BIOL 1113 (General Biology 2) Exam 1 Mary Susan Potts Santone
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
181 Terms
Species
Group of related organisms that share a distinctive form; in species that produce sexually, they are capable of interbreeding
Population genetics
Study of genes and genotype in a population
Genetic drift
Changes in allele frequencies due to random chance; occurs quickly in small populations
Non-Darwinian evolution
Idea that much of the modern variation in gene sequences is explained by neutral variation rather than a natural variation
Hybrid sterility
Postzygotic isolation mechanisms where an interspecies hybrid may be viable but sterile
Hybrid breakdown
Postzygotic isolating mechanism where a hybrid may be viable and fertile, but the subsequent generations may harbor genetic abnormalities that are detrimental
Intron sequences
Which type of DNA sequence is likely to change fairly rapidly?
Characteristics of Living Organisms
Cells and organization; energy use and metabolism; response to environmental change; regulation and homeostasis; growth, development and adaptation; biological evolution
Biological Organization
Cell (most basic unit of life) > tissue > organ > organ system > organism > population > community > ecosystem
Metabolism
All chemical reactions in a cell
Homeostasis
maintenance of internal conditions within certain boundaries
Growth, Development, Reproduction, DNA (characteristics of living organisms)
Growth produces more or larger cells; development produces organisms with defined set of characteristics; reproduction sustains species over generations; genetic material causes offspring to have traits like their parents
(Biological) Evolution
Populations of organisms change over generations; heritable change in one or more characteristics of a population or species over generations hat promote survival and reproductive success; descent with modification
Structure Determines Function
When a biological structure comes about as a species adapts to its environment
(Characteristics of) cell like structures
Boundary; polymers inside contain info; polymers inside w/ enzymatic function; self-replicating
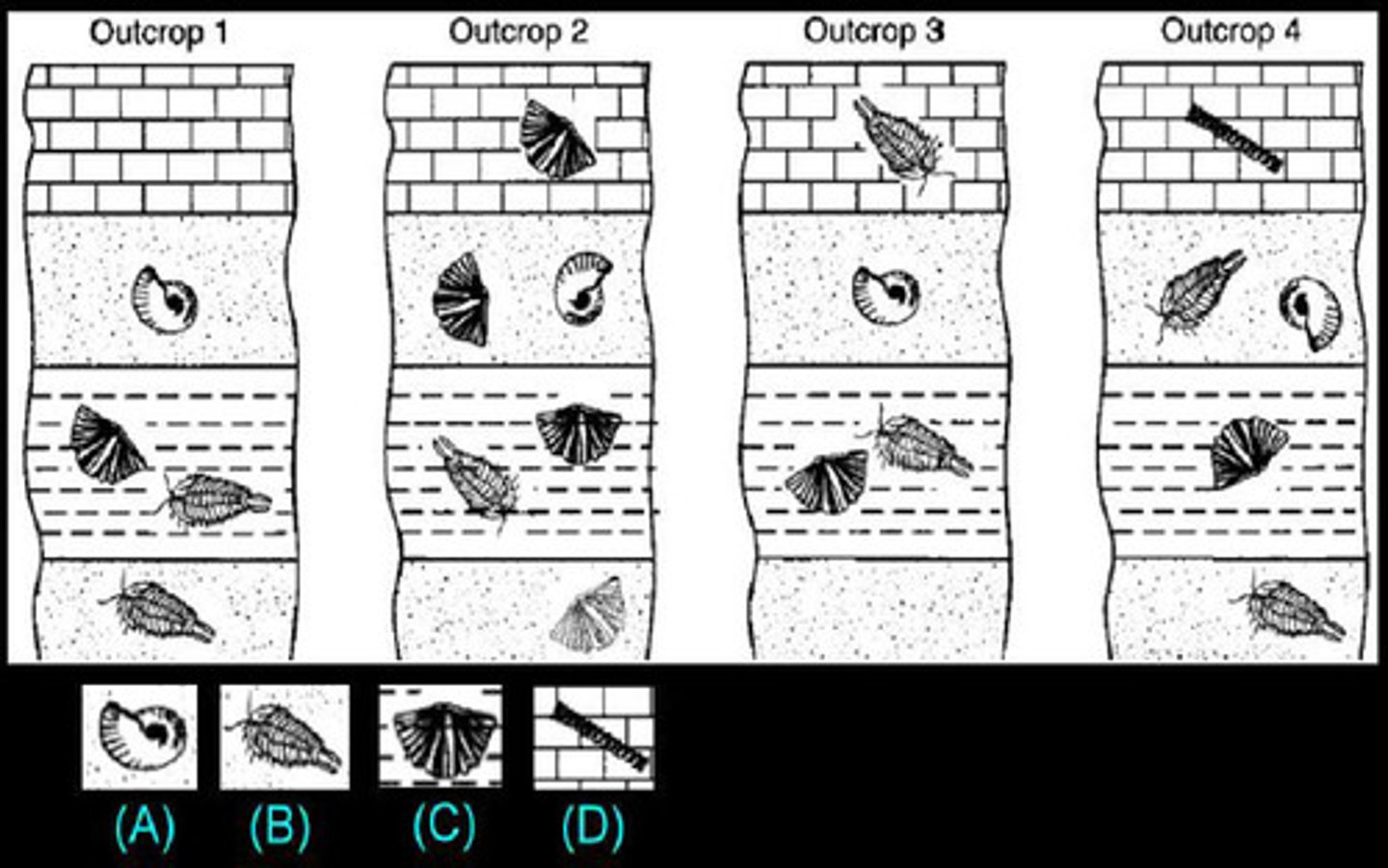
Strata
A layer of sedimentary rock whose composition is more or less the same throughout and that is visibly different from the rock layers above and below it

Index species/fossils
Fossils that help define and identify geologic periods (used in relative dating)
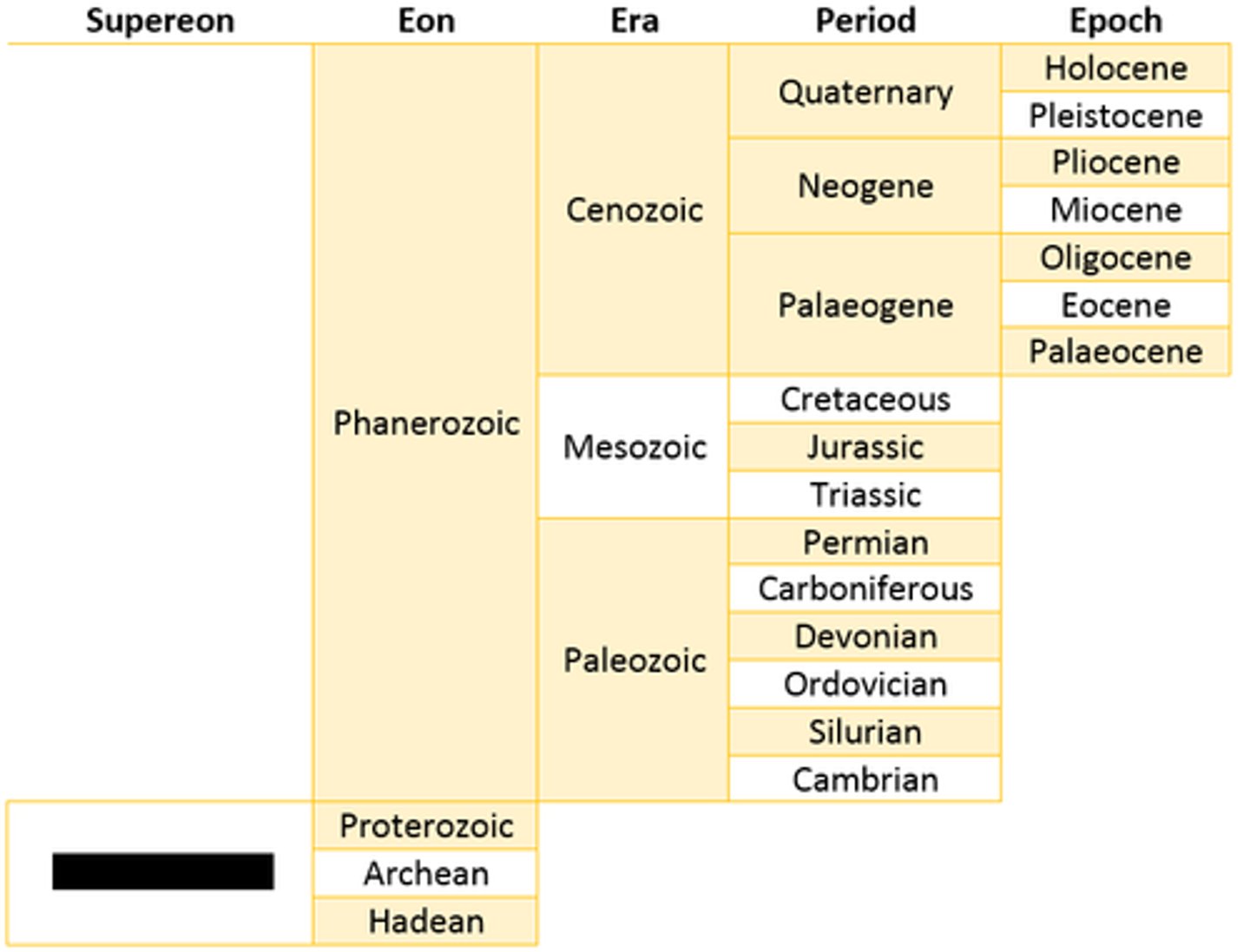
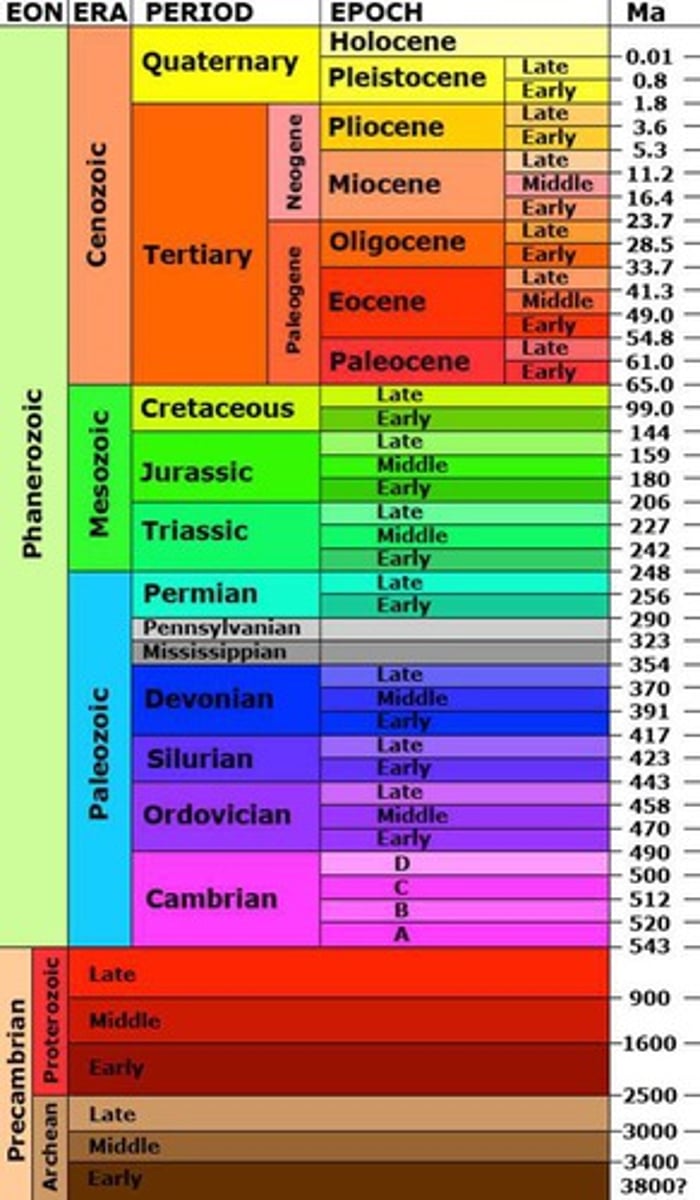
Geological timescale
Timeline of Earth's history and major events from its origin approximately 4.55 bya to the present
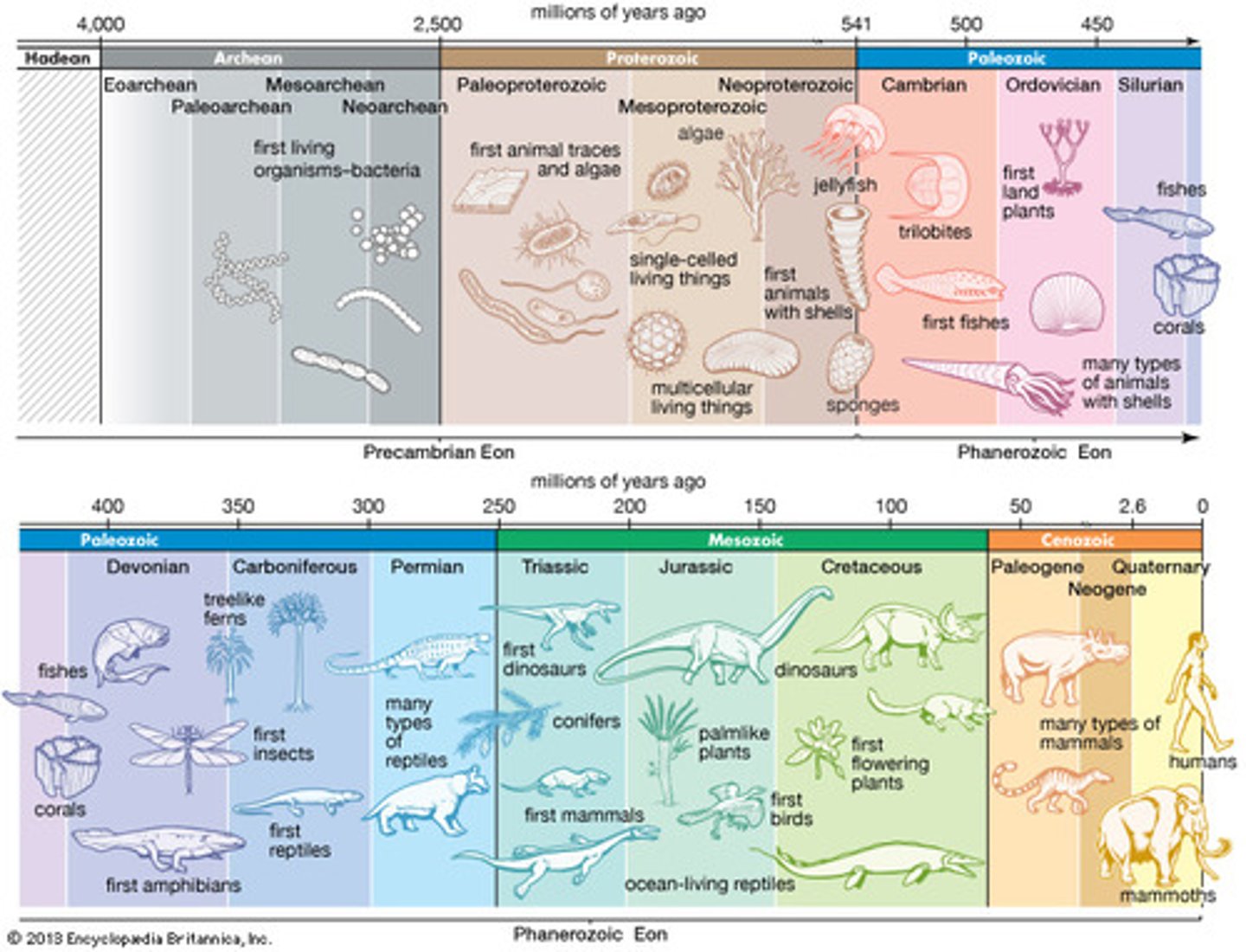
Cambrian period
The first period in the Phanerozoic eon and Paleozoic era; Cambrian explosion
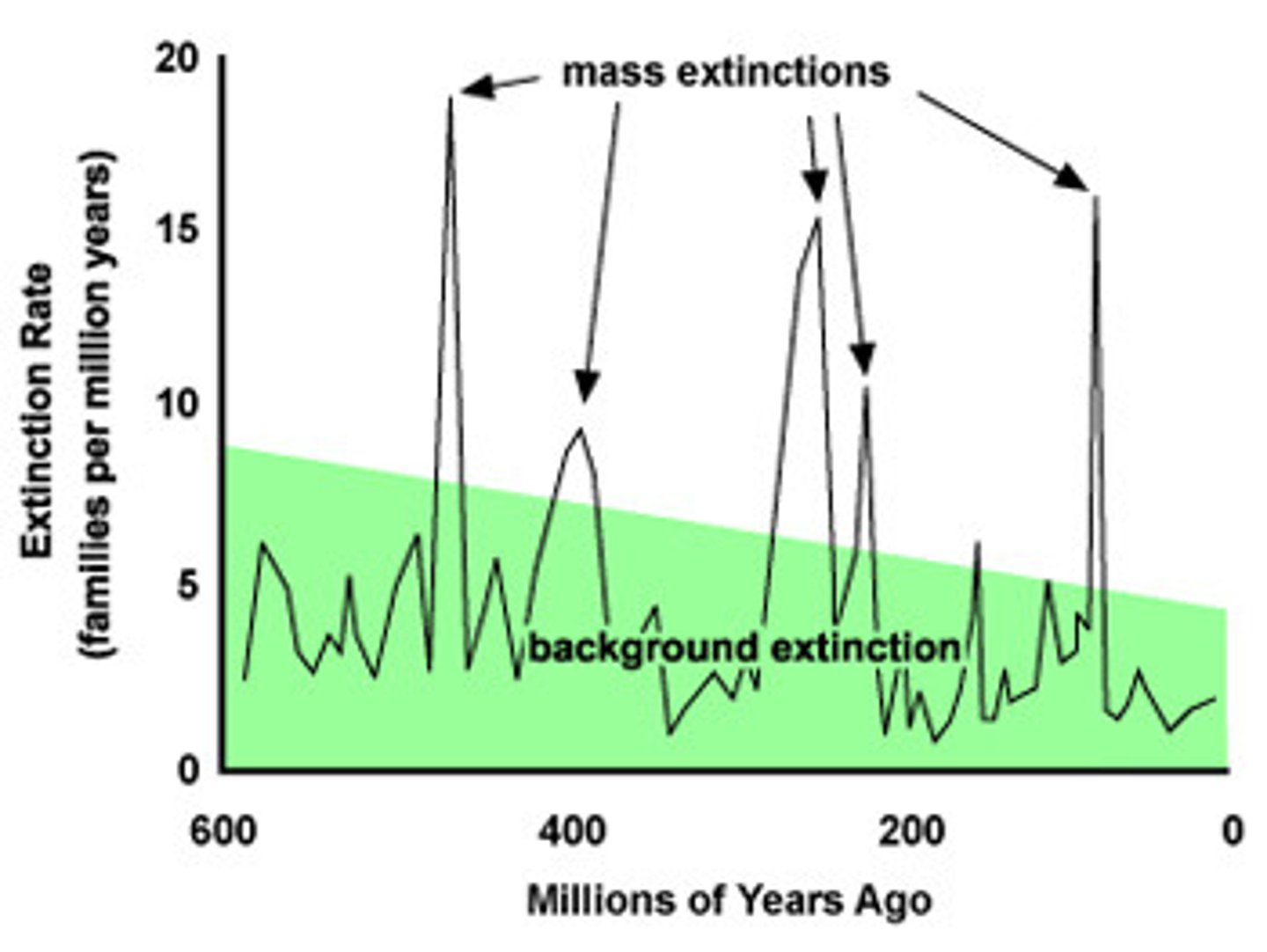
Extinction
The complete loss of a species or group of species
5(+) mass extinctions
The ends of the Ordovician, Devonian, Permian, Triassic, and Cretaceous periods are defined by this; quaternary period is potentially defined by a 6th mass extinction
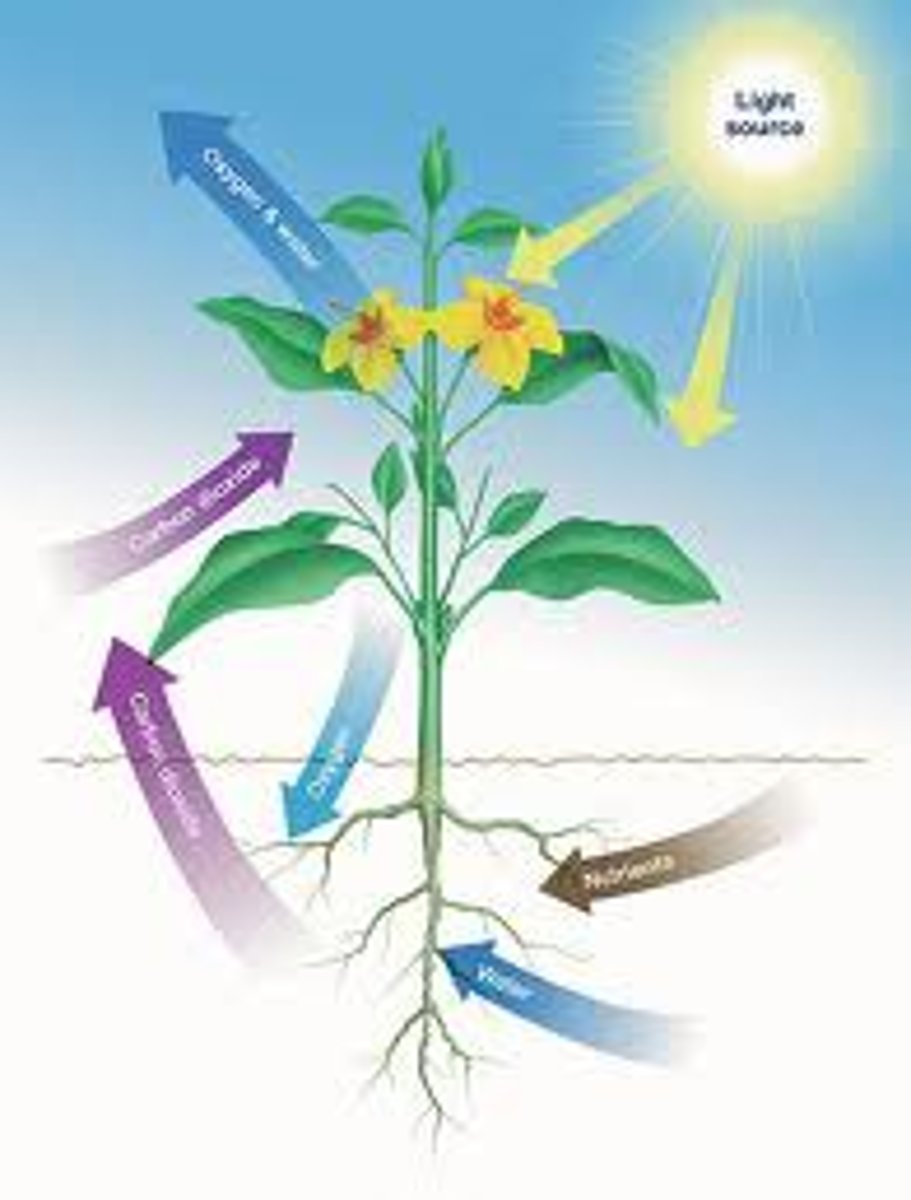
Changes in the atmosphere
Prior to 2.4 bya there was little oxygen in the atmosphere, but the emergence of photosynthetic organisms caused the increase of O2 to become 21% of the atmosphere today. This describes what?
Autotroph
Organisms that produce their own organic molecules from inorganics and/or light
Phanerozoic eon
The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras are a part of which eon?
Hominoids
A member of a group of primates that includes humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans, and gibbons, plus all of their recent ancestors
Molecular evolution
Changes at the level of genes and proteins that underlie the phenotypic changes associate with evolution
Biogeography
Study of the geographic distribution of extinct and living species
Vertical evolution
Process in which species evolve from pre-existing species by the accumulation of mutations
(Georges) Cuvier
Early 19th century French zoologist and paleontologist who was first to use comparative anatomy to develop a system of classification; founded scientific field of paleontology; proposed catastrophism - events in past had case later strata to have new mixes of fossils

(Jean-Baptiste) Lamarck
18th century naturalist; first biologist to propose evolution and to link diversity with environmental adaptation; proposed Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
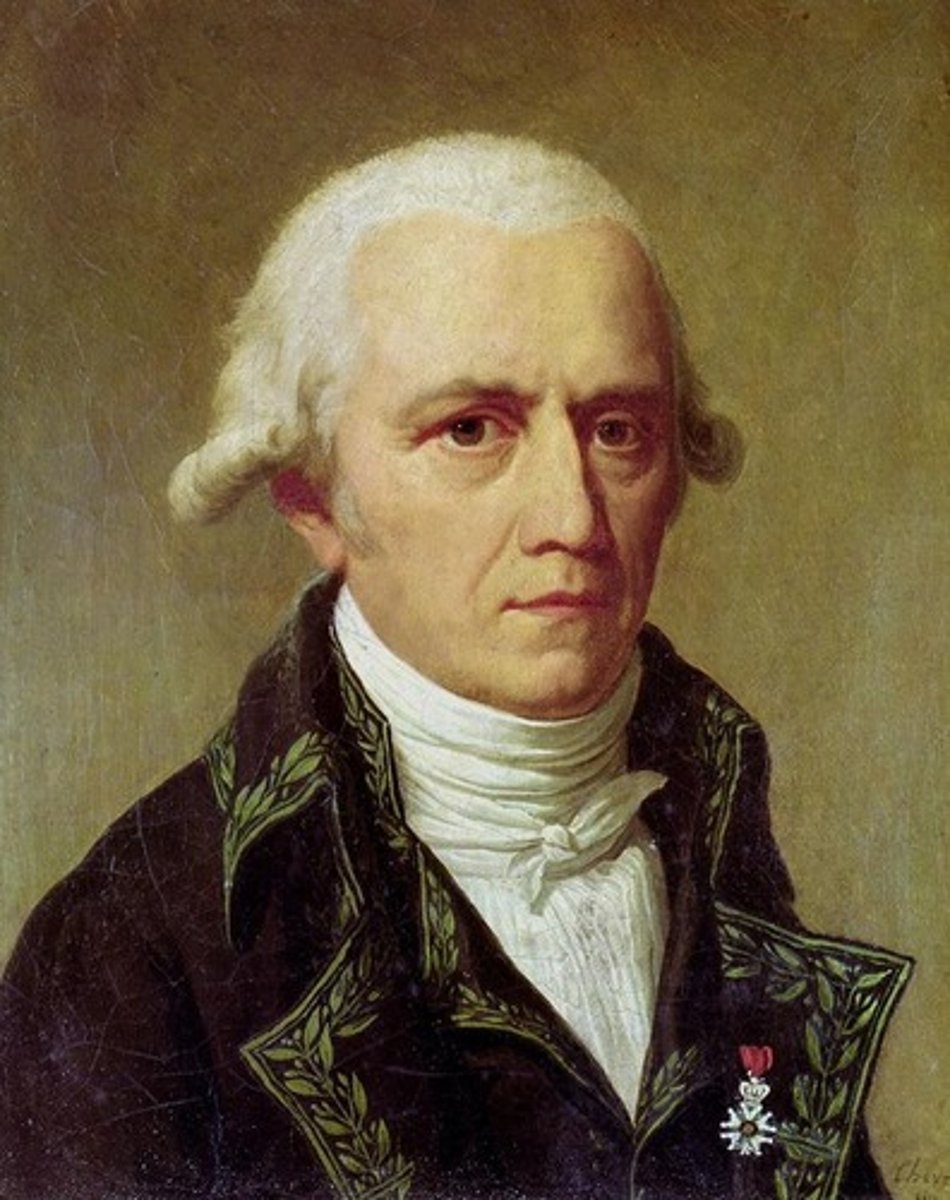

(Charles) Lyell
Early 19th century Scottish geologist; suggested changes in the Earth are directly cause by recurring events; proposed uniformitarianism - rates and process of change were constant
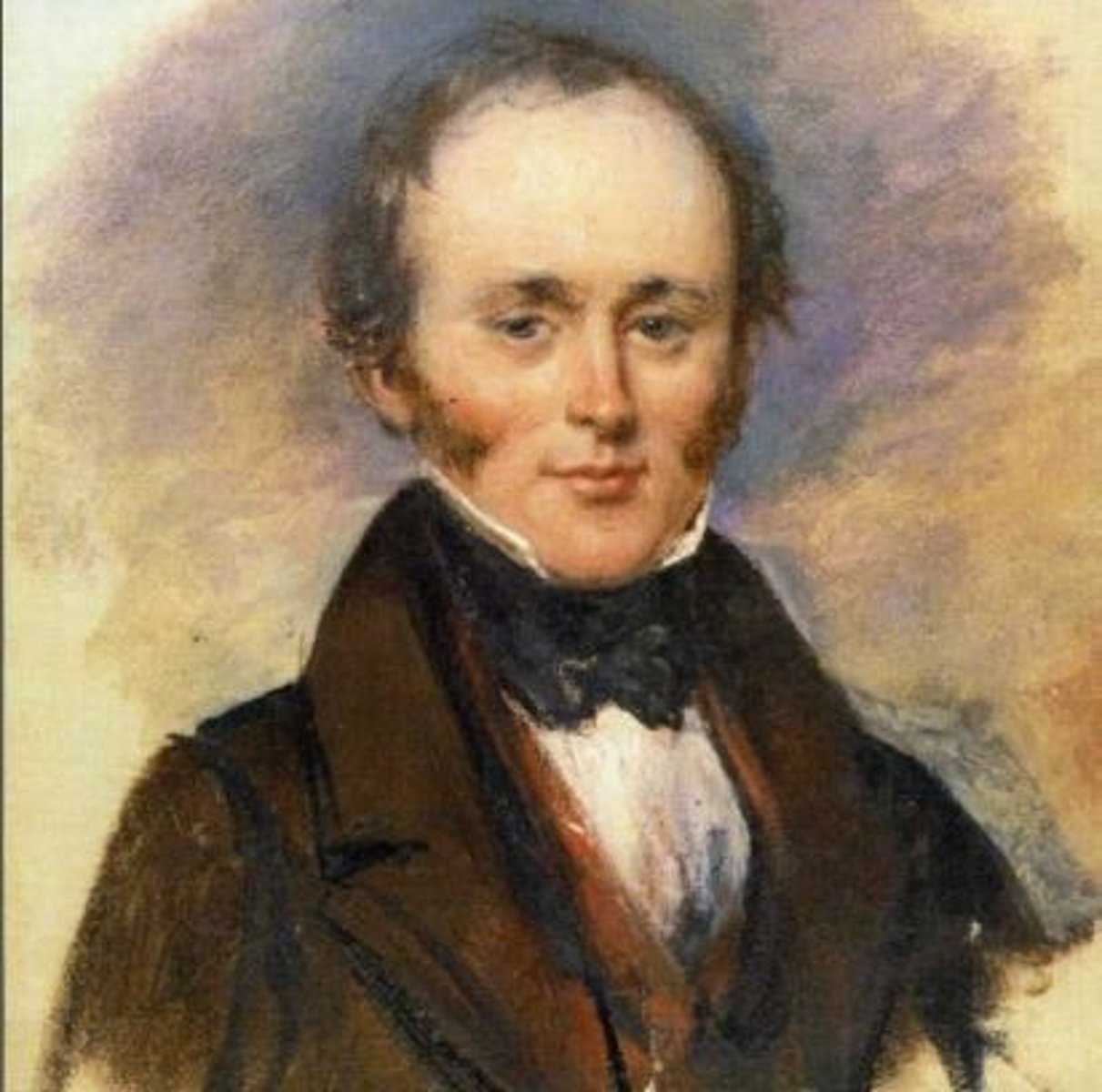
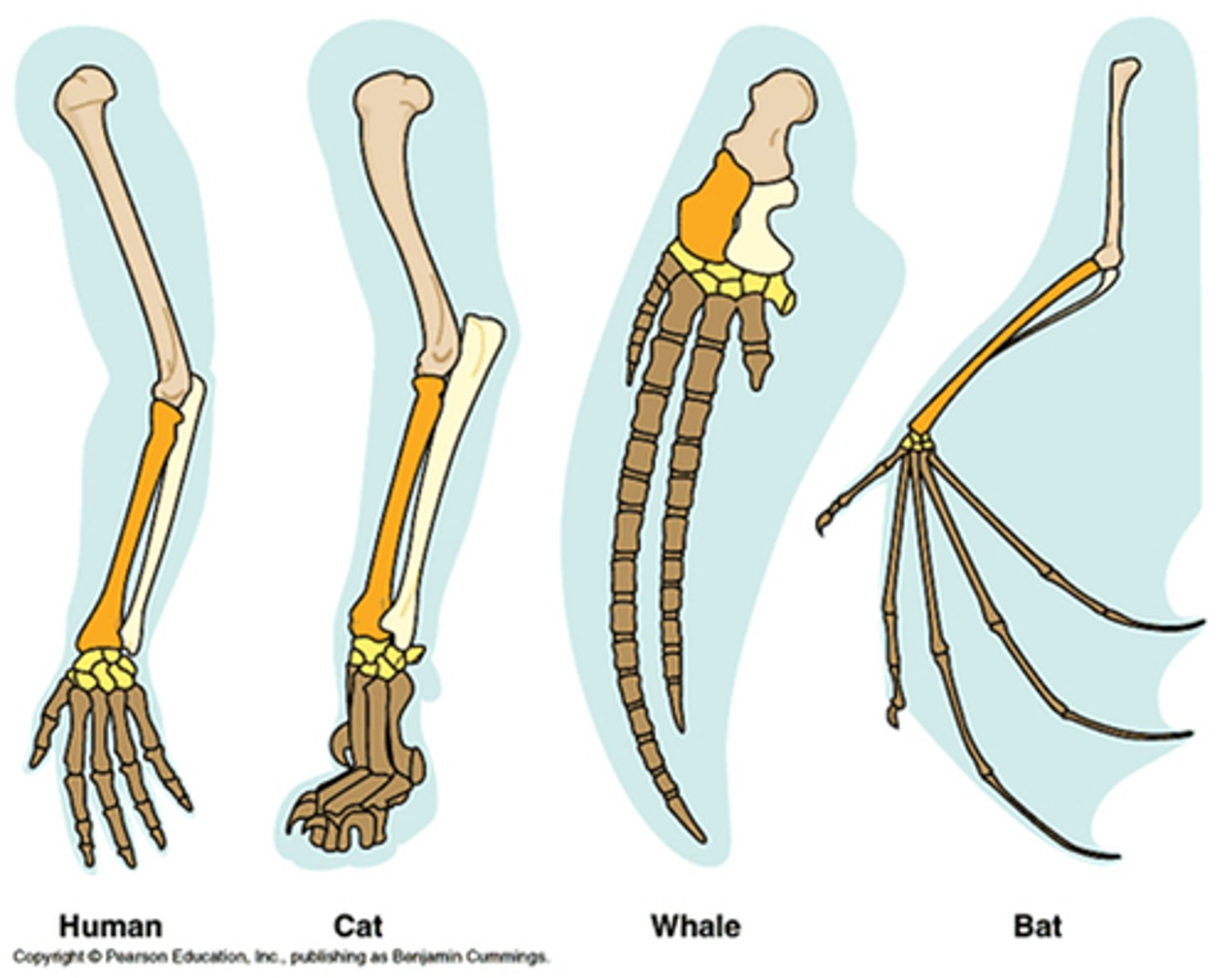
Homologous structures
Structures that are similar to each other because they are derived from a common ancestor
Gene pool
All of the alleles for every gene in a given population
Polymorphic gene
A gene that commonly exists as two or more alleles in a population
Monomorphic gene
A gene that exists predominantly as a single allele in a population
Hardy-Weinberg equation
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 ; relates allele and genotype frequencies;
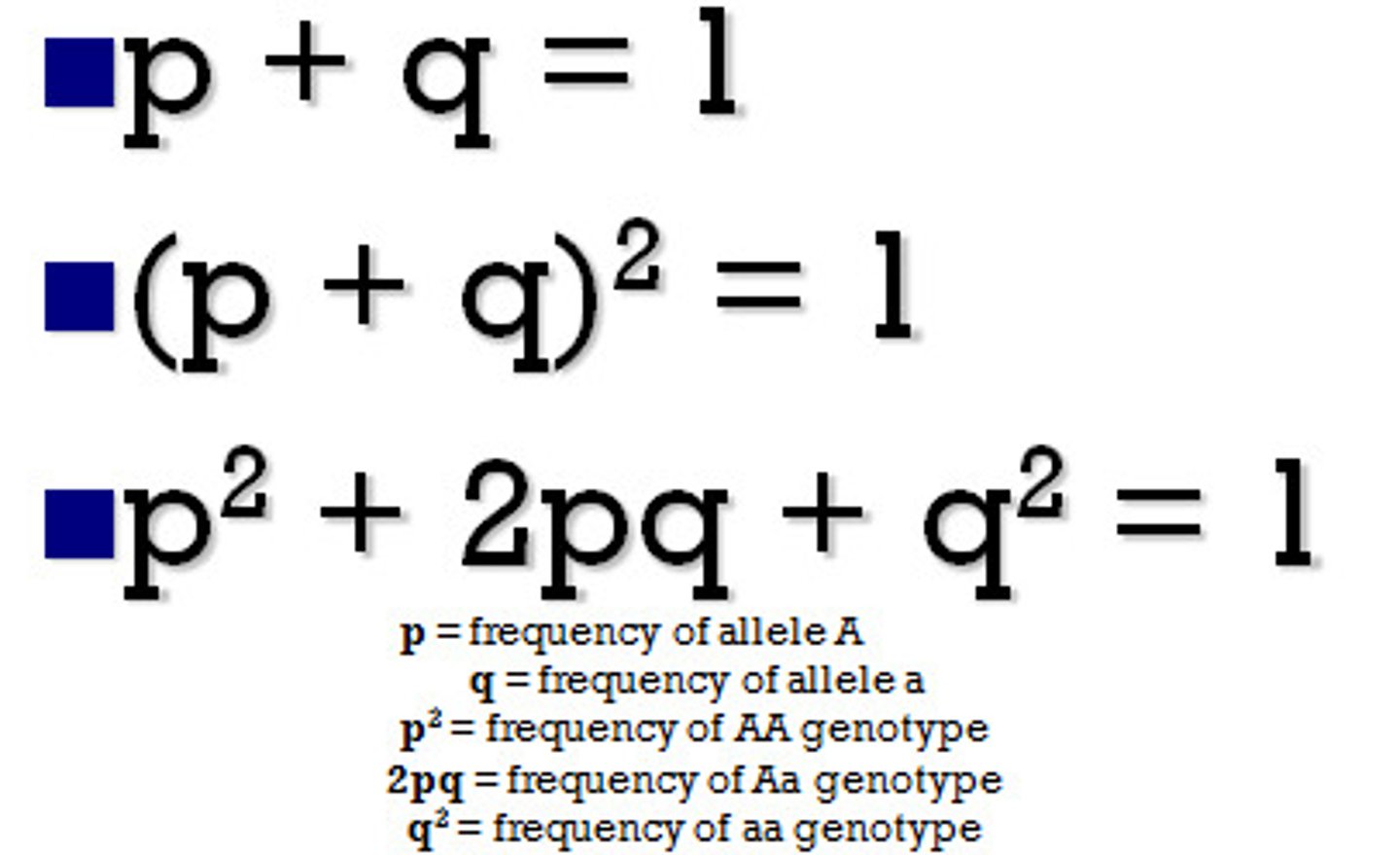
2pq
genotype frequency of C^R C^W heterozygotes
Evolutionary mechanisms
Natural selection, genetic drift, migration, nonrandom mating are what type of mechanisms that alter frequencies of existing genetic variation?
Intersexual selection
Sexual selection where members of one sex choose their mates from individuals of the other sex on the basis of certain desirable characteristics

Neutral variation
Changes in genes and proteins that do not have an effect on reproductive success
Migration
Movement of individuals between two established populations; tends to reduce differences in allele frequencies between neighboring populations; causes gene flow between two populations
Directional selection
Individuals at one extreme of a phenotype range have greater reproductive success in a particular environment; curve shifts in that diretion
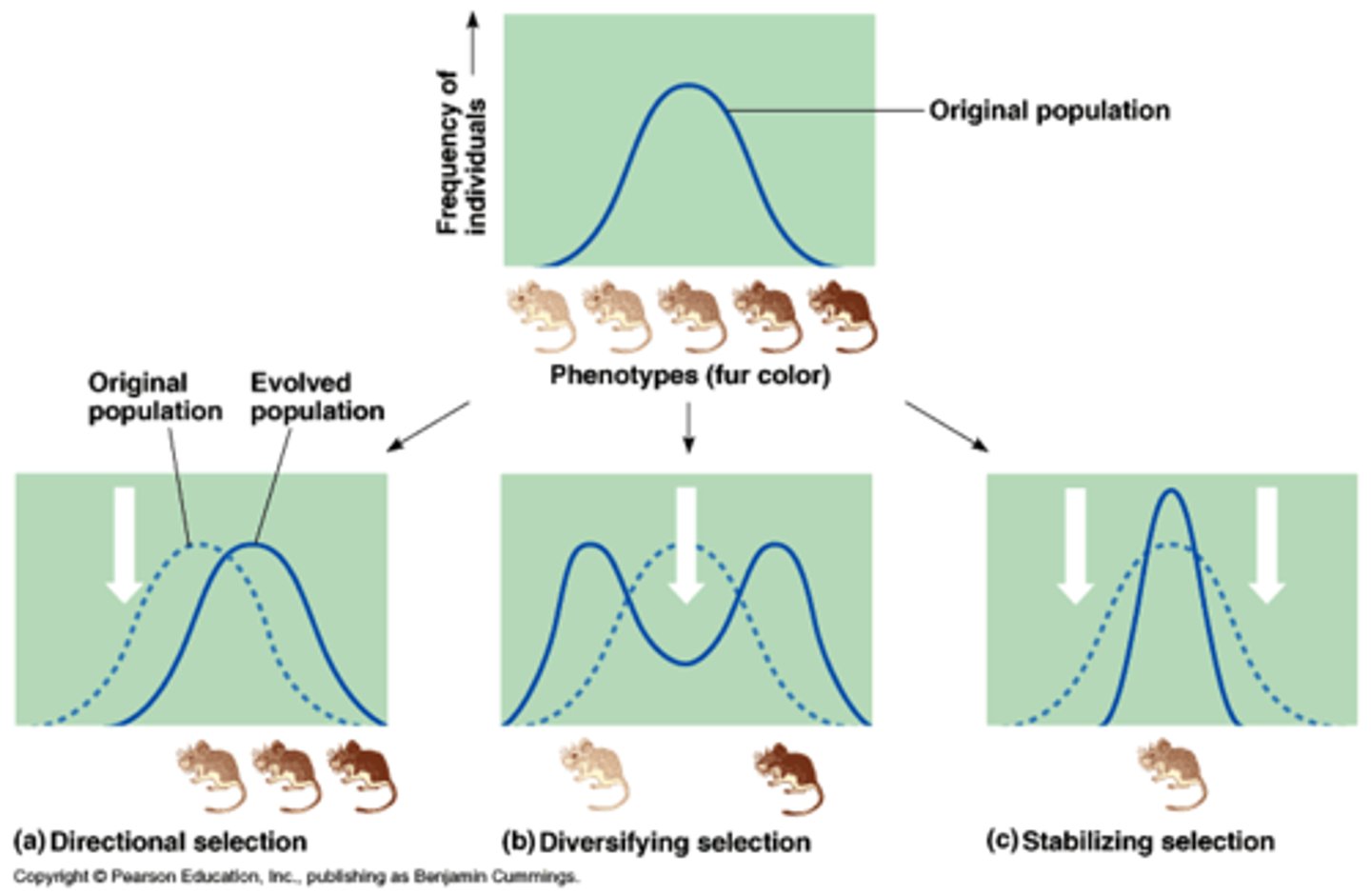
Reproductive success
Likelihood of an individual contributing fertile offspring to the next generation
Diversifying selection
Type of selection that favors the survival of two or more different genotypes that produce different phenotypes.
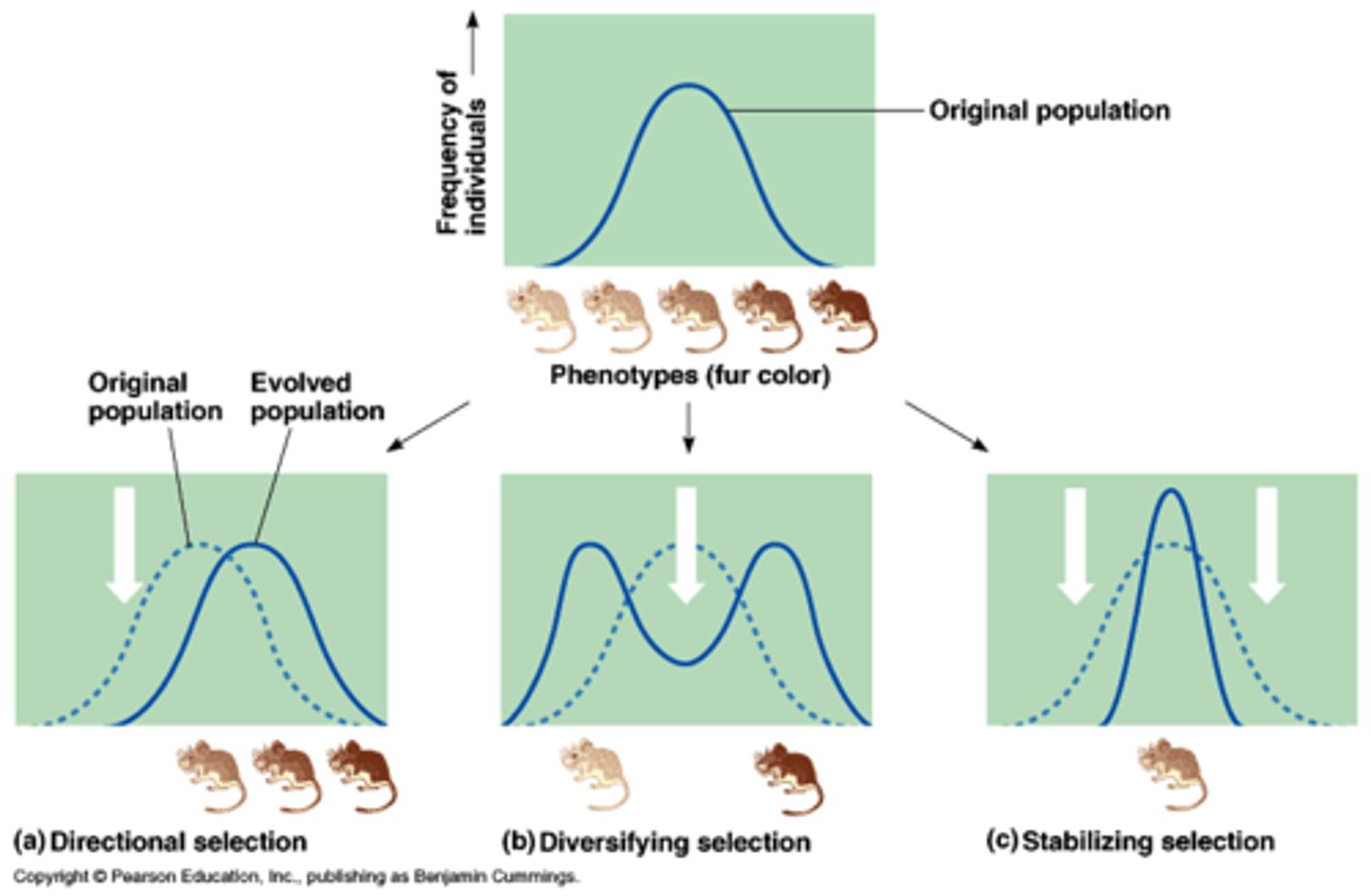
Negative frequency-dependent selection
Natural selection where the fitness of a genotype decreases when its frequency becomes higher
Speciation
The formation of a new species
Cladogenesis
The splitting or diverging of one species into two or more species

Subspecies
Subdivision of a species; when two or more geographically restricted groups of the same species display one or more traits that are somewhat different but not enough to warrant their placement into different species
Ecological species concept
Concept when species are distinguished by their ability to successfully occupy their own ecological niche or habitat, incl. their use of resources and impact on the environment
Temporal isolation
When species happen to reproduce at different times of the day or year acts as an interbreeding barriers

Taxonomy
Science of describing, naming, and classifying extant and extinct species
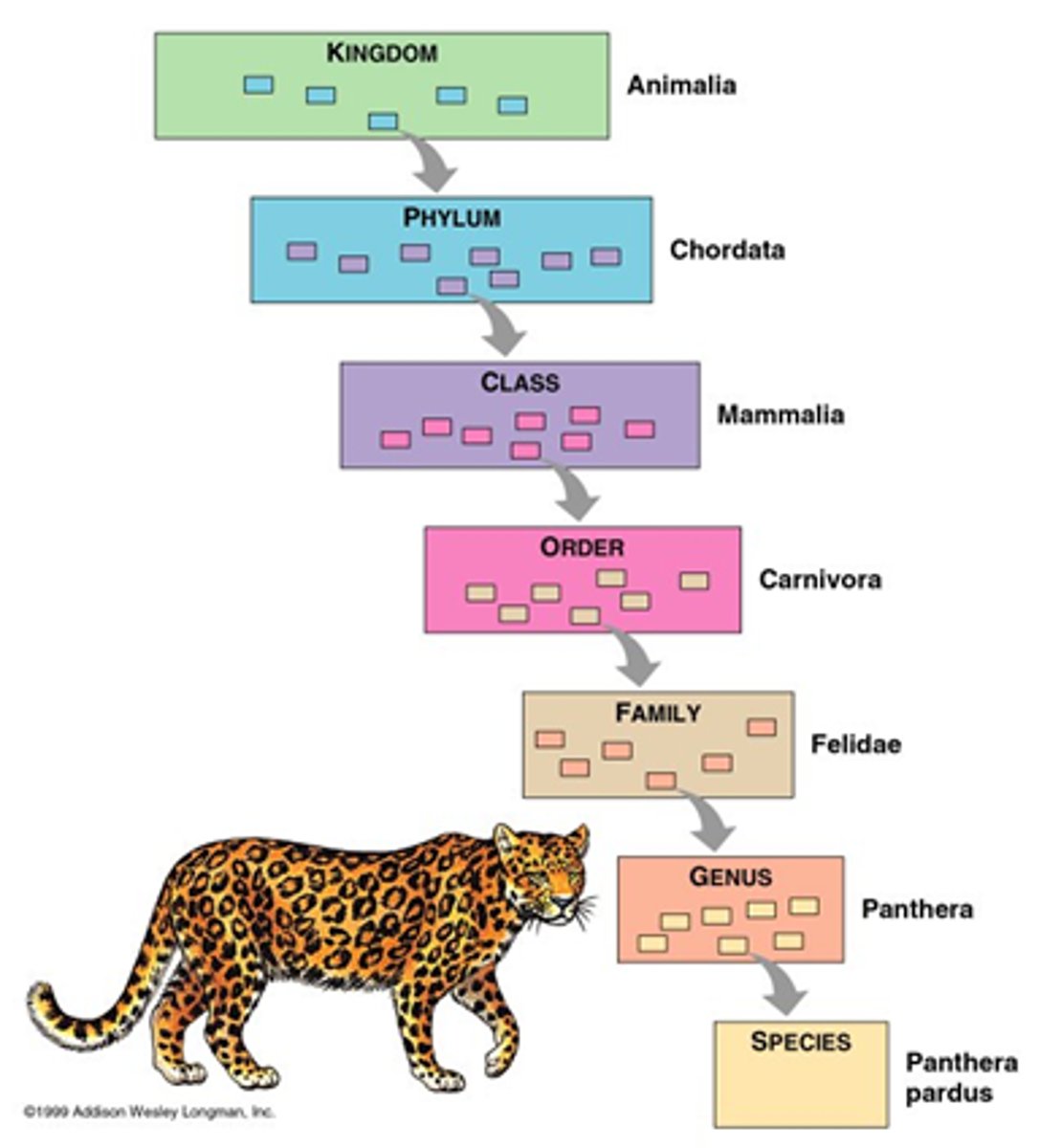
Molecular systematics
Type of systematics that involves the analysis of genetic data to identify and study genetic homologies and propose phylogenetic trees

Adaptation
Any modification that makes an organism better suited to its way of life
4 Overlapping Stages (for life to occur)
1. Nucleotides and amino acids produced prior to existence of cells
2. Nucleotides and aas become polymerized to from DNA, RNA, and proteins
3. Polymers became enclosed in membranes
4. Polymers enclosed in membranes evolved cellular properties
Abiotic synthesis (Reducing atmosphere hypothesis)
Theory of the origin of life; primitive atmosphere contained H20 vapor, N2, CO2 with small amounts of H2 and CO; little free oxygen resulted in reducing atmosphere; spontaneous formation of organic molecules; monomers evolved and joined into polymers
Oparin-Haldane (Hypothesis)
Hypothesis: if the primitive atmosphere was reducing and if there was an appropriate supply of energy, then a wide range of organic compound might be synthesized
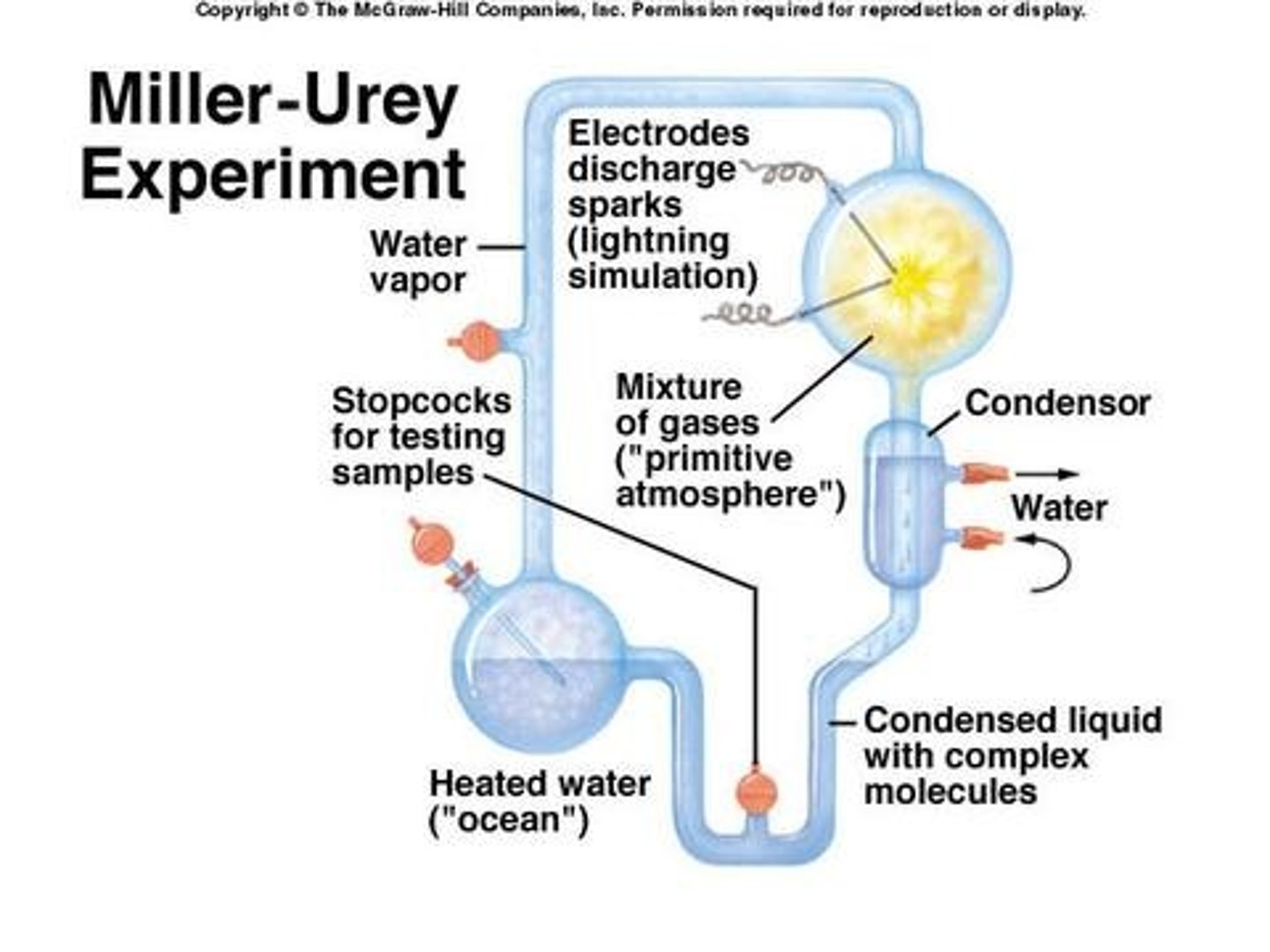
Miller and Urey's Experiment
Experiment that showed that biochemicals could be produced from simple non-biological sources through primitive atmospheric gas and strong energy sources
Extraterrestrial Hypothesis
Theory of the origin of life where organic carbon, amino acids, and nucleic acid bases from asteroids and comets of the carbonaceous chondrite family gave earth large amounts of organics
Deep sea vent hypothesis
Theory of the origin of life where key organics arose at deep-sea vents; superheated water rich in H2S and metal ions mixed with cold sea water and organics formed in temperature gradients around vents
Clay hypothesis
Theory of the origin of the first cell; simple organics polymerize on solid surfaces (clay, mud, inorganic crystals) and from into more complex organics
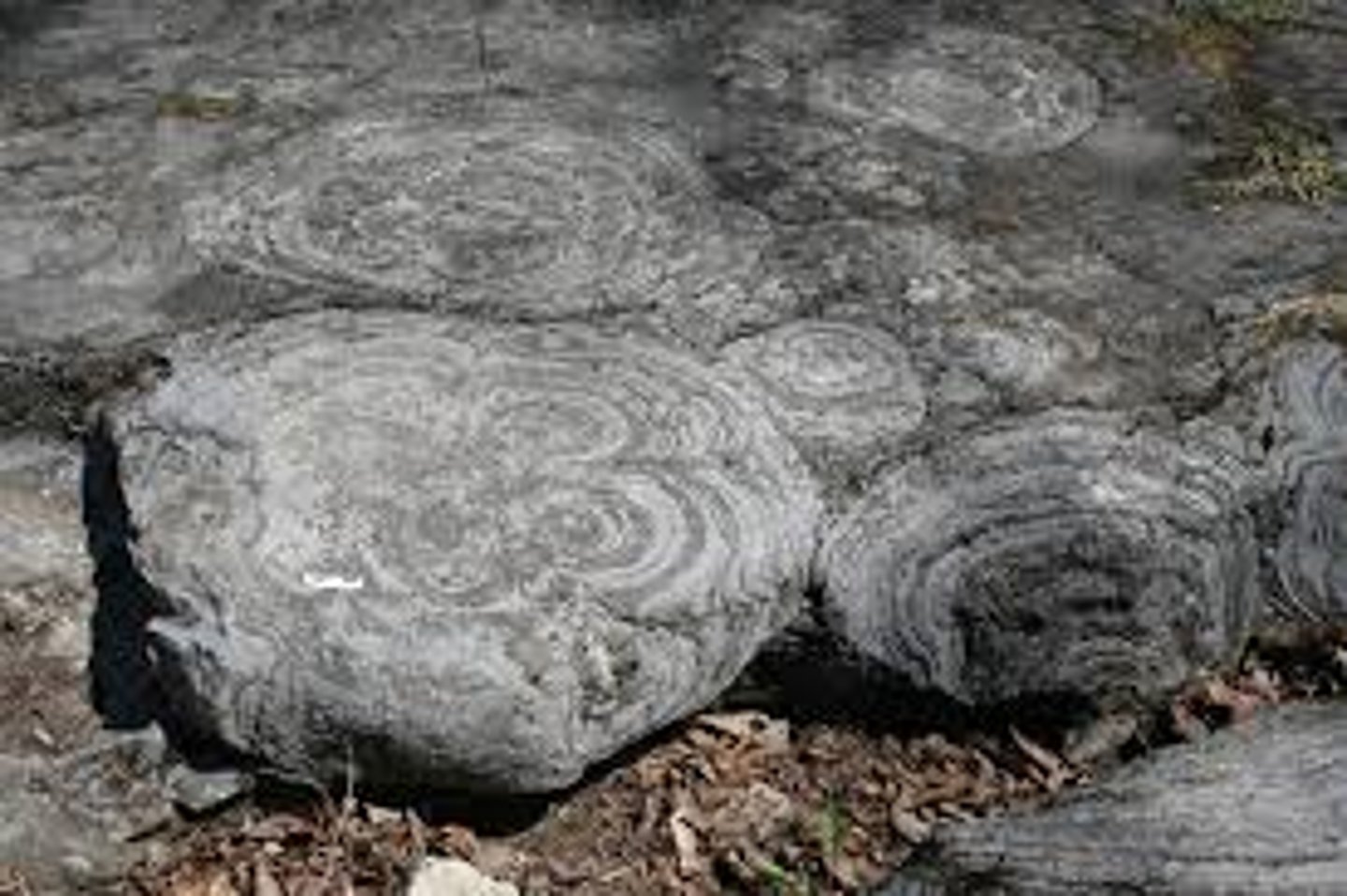
Stromatolite
Mats of mineralized cyanobacteria

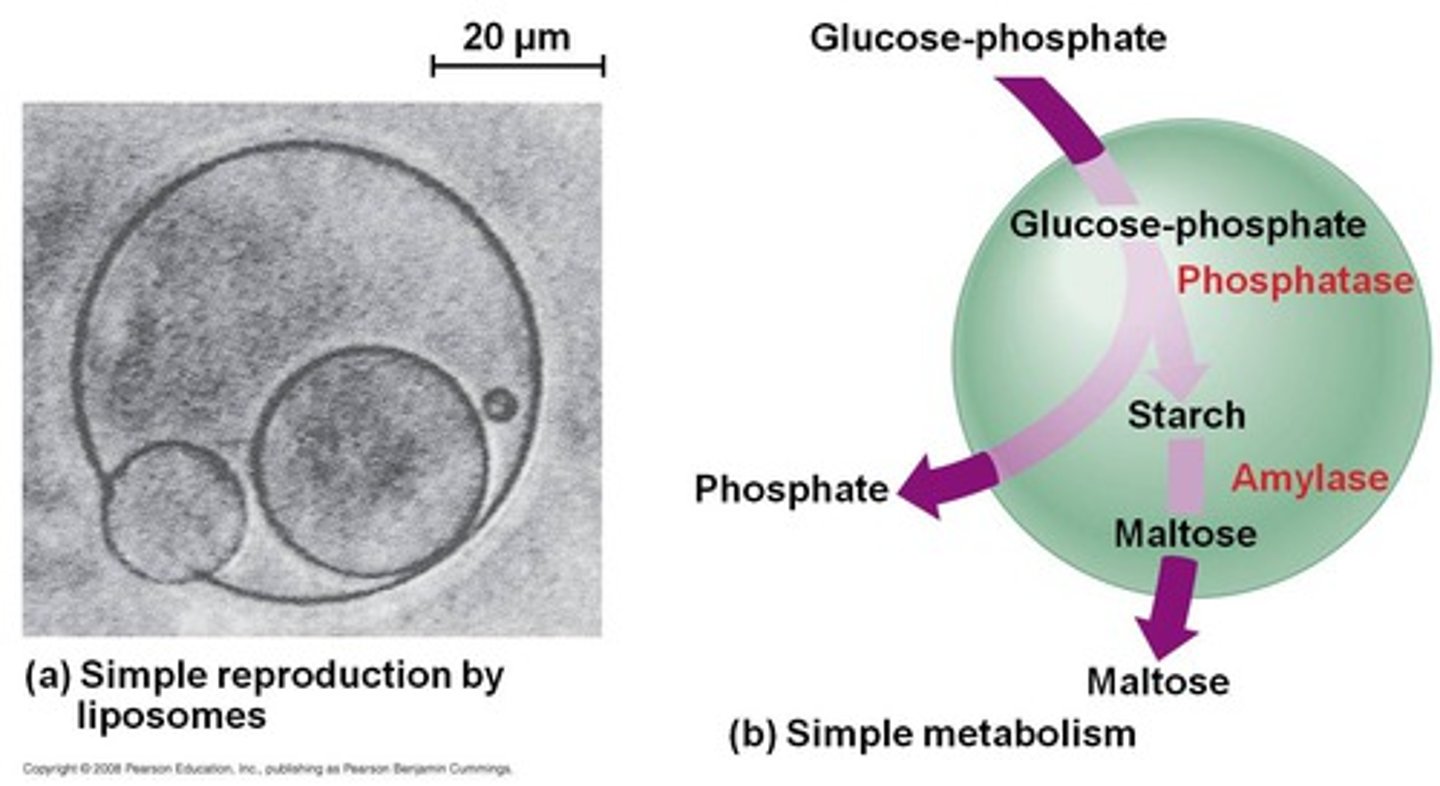
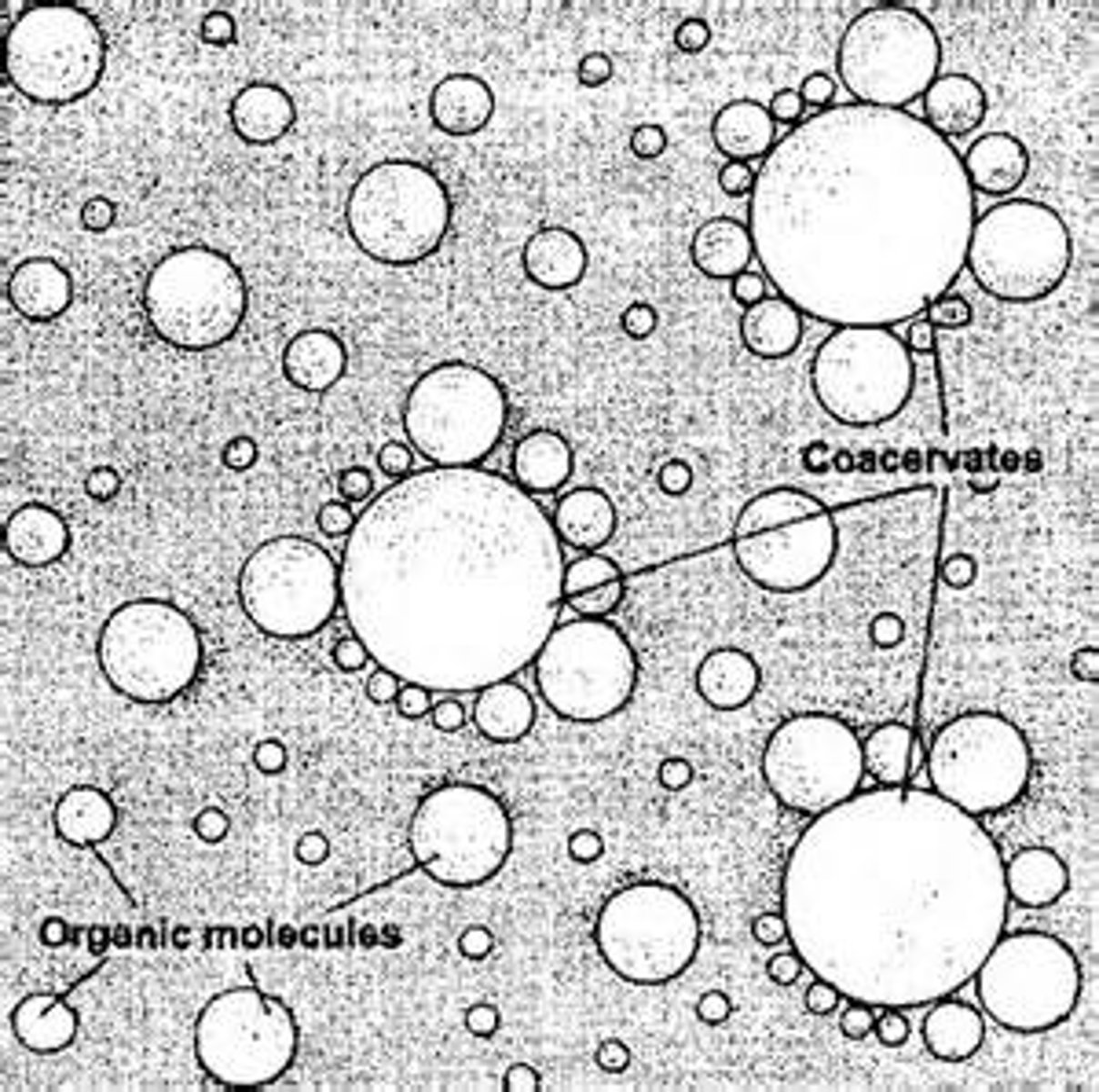
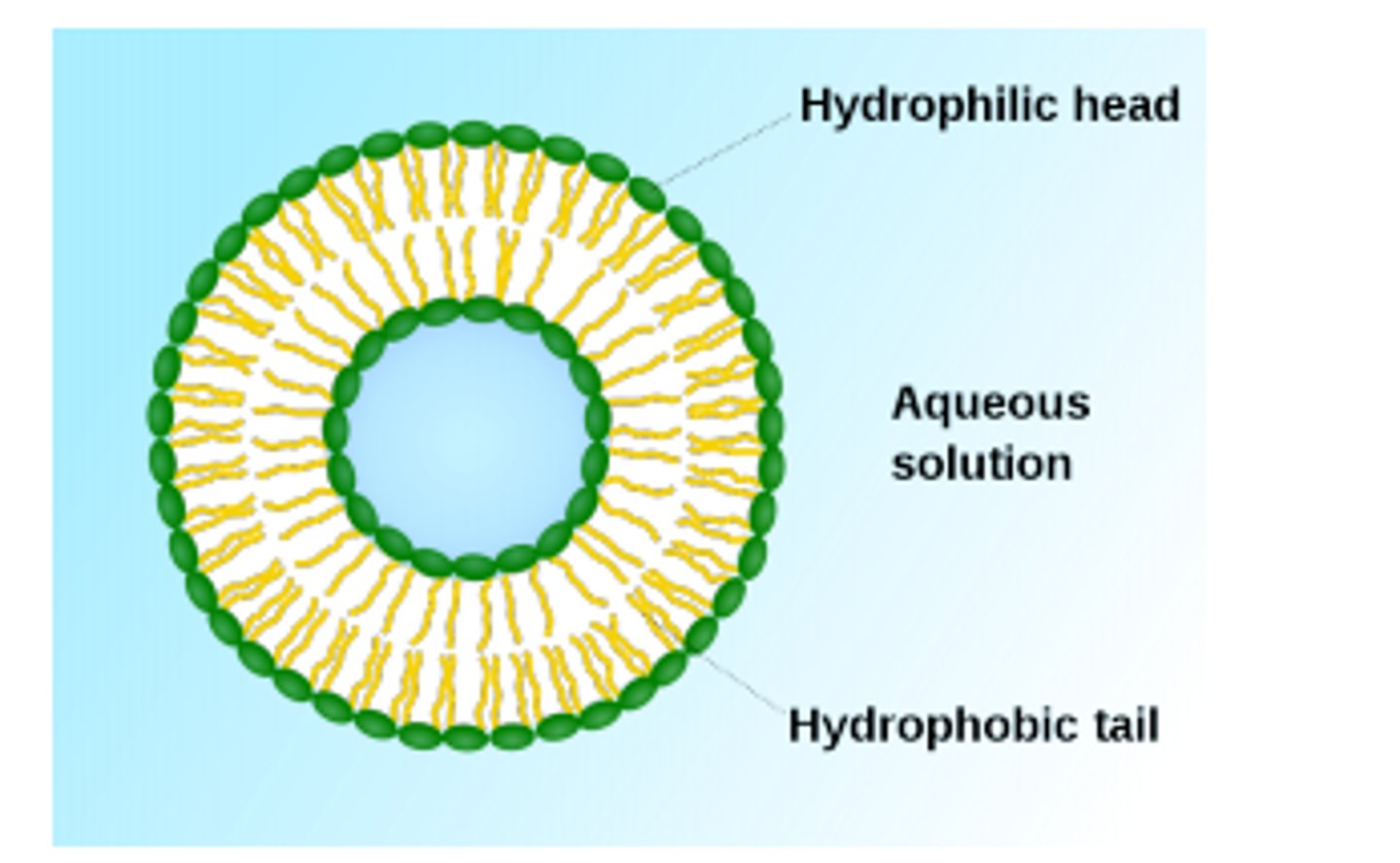
Protobiont
An collection of pre-biotically produced (macro)molecules that acquired a boundary, such as a lipid layer (liposomes) or coacervates, which allowed it to maintain an internal chemical environment
Coacervate
Droplets that form spontaneously from the association of charged polymers such as proteins, carbohydrates, or nucleic acids surrounded by water
Liposome
Vesicle surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer
RNA
This macromolecule:
1. Can store information in its nucleotide base sequence
2. Due to base pairing, has capacity for self-replication
3. Can perform a variety of catalytic functions
Chemical selection
When a chemical within a mixture has special properties or advantages that cause it to increase in number relative to other chemicals in the mixture
Chemical evolution
When a population of molecules changes over time to become a new population with a different chemical composition; Chemical selection results in this
RNA world
hypothetical period on early Earth when both the information for life and the catalytic activity of living cells were contained solely in RNA molecules
Advantages of RNA/DNA/Protein world
1. Better information storage: DNA relieve RNA of informational role and allowed for other functions, DNA less likely to mutate
2. Improved metabolism +: prtein have a greater catalytic efficiency, protiens can perform other tasks
Fossil
Preserved remain of past life on Earth
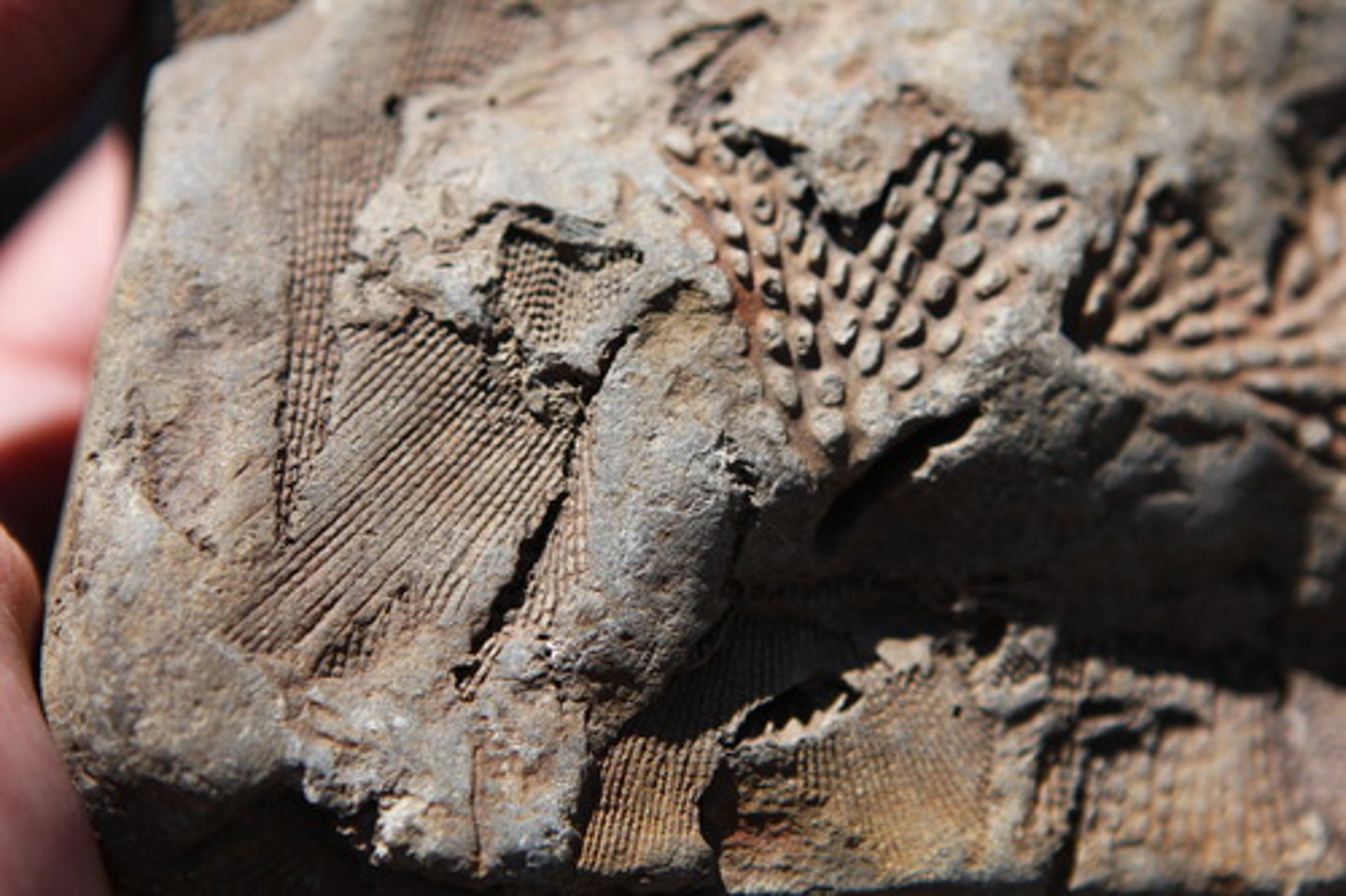

Paleontologist
Scientist who studies fossils
Sedimentary rock
Types of rock that are formed by the deposition and subsequent cementation of that material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water

Sedimentation
Collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle in place.
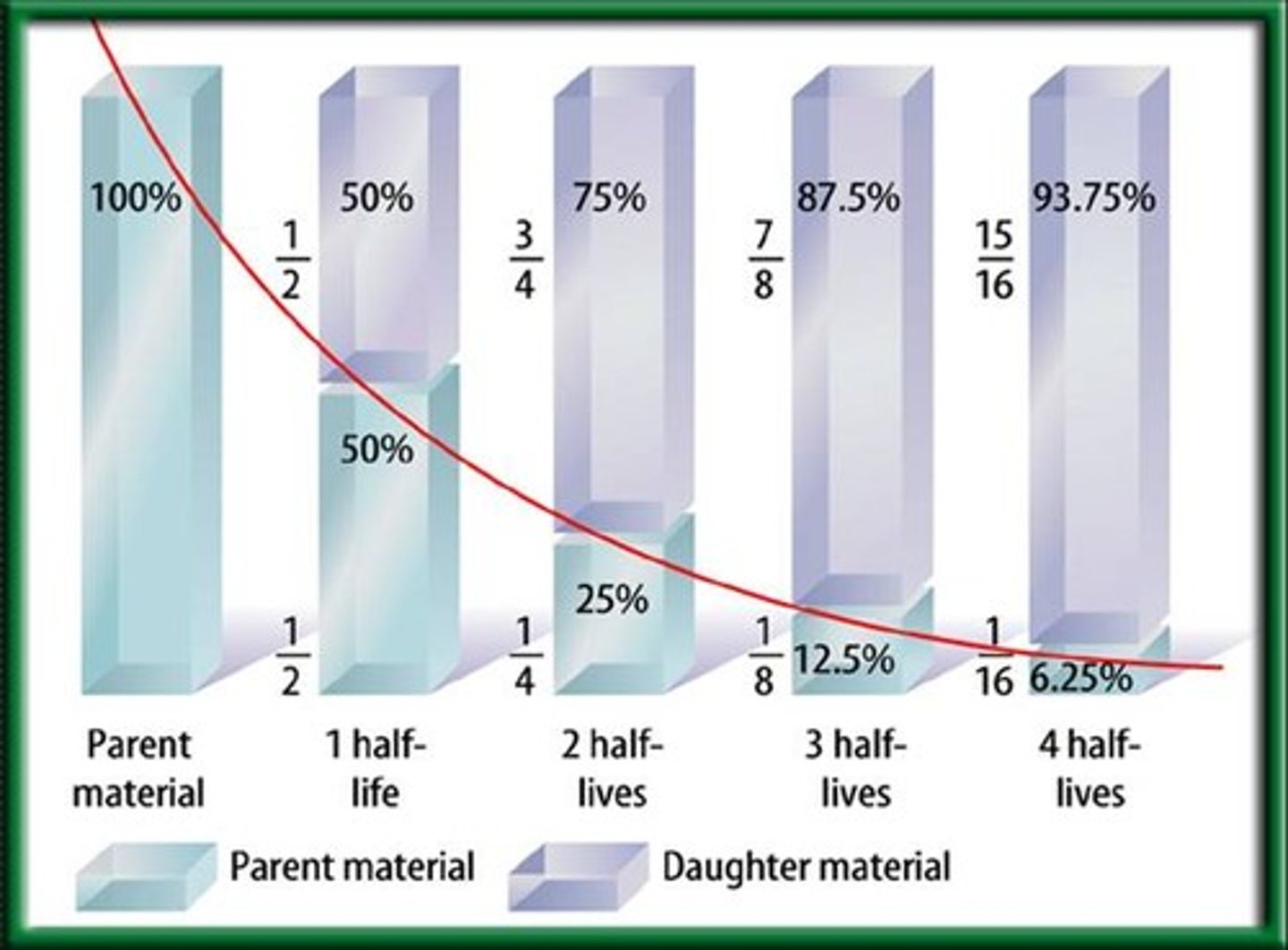
Radiometric dating
A way to estimate the age of a fossil by analyzing the decay of radioisotopes within the accompanying rock (used in absolute dating)

Half life
The length of time require for a radioisotope to decay to exactly half of its initial quantity (used in absolute dating)
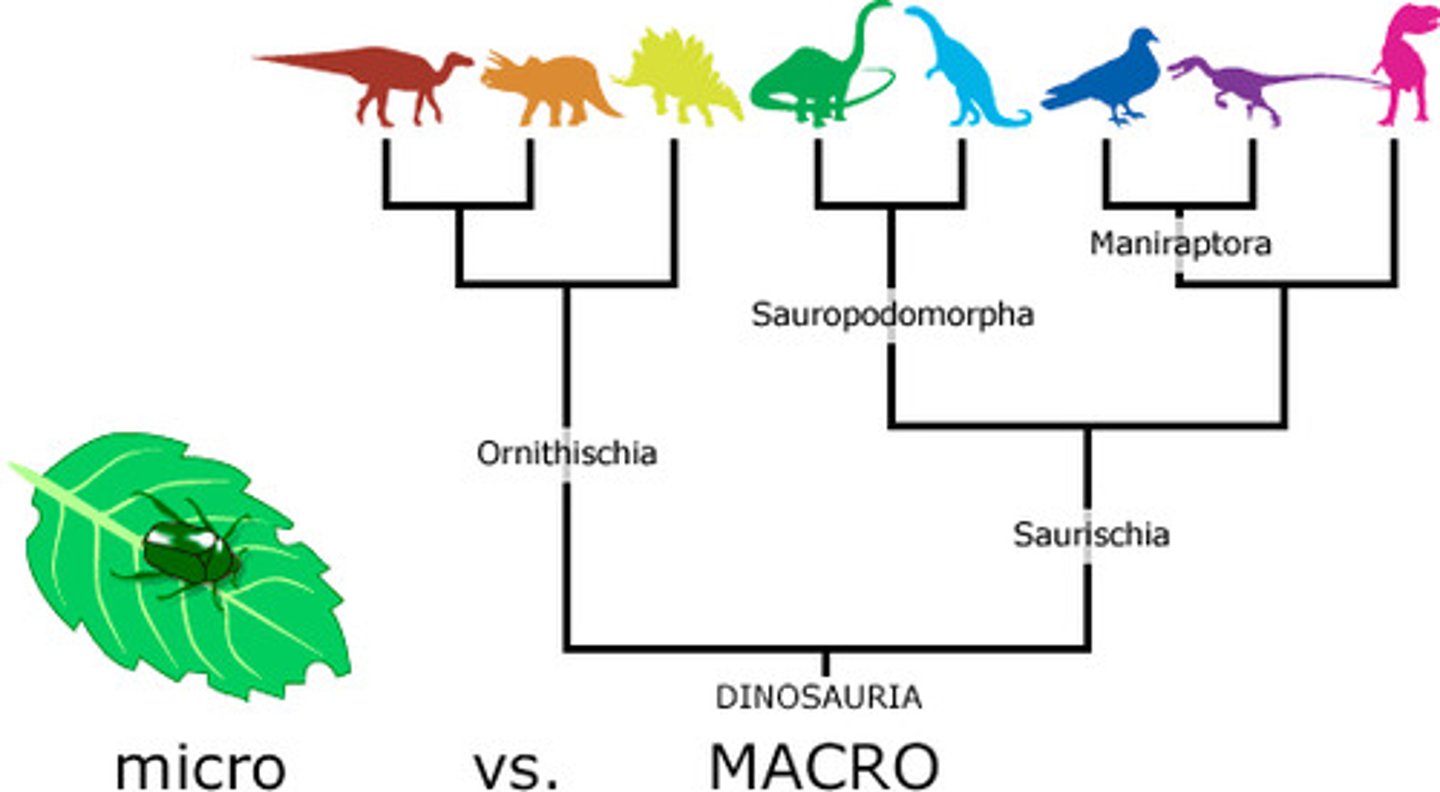
Macroevolution
Formation of new species or groups of species
Factors that affect the fossil record
Anatomy, size, number, species, environment, time, geological processes, and the interest of paleontologists are all what?
Four eons
Hadean, Archaen, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic
Precambrian time
The Hadean, Archaen, an Proterozoic eons make up this time
Factors that influence patterns (in the geological timescale)
Climate/temperature, atmosphere, land masses (continental drift), floods/glaciation; volcanic eruptions; meteorite impacts
Archaean Eon
When did the first prokaryotic cells develop?
Heterotroph
Organisms that must obtain organic food from other organisms

Paleozoic era
The Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian periods are a part of which era?
Cambrian Explosion
Event during the Cambrian period where there was an abrupt increase in the diversity of species; 543-490 mya
Mesozoic era
The Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods were a part of this era, that saw the rise and fall of the dinosaurs
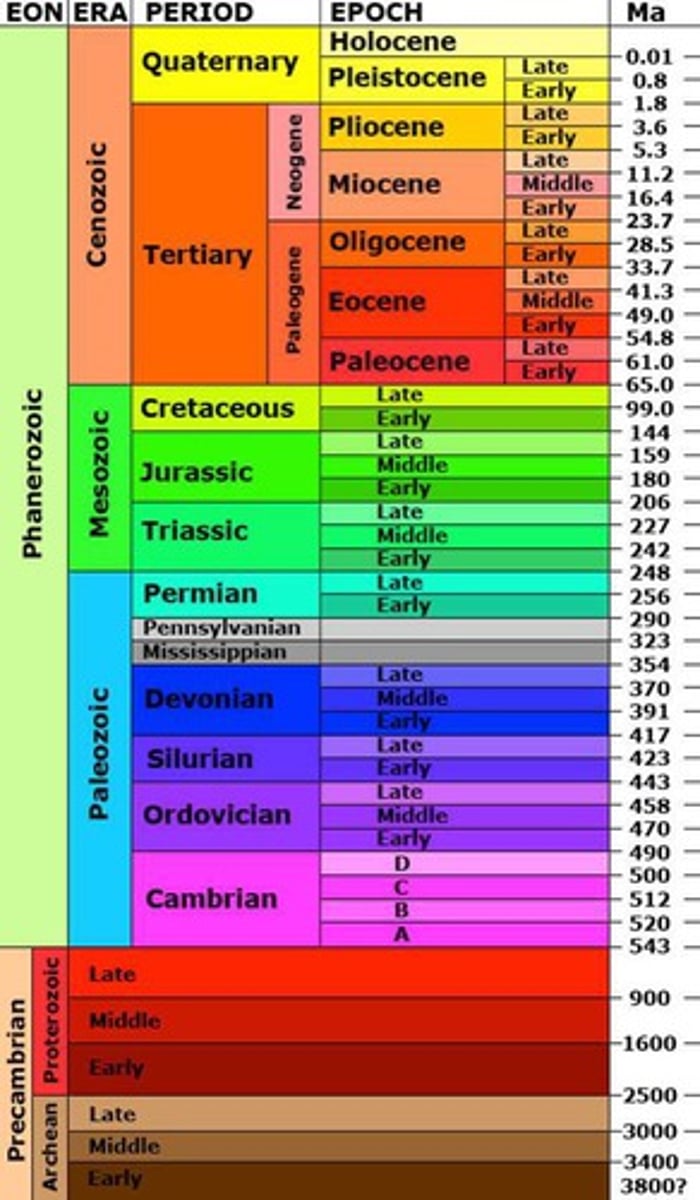
Cenozoic Era
The Tertiary and Quaternary periods make up this, most recent/current era ; Age of Mammals; 65 mya - today

Angiosperm
Any plant that has flowers and produces seeds enclosed within a carpel

Population
Members of a species that live in the same area at the same time and have the opportunity to interbreed.
Microevolution
Changes in a single gene in a population over time
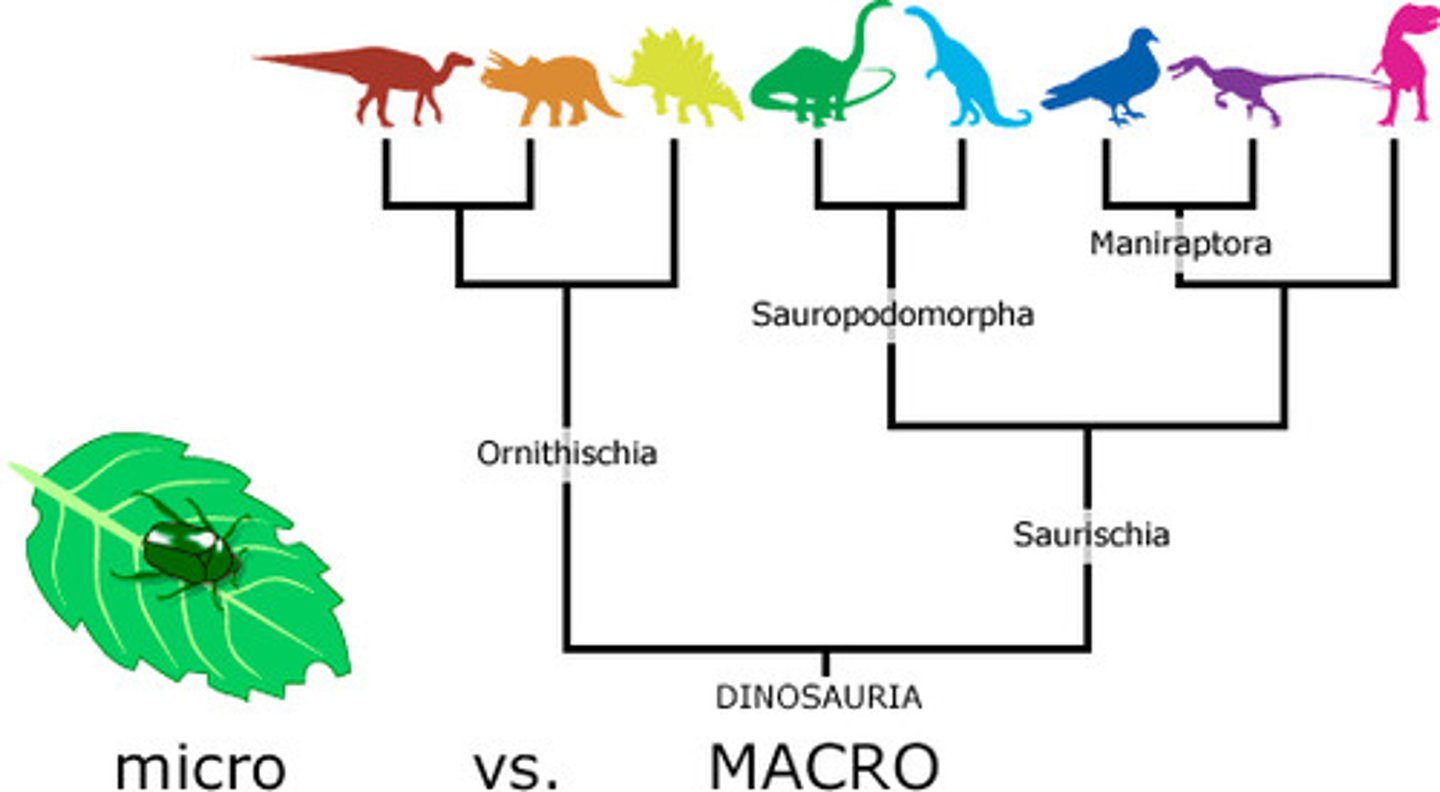
Evidence of biological evolution
Studies of natural selection, fossil record, biogeography, convergent evolution, selective breeding, homologies (anatomical, developmental, molecular) are used as what?
Transitional form
An organism that provides a link between earlier and later forms in evolution
Endemic
Species that are naturally found only in a particular location (islands commonly have this)
Convergent evolution
Process in which two species from different lineages have independently evolved similar characteristics because they occupy similar environments
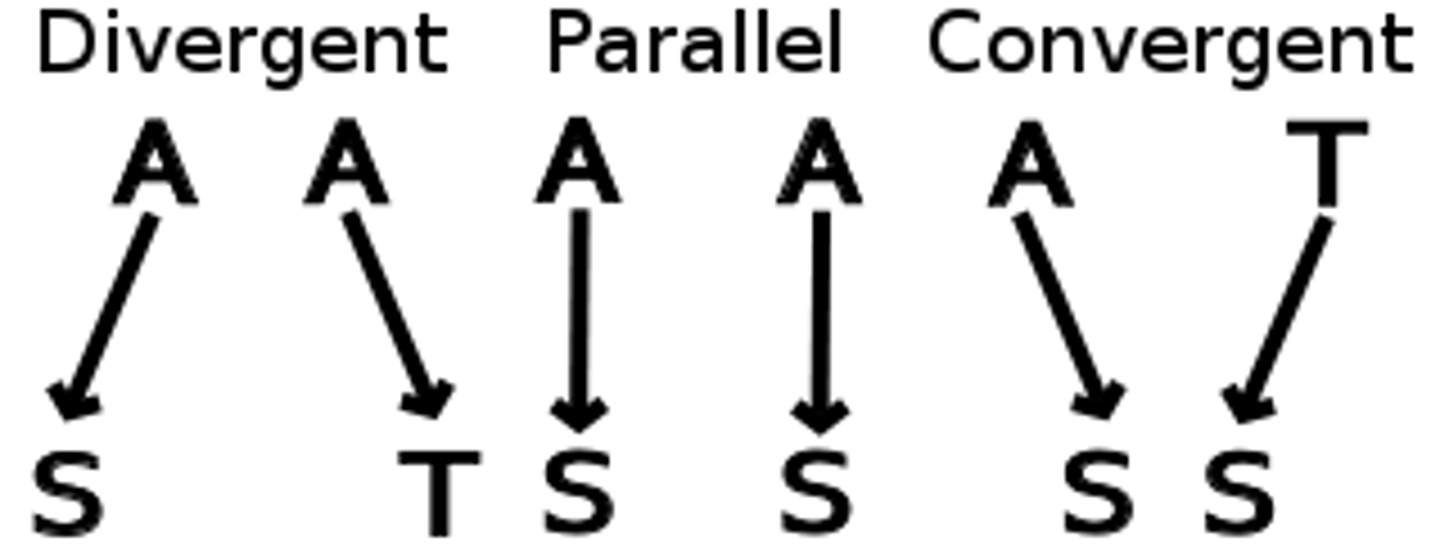
Homologous genes
Two or more genes derived from the same ancestral gene
Paralogs
Two or more homologous genes within a single speices
Gene family
Set of paralogs (related genes) within the genome of a single species; ie globin genes
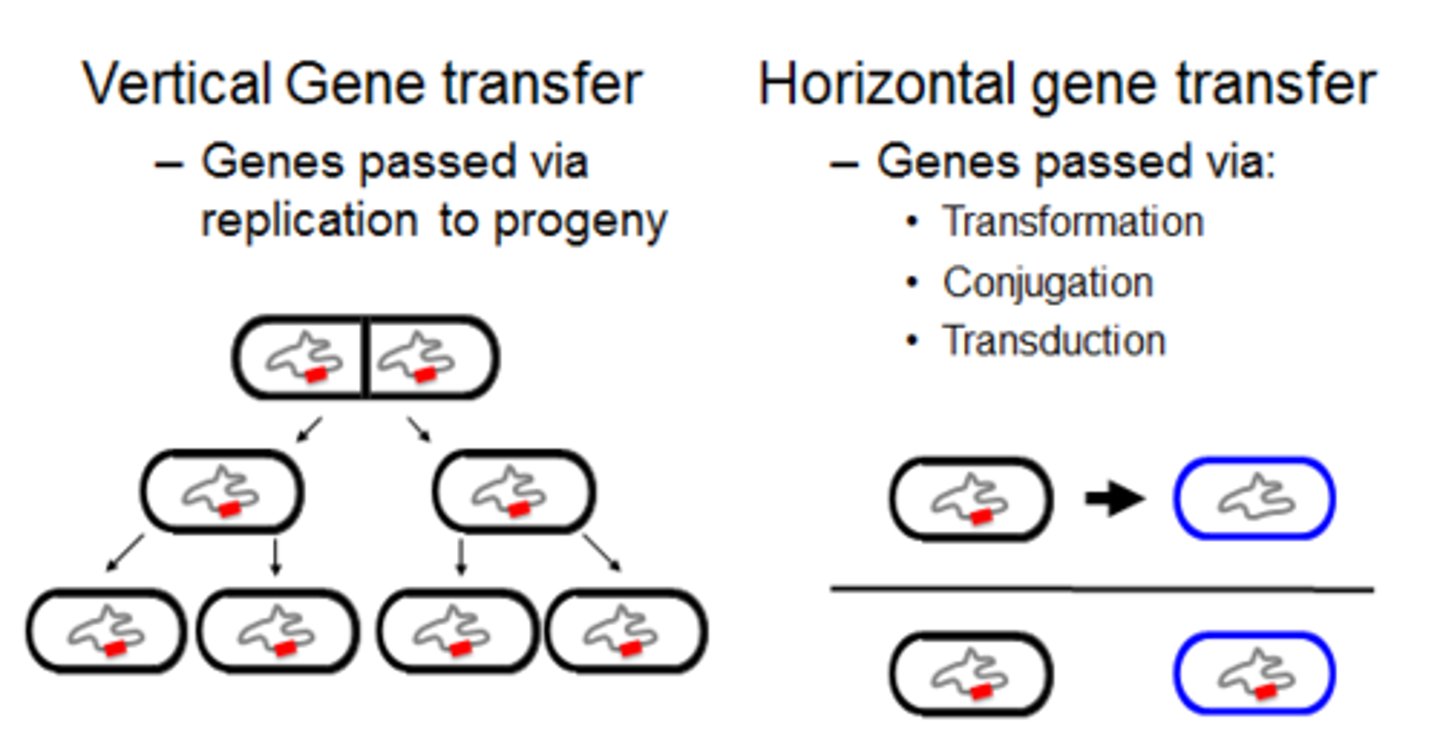
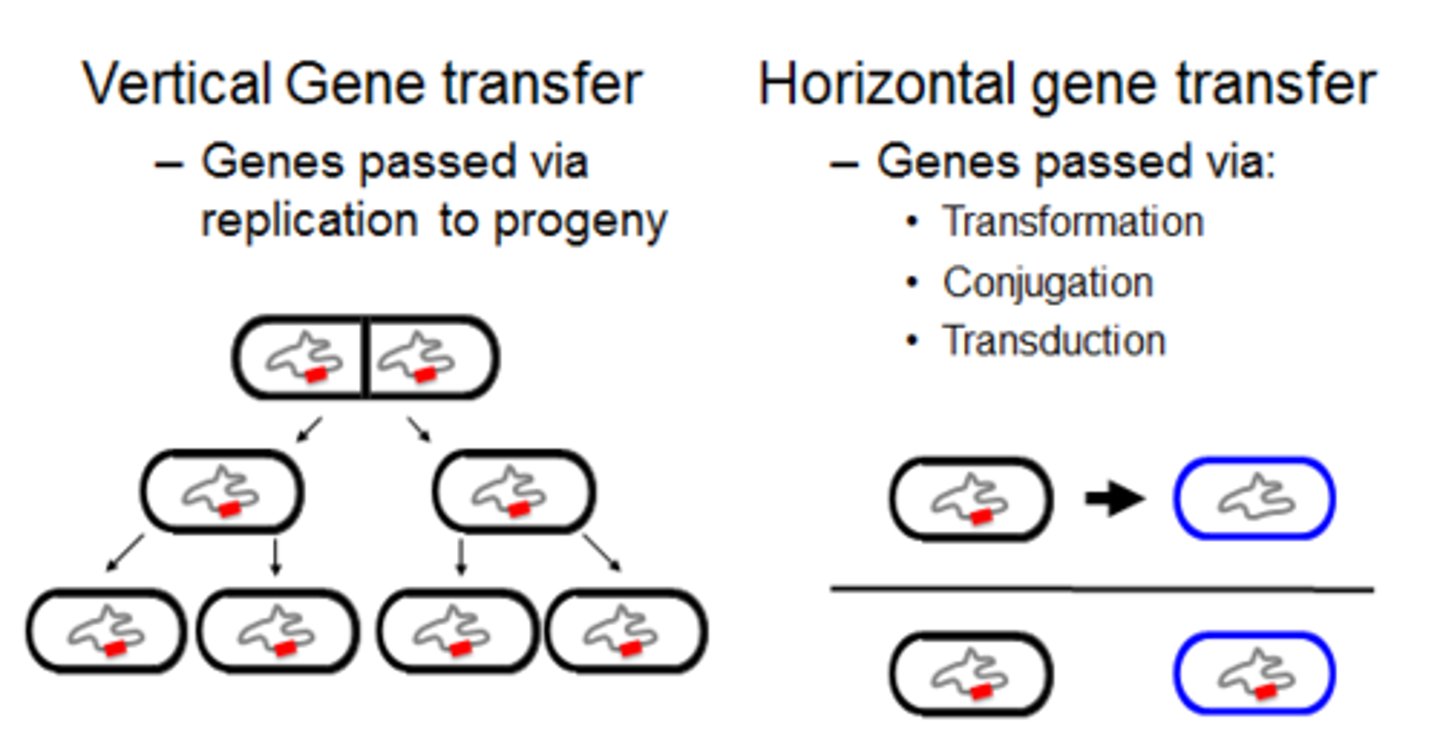
Horizontal gene transfer
Process in which an organism incorporates genetic material from another organism without being the offspring of that organism
Empirical thought
Thought that relies on observation to form an idea or hypothesis rather than trying to understand life from a nonphysical or spiritual point of view
Anaximander
Ancient greek philosopher who first suggested organisms evolve over time
Plato
Ancient greek philosopher that supported "essentialism:" objects are temporary reflection of ideal forms