Biology: Reproduction in Plants
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
asexual reproduction
process of production of genetically identical offspring from one parent
Characteristics of Asexual Reproduction
-no sex cells or fertilization
-no fusion or gametes
-no mixing of genetic variation
Binary fusion
happens in bacteria
Budding
done by yeast produce chain of buds
spore formation
done by fern/fungi
Stem tuber
-underground storage system
-buds grow into plants by using the food stored
Rhizomes
-underground storage system
-buds grow into plants by using the food stored
Runner
-Slender roots grow horizontally at soil surface
-each bud along runner develops into a new plant
Advantages of population of species in the wild and crops plant
-faster than growing from seeds
-rapidly colonise new areas
-maintain the desirable quantaties
sexual reproduction
-two parents required
-Offspring are genetically different
-Fertilization when gametes fuse to form zygote
nuclei of gametes
haploid (half set of chromosomes)
nuclei of zygote
diploid (full set of chromosomes)
advantages of sexual reproduction
-produce different varieties of plants with good quality
-Grow/mature faster
-higher resistance to disease
-better adapted to different environmental conditions
disadvantages of sexual reproduction
-dependent on pollination/pollinators
-slower method
-wastage of energy and pollen grains
structure of insect pollinated plants
Carpel (male)
-filament
-anther
Stamen (female)
-stigma
-style
-ovary
-ovules
Others
-petal
-sepal
-receptal
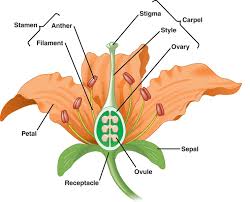
Stigma
-secretes sucrose so protein grains stick to it
Style
holds stigma where it can best get pollen
Ovary
contains ovule
Ovules
Contain egg cells
Filaments
holds anther where it can best deliver protein
Anther
makes pollen
Petal
provides color,scent and sometimes nector to attract nector to attract pollinators
Sepal
protects bud
Receptacle
flower stalk to attach flower to the stem
pollen grains insects pollinated flowers
-larger in diameter
-heavier in weight
-fewer numbers of grains produced
-Contains spikes or hooks on the outside of grain
pollen grains of wind pollinated flowers
-fewer in diameter
-lighter in weight
-greater numbers of grains produced
-No spikes or hooks on the outside of grain
Stigma of wind pollinated flowers
Extends outside the plant and is feathery to catch pollen easier
Anther of insect pollinated flowers
Hang outside the flower so the wind can carry more pollen grains
Pollination
Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma
Self pollination
pollen grains from same flower/plant
Self pollination characteristics
-little or no genetic variation
-less well adapted to changing conditions
-less wastage of pollen grains
Cross pollination
pollen grains between 2 points of the same species
Cross pollination characteristics
-produce genetic variation
-lwell adapted to changing conditions
-higher wastage of pollen grains
fertilization
occurs when a pollen nucleus fuses with a nucleus in the ovule
What happens when a pollen grain lands on the stigma?
It sticks to the stigma and begins to germinate, forming a pollen tube.
Where does the pollen tube grow?
Down through the style toward the ovary.
How does the male gamete travel to the ovule?
The male nucleus moves down the pollen tube into the ovule.
What happens when the male nucleus reaches the female nucleus in the ovule?
They fuse together in fertilization to form a zygote.
After fertilization, what does the ovule and ovary become?
Ovule → seed; Ovary → fruit.
What is germination?
The process by which a seed develops into a new plant.
Why is water important for germination?
It activates enzymes that break down stored food in the seed.
Why is oxygen important for germination?
It allows respiration to release energy for growth
Why is warmth important for germination?
It provides the optimum temperature for enzyme activity.