physics chapter 1
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Time
any unit of duration - s, ms, micros
what is sound
pressure wave that requires a mechanical action
distance
any length measurement
frequency
cycles/second - Hz, MHz
velocity
unit of length divided by time
area
any distance unit squared
volume
any distance unit cubed or volume unit (cm³ or mL)
Good Men Kick Habits Dead Because Dead Can’t Make Me Nuts
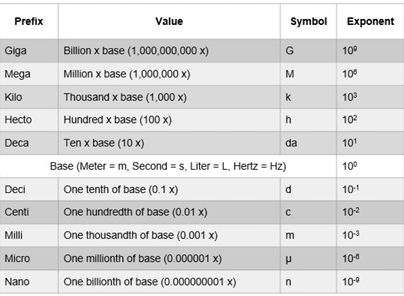
what are the pirmary acoustic variables
pressure, density, distance
define pressure and units
concentration of force within an area, Pascals
define density and units
concentration of mass within a volume, kg/cm³
define distance and what units
measurement of particle motion, any length unit
defind wavelength
length of single cycle of sound - LENGTH
what are the 7 parameters of sound
period, frequency, amplitude, power, intensity, propogation speed, wavelength
what is period (T)
amount of time of one cycle (beginning of one to beg of another) TIME
what determines period
machine - not adjustable
if frequency of sound is 12 Hz, what is period
1/12 of second
what determines frequency
machine - not adjustable
period and freuqncy are ___________
inversely related, reciprocals
what is amplitude
amount of force
5 oscillations in 1 second = __________ Hz
5
define propogation speed
speed of soundwave through medium
what determines propogation speed
medium
what is formula for propogation speed
speed (C) = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (lambda)
what is standard for speed through soft tissue
1540 m/s (1.54 mm/microS)
what properties of the medium determine speed of sound
siffness and density
what determines wavelength
machine and medium, not adjustable - only acoustic parameter determined by both
lower the frequency, ___________ the wavelength
longer
formula for wavelength
propogation speed (1.54 Mhz)/frequency
what is wavelength of 2 MHz transducer
1.54 divided by 2 (soft tissue prop speed) = 0.77 mm
what parameters affect strength of a soundwave
amplitude, power, intensity
define amplitude
max increase or decrease of acoustic variable from baseline of that variable
what are amplitude variables
particle motion (pressure, density, distance)
what units are amplitude variables in
pascals, kg/cm³, mm, dB
what determines amplitude variables
machine initially, then medium causes decrease - it is adjustable by changing output power
define power
the rate at which work is performed or energy is transmitted
what determines power
initially machine, decreases w/medium - adjustable by sonographer
how is power proportional to amplitude
increase power = increase amplitude²
define intenstiy
power of a wave divided by area of which it is spread (W/cm²)
what unit is used for intensity
W (power)/cm²
what determines intensity
machine initially then decreases w/medium - adjustable by sonographer
intensity is _______ to power
directly proportional - equally
intensity is _____ to amplitude²
proportional - if amplitude² is doubled, intensity is x4
what is the amount of impedence dependt on
density and propogation speed
what unit is used for impedence
Rayls
what controls impedence
medium
transmission of Pulse echo converts _____________
electrical energy to sound
reception of pulse echo converts
sound into electricity
what are pulsed wave parameters
pulse repetition freqency (PRF), pulse repetition period (PRP), pulse duratoin (PD), duty factor (DF), spacial pulse length (SPL)
what is PRF/pulsed repetition frequency
number of pulses per second (one pulse can have mult. cycles)
the deeper the area of interest, the faster/slower the PRF
slower
define PRP/pulse repitition period
time taken for pulse to occur (on/trasmit and off/listening times)
PRP and PRF are _________ related
inversely related, reciprocals
pulse duration
“talking” time measurement - # cycles (n) x period (T)
pulse duration determined by
machine
what is spatial pulse length
number of cyclex (n) x wavelength
if wavelength increases, spatial pulse length __________
increases
SPL determined by
machine and medium
attenuation
decrease of amplitude, power, and intesity
what are mechanisms of attenuation
absorption, scattering, reflection
what is the unit for attenuation
decibels dB
absorption creates ___________
heat - thermal bioeffects - (sound to heat)
How are attenuation and frequency related
Directly
distance (path length) and attenuation are __________ related
directly
if intensity or power doubles, decibels changes by
3 dB
if intensity or power decreases by half, decibel changes by
-3 dB
what is wavelength of 1 MHz transducer
1.54
what is wavelength of 2 MHz transducer
0.77
Intensity formula
power/area W/cm²
formula for impedance
prop speed (p) x density
what is PRP
puls repetition period - one pulse length
what is spatial pulse length
length of pulse
formula for PD
pulse duration = n of cycles x period
formula for DF
duty factor - PD/PRP
when increaseing dB by 3, what is intensity/power
doubled
when decreasing dB by 3, what is intensity/power
1/2
when increasing dB by 6, what is intensity/power
quadrupled
when decreasing dB by 6, what is intensity/power
1/4th
when increasing dB by 10, what is intensity/power
10 x
when decreasing dB by 10, what is intensity/power
1/10th
when increasing dB by 20, what is intensity/power
100 (#0’s)
formula for attenuation coefficient
½ frequency
formula for HID/half intensity depth
6/f
what is specular reflectors
90 deg, smooth
what is Rayleigh scattering?
only seen in RBC, omnidirectional scattering
formula for Raleigh scattering
frequency to the 4th power
what are the two criteria required for reflection
normal incidence (90 degrees), media w/different impedances/PORNN
What does PORNN stand for
Perpendicular, orthogonal, right angle, 90°, normal - all same meaning
angle of reflection and angle of incidence will always equal
each other and add to 90 degrees
what is intensity transmission coefficient
% of sound transmitted at an interface
formula for intensity transmission coefficient
1 minus % of sound reflected at an interface/intensity reflection coefficient - ITC=1-IRC ITC and IRC = 100%
what is refraction
Angle of transmitted sound - a redirection of a sound beam, not reflection, Snell’s law
what are two requirements of refraction
oblique incidence, different prop speeds of 2 media
will media with faster speed have greater or lesser refraction/angle
greater
formula for inensity
power/area
what is PW “pulse”
talking time
what is PW temporal
all time - transmit and receive
where is spatial peak measured
at center of beam
what is BUR/beam uniformity ratio?
spatial peak/average
at what intensity is PW usually at
0% - usually listening, not transmitting