Pediatric tut 1
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Contraindications of breast feeding for mother & child:
Mother
Relative CI:
Psychiatric disorder
Acute fever, TB, chronic nephritis, breast abscess, septicaemia, post-partum psychosis
Temporary CI:
Inverted nipples, cracks of nipples, and fissures.
Absolute CI:
Cancer treated with anticancer agents
Child
Absolute CI:
Galactosemia (galactose from lactose in breast milk may worsen condition)
Phenylketonuria
Any condition where child cannot suck
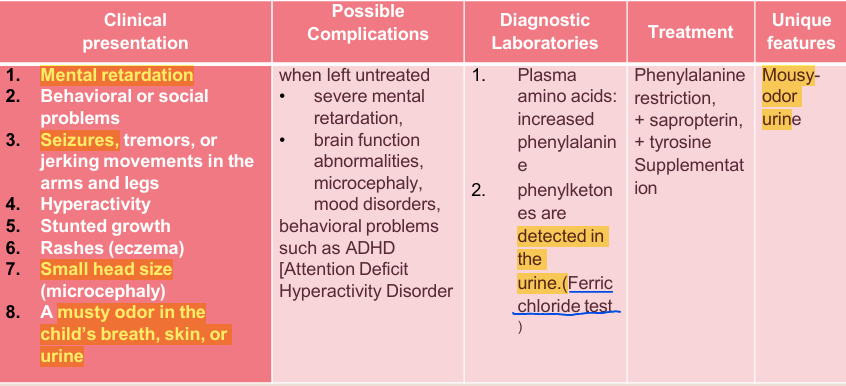
Describe phenylketonuria (PKU).
An autosomal recessive genetic disorder where there’s a deficiency in the phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme (PAH), so phenylalanine isn’t metabolized and becomes phenyl ketones (phenylpyruvate, phenylacetate, phenethylamine). They accumulate and cause brain damage.
PKU features:
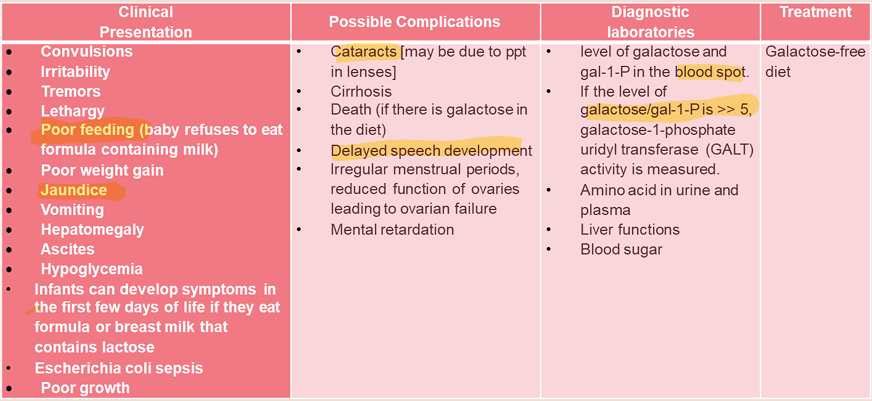
Describe galactosemia.
A disorder or inability to breakdown galactose or its metabolite galactose-1-phosphate (gal-1-P).
Galactosemia features.
Types of breast milk.
Colostrum: produced at the latest stage of pregnancy; high in protein, low in carbohydrates
Traditional milk: between week 1 and 2 after delivery; fat and sugar content increase.
Breast milk: 10 days from delivery; high in carbohydrates but low in protein.
Breast milk composition:
Nutritional components
Minerals & vitamins
Hormones & GF
Microbial communities
MicroRNAs
Evaluating adequacy of BF:
Infant sleeps 2-3 hrs after BF.
Weight gain
6-8 well-formed stools per day
Breasts soft after
Milk analysis
Frequent feeding approx. 10 times/day.
Poor weight gain causes even after breast feeding.
Technique problem (most common cause): flutter sucking—ineffective suckling—decreased BF frequency
Infant health problems or deformity: congenital mouth anomalies—cleft lip
Maternal health problems: decreased nutritional status—decreased hydration—-retained placenta
Evaluation of infant for poor weight gain.
Routine history (frequency or duration) of feeding
Pain when nursing—→ stress—→ dec. prolactin & oxytocin
No. of bowel movements/stools < 3 or 4 times/day
Physical examination of infant mouth and suckling
Maternal breasts examination
Observation of technique and attachment (latching)
Management of poor weight gain
Correction of technique and attachment
Increase frequency and duration of feeding
Electric pump bw feedings to express milk (increases prolactin production)
Monitor baby weight every 2-4 days; weight gain should be 20-30 g/day.
Baby’s weight should be:
At birth: 3-3.5 kg
4 months: 6 kg
8 months: 8 kg
12 months: 9 kg
Equations:
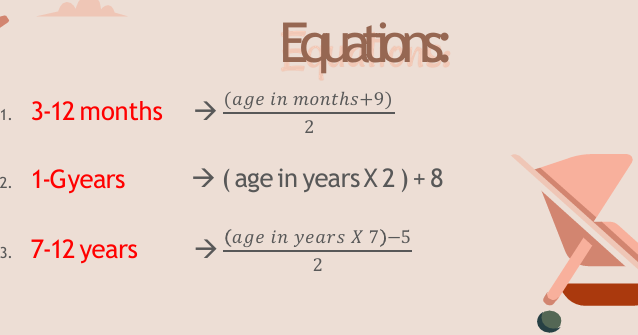
How can a mother increase her milk supply?
Using a pump at least 5 or 6 times a day.
Nursing as much as possible.
If a mother is not present or sick and can’t nurse, what other options are available.
Cup feeding
Finger feeding
When might finger feeding be used.
Mother is unable to breast feed.
Baby refuses to feed or too sleepy
Baby is getting trained, weak or too lazy to suck