MicroBio Midterm 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:08 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
proteins on or in cells that recognize specific compounds unique to microbes or tissue damage, allowing the cells to sense the presence of invading microbes or damage
2
New cards
Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
transmembrane protein of immune cells that recognizes pathogens and activates an immune response directed against those pathogens
3
New cards
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
Molecules associated with groups of pathogens that are recognized by cells of the innate immune system.
4
New cards
Cytokines
Proteins that regulate the intensity and duration of immune response
5
New cards
Physical barriers to infection
skin, mucous membranes, ciliary escalator, lacrimal apparatus, saliva, urine, vaginal secretions, earwax
6
New cards
Chemical barriers to infection
acidic pH, lysozyme, saliva, gastric juices, urine, vaginal secretions
7
New cards
Normal Microbiota line of defense
Competitive exclusion, produce substances, building an immune system, probiotics, probiotics
8
New cards
Lymphatic system
Structures and organs containing lymph tissues, containing large numbers of lymphocytes (T and B cells), filers that trap microbes, macrophages and dendritic cells
9
New cards
Neutrophils (PNMs)
Highly phagocytic, Motile, active in initial stages, can leave blood and enter infected tissues, destroyer of microbes and foreign particles
10
New cards
Basophils
Release histamines, important for inflammation
11
New cards
Eosinophils
Somewhat phagocytic, can leave blood, can discharge peroxide ion, kills certain parasites
12
New cards
Natural Killer (NK) cells
Destroys targets by cytolysis and apoptosis. Toxic substances released from lytic granules, blood spleen, lymph nodes, red bone marrow, cause pores, recognizes reduced number of MHC-I molecules
13
New cards
T cells
Cell-mediated immunity
14
New cards
B cells
Produce antibodies, carries immunoglobulin on surface, host are IgM and IgD - all recognize same epitope
15
New cards
Macrophages
Phagocytosis; process and present antigens to lymphocytes for the immune response
16
New cards
Dendritic cells
Phagocytosis and initiate adaptive immune response
17
New cards
Monocytes
Not actively phagocytic until they leave the blood and mature into macrophages
18
New cards
phagocytosis
Ingestion of microorganisms or other substance by a cell
19
New cards
Fixed macrophages
Reside in particular tissues
20
New cards
Free macrophages
Roam and gather at sites of infection
21
New cards
Chemotaxis
Microbial products, components of damaged tissue and WBC, peptide
22
New cards
Adherence
PAMPs to receptors, causes phagocytes to release cytokines, uses opsonins to make recognition easier
23
New cards
Ingestion
Pseudopods surround microbe, meet and fuse creating a phagosome (phagocytic vesicle)
24
New cards
Digestion
Fusion of the phagosome with a lysosome to create and phagolysosome, undigested material is discharged
25
New cards
Inflammation
Damage caused by microbes, physical, or chemical agents - trigger a local defense mechanism (pain, redness, immobility, swelling, heat)
26
New cards
Acute inflammation
Rapidly develop, last short period of time, mild self-limiting, neutrophils principal mechanism
27
New cards
Chronic inflammation
Slower developing, longer lasting period, severe and progressive, monocytes develop into macrophages
28
New cards
Histamines
vasodilation and increased permeability of
blood vessels
blood vessels
29
New cards
Kinins
vasodilation and increased permeability;
chemotaxis of neutrophils
chemotaxis of neutrophils
30
New cards
Prostaglandins
intensifies histamines and kinin
response; helps phagocytes move through capillary
walls; associated with pain
response; helps phagocytes move through capillary
walls; associated with pain
31
New cards
Leukotrienes
increased permeability; help phagocytes
attach to pathogen
attach to pathogen
32
New cards
Cytokines
produced by fixed macrophages; vasodilation and increased permeability of blood vessels, chemotaxis of phagocytes and adaptive immune cells
33
New cards
margination
blood flow decreases and Neutrophils and Monocytes
migrate to area and stick to the lining of blood vessels
migrate to area and stick to the lining of blood vessels
34
New cards
diapedesis
Phagocytes squeeze through blood vessel cells
35
New cards
Fever
systemic (whole body) response of abnormally high body temperature
Slows growth of bacteria
Speeds up body's reactions
Speeds of antiviral interferons
Decreases iron available to microbes
Help increase T cell production
Slows growth of bacteria
Speeds up body's reactions
Speeds of antiviral interferons
Decreases iron available to microbes
Help increase T cell production
36
New cards
Complement protein activation
Complement proteins are inactive until split into fragments - cascade reactions
37
New cards
Classical activation
antibodies attach to antigens - Antibody-antigen complexes activate cascade
38
New cards
Alternative activation
C3 combines with complement proteins factors
B, D and P (Properdin) at the microbes surface
B, D and P (Properdin) at the microbes surface
39
New cards
Lectin activation
Cytokines stimulate liver to produce lectins (proteins that bind carbohydrates), enhance phagocytosis, create cascades
40
New cards
Interferons
cytokines produced by cells; have antiviral activity, play major role in acute viral infections
41
New cards
Siderophores
Bacteria produced, compete to gather iron by stealing it from other proteins by binding iron more tightly
42
New cards
Hemolysis
Lyses RBC, hemoglobin is degraded to get the Iron
43
New cards
Antimicrobial Peptides (AMP)
Short peptides of 15-20 amino acids, produced in response of protein and sugar molecules on microbes
Inhibits cell wall synthesis
Forms pores in plasma membrane (lysis)
Destroys DNA ands RNA
Broad spectrum
Synergistic with other AMPs
Inhibits cell wall synthesis
Forms pores in plasma membrane (lysis)
Destroys DNA ands RNA
Broad spectrum
Synergistic with other AMPs
44
New cards
Lack of immunity
Susceptibility
45
New cards
Adaptive Immunity
Defenses that target a specific pathogen after exposure
46
New cards
Humoral Adaptive Immunity
B cells & Antibodies, fight extracellular invaders, B cells matured in red bone marrow, found in blood and lymphoid organs
47
New cards
Cellular Adaptive Immunity
T cells & Cell mediated immunity, TCRs, produce cytokines, precursors made in red bone marrow, mature T cells produced by Thymus, Fight antigens intracellularly
48
New cards
Where do stem cells develop into blood cells
Red bone marrow
49
New cards
Active Adaptive immunity
Immunity produced by the person infected, long lasting
50
New cards
Passive Adaptive immunity
Antibodies transferred from one person to another, transfer of antibiotics from mother to infant, lasts as long as antibodies are present (mostly a few weeks to months)
51
New cards
Artificially acquired active immunity
Exposure to antigens from vaccine, immune response with no infection
52
New cards
Artificially Acquired Passive immunity
Injections of antibodies, post exposure prophylaxis, short lived, delivers immediate immunity
53
New cards
Cytokines
Chemical messengers produced in response to a stimulus, communication between cells, soluble proteins or glycoproteins, produced by immune cells, react on cells that have receptors for them
54
New cards
Interleukins (ILs)
Cytokines communication between leukocytes
55
New cards
Chemokines
Induce migration of leukocytes to infection or tissue damage
56
New cards
Interferons (INFs)
Interfere with viral infections of host cells
57
New cards
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a)
Involved in inflammation
58
New cards
Hematopoietic cytokines
Control stem cells that develop into red and white blood cells
59
New cards
Cytokine Storm
Production of cytokines causing more cells to produce cytokines (can do damage to tissues - flu, ebola)
60
New cards
Antigens
Typically a pathogen, substance that causes the production of antibodies, detection causes SPECIFIC antibody
61
New cards
Antibodies
Soluble proteins designed to recognize and bind to a specific antigen, have at least 2 identical antigen binding sites (to bind to specific epitope)
62
New cards
Epitopes
Part of the antigen molecule in which an antibody attaches itself
63
New cards
Antigenic determinants
The part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, and T cells
64
New cards
Hapten
Low molecular mass antigen that needs a carrier molecule
65
New cards
Humoral Adaptive Immunity
B cells, antibodies, Recognize and combat antigens, Fight extracellular, Found in blood and lymph rogans, ,matured in red blood cells
66
New cards
Cellular Adaptive Immunity
T cells, Cell mediated response, TCR, destroys cells and produces cytokines, T cells produced in Thymus, fights intracellularly
67
New cards
Valence
Number of antigen binding sites on an antibody
68
New cards
Variable regions
Part of the antibody that bind to antigen
69
New cards
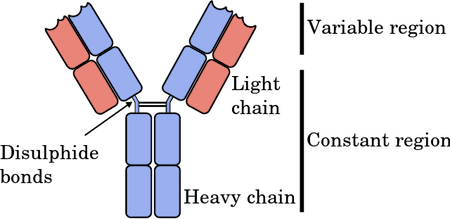
IgG antibody
Monomer, 80% of total antibodies found, triggers complement system, bivalent, enhances phagocytosis, can cross placenta
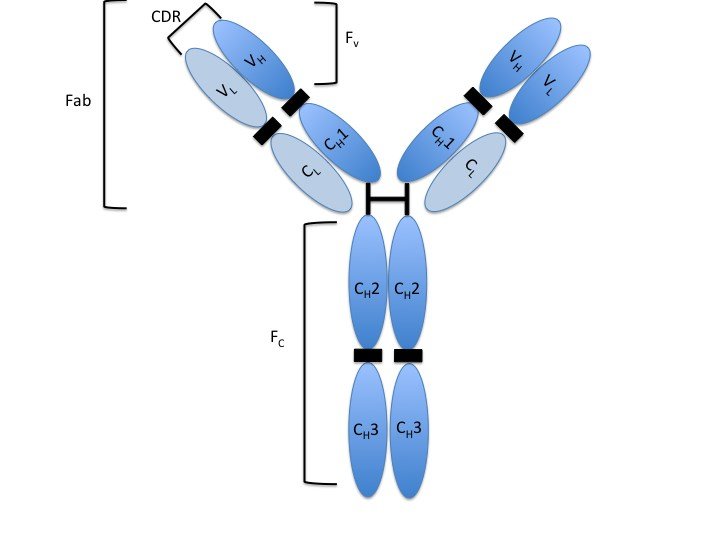
70
New cards
IgM antibody
Pentamer, 6% of total antibodies, short lived, activates complement system, valency is 10
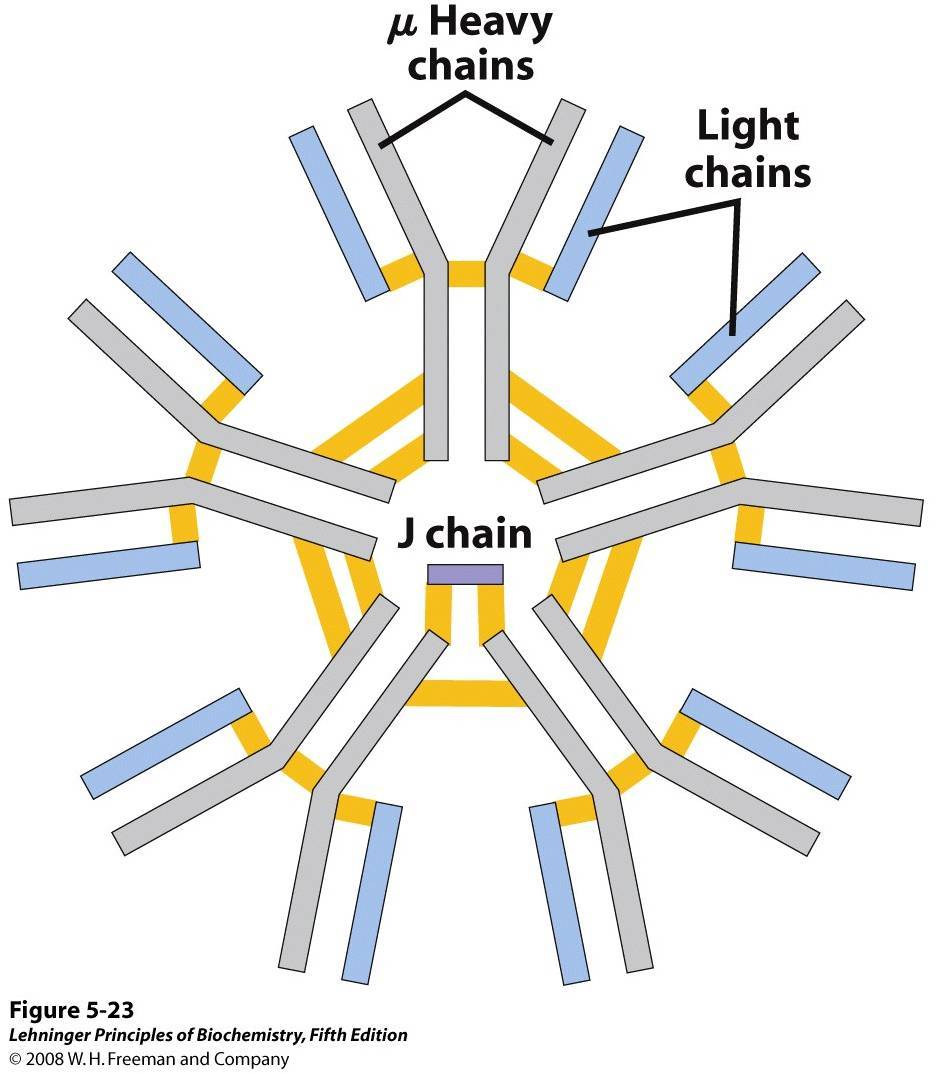
71
New cards
IgA antibody
Dimer with Secretory component, 13% of antibodies, most common in mucous membrane and bodily secretions, prevents attachment of pathogens, short lived
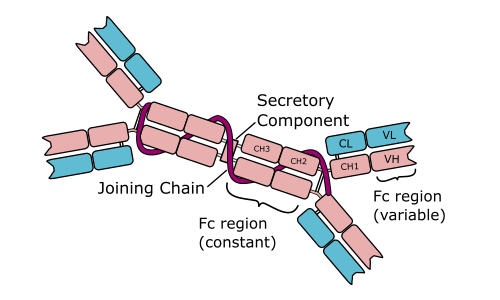
72
New cards
IgD antibody
Monomer, 0.02% of antibodies found, B-cell surface, blood, and lymphs, short lived, helps with immune response
73
New cards
IgE antibody
Monomer, 0.002% of antibodies, bound to mast cells and basophils, percentage increase with allergic reactions and parasites, short lived, bivalent
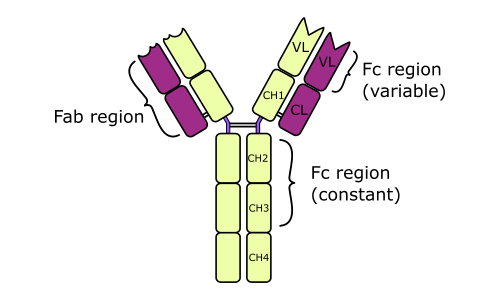
74
New cards
Immature lymphocytes
Lack fully developed antigen specific receptors
75
New cards
Naive lymphocytes
Have receptors but have not yet encountered "correct antigen"
76
New cards
Activated lymphocytes
Have bound antigen and received confirmation, are able to proliferate
77
New cards
Effector lymphocytes
Descendants of activated lymphocytes (Ex. plasma cells for B lymphocytes)
78
New cards
Memory lymphocytes
Long-lived descendants of activated lymphocytes; responsible for rapid secondary response if antigen is encountered again
79
New cards
Clonal deletion/Negative Selection
B cells are exposed to "self antigens" and undergo apoptosis and are killed is they bind - prevents autoimmune disease
80
New cards
B cell receptor (BCR)
anchored protein to surface of B cell, allows B cell to recognize its target epitope
81
New cards
T-dependent antigen
Antigen requires a T helper cell to activate B cell
82
New cards
T-independent antigen
B cell can be activated directly by the antigen, antigens provoke weaker immune response, no memory cells generated
83
New cards
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
present potential antigenic fragments to T cells, associated with cellular immunity
84
New cards
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
collection of glycoprotiens in the cells plasma membrane
85
New cards
Agglutination
Antibodies cause antigens to clump together
86
New cards
Opsonization
Coating of the antigen with antibodies, enhance phagocytosis
87
New cards
Neutralization
Coat bacteria, virus, or toxin - block adhesion and attachment to host
88
New cards
Activation of complement
Inflammation and lysis
89
New cards
Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity
Antibodies attach to target cells, cause destruction by macrophages, eosinophils, and NK cells
90
New cards
Thymic selection
Immature T cells that recognize hosts and are eliminated
91
New cards
CD4+
T help cells, work with B cells mainly by cytokine signaling, bind to MHC II antigen, activation results in proliferation and secretion of cytokines
92
New cards
CD8+
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes, bind to MHC I antigen
93
New cards
Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs)
Have MHC on their surfaces, present potential antigenic fragments to T cells. Consist of B cells, Dendritic cells, Activated Macrophages, and possibly Neutrophils
94
New cards
Dendritic Cells - APC
Main APC, sentinel: engulf invaders, degrade and transfer them to lymph nodes to display to T cells
95
New cards
Activated Macrophages
Ingestion of antigenic material that can activate macrophages, more effective than phagocytosis
96
New cards
TH1 cytokines
activate macrophages, stimulate production of antibodies through activating B cells, activated Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
97
New cards
TH2 cytokines
Stimulate production of antibodies through activation of B cells, activation of eosinophils
98
New cards
TH17 cytokines
Recruit neutrophils to act on certain infections of extracellular bacteria and parasites
99
New cards
Treg
Combat autoimmune reactions by suppressing T cells that escaped Thymus deletion, protect resident microbiota
100
New cards
Perforin
Forms pores - useful in apoptosis