Bio 30-1 Ch 14 The Senses
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Explain Sensory Adaptation
Sensory receptors/neurons adjust to a stimulus and cease to fire despite the stimulus still being there. The threshold level has moved up.
Whats the difference between how taste and smell detect stimulus
Taste - detects dissolved chemicals
Smell - detects airborne chemicals
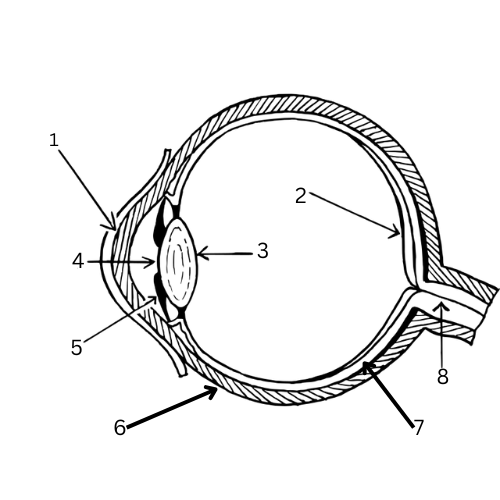
What is 1 & its function?
Cornea - Transparent cells to bend light towards pupil
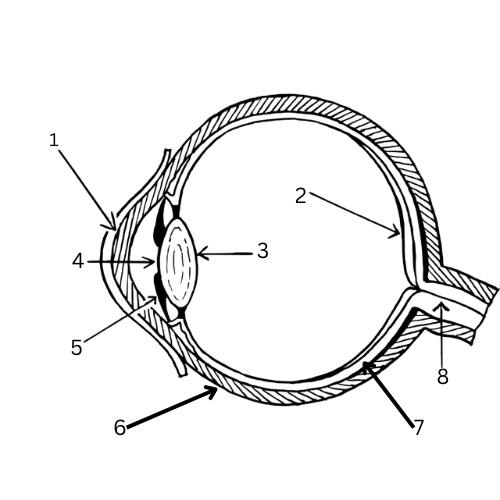
What is 2 & its function?
Retina - contains light-sensitive cells called rods and cones
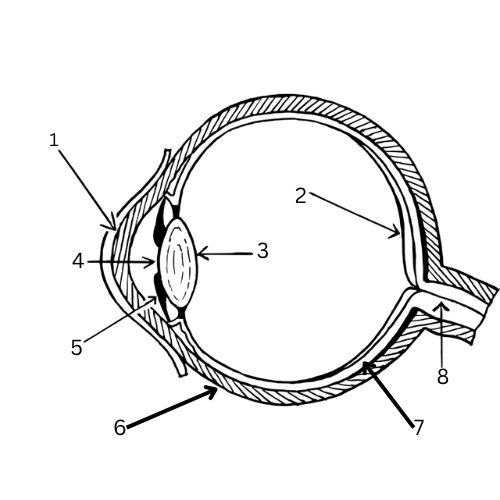
What is 3 & its function?
Lens - focuses the image onto the retina
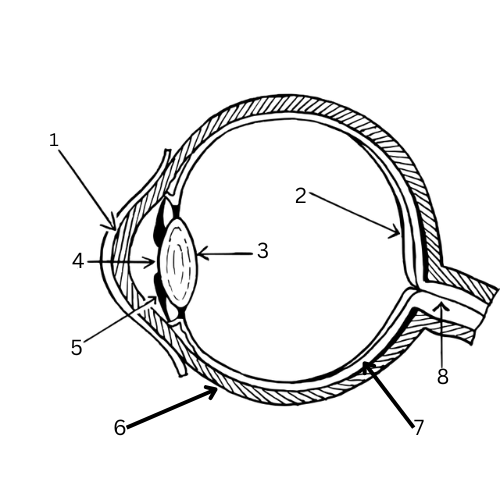
What is 4 & its function?
Pupil - Opening in the iris where light is let into the eye
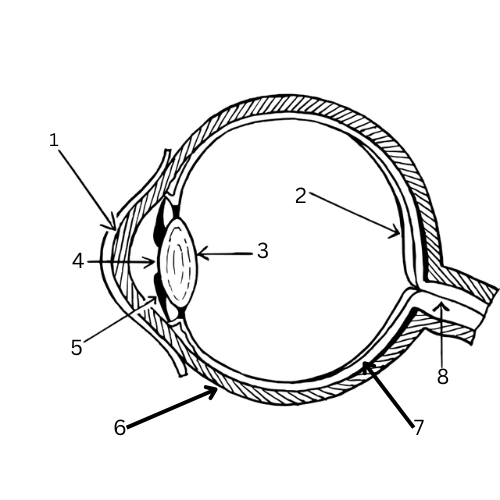
What is 5 & its function?
Iris - A muscle that controls the size of the pupil and therefore the amount of light let into the eye
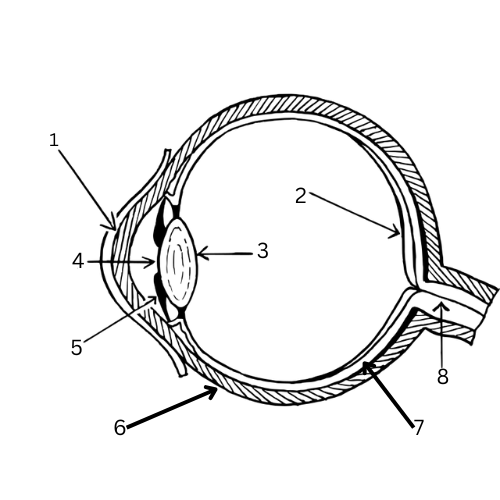
What is 6 & its function?
Sclera - White outer layer that maintains the eye’s shape and protects it.
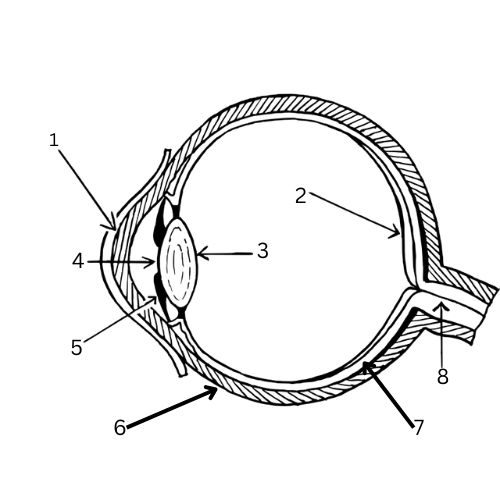
What is 7 & its function?
Choroid layer - contains blood vessels
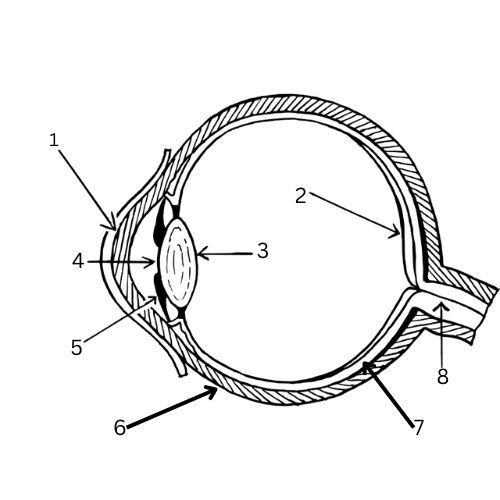
What is 8 & its function?
Optic nerve - Carries the stimulus to the brain
What’s the function of Rods & Cones?
Rods - B&W vision, high light sensitivity, used for seeing in the dark, low definition, peripheral
Cones - Colour vision (3 types of cones), requires bright light Fovea Centralis
Explain the difference between Fovea Centralis & Peripheral vision
Peripheral vision - High Rods
Fovea Centralis - High SA & Cones & most sensitive part of the eye
Know Vision Defects brah
cataracts, glaucoma, astigmatism, colourblindness, near/far sightedness