AP Chemistry Unit 3 (3.1-13)
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
how is this even possible
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
A nonpolar molecule with more electrons is more __________, meaning it has stronger _________
polarizable, LDFs
When molecules are the same size, ______ forces are stronger than _______ forces
dipole-dipole, London disperson
When two molecules have a large difference in size, the strength of their _______ (whether polar or nonpolar) scales with their size
IMFs
Although CCl4 has only LDFs, while HCl has dipole-dipole forces AND LDFs, CCl4 has a stronger IMFs because…
It is much larger than HCl (more electrons)
Hydrogen bonds are really just extra-strong ________ forces
dipole-dipole
What must a molecule have to be a hydrogen bond DONOR?
Hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to F, O, or N
What must a molecule how to be a hydrogen bond ACCEPTOR?
F, O, or N with a lone pair of electrons on it and a partial negative charge (part of a polar bond)
Hydrogen bond ACCEPTORS don’t need to have…
Hydrogen, just F, O, or N with lone pair
In a large molecule, it is possible for hydrogen bonding forces to be formed between a _____________________ and the _______________
hydrogen atom (bonded to F, O, or N); negative end of a dipole formed by F, O, or N
Ion-dipole forces
Attractive force between ion and polar molecule, usually occurring in a solution
Ion-dipole forces occur when an ionic compound is ___________ in a polar _________, such as…
dissolved, solvent, H2O
Dipole-induced dipole forces
Attractive force between polar and nonpolar molecules → polarity of polar molecule causes a nonpolar molecule to form a temporary dipole
Dipole-induced dipole forced increase with the __________ of the polar molecule and the ____________ of the nonpolar molecule
magnitude, polarizability
Polarizability
The case with which the electron cloud in an atom or molecule can be distorted (larger electron cloud = more polarizable)
London dispersion forces
Attractions between nonpolar atoms/molecules that are caused by temporary dipoles
Dipole-dipole forces
Attractions between polar molecules in which the partial negative charge of one polar molecule is attracted to the positive partial charge on another nearby molecule
If two compounds have the same formula, but one structure has a larger surface area, it will have __________ IMFs
stronger
Amorphous network solid
Solid with a random, disordered arrangement of atoms or molecules
Crystalline network solid
Three-dimensional, repeating arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules
Ionic and covalent network solids have ________ melting points, while molecular solids have _______ melting points
high, low
_____ solids are hard and brittle
Ionic
_____ solids are hard and rigid
Covalent network
_____ solids are soft
Molecular
_____ solids are malleable and ductile
Metallic
Which is the only SOLID that conducts electricity?
Metallic
Metalloids form _________ bonds with nonmetals
covalent
A higher vapor pressure implies many _________
collisions
Vapor pressure
Pressure exerted by a gas in equilibrium with its liquid phase at a given temperature
Network solids only have _________ and lack ________, giving them ridiculously high _______________
bonds, IMFs, boiling points
When comparing two liquids at the same temperature, the liquid that has a higher ____________ should have a lower ____________
vapor pressure, boiling point
Boiling point
Temperature which the vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the external pressure surrounding the liquid
Normal boiling point
Situation in which the vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level (1 atm/760 torr)
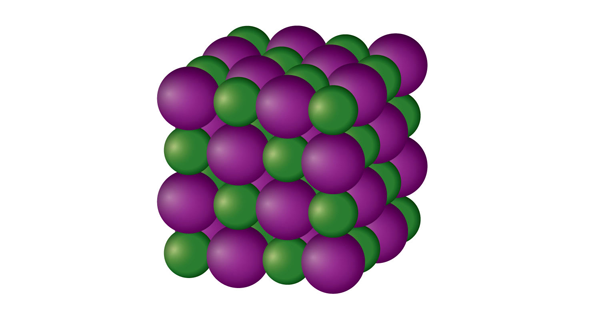
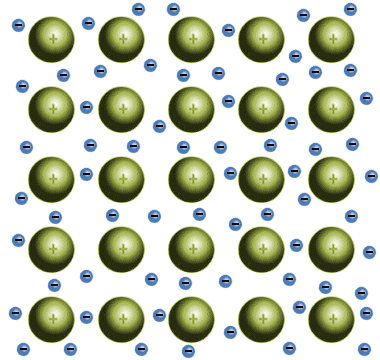
Which solid is represented by the particles?
Ionic
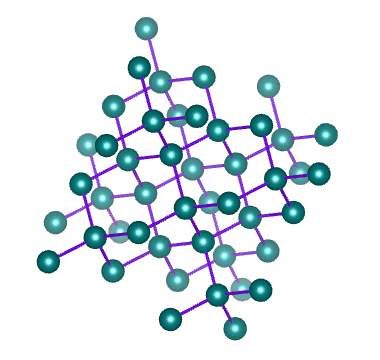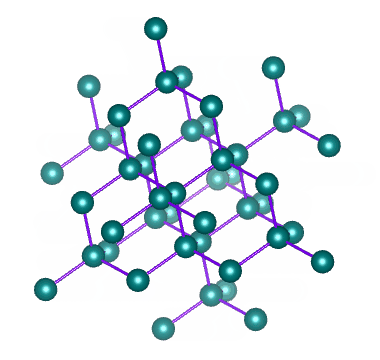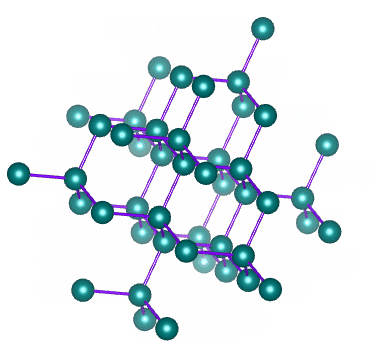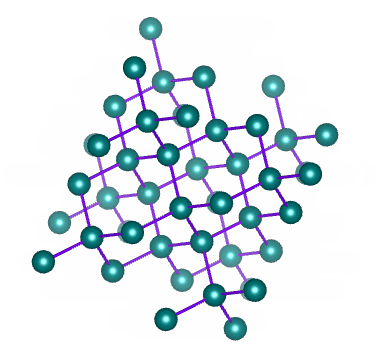
Which solid is represented by the particles?
Covalent network
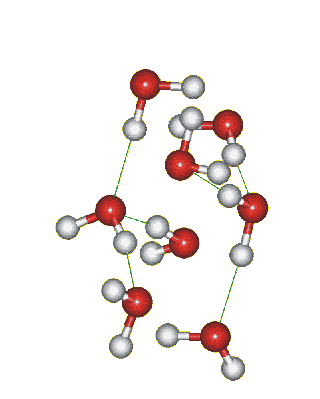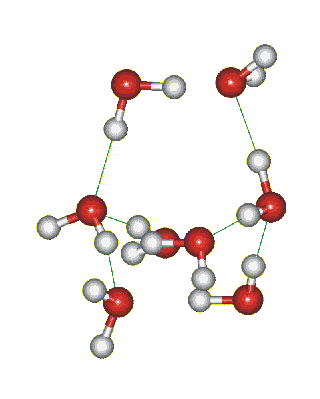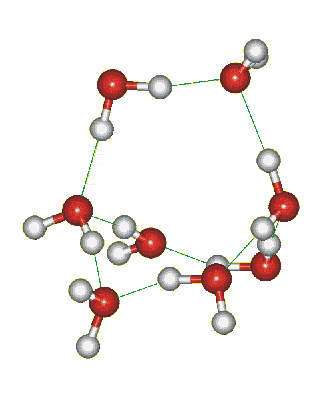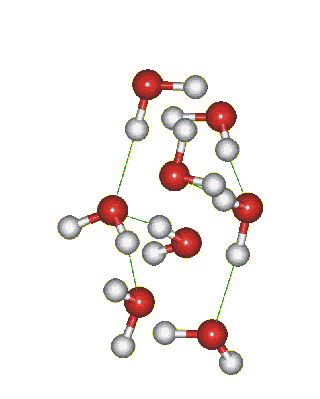
Which solid is represented by the particles?
Molecular
Which solid is represented by the particles?
Metallic
Does Nick Forest know what polarizability is?
No lol
Is Mr Ionic the goat?
[[YES]]
![<p>[[YES]]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a7d4cfe8-c0d4-4e3e-b511-9af8a7a0da12.png)
What is the universal gas constant used in ideal gas laws problems?
0.08206
How many torr is in 1 atm?
760
Kinetic energy is related to ___________
temperature
If temperature is the same between two samples, so is the _________________
kinetic energy
A lower kinetic energy indicates a _________ average particle speed
lower
A particle that is lighter travels at a _________ average speed than a heavier particle at a given temperature
fatser
A higher average speed indicates _________ pressure
greater
What does it mean for a tank to be flushed?
For it to be removed of all dry air
What is the density of water?
1 g/mL
Which elements exist as diatomics?
Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine
In terms of ideal gas law, what can P be set equal to?
(nRT)/v
What is the formula for total pressure, given gasses A, B, and C?
PA + PB + PC
What proportion is set up for partial pressure when given moles?
PA / PTotal = nA / nTotal
The peak of a Maxwell-Boltzman distribution curve represents…
The most probable speed
As the average speed of a particle increases, there is a _________ range of values for particle speed
wider
As the average speed of a particle increases, the slope of the Maxwell-Boltzman curve becomes _________
flatter
As the average speed of a particle increases, the peak of the Maxwell-Boltzman curve moves to the ________
right
The average molecular speed of a gas is higher when the gas has a _____________ temp and a _____________ molar mass
higher; lower
In an ideal gas, it is assumed that there are no ______________ between the particles
attractive forces
The particles of a ___________ gas experience attractive forces
real
Deviations from ideal gas law occur as a result of _________________ and ________________
interparticle interactions; finite particle volumes
The effect of interparticle forces is especially noticeable when the gas temperature is relatively __________
low
Negative pressure deviations (lower than ideal) occur due to…
interparticle interactions, causing gasp particles to strike the container less often
Positive pressure deviations (higher than ideal) occur due to…
nonnegligible particle volumes, which cause particles to strike container walls more often
In an ideal gas, it is assumed that the volume occupied by the gas particles themselves is _____________, or _____________
zero; negligible
A gas sample should exhibit ideal behavior at relatively _____________ temperatures and ____________ pressures
high; low
A higher pressure means that the particles are ____________ compact, encouraging the formation of ______________
more; IMFs
Solvent
The substance that dissolves another
Solute
The substance that is dissolved by another
In a mixture, there is usually __________ solvent than solute
more
__________ is the universal solvent
Water
Molarity equation
(Moles of solute)/(liters of solution)L
Larger molarity = _________ concentration
larger
A solution in which a substance is dissolved completely in water is known as an _______ solution
aqueous
How do you perform a dilution?
Add distilled water to a solution
What formula can you use to figure out molarity in a dilution?
M1V1 = M2V2
Why do you rinse the weighing paper when adding solute to a solvent?
Solute may stick to the weighing paper/container
What kind of flask is used for a dilution?
Volumetric flash
The components of a liquid solution cannot be separated by…
filtration
What are the two methods in which a liquid solution can be separated?
Chromatography, distillation
Chromotography
Separates chemical species by taking advantage of the differential strength of the IMFs between and among the components of the solution/mobile phase and with the surface components of the stationary phase
Chromatography can help infer the relative _____________ of components in a mixture
polarities
Stationary phase
A solid that provides support for the chromatography experiment, but does not move → can be piece of paper, piece of metal/glass coated with a porous solid, or a glass column filled with a porous solid
Mobile phase
A liquid or gas that moves, carrying the components of the mixture over or through the stationary phase
In a chromatography experiment, if Component X travels farther away from a nonpolar solvent/mobile phase than Component Y, Component X is more ___________
nonpolar
Substances with ____________ IMFs tend to be more soluble in one another; in other words, _________ dissolves _________
similar; like dissolves like
Solvent front
In a chromatography experiment → the mark on the paper that indicates how far the solvent has moved up the paper
Retention factor (Rf) formula
(Distance traveled by one component)/(distance traveled by the solvent)
The larger the Rf value is the farther _____ the paper he component of the mixture has traveled relative to the solvent front
up
Distillation
Separates chemical species by taking advantage of the differential strength of IMFs between and among the components and the effects these interactions have on the vapor pressures of the components in the mixture; separates components of a mixture that have different boiling points
In a distillation, the mixture is heated gently until the component with the ________ boiling point begins to boil. The vapor rises up through the glassware, and reaches the ____________, which is the portion of the apparatus that is surrounded by cool _____________. The vapor condenses into a liquid and is collected in a separate container, The liquid that is produced in a distillation experiment is known as the _______________. The component of the mixture that appears first in that is the one with the _____________ boiling point.
lowest, condenser, water, distillate, lowest
Ionic compounds MUST dissolve in _________
water
Polar and nonpolar only refers to _____________ molecules
nonmetal
What are the three types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR)?
Microwave, infrared, ultraviolet
Microwave radiation causes a molecule to…
rotate
Infrared radiation (IR) causes the bonds in a molecule to…
vibrate
Visible/ultraviolent (UV) radiation causes electrons in the molecule to…
move up to higher energy levels
Wavelength (𝜆)
Length of wave (period) in meters/nanometers
Frequency (v)
Number of cycles passing a point in a given time (cycles per second → hz)
Speed (c)
The speed of light, at which all electromagnetic radiation travels at
How do wavelength, frequency, and speed relate?
c = 𝜆v