Lecture 9 -- Locomotion & Proprioception
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is gait?
Repeating sequence of leg movements with swing and stance phases.
What is the swing phase?
The phase when the leg is in the air during locomotion.
What is the stance phase?
The phase when the leg is on the ground during locomotion.
What are Central Pattern Generators (CPG)?
Autonomous rhythmic activity generated in the spinal cord for each limb
Once the brain start initiated and we start walking, CPG take over and do it automatically for us = We don’t have to caonstantly think about that
How is speed determined in locomotion?
Stride frequency x stride length.
What is proprioception?
Sense of the relative position of body parts and their movement.
Give examples of proprioceptors.
Muscle spindles, GTO, joint receptors, skin tactile & mechanoreceptors, vestibular system hair cells.
What is required for an animal to demonstrate normal proprioception?
Normal motor function.
What is conscious proprioception associated with?
Complex voluntary movement.
What is subconscious proprioception associated with?
Rhythmic, subconscious movements.
How do the neurons of subconscious proprioception travel to the cerebellum?
Proprioceptor in the body → Travel to the spinal cord via neurone → Synapse in spinal cord grey matter → Travel up to the cerebellum via 2nd neurone through the spinocerebellar tract white matter → Ipsilateral cerebllum
What is the deficit of subconscious proprioception called?
Ataxia
What are signs of subconscious proprioceptive deficits?
Swaying of the body, base wide/narrow stance, non-intention tremor.
If an animal has a lesion of the left cerebellum, on what side would you expect the subconscious proprioceptive deficits?
Ipsilateral → left side affected → Non-intention tremor on left side + Narrow stance + Swaying of the body
Where do the neurons of conscious proprioception travel to?
Proprioceptor input goes into the spinal cord via 1st sensory neurone → Synapse with the 2nd neurone at medulla and decussate → 2nd neurone goes up the thalamus and synapse with 3rd neurones → 3rd neurone goes up to somatosensory cortex (Rostral portion of the parietal lobe)
What are signs of conscious proprioceptive deficits?
Stumbling, knuckling, intention tremor.
Where does the first synapse occur in the conscious proprioception pathway?
Medulla.
Where does the second synapse occur in the conscious proprioception pathway?
Thalamus.
Where does the third neurone of the conscious proprioception pathway terminate?
Somatosensory cortex.
If an animal has a lesion of the left somatosensory cortex, on what side would you expect conscious proprioceptive deficits?
Contralateral = if the lesion is on the left side, the. deficits will be on the right side → Unable to correct knuckled paw + Tripping on right hand side
What is the gracile fasciculus?
Processes conscious proprioception from the hindlimb.
What is the cuneate fasciculus?
Processes conscious proprioception from the forelimb.
What is kinaesthesia?
Awareness of the position and movement of the body
E.g. We are having a swing with a golf club to a golf ball and we miss it for the first time, we are able to adjust our movement
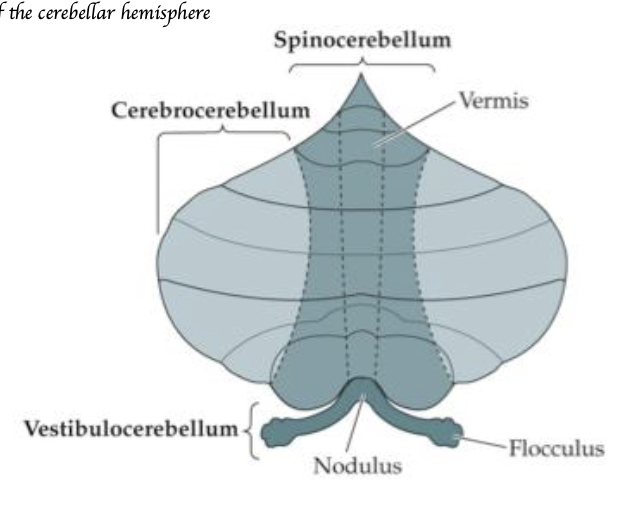
What is the function of the vestibulocerebellum?
Coordinates balance and eye movements.
What is the function of the spinocerebellum?
Coordinates muscle tone and movement.
What is the function of the cerebrocerebellum?
Planning of movements.
Identify where do the functional regions located.
In which spinal cord funiculus do conscious proprioceptive tracts travel?
Dorsal
P.S. Subconscious fact is in the lateral aspect
Which spinal tract carries subconscious proprioceptive input?
Spinocerebllar tracts