MC- molecular shape :Configuration
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
importance of shape , structural isomers , stereoisomers and cahn ingold priority rules
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
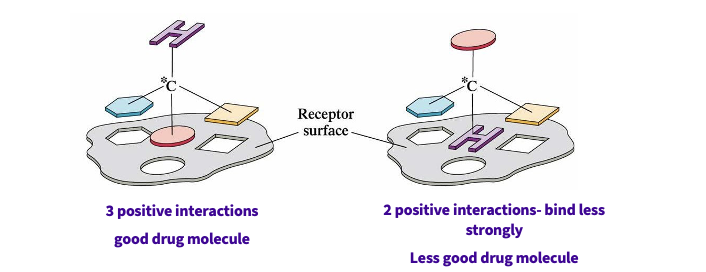
Why does shape matter?
interaction of a drug with a receptor ( action)
interaction of a drug with an enzyme( metabolism and action)
recognition of shape = vital
more positive interactions = good drug molecule = binds strongly
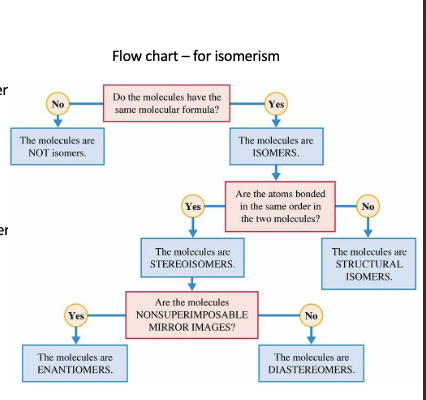
What is a structural isomer ( constitutional isomers)?
same molecular formula
can have different functional groups
differences - atoms/ groups are attached differently
What is a stereoisomer?
same molecular structure , atoms are connecte din te same way , not structural isomers
same functional groups
atoms orientated differently in space
What are the different types of stereoisomers?
enantiomers ( optical isomers) - chiral centres
Stereoisomers- cis- trans isomers
What are the key processes/factors to consider for distinguishing between types of isomerism ?
same molecular formulas
are they bonded in the same order
are they non- super impossable mirror images
What are the properties for enantiomers ?
sp3 hybridized carbons - tetrahedral in shape
carbon has 4 sigma bonds
the carbon needs to have a chiral centre - which means there are 4 different groups/atoms attached to it
How do you draw enantiomers?
-tetrahedral shape
-dashed = away from you
-wedged= towards you
some are mirror images of each other
What is an enantiomer?
two forms that cannot be interchanged without breaking a bond - configurations
non super imposable , one cannot be rotated to be identical to the other
the central carbon atom is a chiral centre * - the molecules are called chiral molecules
the rotate polarised light differently
What is a racemate ?
when chiral compounds exit as a 50:50 mixture of both mirror images for,s a racemate
but many important biological molecules are only active in one form
How do we get only one form of the enantiomer or use a racemate in medications ?
purify drugs , separate mixture or prove that one enantiomer doesn’t do harm
mixtures - cheaper no purification needed
one form of the enantiomer= could be harmful
when you rotate each an enatniomer they wont’ be the same
What is a molecule that doesn’t have a chiral centre called ?
Achiral
molecules can be super imposed on their mirror images
eg- glycine
How do you distinguish the configurations of an enantiomer ?
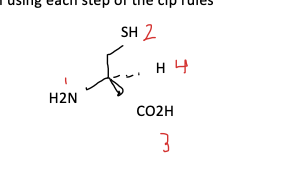
use CIP rules 1.
assign high , low priorities to each substituents based on atomic numbers
is atoms have the same priority move along to the main chain to the next atom
arrange molecules such that the lowest priority substituents go away from you
label the groups
if the go clockwise = R
if they go anti-clockwise = S
note- if the hydrogen isn’t away ( lowest then do normally rather than redrawing and then flipp the answer )
what is the lowest priority group isn’t away from you ?
assign the priorities
work out configurations
then reverse the answer
What is the configuration of amino acids ?
all aa are S apart from cysteine
Cysteine - R because of the sulphur substituent
Whta is a diastereoisomer ?
two forms that cannot be interchanged without breaking a bond
not mirror images
different chemical properties
eg- geometrical isomer/ cis- trans isomers
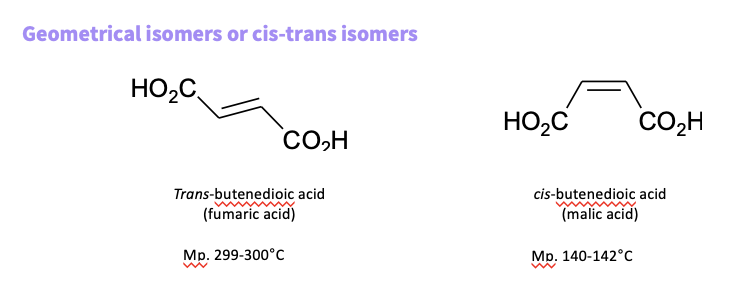
How do you distinguish between diastereomers ?
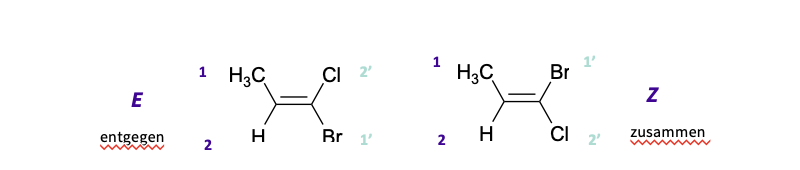
also known as E , Z
use CIP RULES
assign a priority to each carbon
if the two high priorities are on the same side. of the molecule - Z
if the two high priorities are on different sides -E
Are diastereoisomers just for compounds with double bonds ?
No
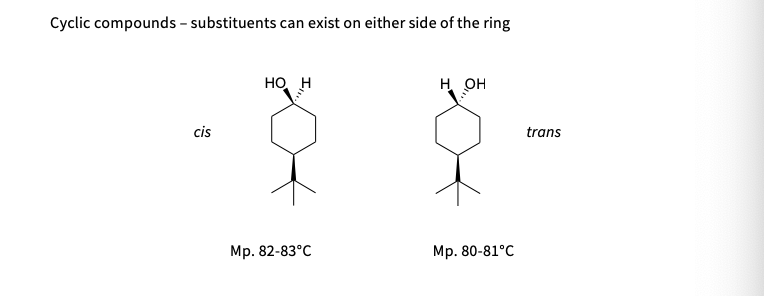
cyclic compounds - substituents can exist on either side of the ring
look at the side with higher priority ( split th emolecule in half )