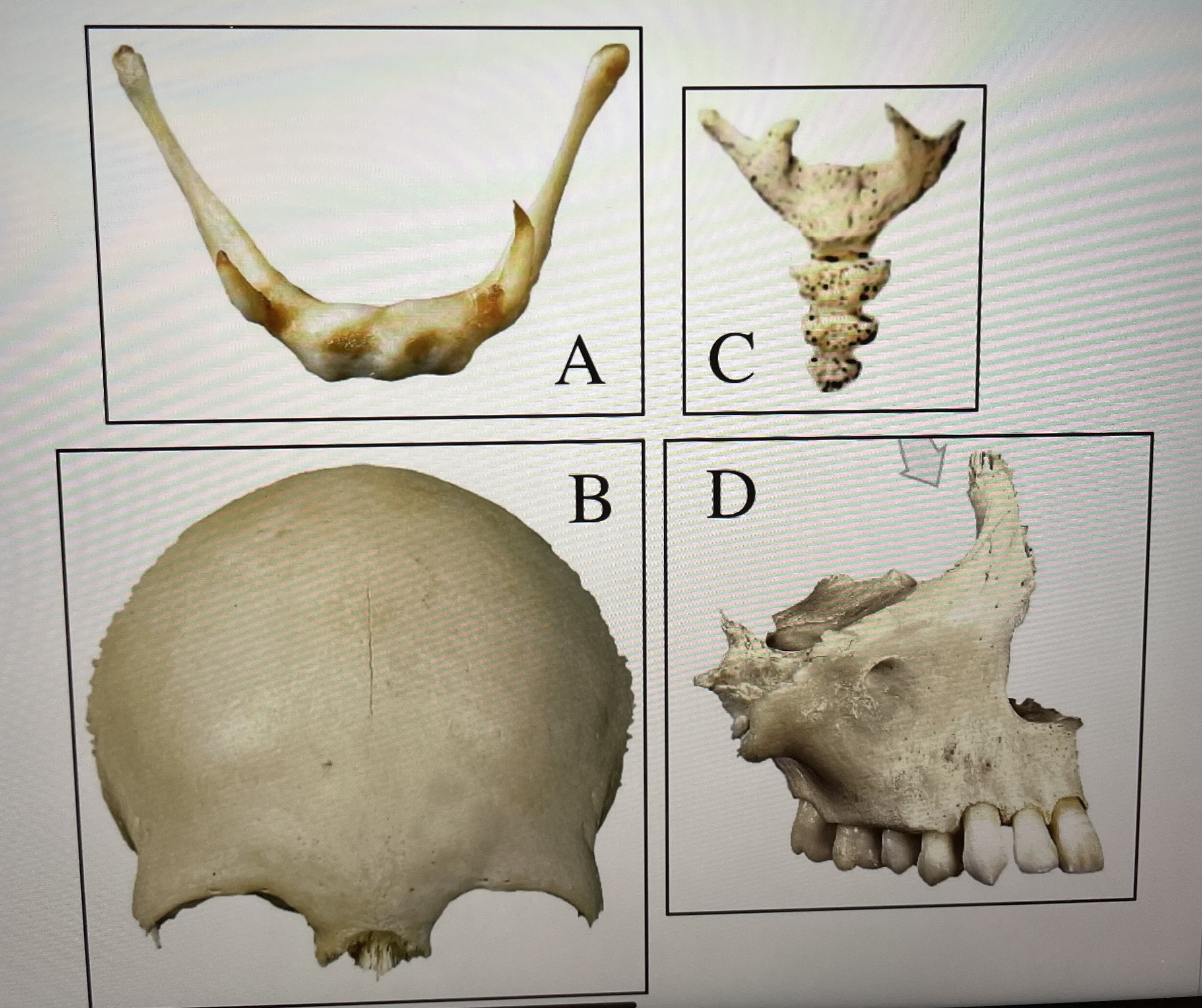
maxillae
D
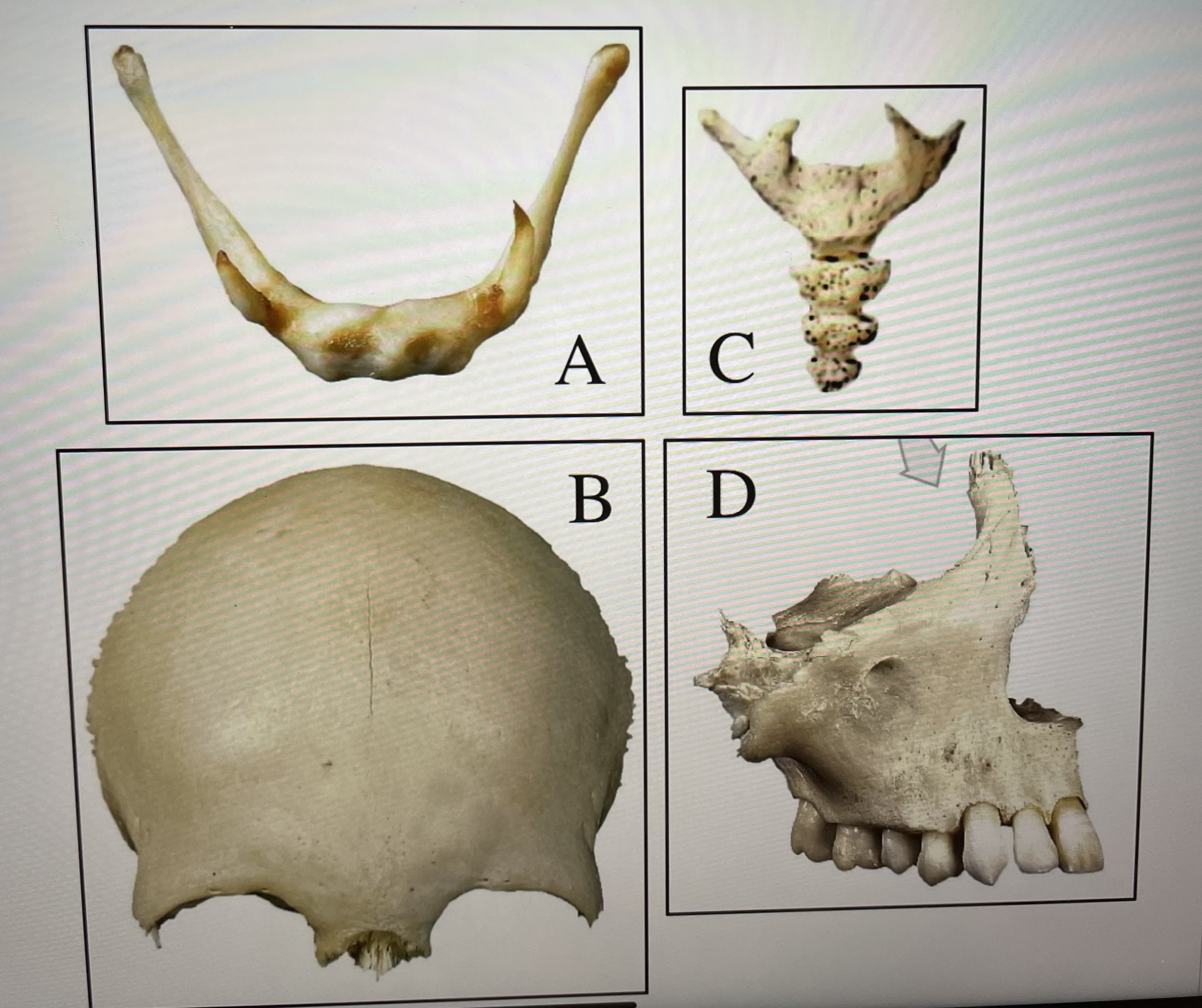
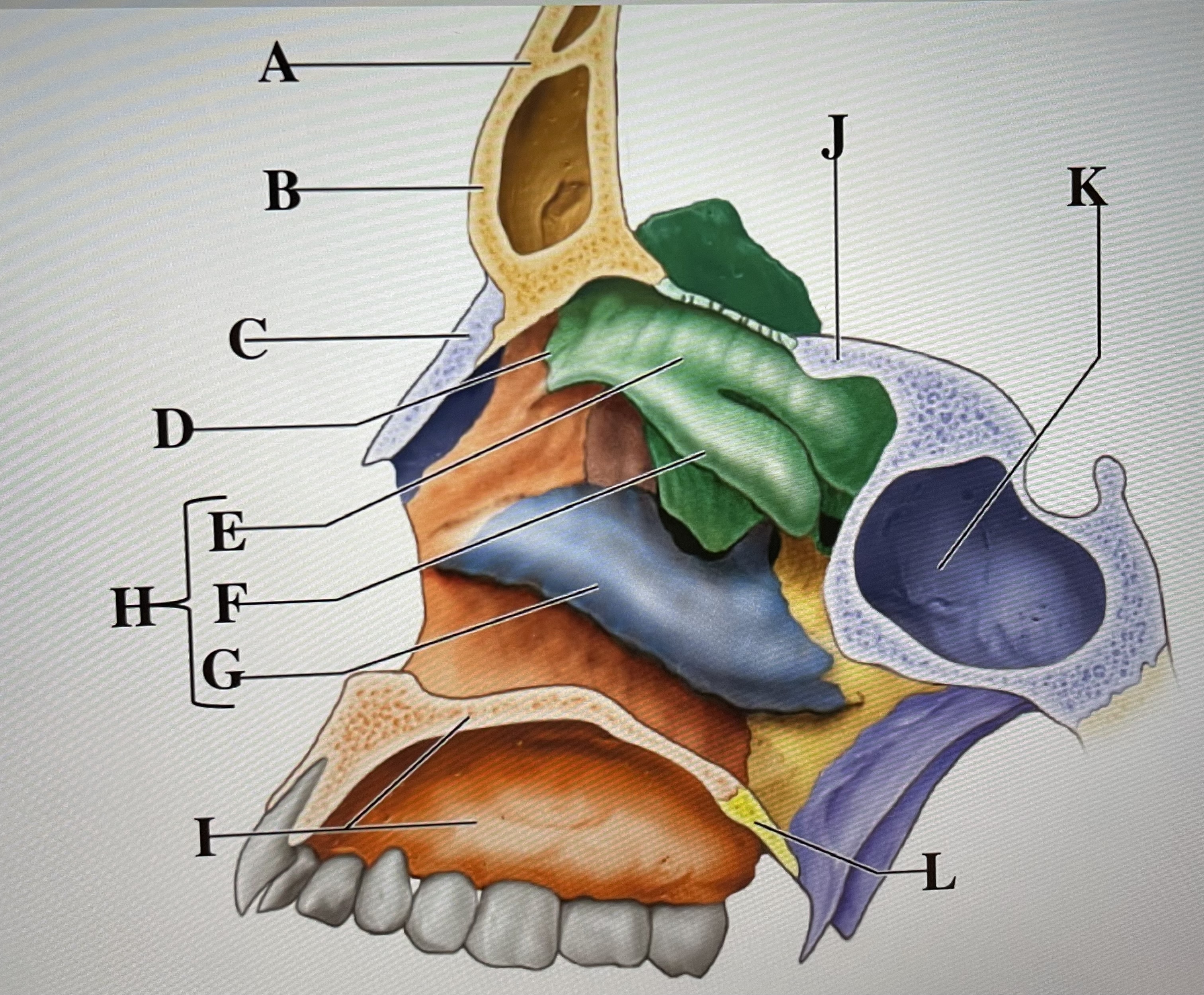
frontal bone
A
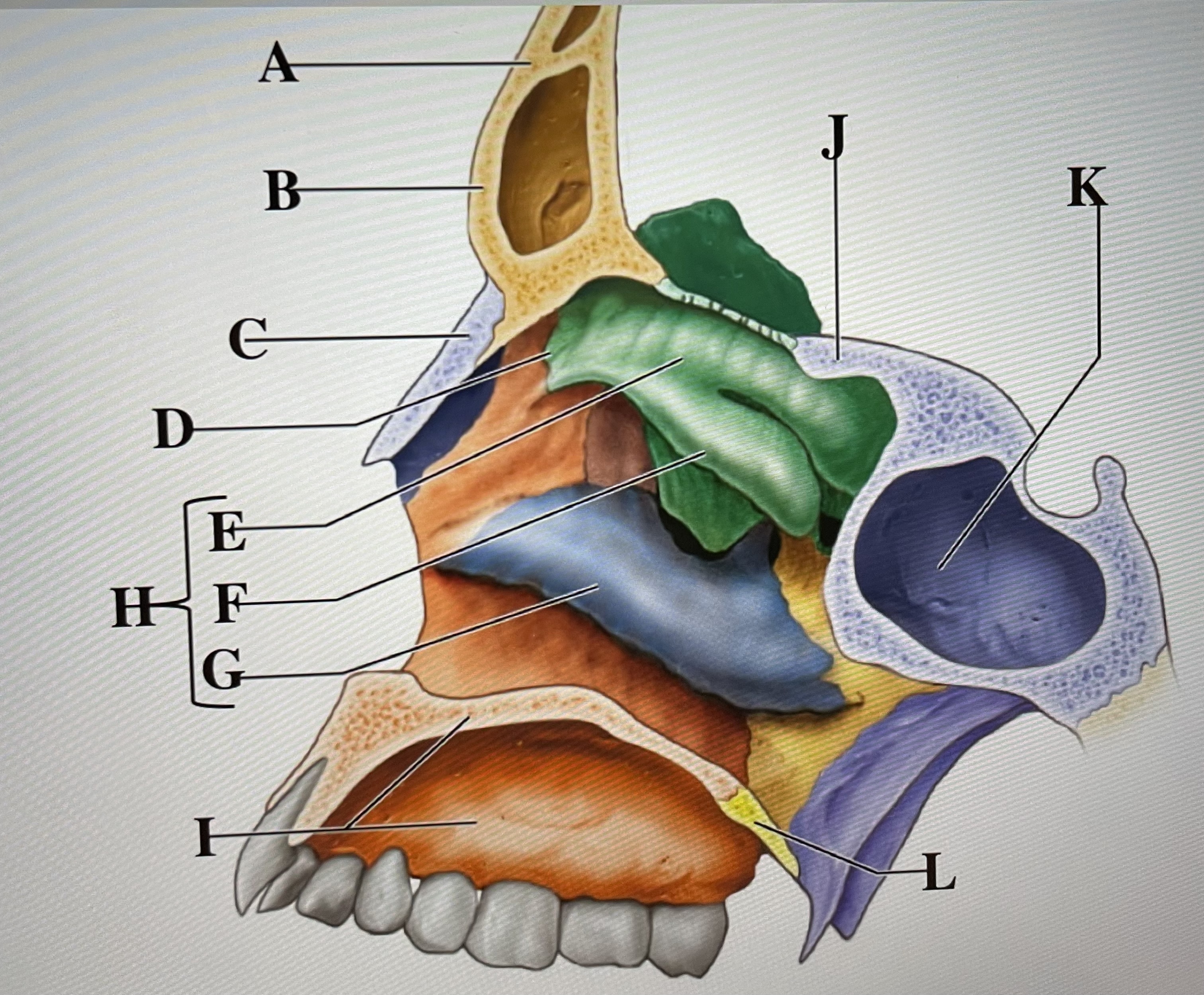
frontal sinus
B
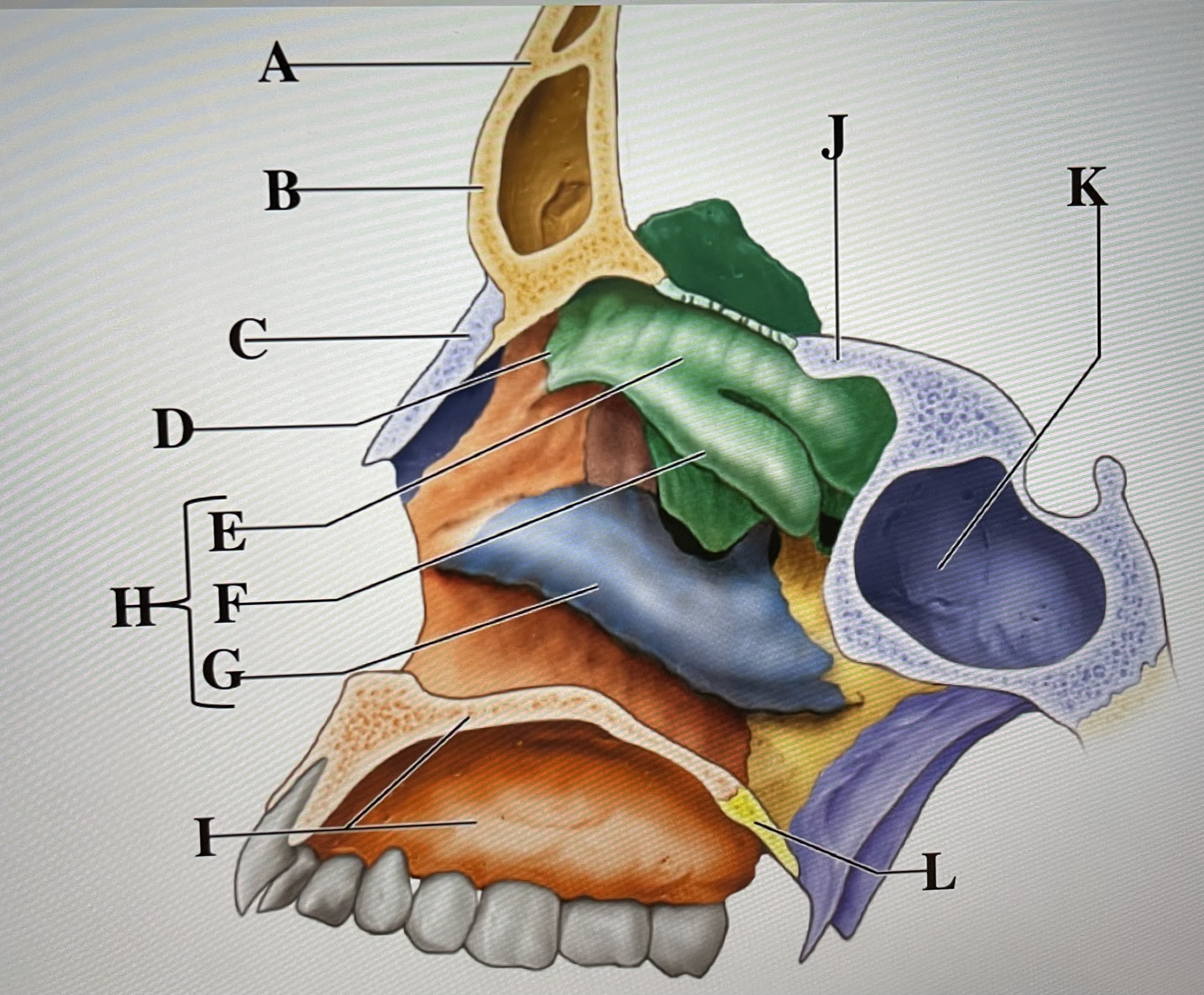
Nasal bone
C
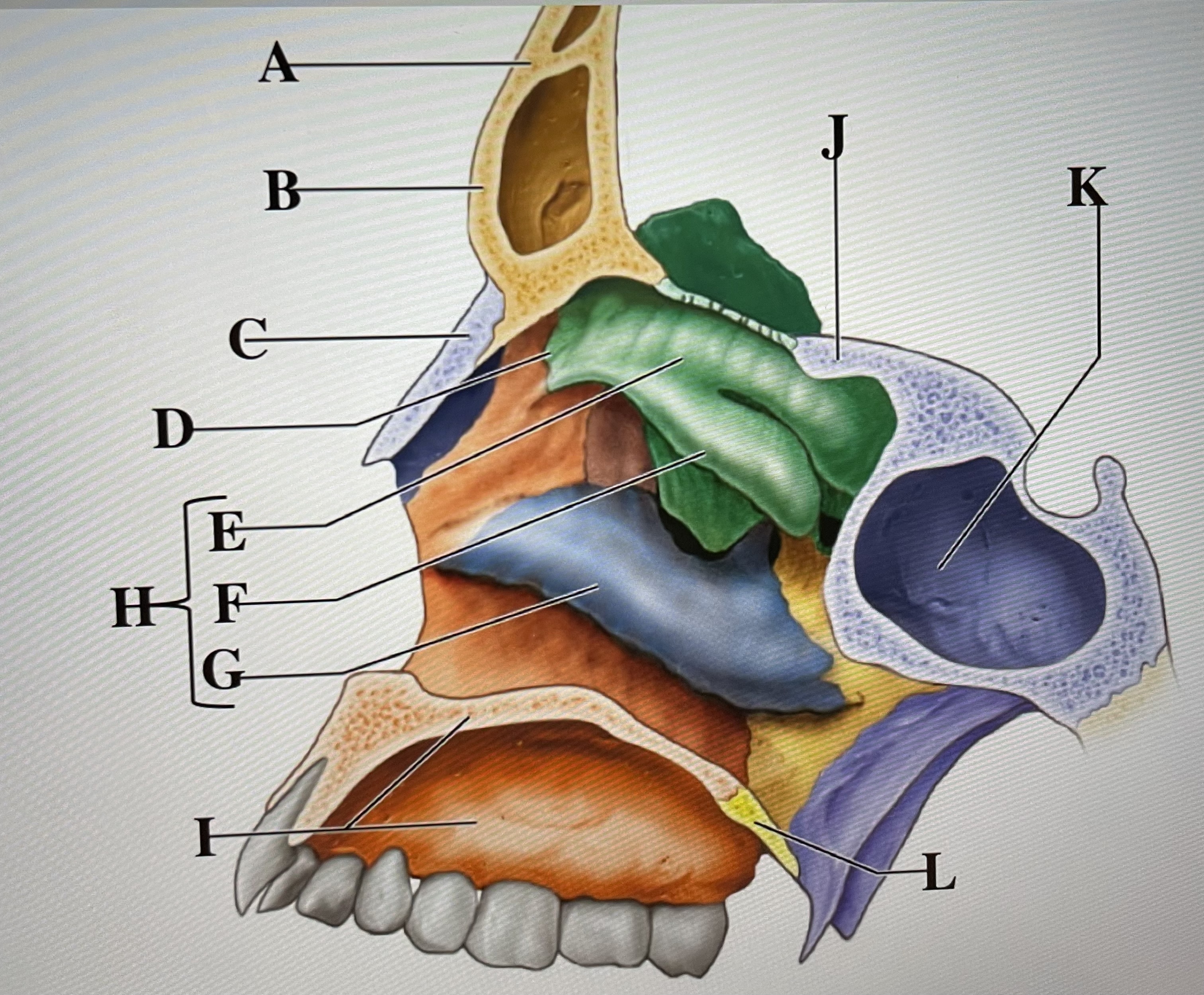
ethmoid
D
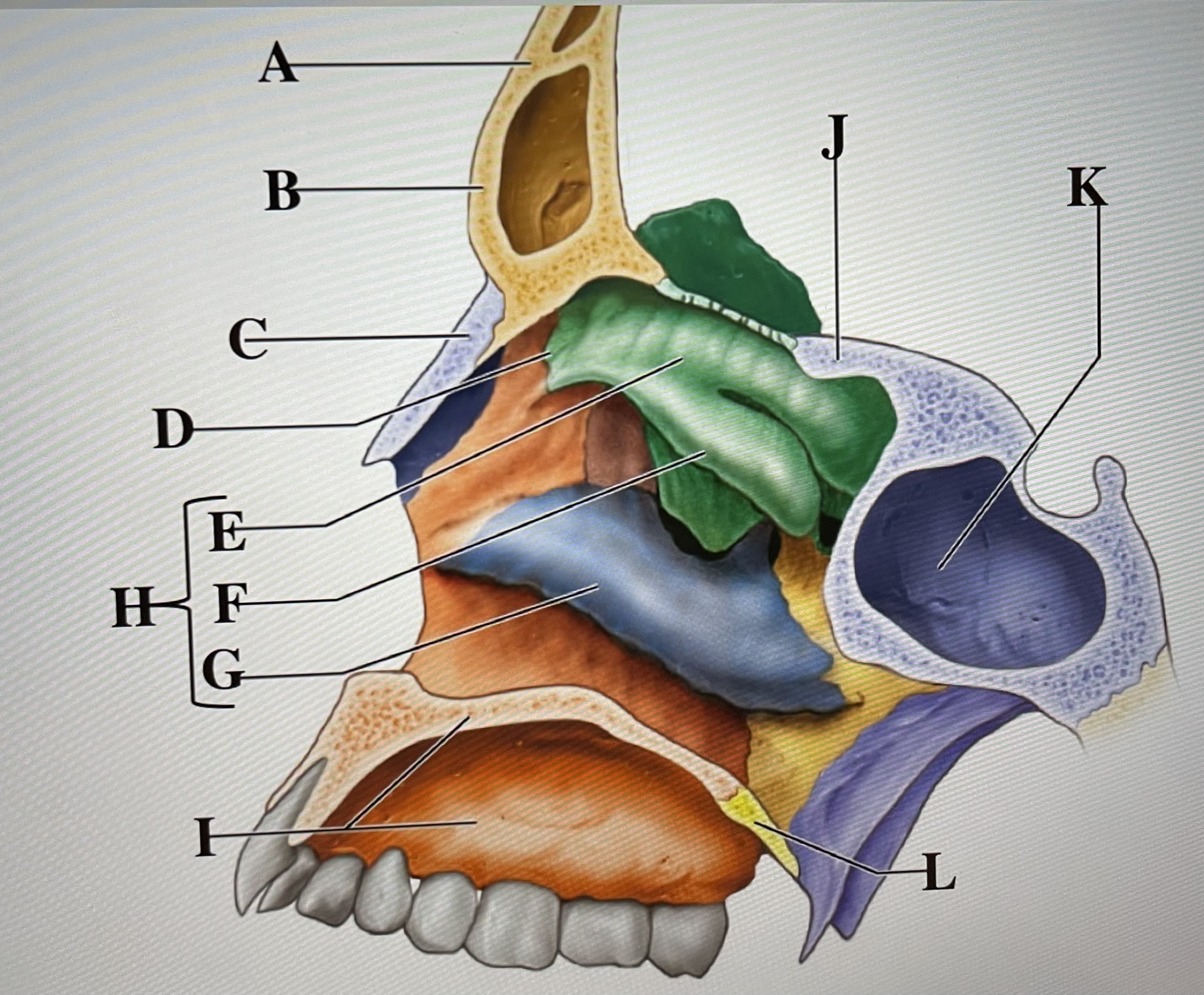
superior conchae
E
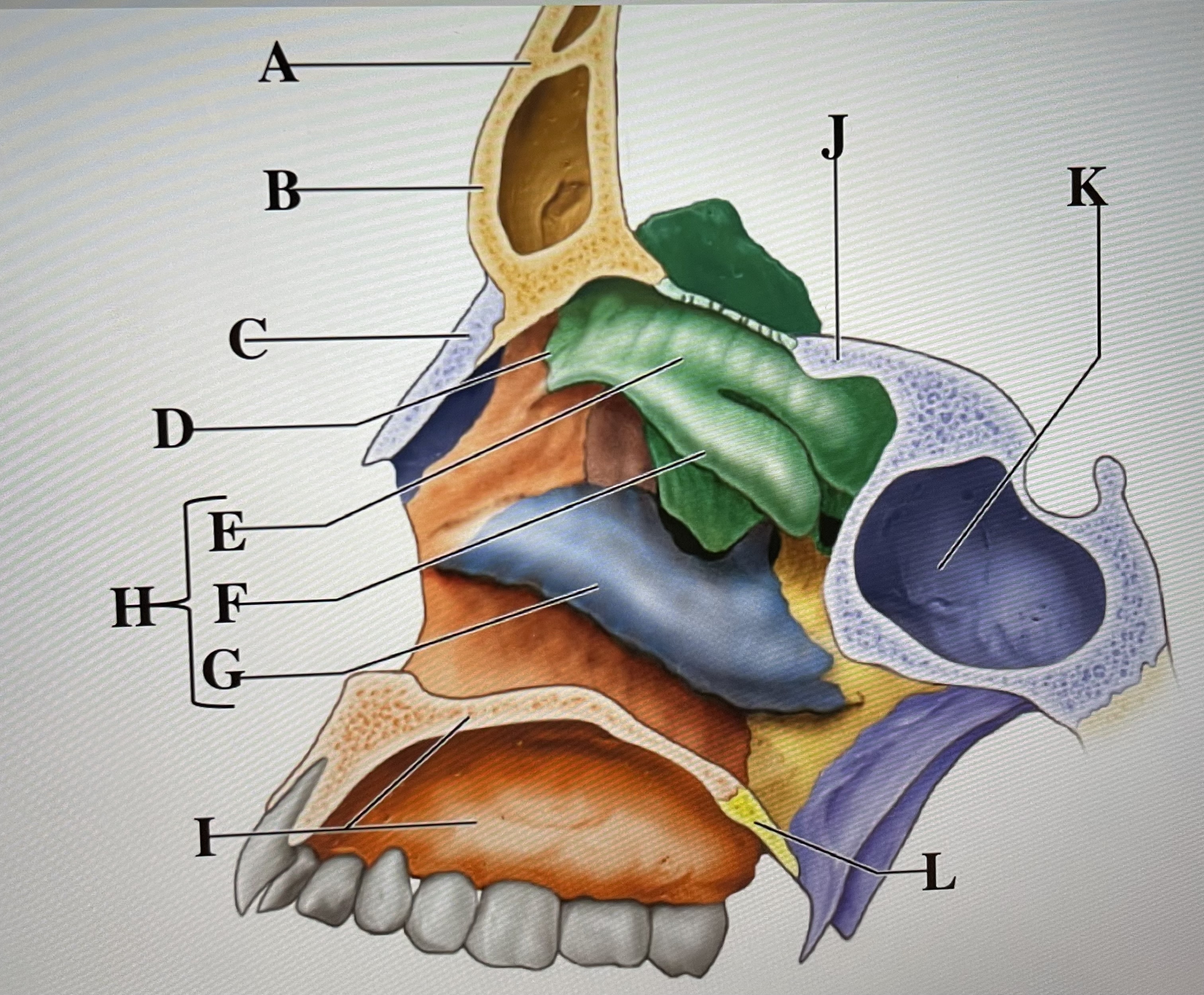
middle conchae
F
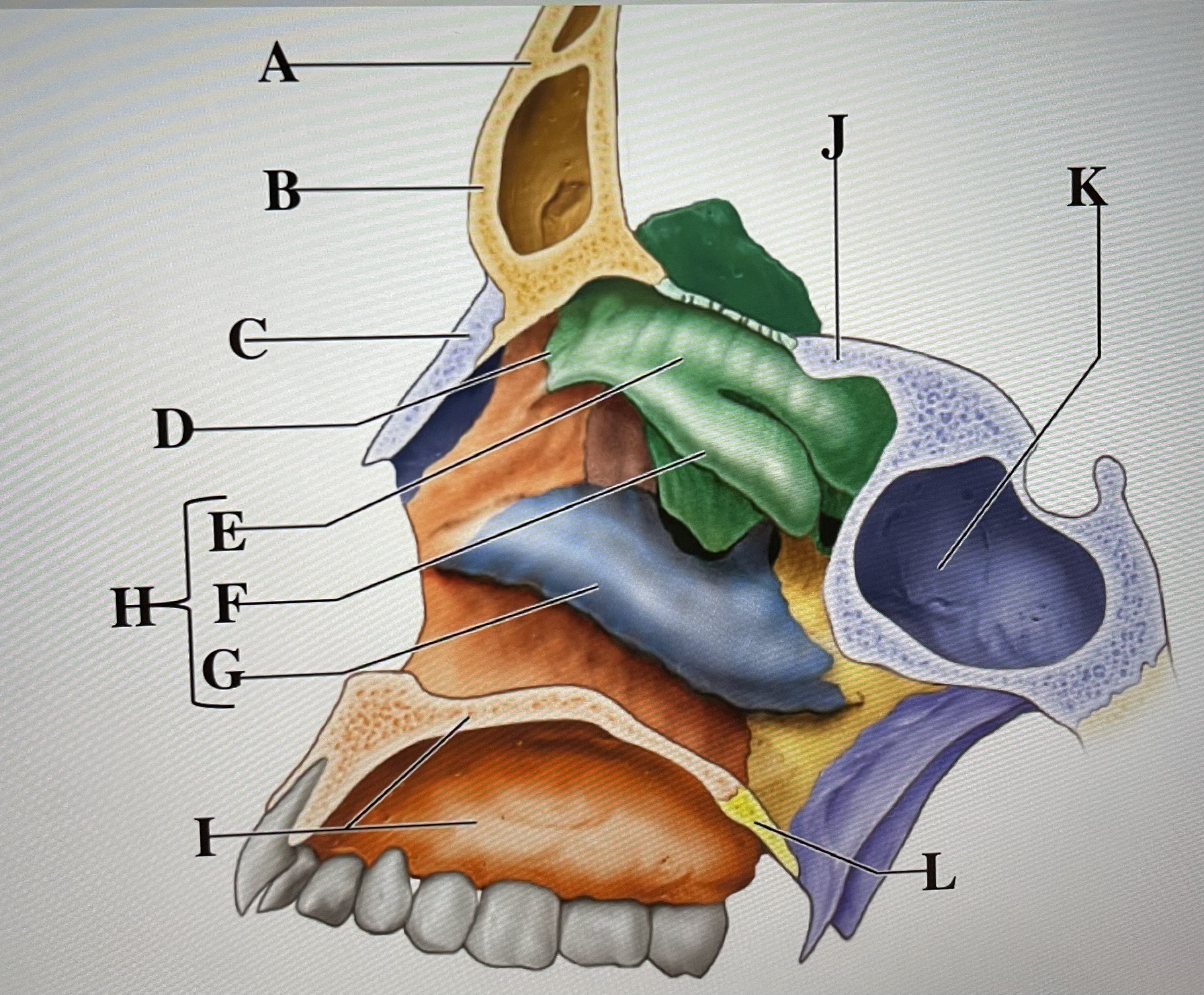
Inferior conchae
G
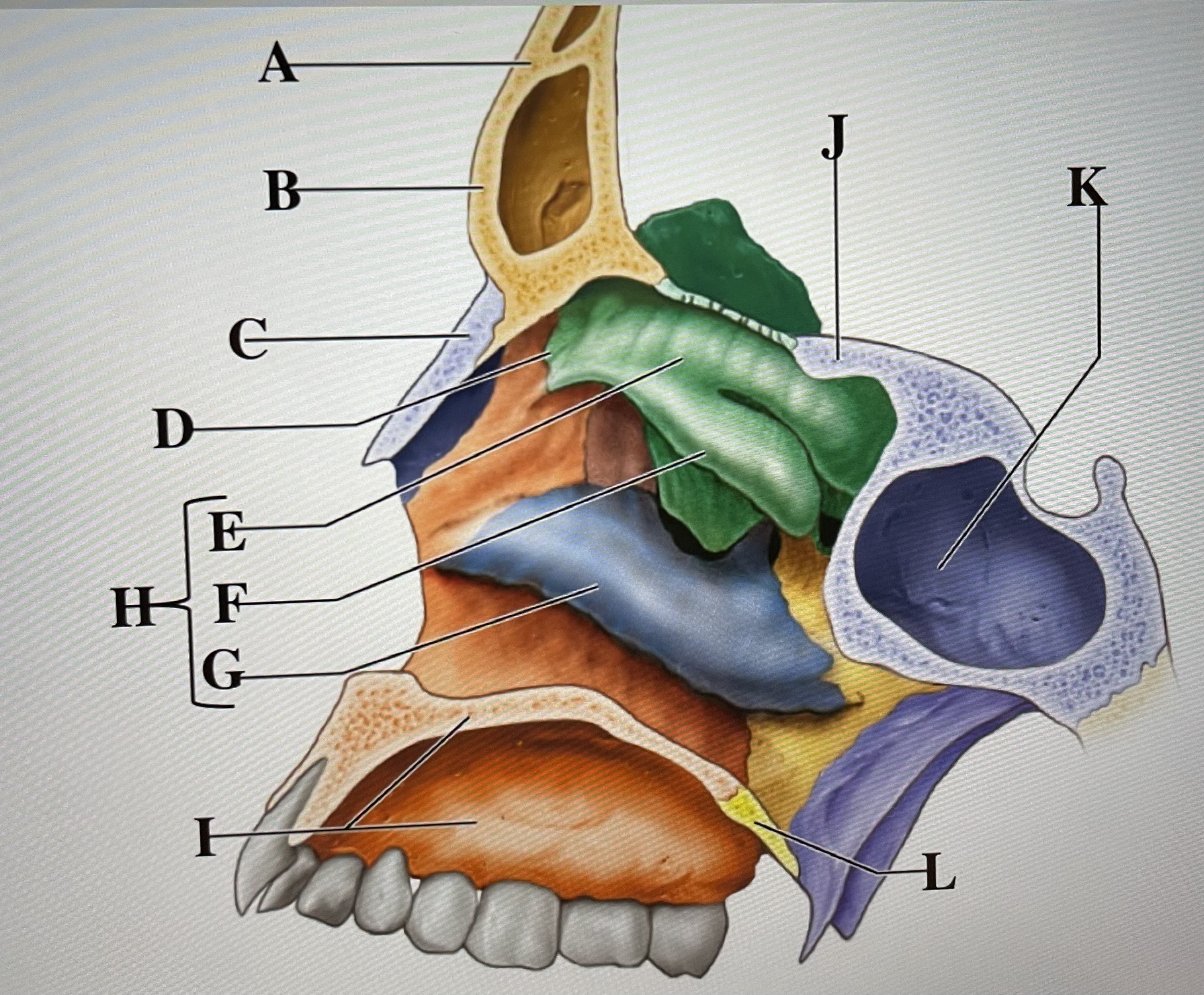
Nasal conchae
H
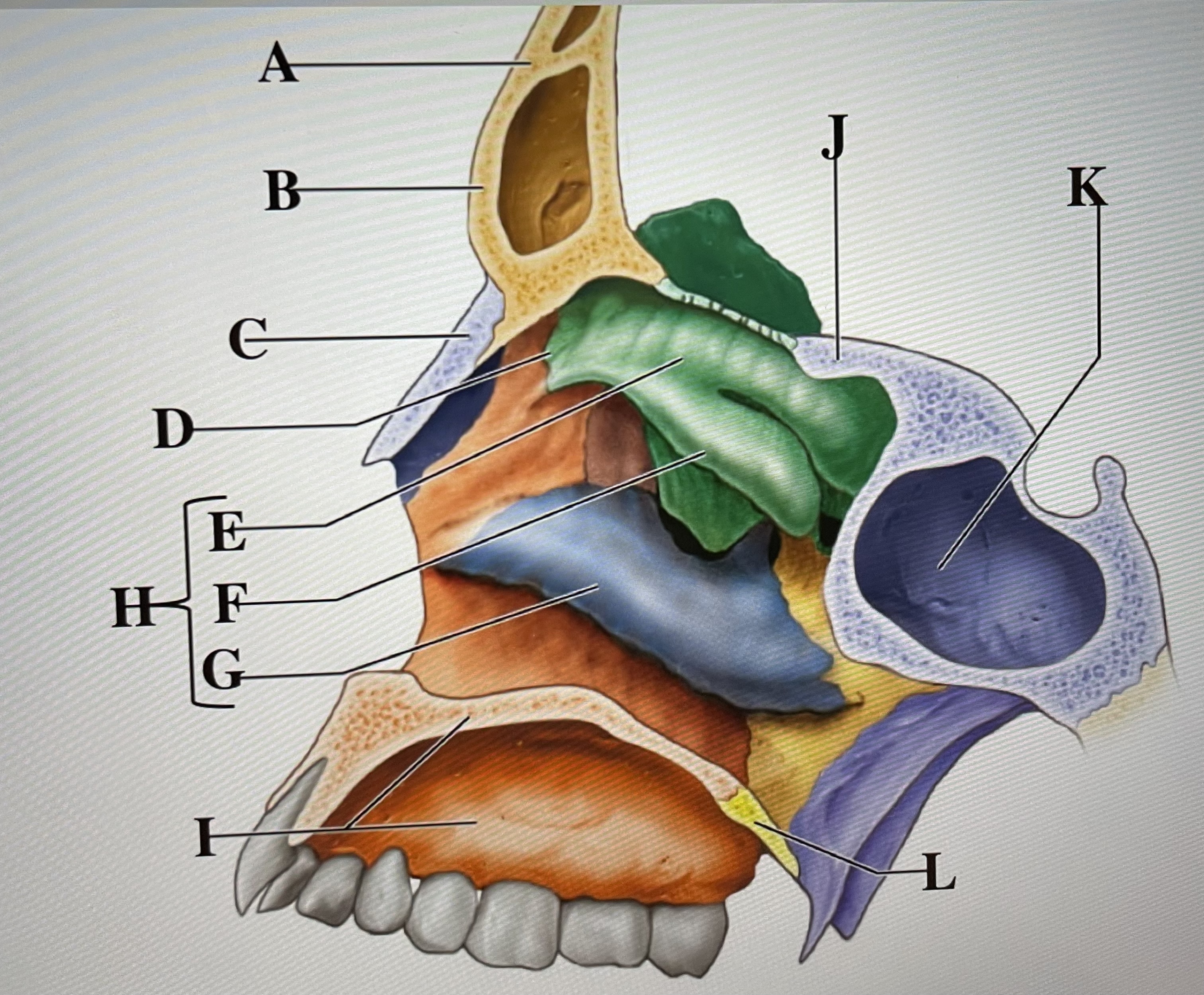
maxilla (bony palate)
I
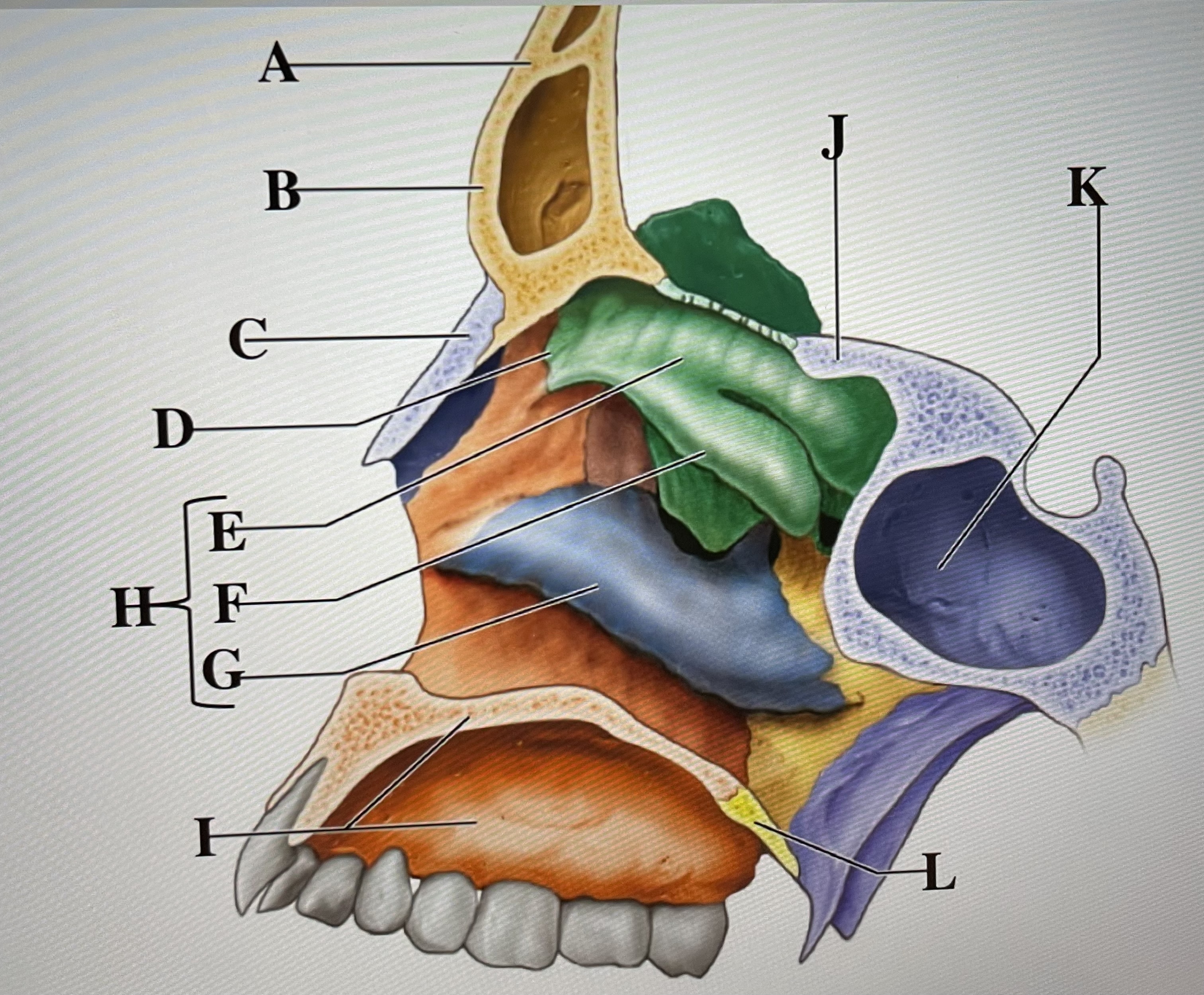
sphenoid
J
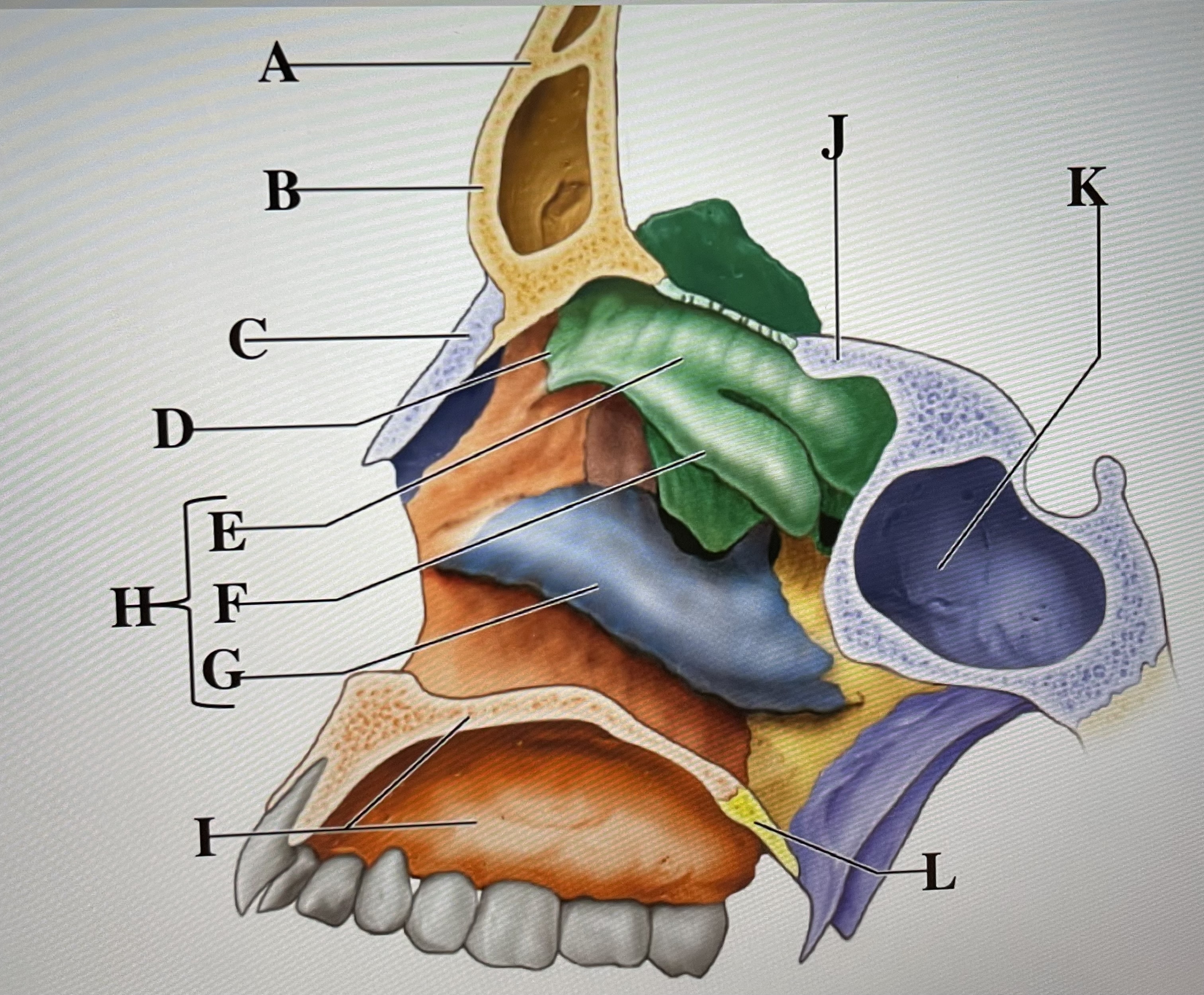
sphenoidal sinus
K
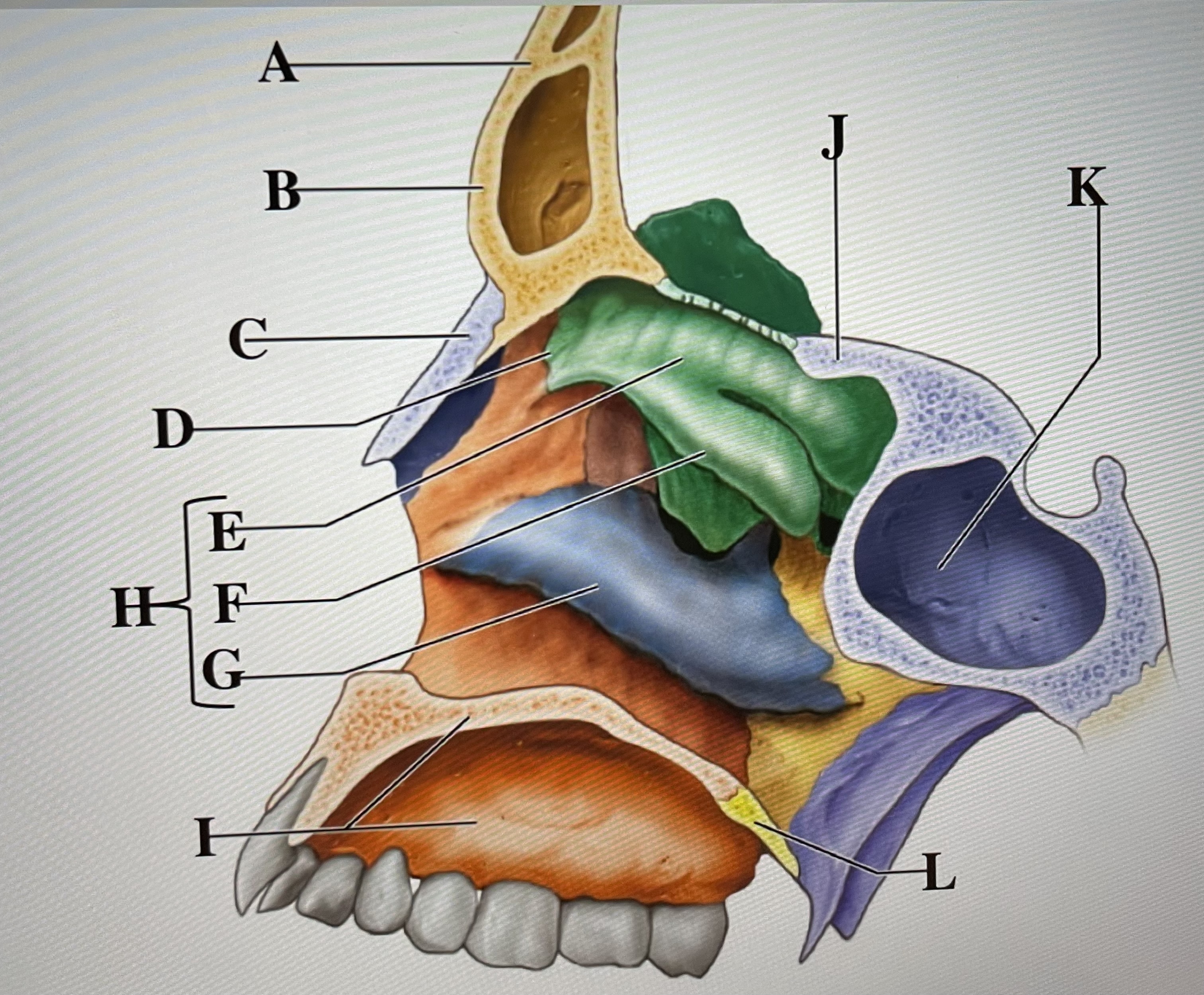
palatine bone
L
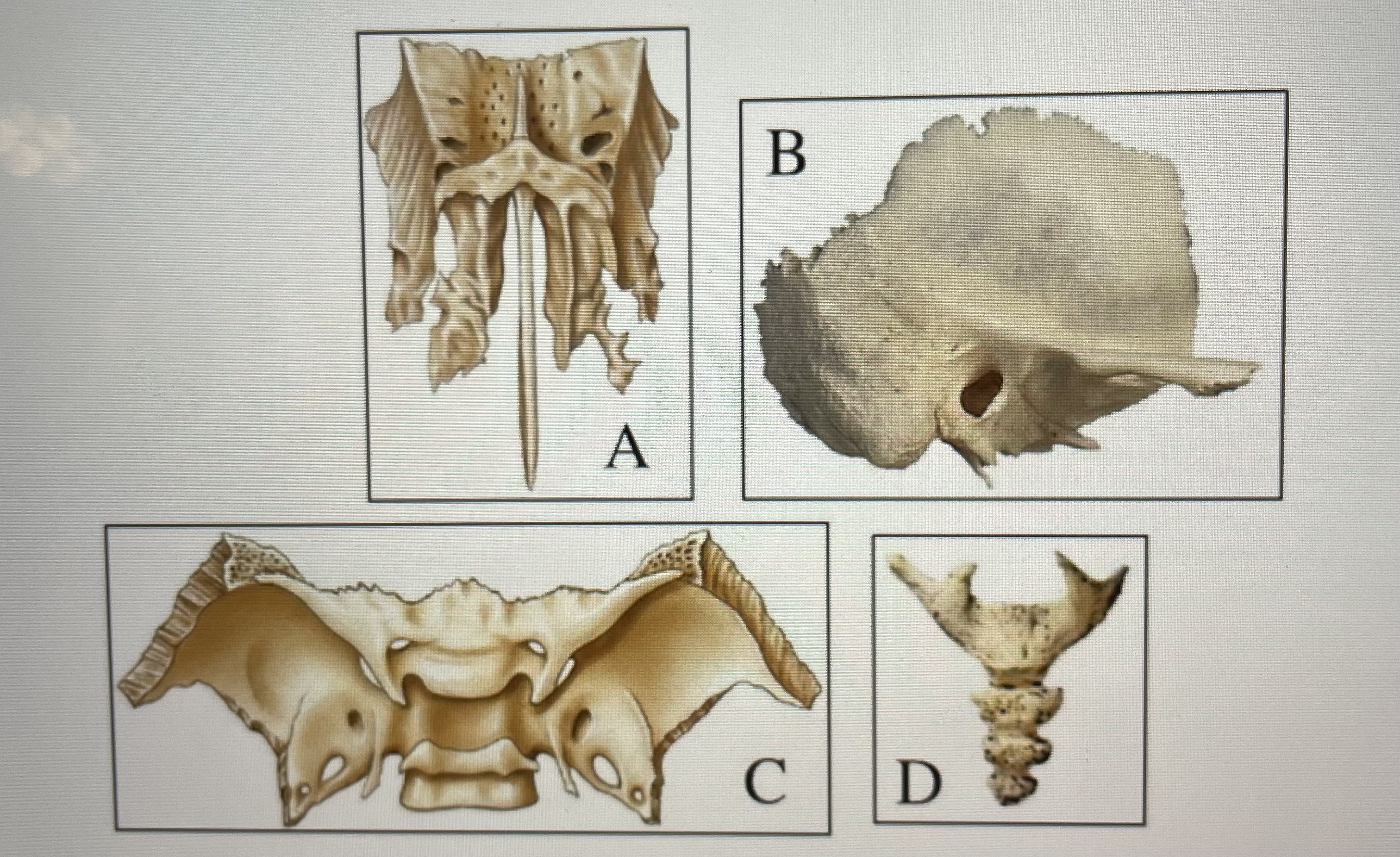
name the bones
a) ethmoid
b) temporal
c) sphenoid
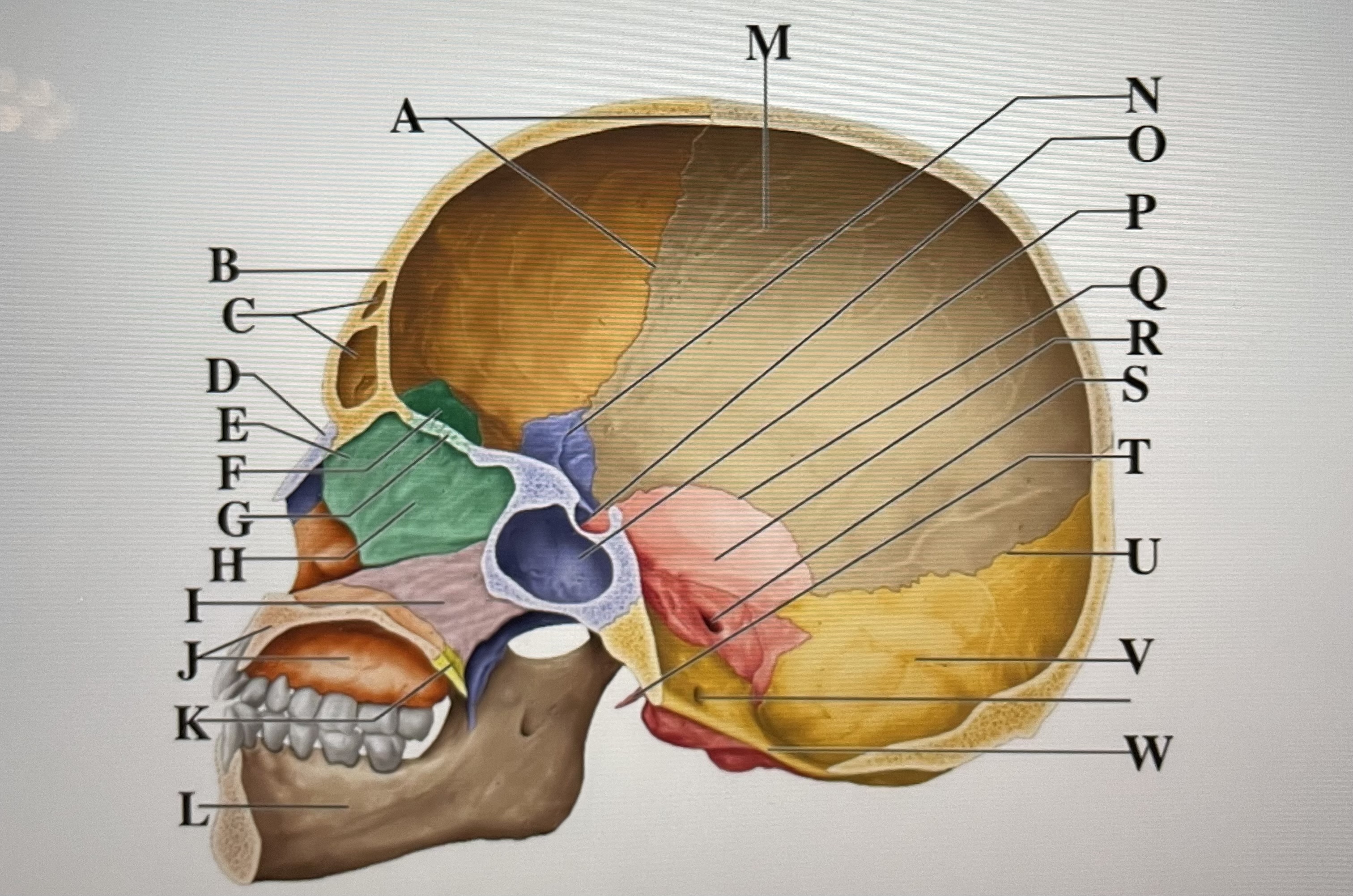
coronal suture
A
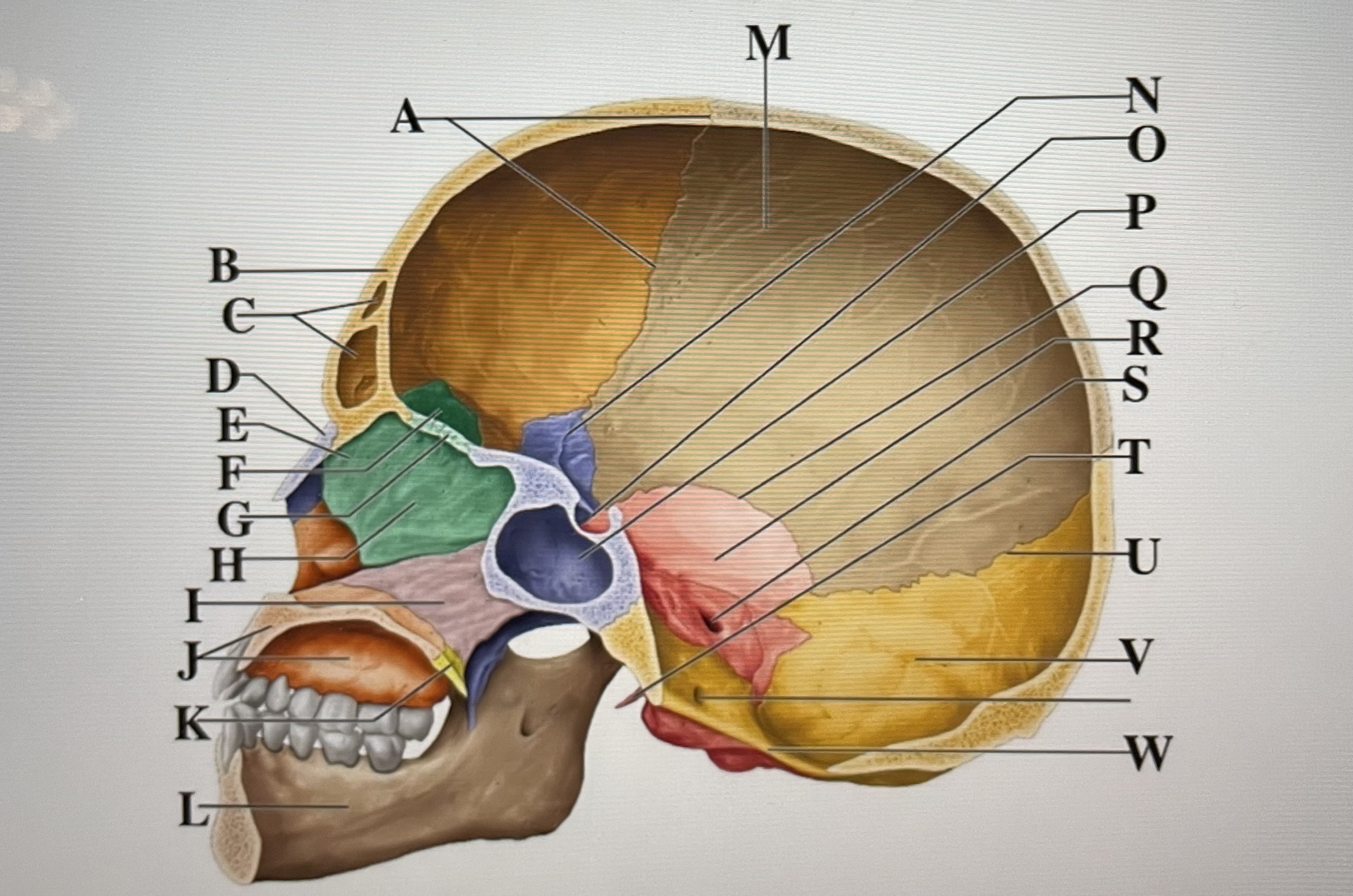
frontal sinuses
C
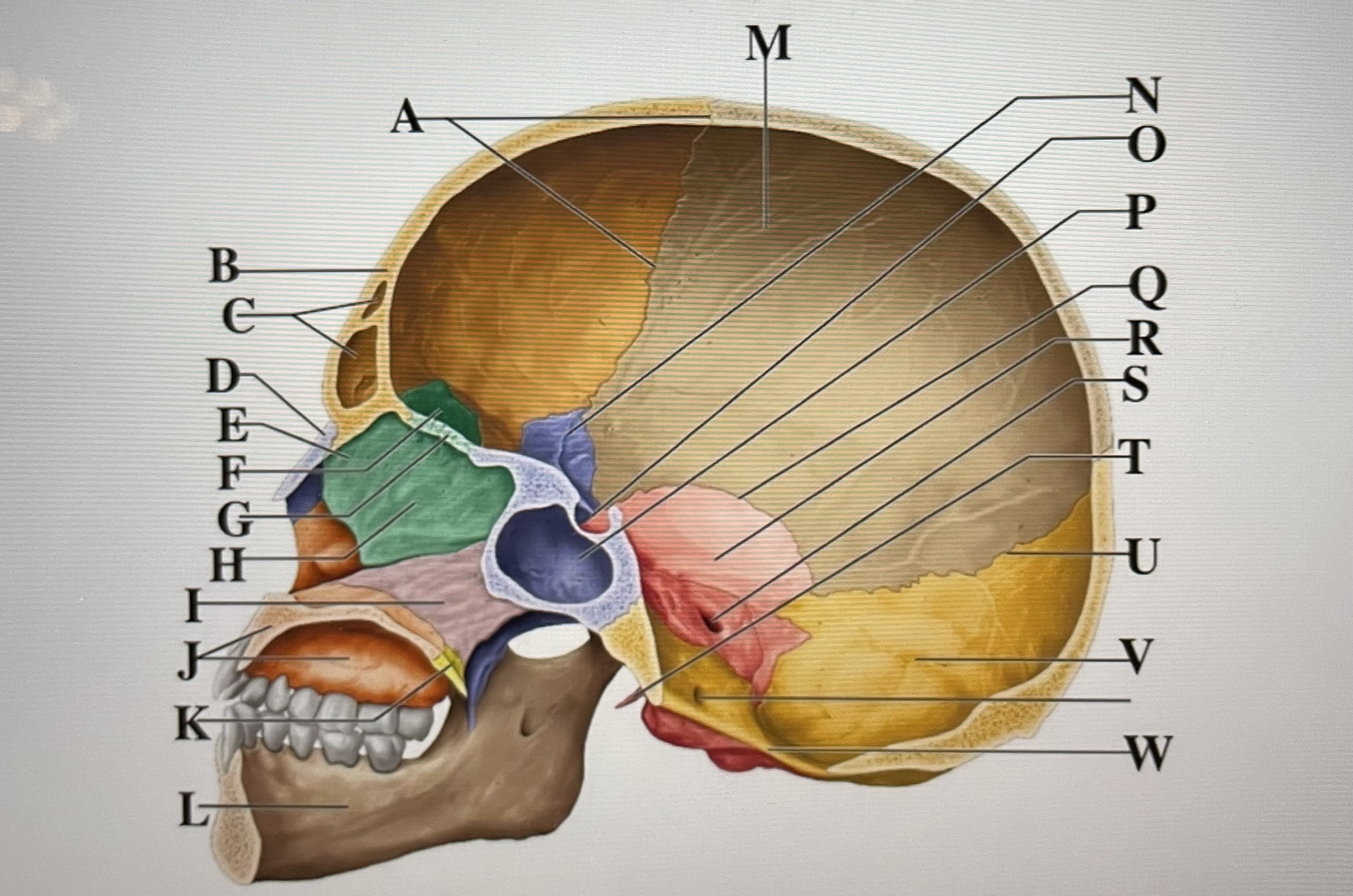
nasal bone
D
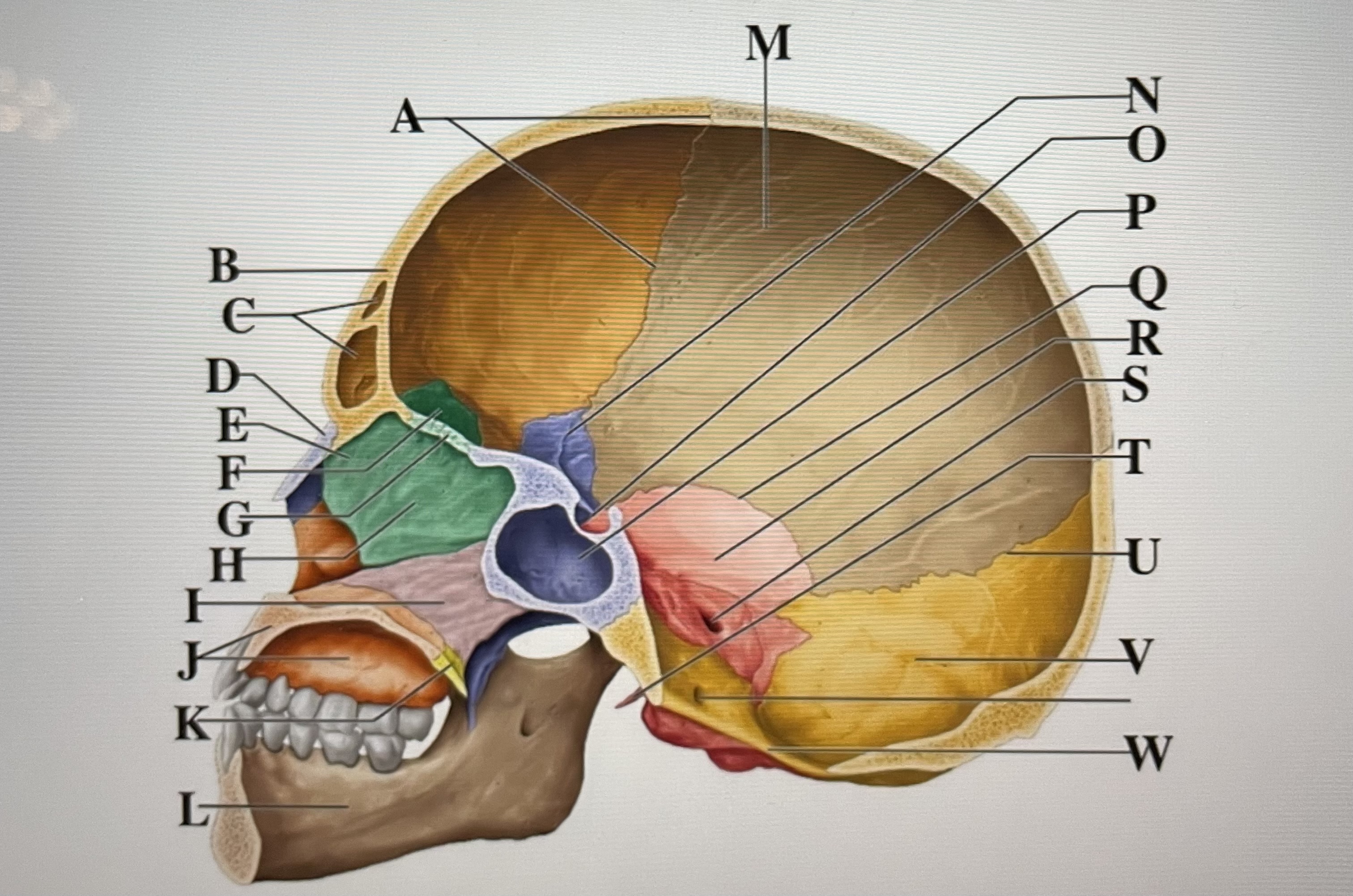
ethmoid
E
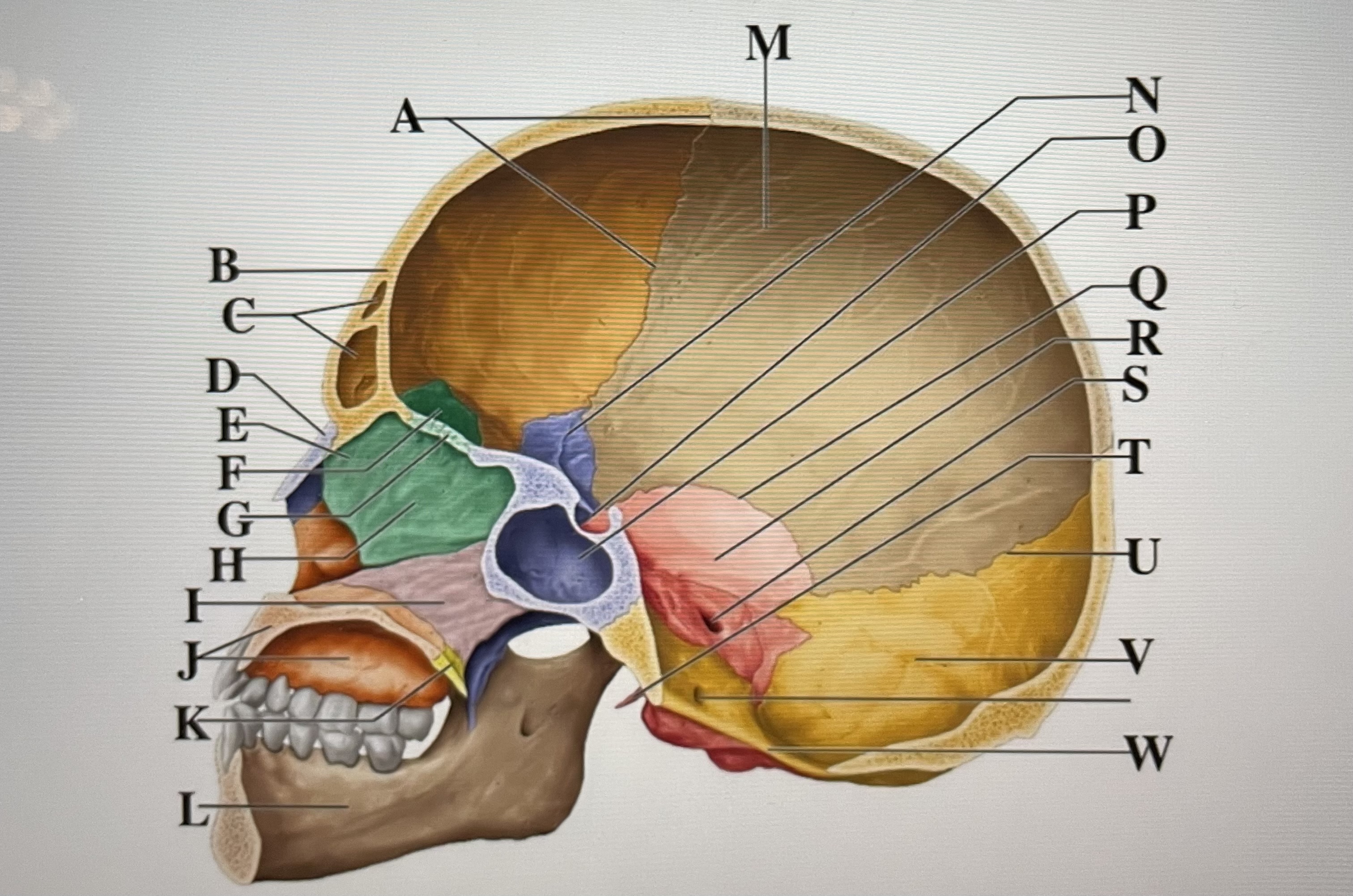
crista galli
F
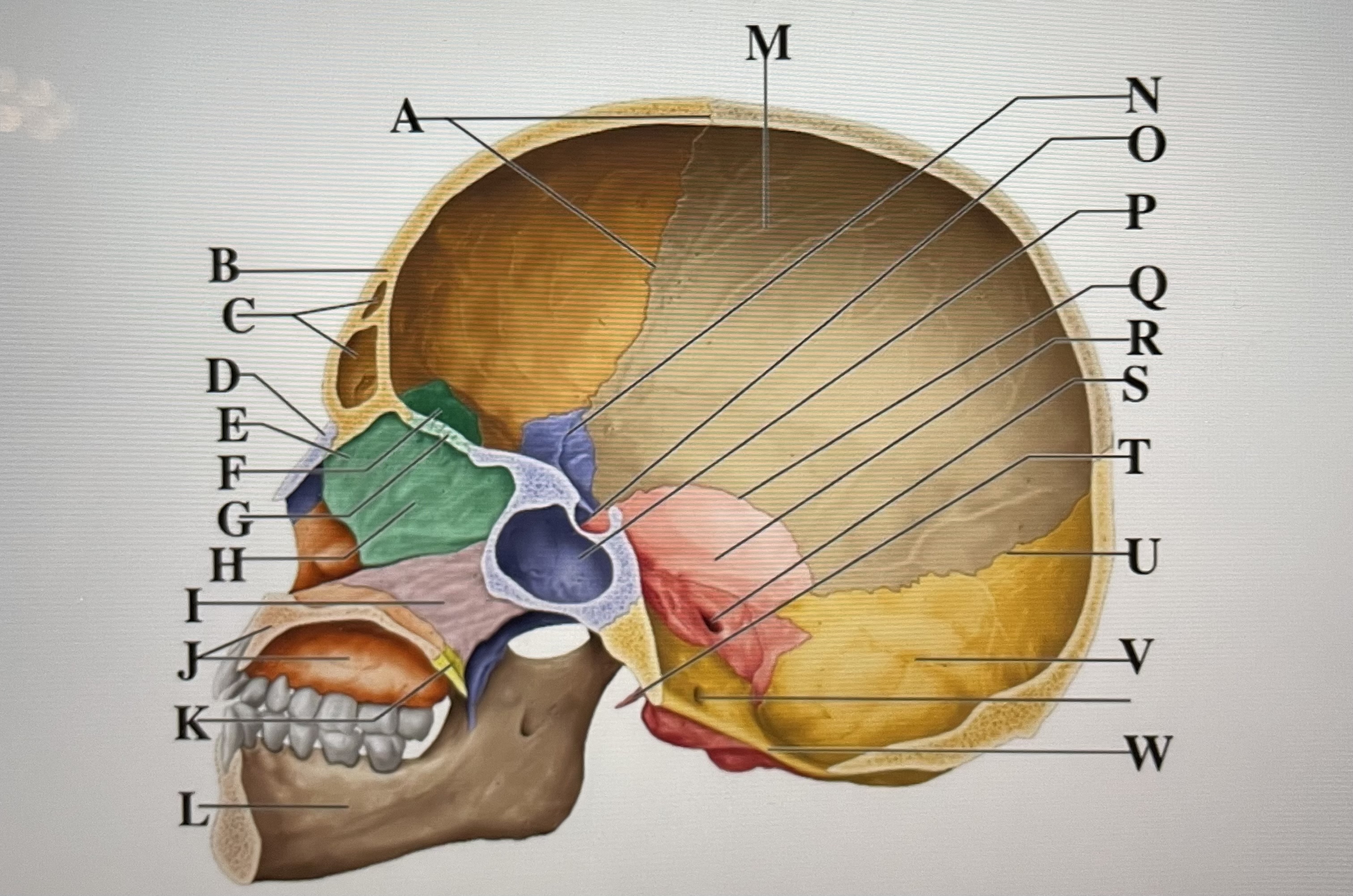
cribriform plate
G
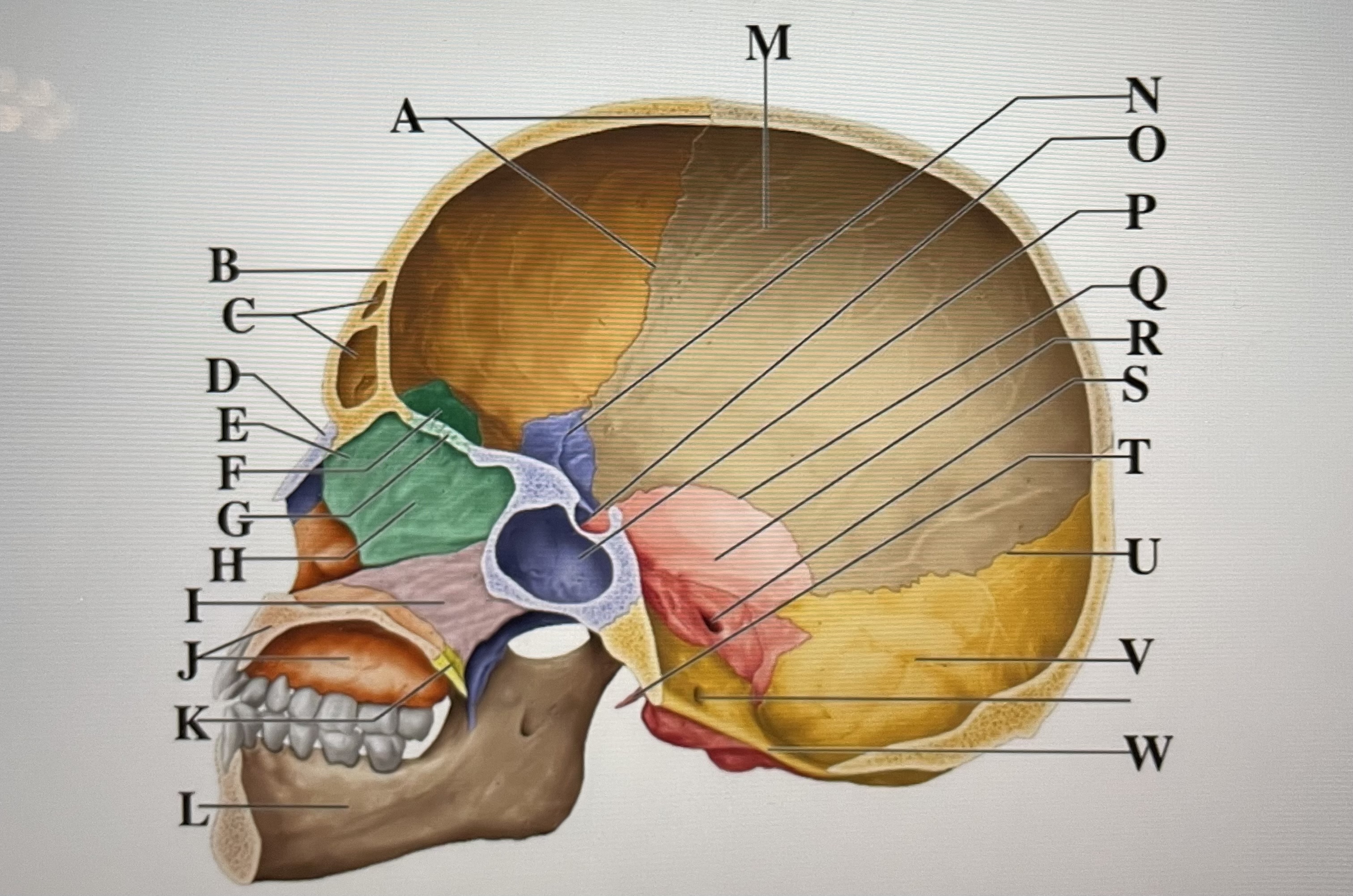
perpendicular plate
H
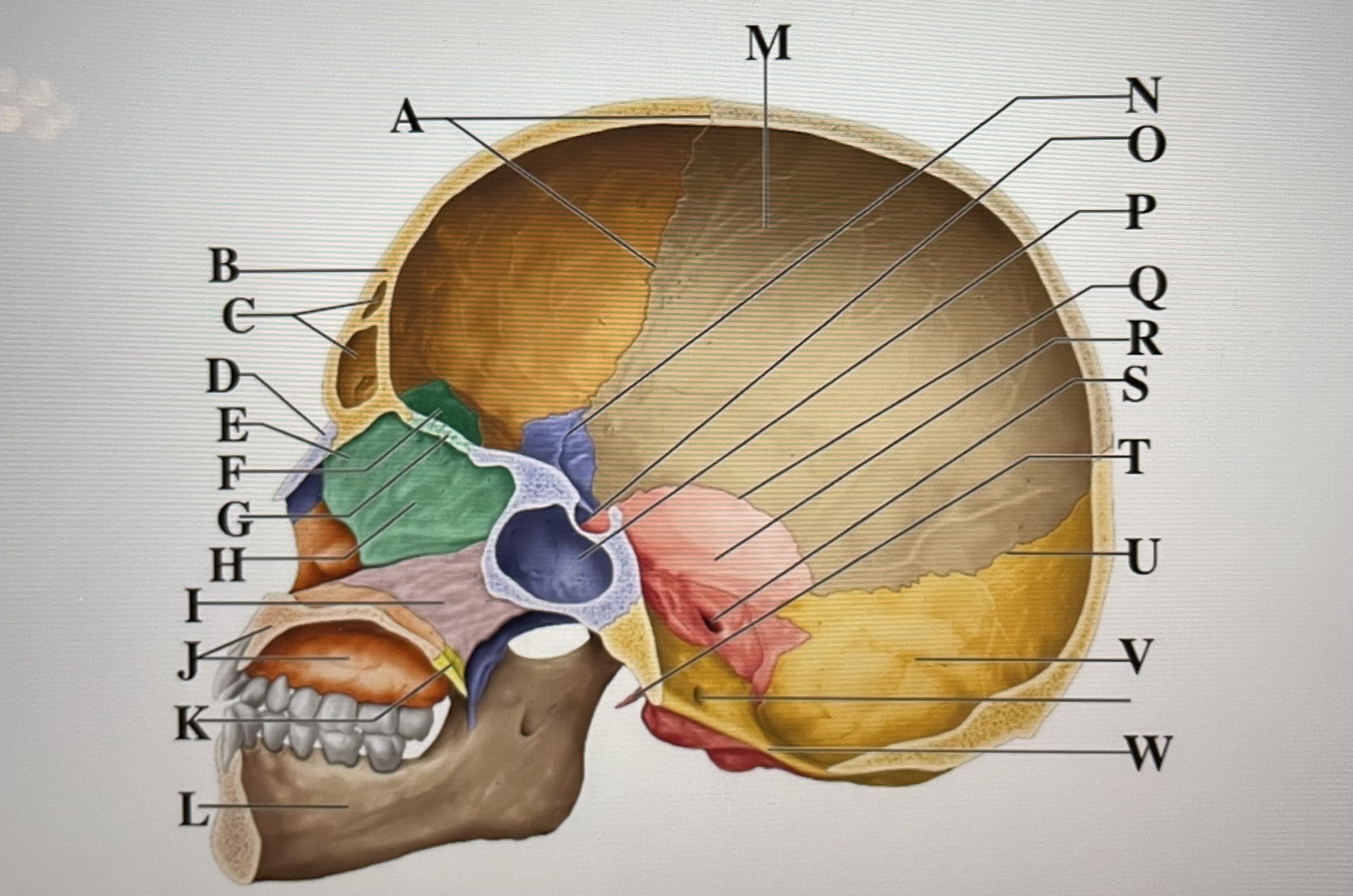
vomer
I
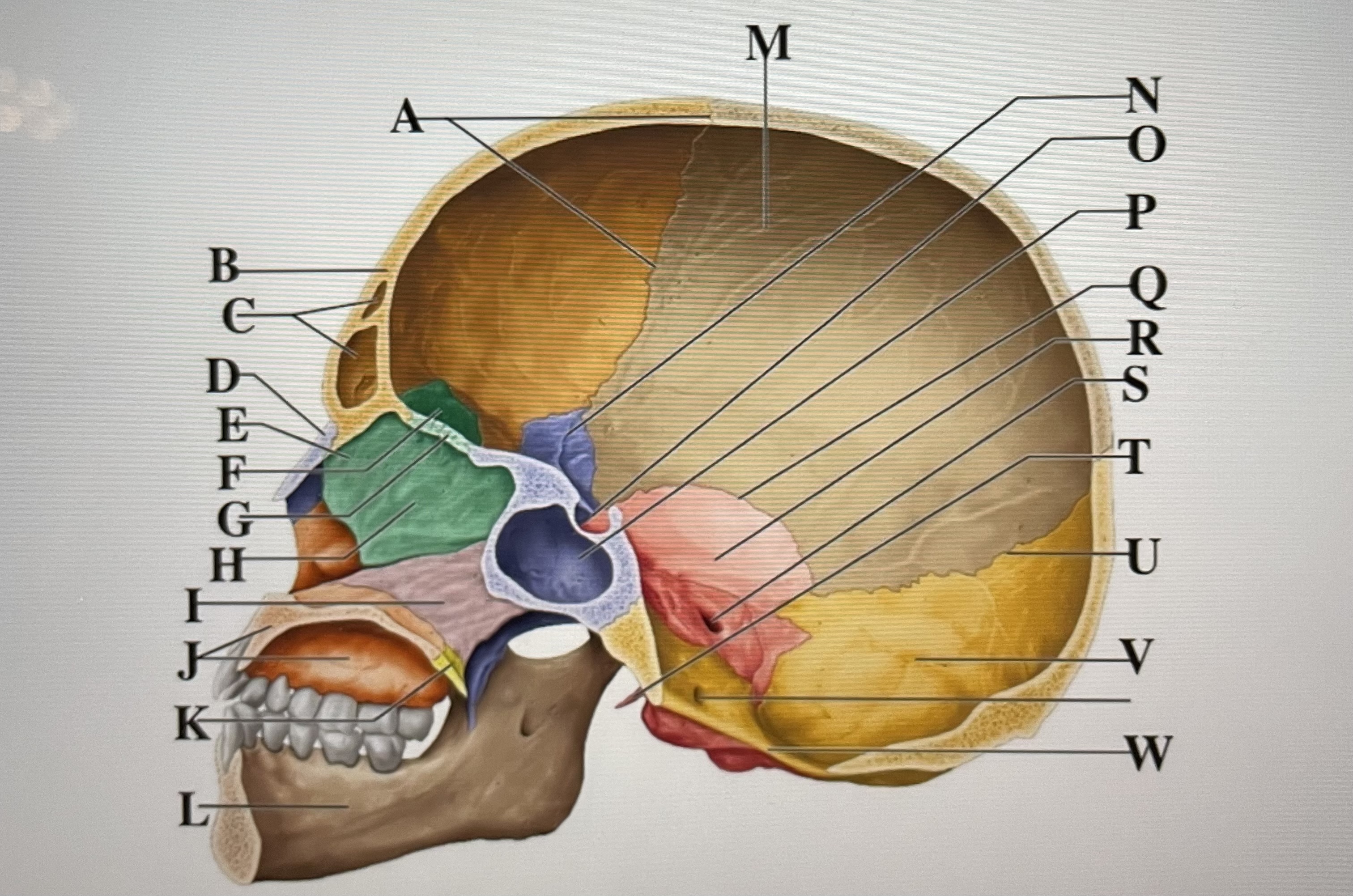
maxilla
J
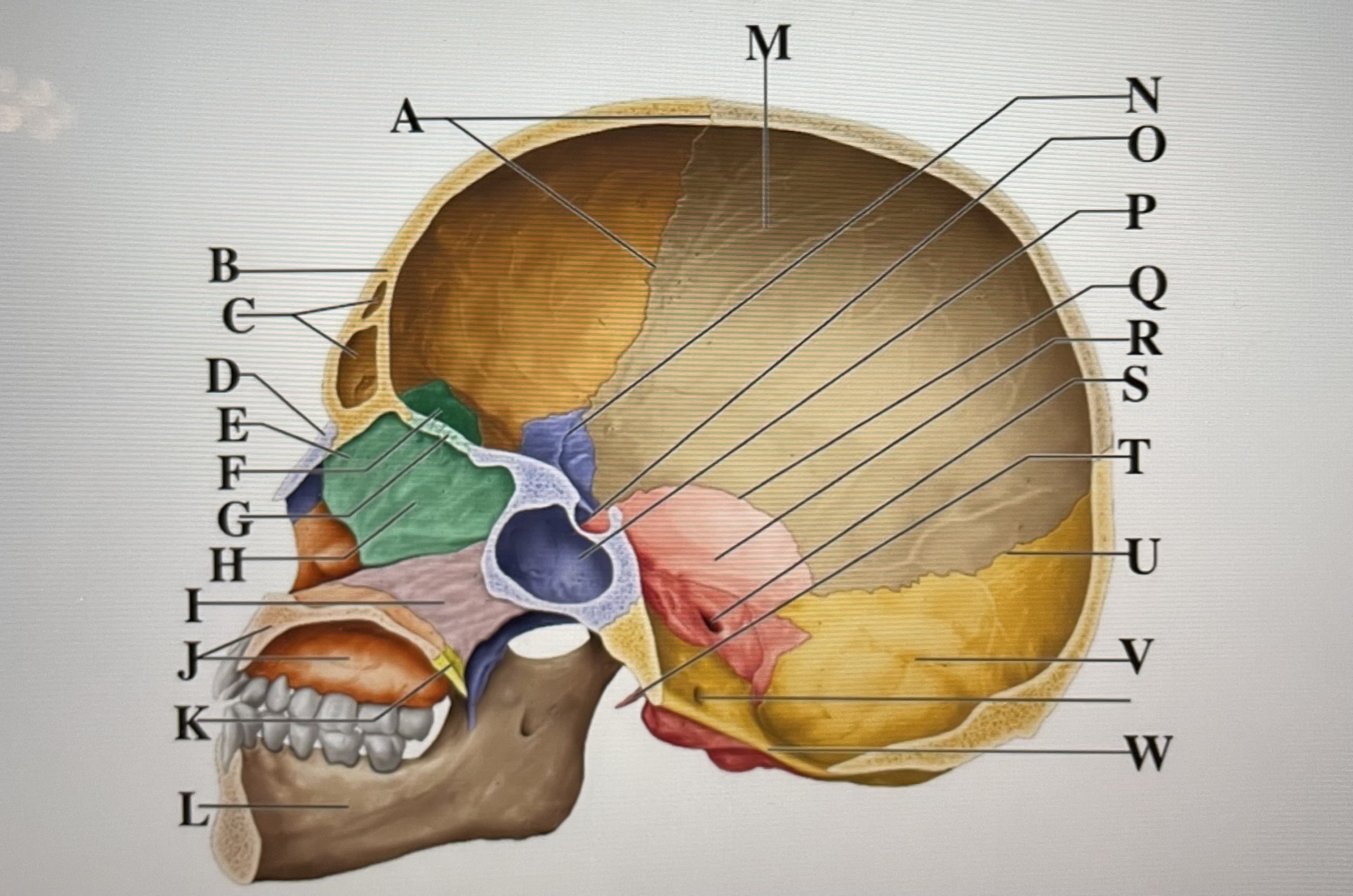
palatine bone
K
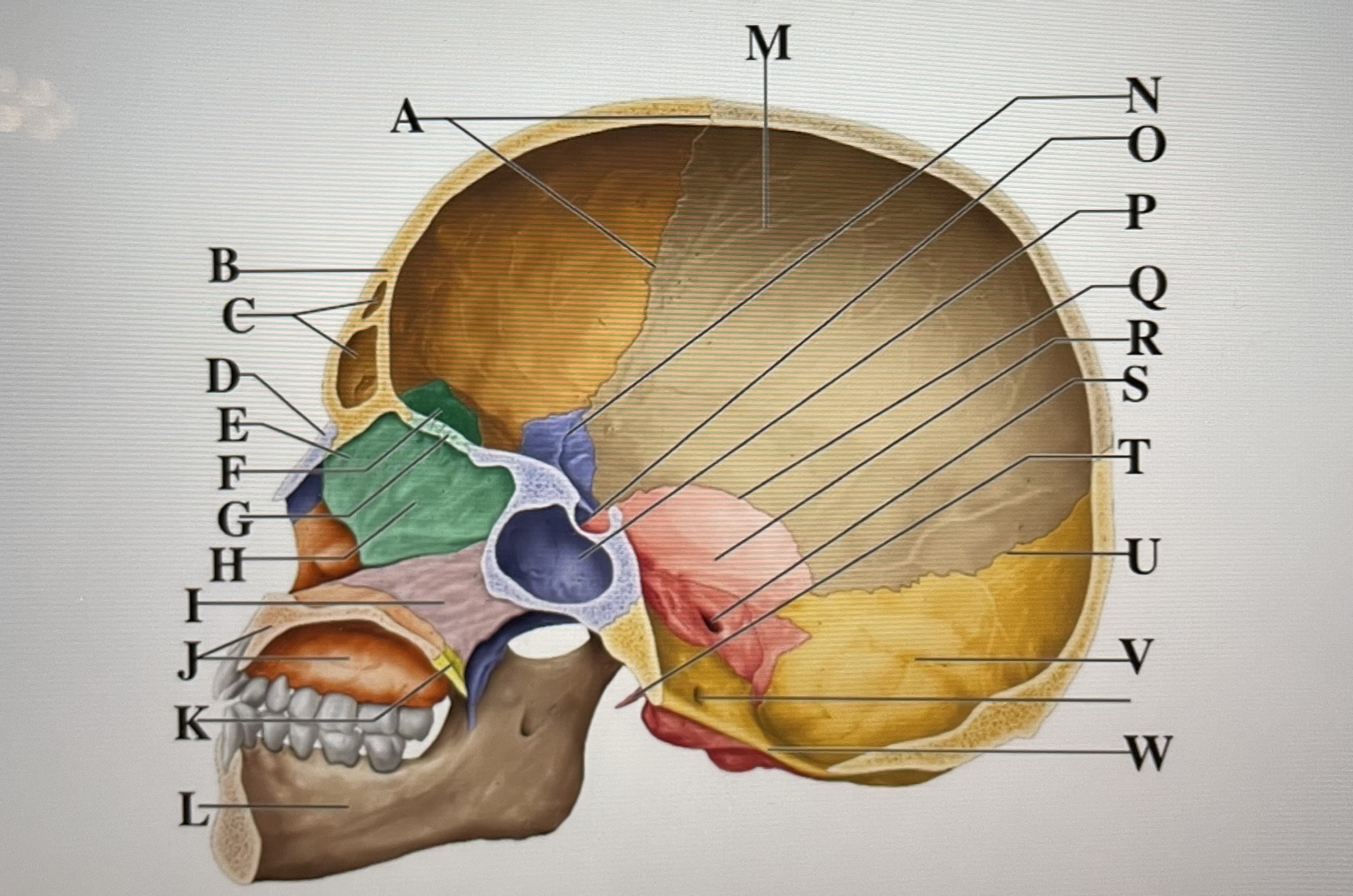
parietal
M
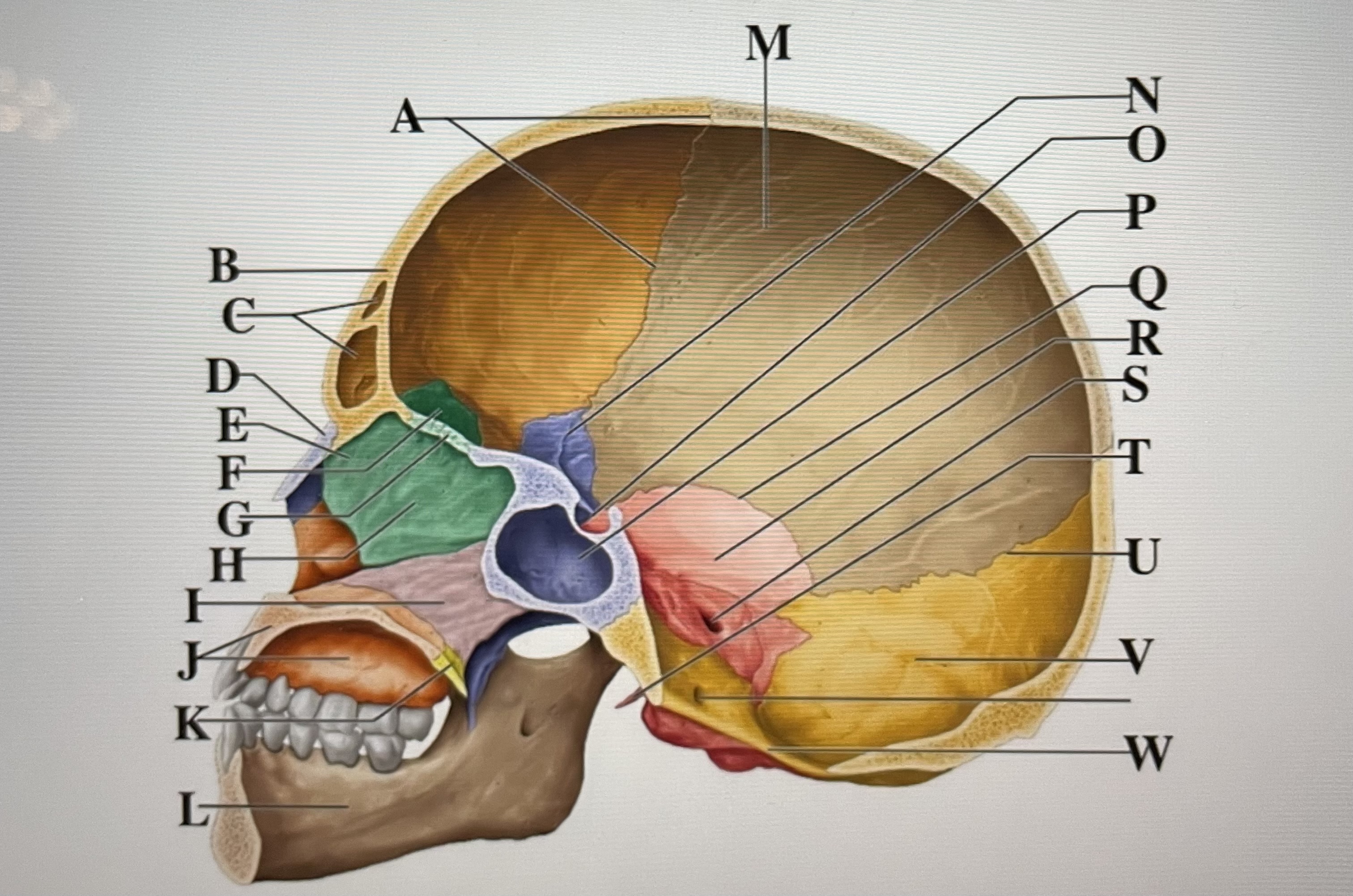
sphenoid
N
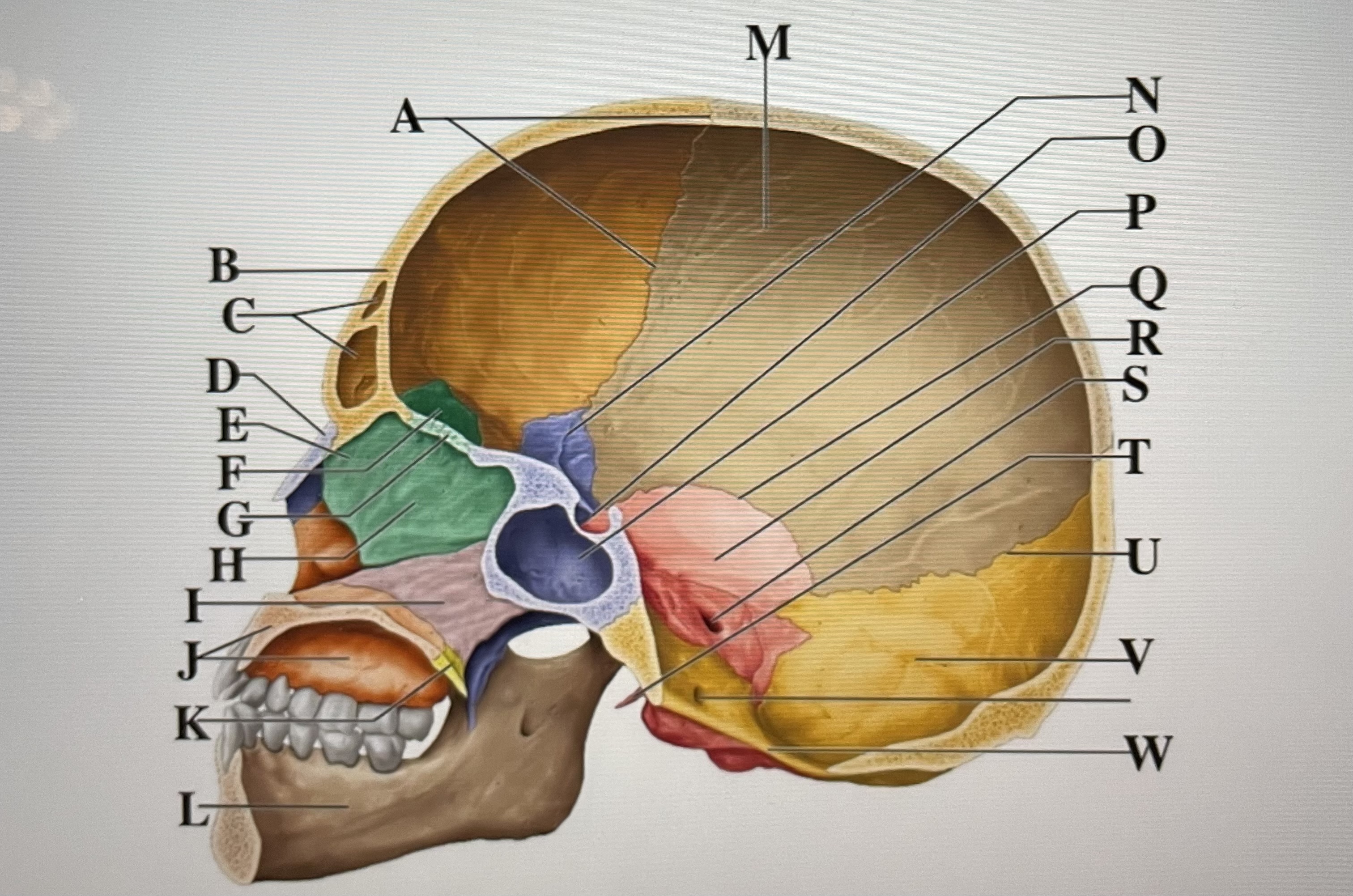
Hypophyseal fossa
O
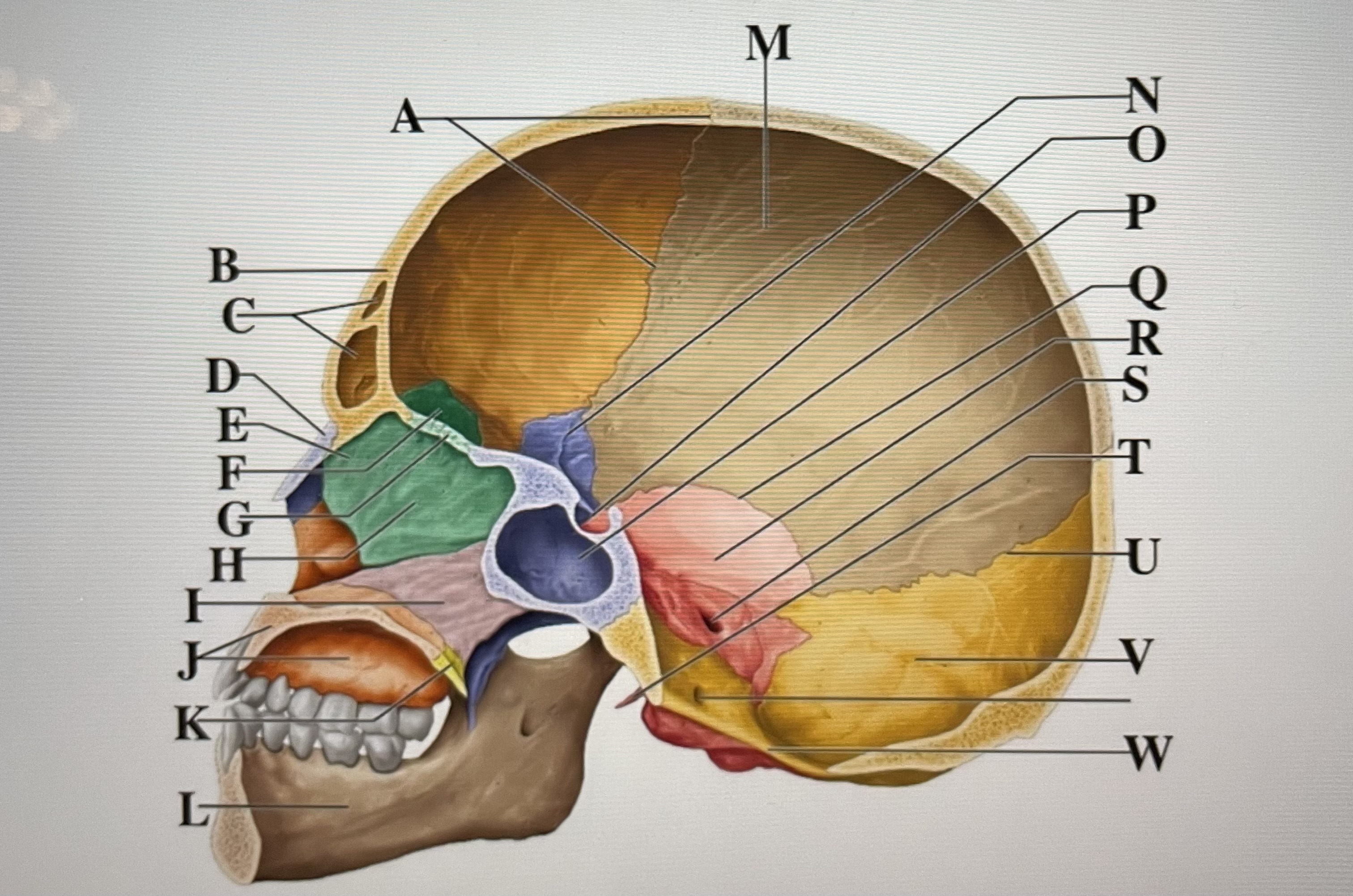
sphenoidal sinus
P
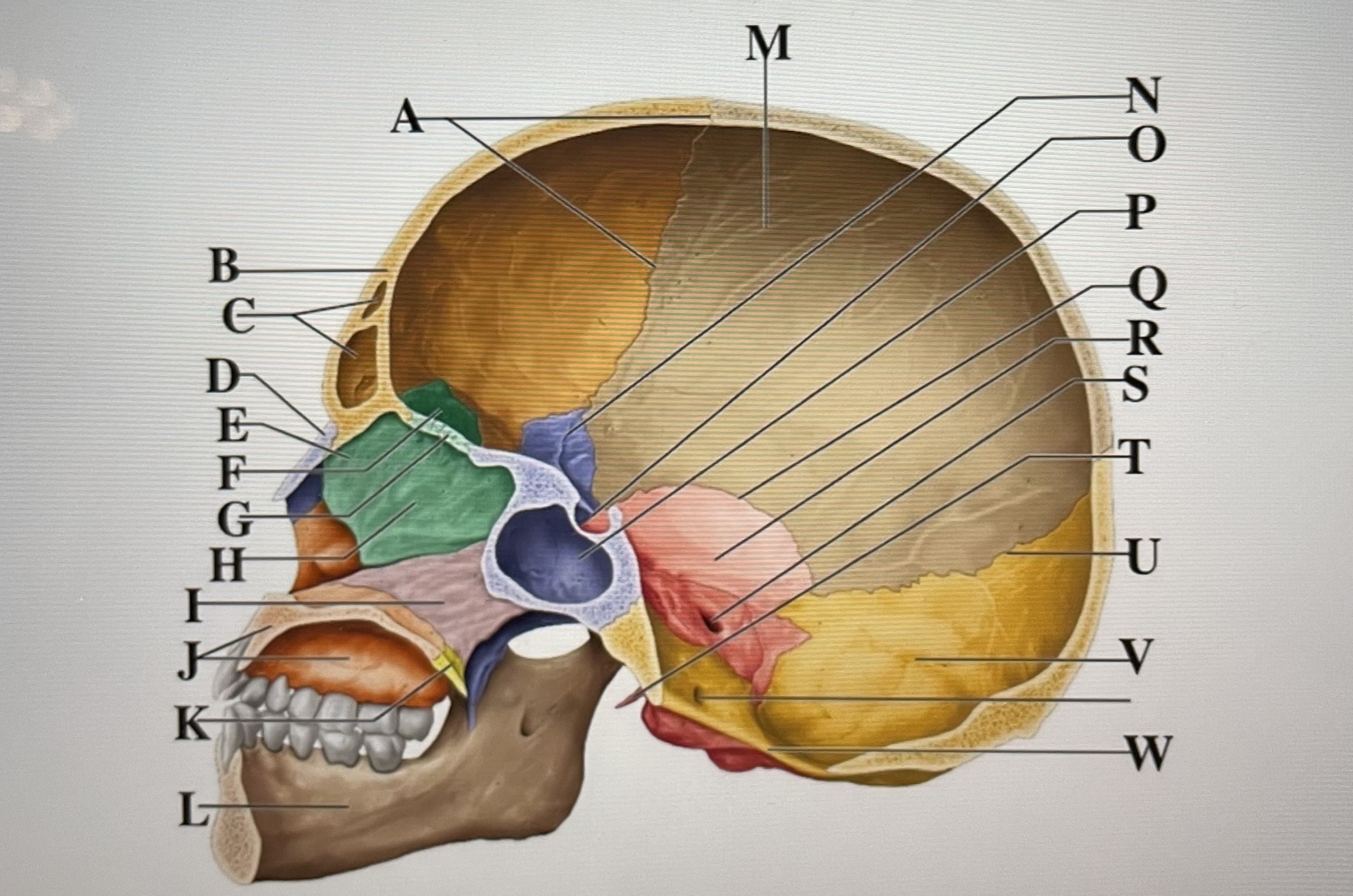
squamous suture
Q
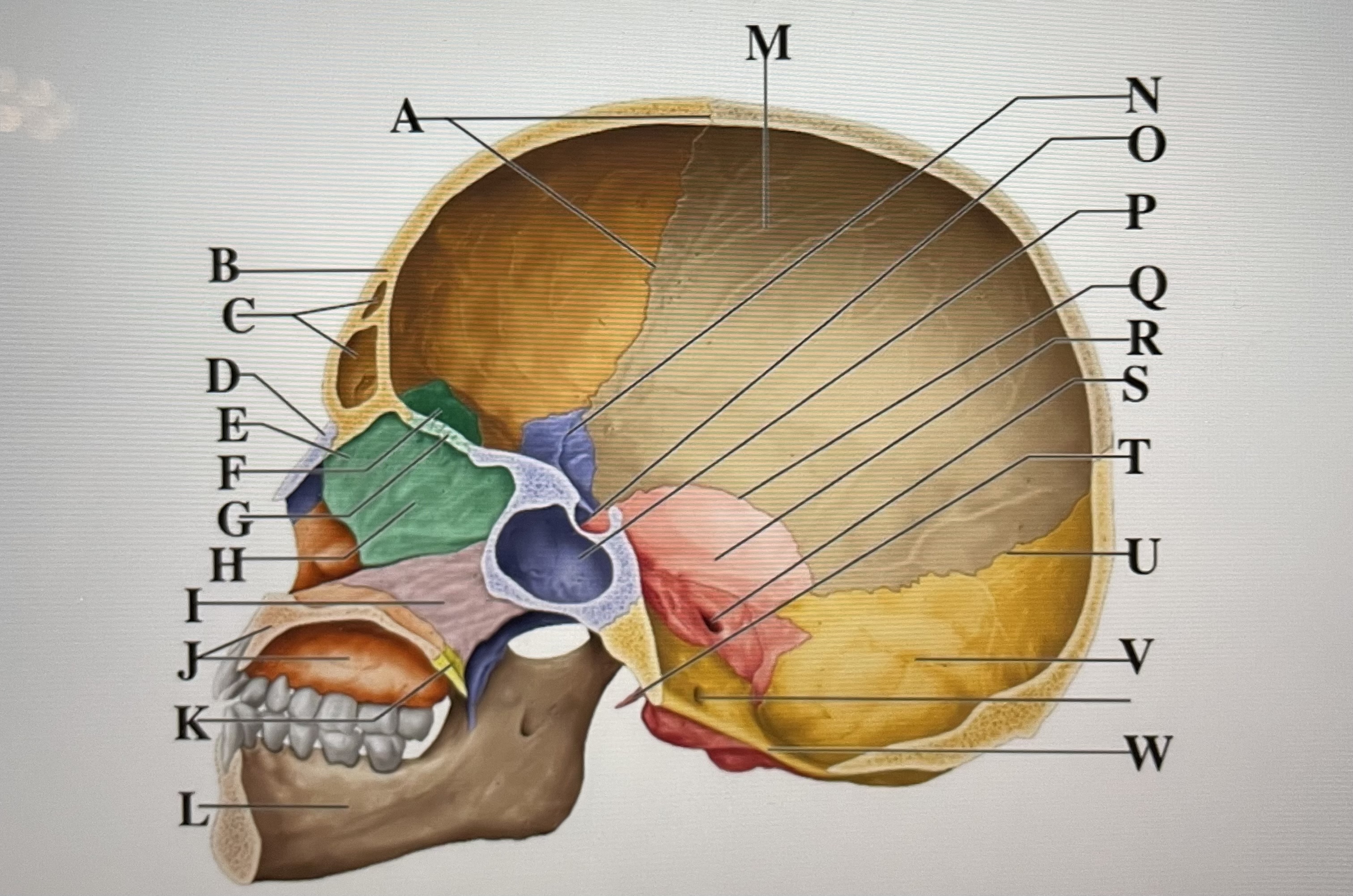
temporal
R
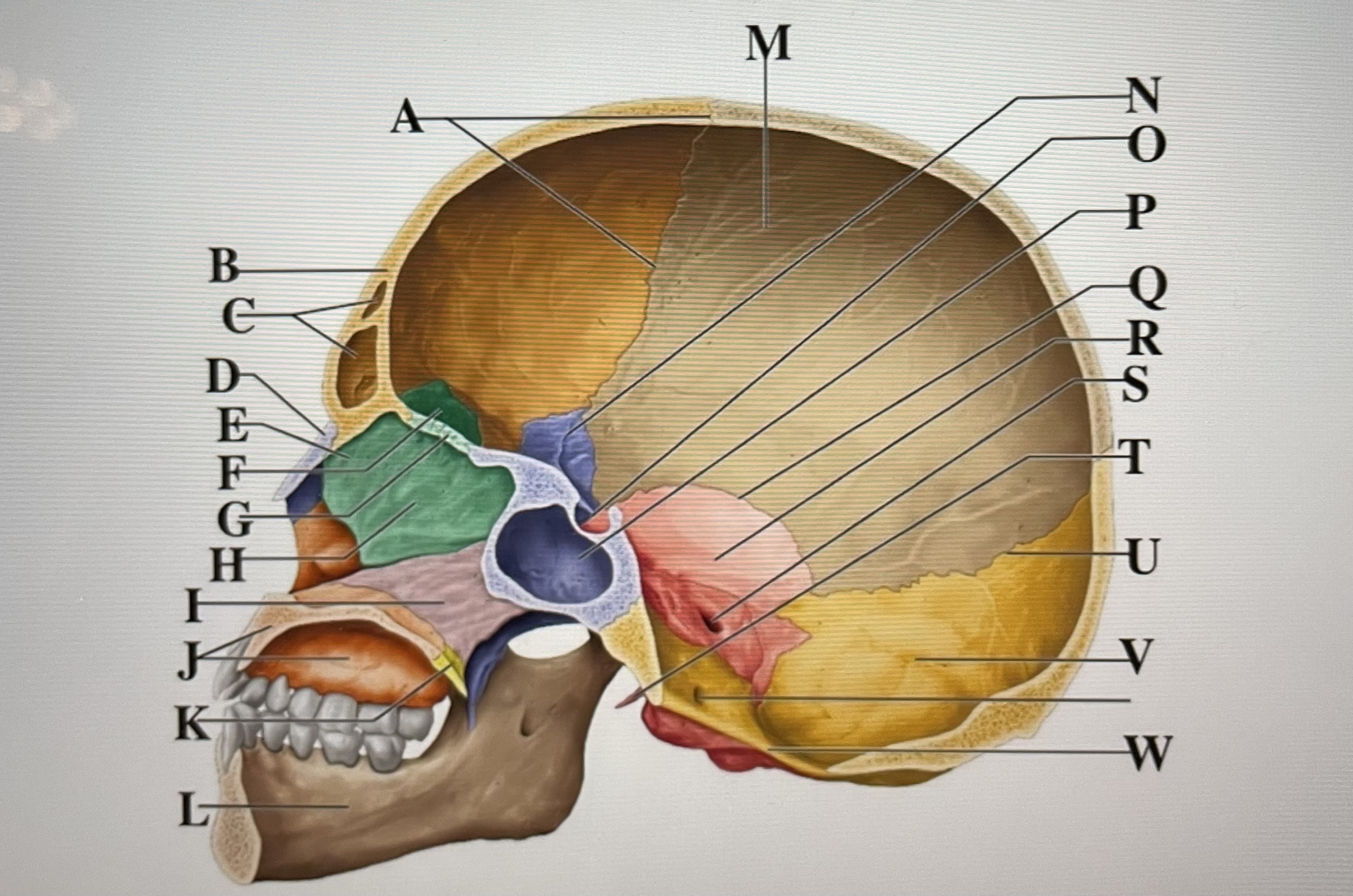
internal acoustic meatus
S
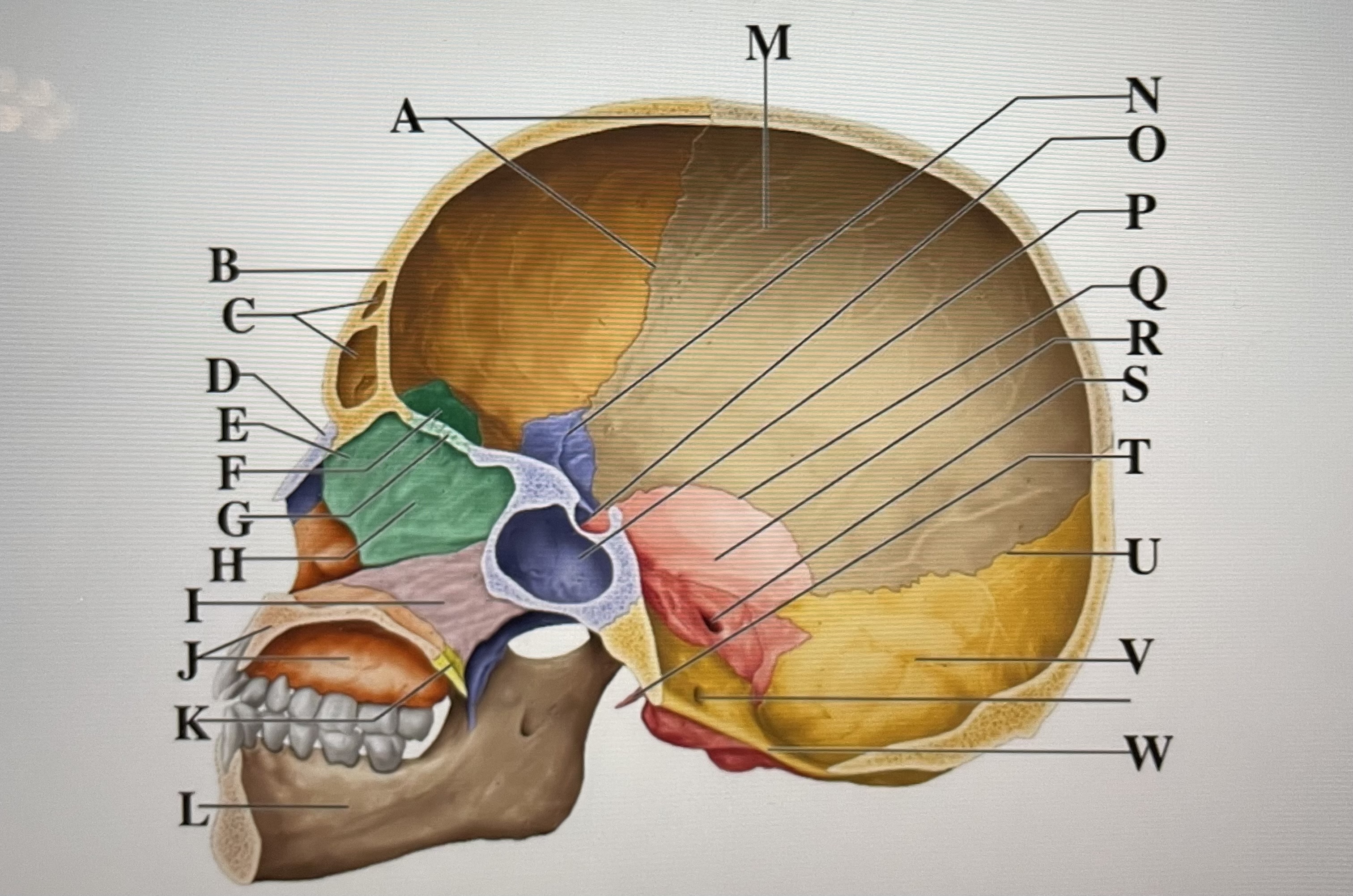
lambdoid suture
U
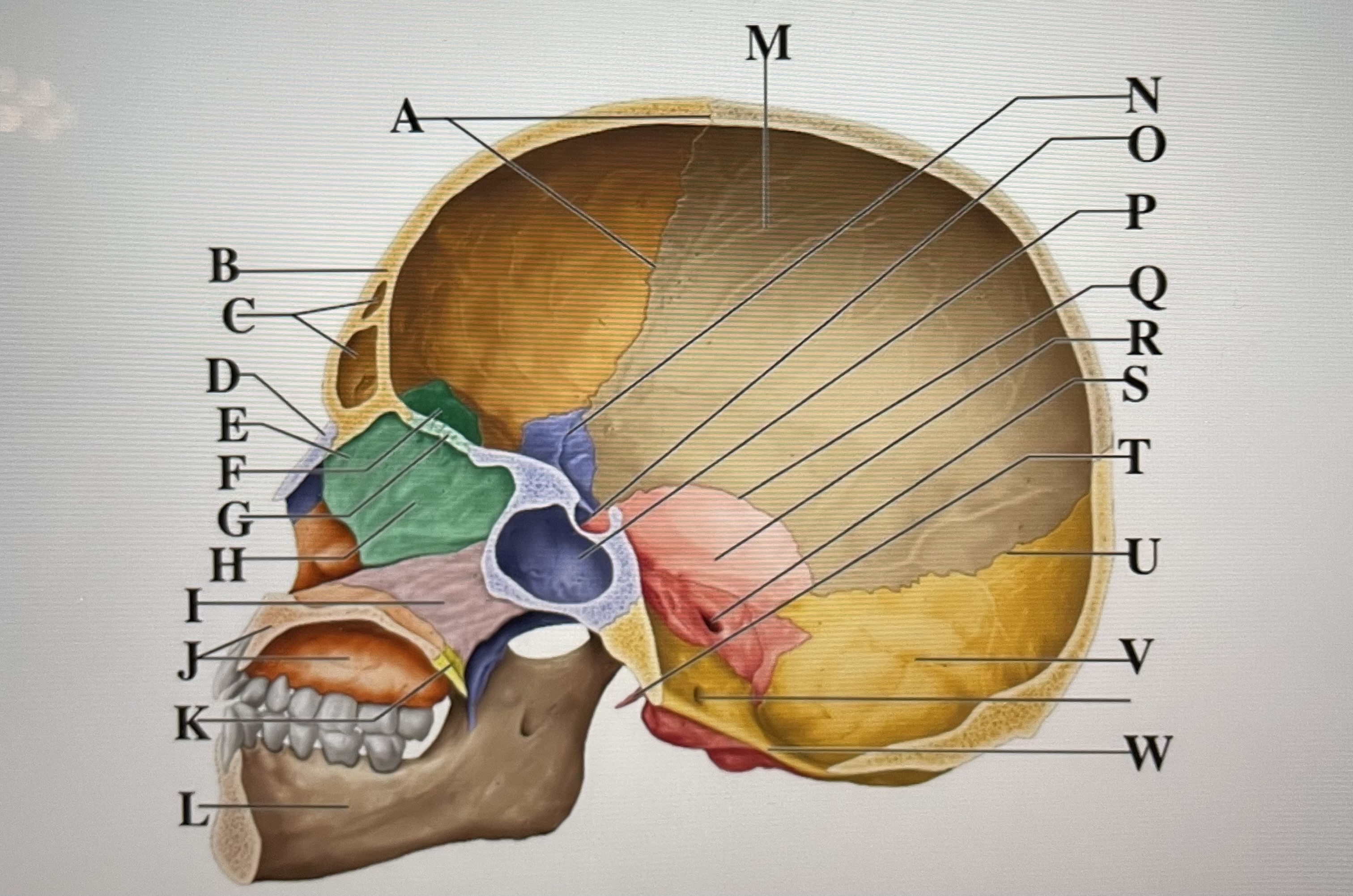
styloid process
T
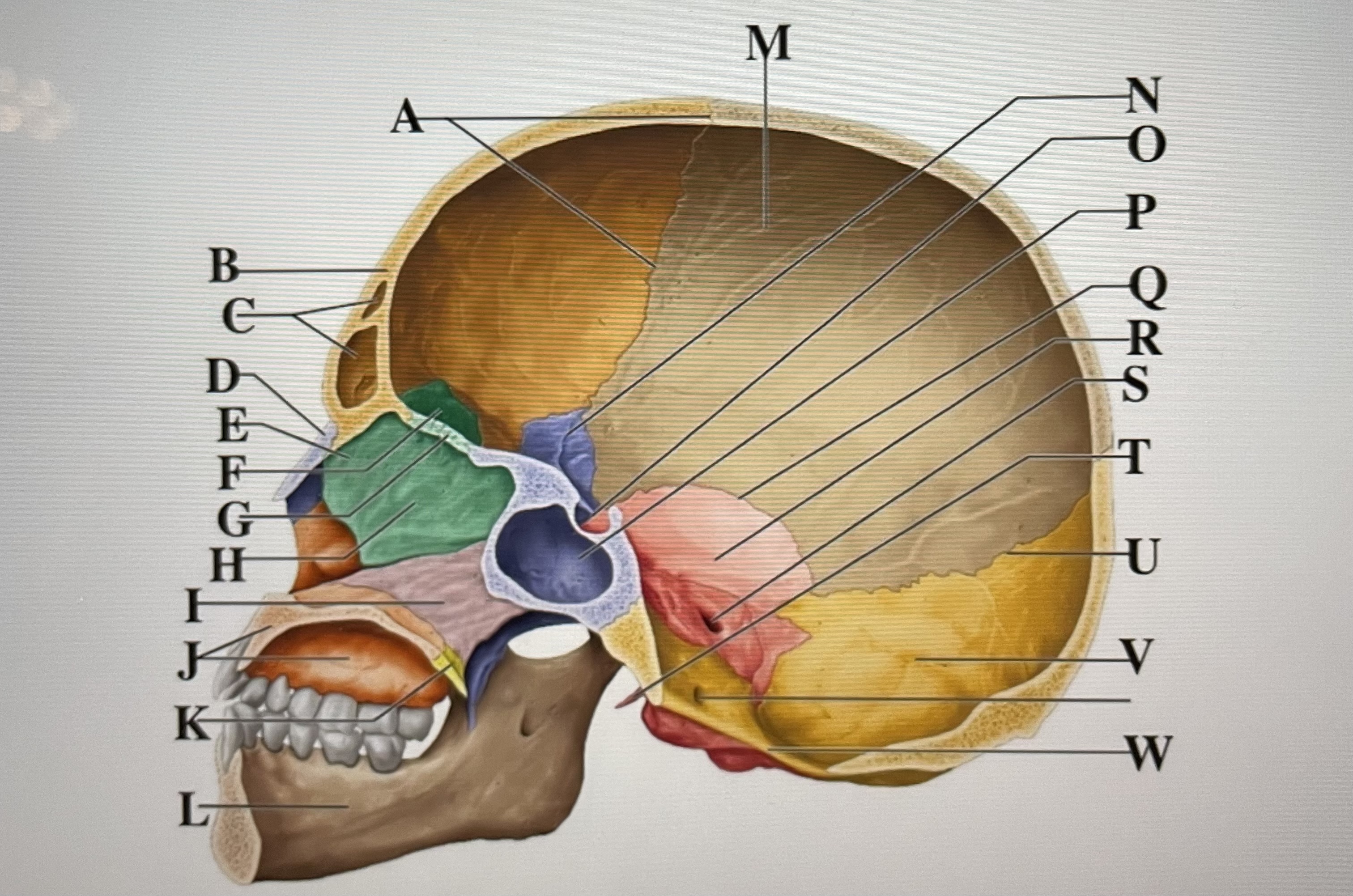
occipital
V
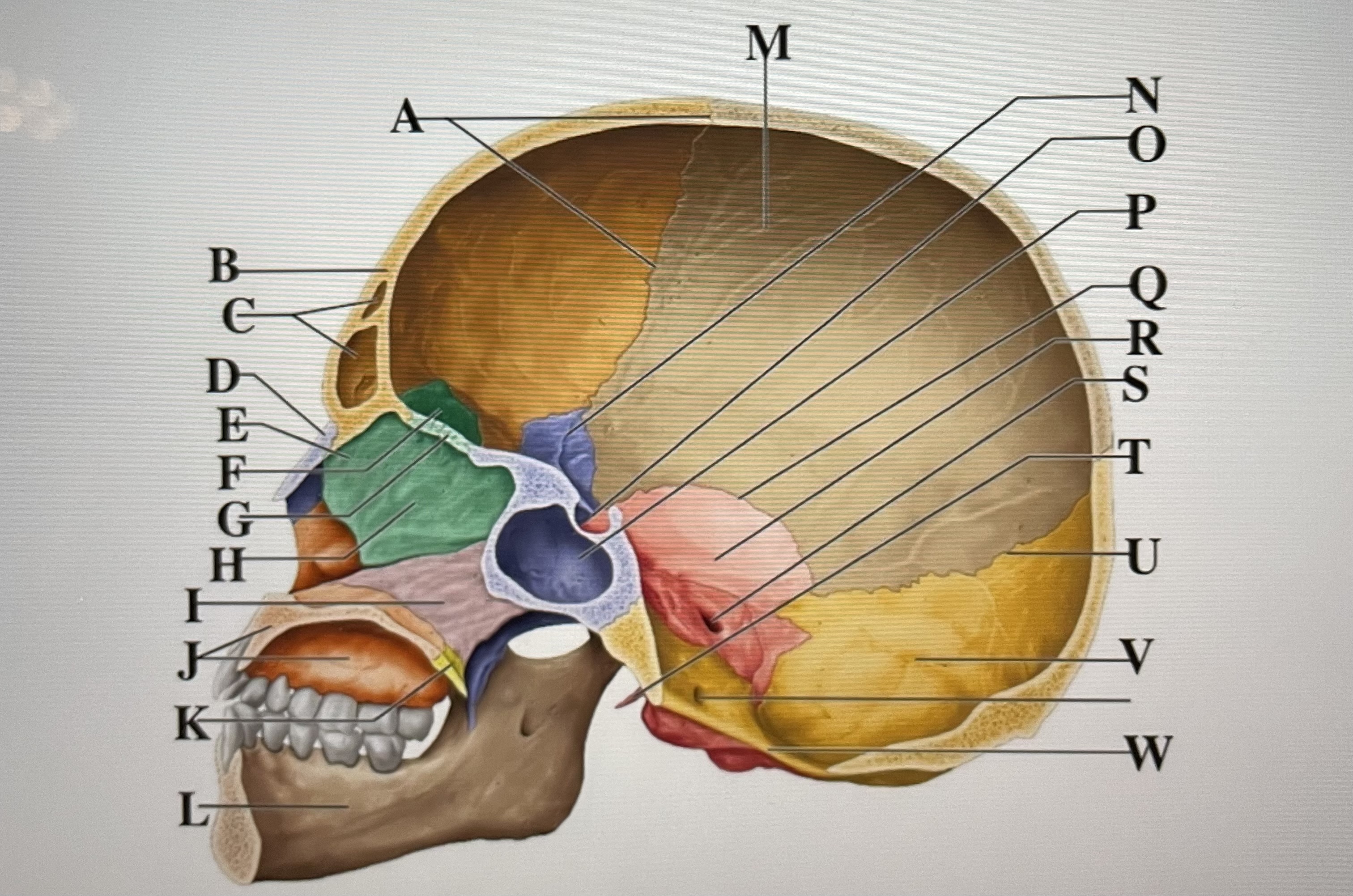
foramen magnum
W
concentric lamellae
A
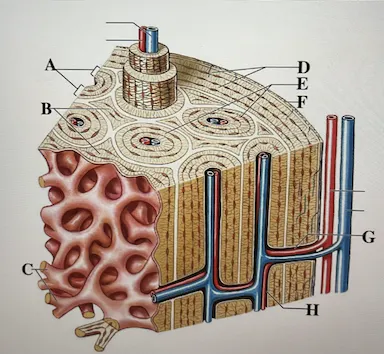
interstitial lamellae
B