Bacterial Genetics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
A bacterial genome is typically
a single circular DNA molecule.
Semiconservative DNA replication means that
each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand.
The bacterial chromosome is
both circular and found in a nucleoid.
The events of ________ are initiated at sequences called origins.
DNA replication
In conjugation, F+ cells
contain an F plasmid.
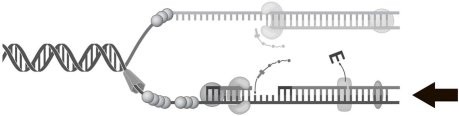
The process indicated by the arrow in Figure 7.1 represents
lagging strand synthesis.
Which of the following is found in both archaeal and eukaryotic genomes?
histones
Which of the following is found at the 5' end of a DNA strand?
a phosphate group
Typical eukaryotic genomes are composed of ________ chromosomes.
multiple linear
DNA is composed of four nucleotides, A, C, G and T. Each codon is composed of three nucleotides. The number of possible codons is
64.
RNA polymerase is primarily responsible for
transcription.
Which of the following is involved in translation?
mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA are all involved.
The horizontal transfer process known as transduction
involves a virus.
Genetic elements known as promoters are initiation points in the process of
transcription.
In generalized transduction, viruses carry random DNA sequences from one cell to another.
True
Amino acids are delivered in their appropriate order by
tRNAs.
Which of the following is characteristic of prokaryotic genomes but not eukaryotic genomes?
circular chromosomes
Which of the following causes mutations by creating thymine dimers?
ultraviolet light
Transfer of random pieces of DNA mediated by phage is known as
generalized transduction.
Prokaryotic operons typically include a(n) ________ and a(n) ________ with multiple genes.
operator; promoter