earth sci
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
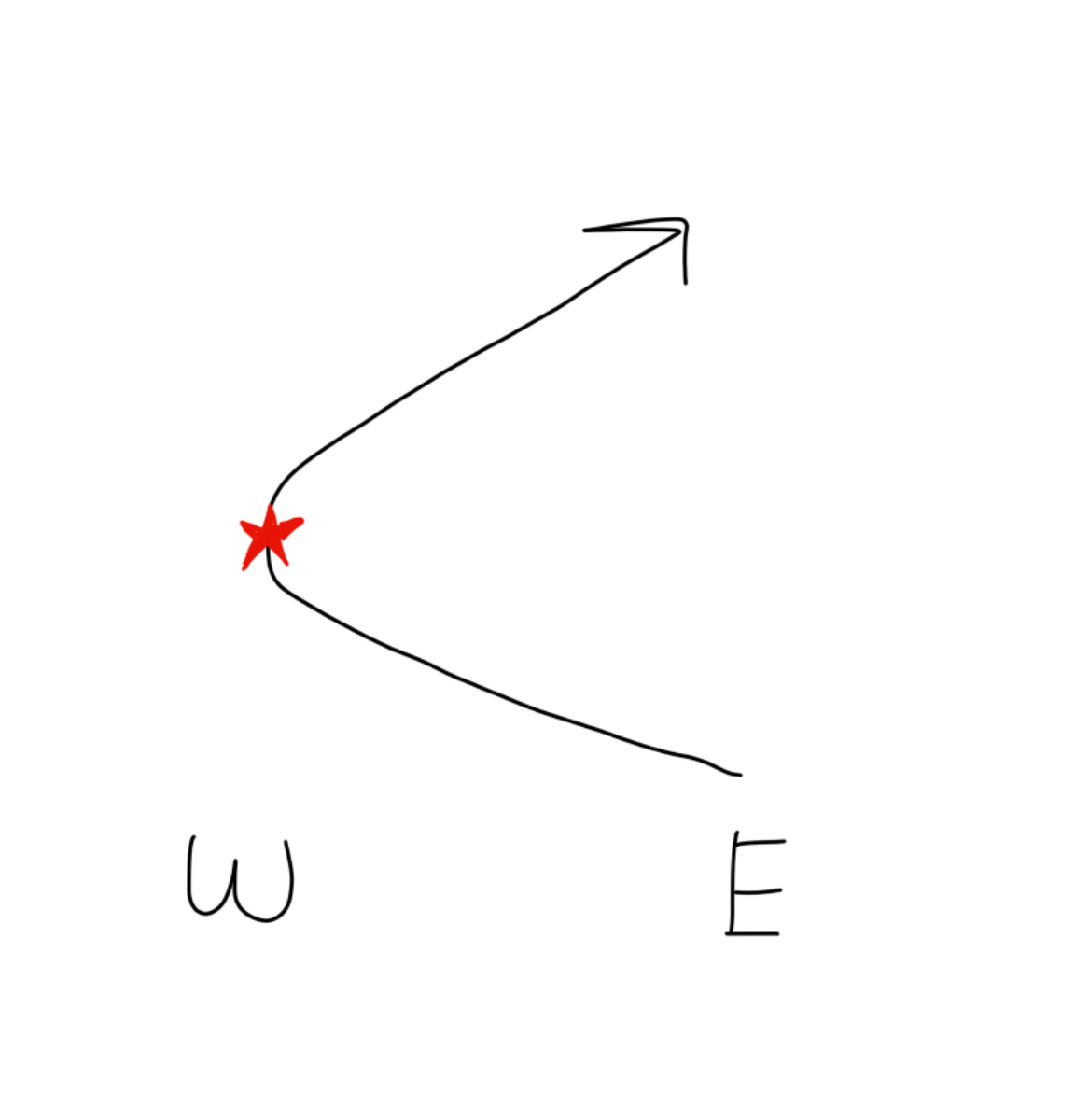
What way do hurricanes travel?
E to W —> W to E
Red vs blue shifts
red = moving away
blue = moving closer
Why is volcanic ash a good geologic time marker?
spreads over a wide area in a short period of time
River valleys vs glacier valleys
river valleys = V-shaped
glacier valleys = U-shaped
Clastic vs bioclastic
clastic = formed from old rock sediments
bioclastic = formed by past living organisms
How does lake affect snow form?
cold air evaporates from warm water —> RECC —> snow
How do glaciers deposit sediment?
unsorted, unlayered
Mafic vs felsic
mafic = dark, dense, Fe & Mg
felsic = lighter, less dense, Si & Al
Extrusive rock characteristics
cools quickly, formed from lava, small crystals
Intrusive rock characteristics
cools slowly, forms from magma, large crystals
Waxing vs waning
waxing = light on the right, begins at new moon and ends at full moon
waning, light on the left, begins at full moon and ends at new moon
Lunar vs solar eclipse
lunar = earth blocks sun from reaching moon
solar = moon blocks sun from reaching earth
Inner core vs outer core
inner core = solid
outer core = liquid
P vs S waves
P waves = pass through solids and liquids
S waves = pass through solids only (absorbed or reflected in liquids)
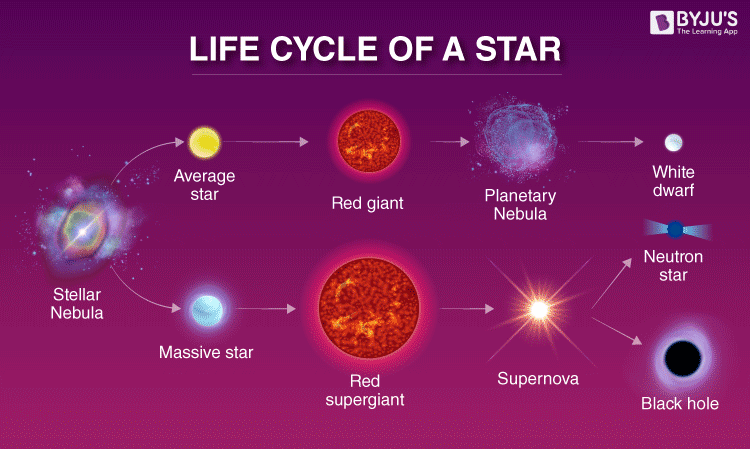
The process that stars go through?
nuclear fusion
Star life cycle
Greenhouse effect
process in which certain gases trap infrared heat on earth
Greenhouse gasses
methane, water vapor, CFC’s, ozone, nitrous oxide
Spring vs neap tides
Spring = new moon & full moon
Neap = first quarter & last quarter
Relationship between particle size and capillarity
as particle size decreases, capillarity increases
Relationship between particle size and permeability
as particle size increases, permeability increases
Relationship between particle size and infiltration
as particle size increases, infiltration increases
Relationship between particle size and porosity
if particle size either increases or decreases, porosity remains the same
Watershed vs delta
watershed = water drained by a river
delta = water flowing into a larger body of water
Glacier landscapes formed from erosion
U shaped valleys
Striations = scratches bedrock
Glacier landscaped formed from deposition
Till = unsorted sediment from melted glacier ice
Moraine = ridges formed from till
Outwash plain = flat area of sediment from meltwater
Esker = long ridges of sediment from meltwater
Kettle lake = depression formed from melted glacier ice
Bedrock structure of mountains
tilted, folded, uplifted
Bedrock structure of plateaus
flat, horizontal, uplifted
Bedrock structure of lowlands
softer sediment, loose, deep
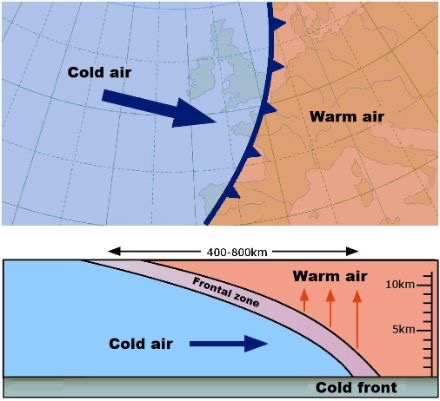
Cold front
short duration, intense storms
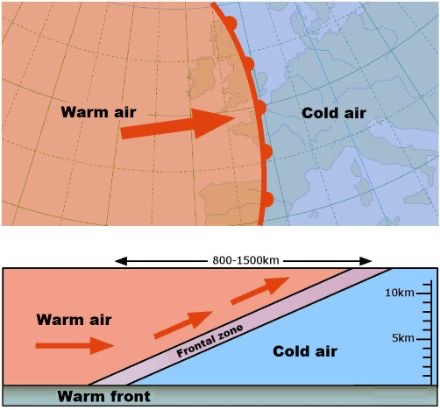
Warm front
long duration, light rain
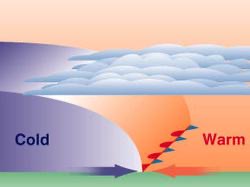
Stationary front
Period of steady rain
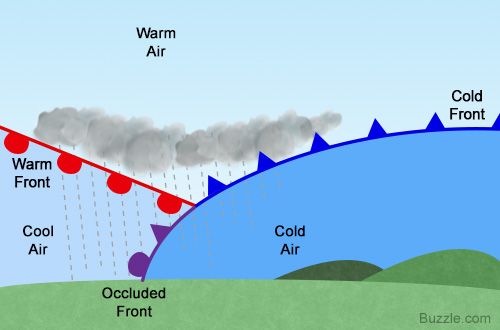
Occluded front
fast-moving cold front overtakes a slow-moving warm front
cloudy, rainy
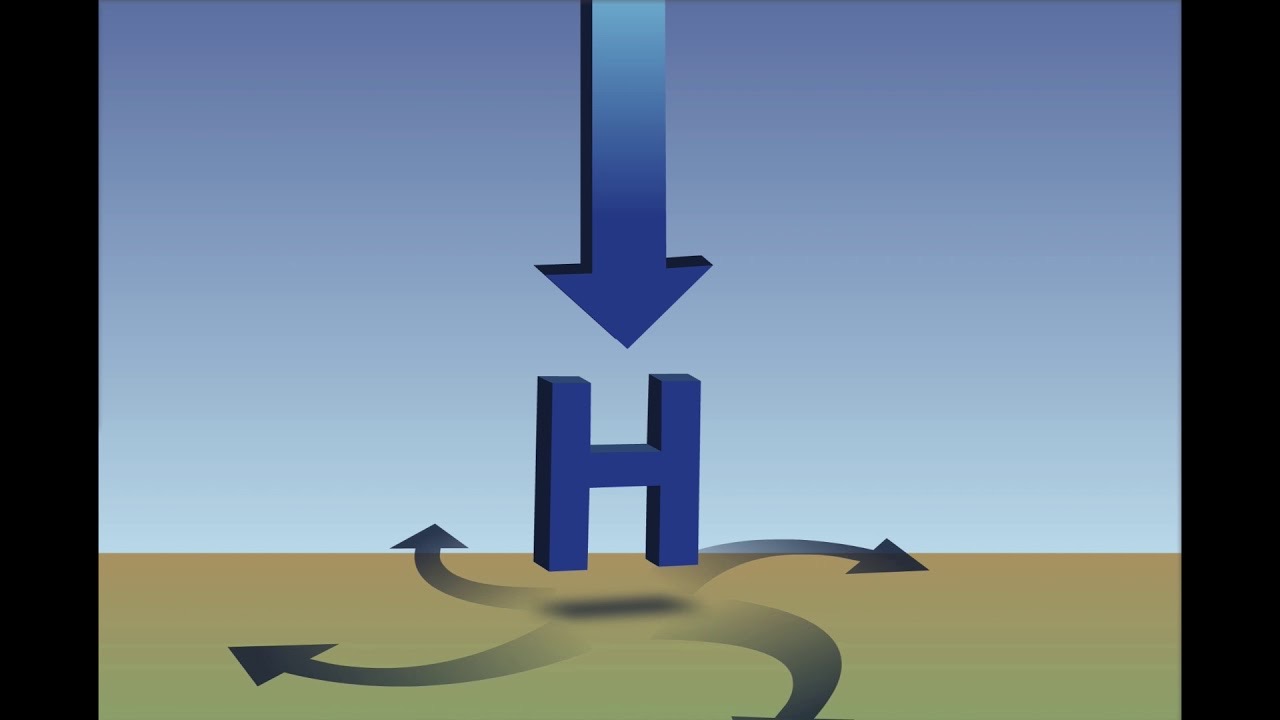
High pressure system
high air pressure
dry conditions
divergent
clockwise motion
downward
cool weather
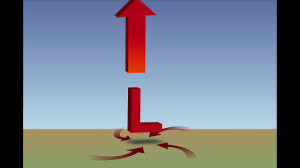
Low pressure system
low air pressure
wet conditions
convergent
counterclockwise motion
upward
warm weather
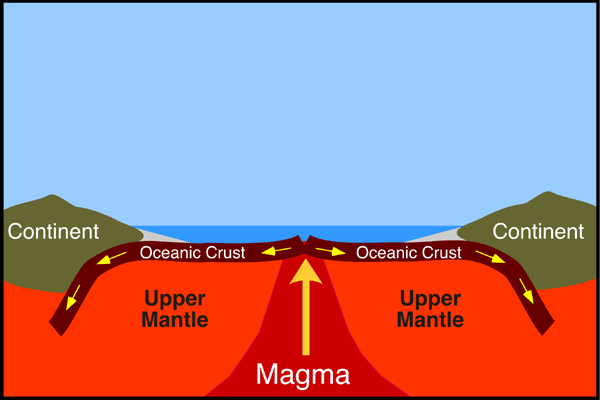
divergent
plates move apart
creates ridges
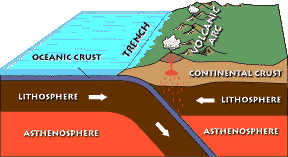
convergent
plates collide
creates mountains, volcanoes, trenches
transform
plates slide across each other
creates earthquakes
What direction does hurricanes and tornadoes spin
counterclockwise
only in northern hemisphere
Coriolis effect
caused by rotation of earth on its axis
wind curves right in northern hemisphere, but curves left in southern hemisphere
Mechanical vs physical weathering
mechanical- frost action, abrasion
chemical- oxidation (rusting), acid rain
Vertical vs horizontal sorting
vertical sorting = larger sediment on bottom
horizontal sorting = smaller on bottom, deposited first
How do landscapes form from bedrock?
Uplift
Erosion
Subsidence
Deposition
Age of universe
13.8 b years old
How is water returned from earth’s surface to the atmosphere?
evaporation and transpiration
What are monsoons and other seasonal weather events caused by?
seasonal shifting of wind patterns and atmospheric pressure changes
Inclusions
inclusions are the same age as the bedrock it formed from
Northern hemisphere winds vs southern hemisphere winds
northern hemisphere winds = northeast winds
southern hemisphere winds = southeast winds
Where does deposition occur in a river?
on the inside of the meanders
Size of pebbles
0.2- 6.4 cm
How are barrier islands formed?
wave action