Lecture 4: Biological Targets and Their Modulation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Biological molecules are modular
Protein:
Linear chain of Amino acids
Amide bonds
Nucleic acids:
Linear chain of nucleotides
Phosphate ester
Polysaccharides:
Liner chains of sugars, some are branched
Acetals
Lipids
Linear chains of acetate or propionate
Chain is modified so the assembly units are hidden
Reduce aldol (1,3 - dicarbonyl)
Modular construction makes life possible
Easily assemble complex structures using simple molecules components
Easily disassemble complex structures and regenerate parts for reuse
Only need 1 enzyme system for each biomolecule type and function
Proteins made by ribosome
Protein disassembled by proteasome
Drugs produce effects by binding to biomolecules
Proteins are the most common target
Nucleic acids are less common
Drugs produce effects by binding to biological molecules
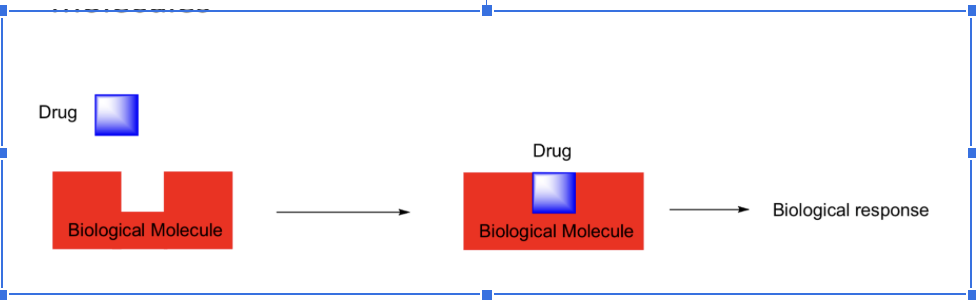
Biomolecules have well-defined 3-D shapes
They create three dimensional chemical environments
Drugs interact with biological molecules in 3-D way
The shape and pattern of electron density determine binding
Non-covalent interactions
Some drugs react chemically with biological molecules
Covalent bonds
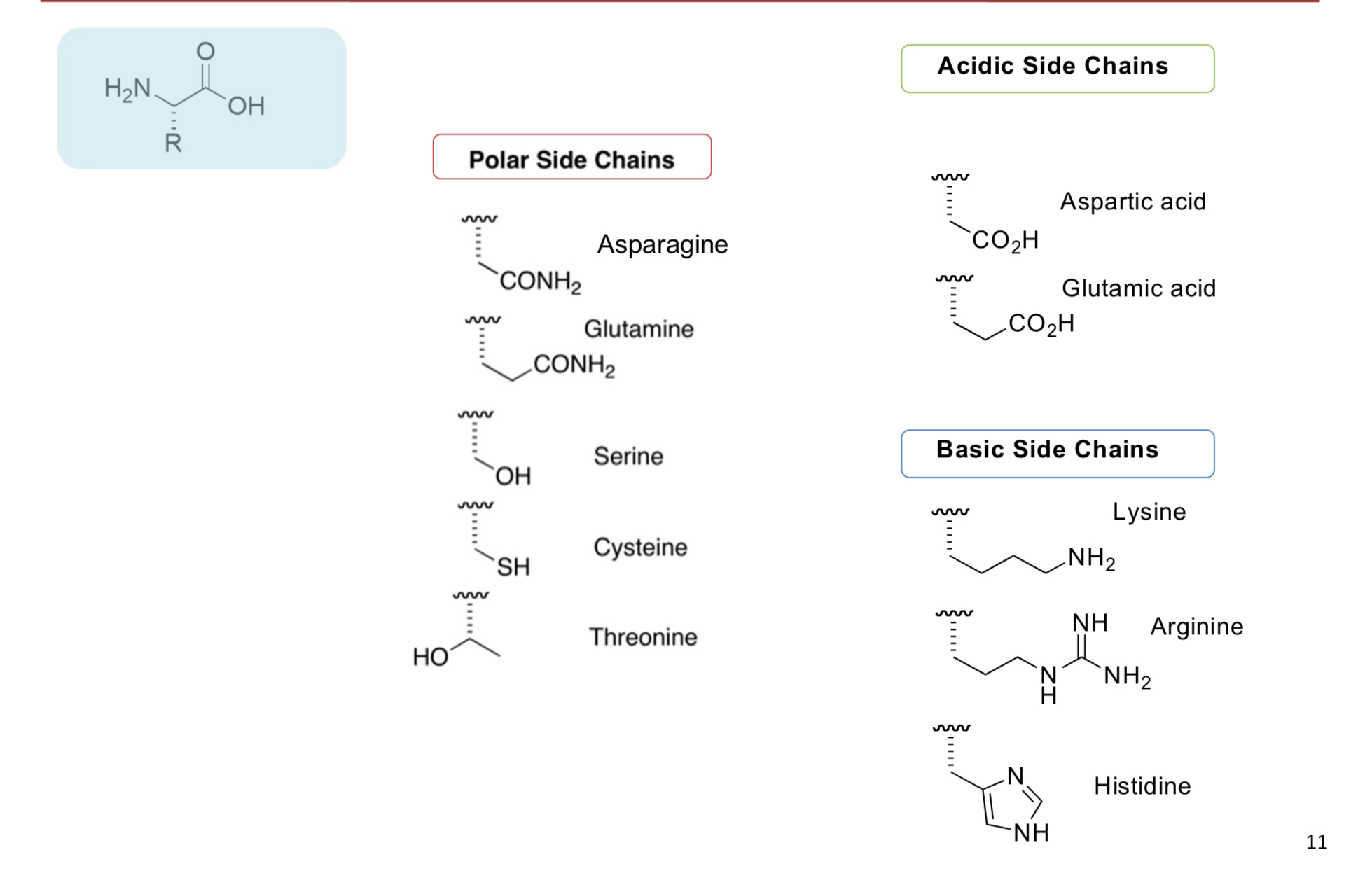
Proteins are made of amino acids
20 different canonical types of amino acid are used
Occasionally, some proteins contain modified or unusual amino acids
Amino acids share the same backbone and stereochemistry, but differ in their side chains (R)
The chemical properties of side chains vary, contributing to the diverse functions of proteins
Amino acid side chain properties
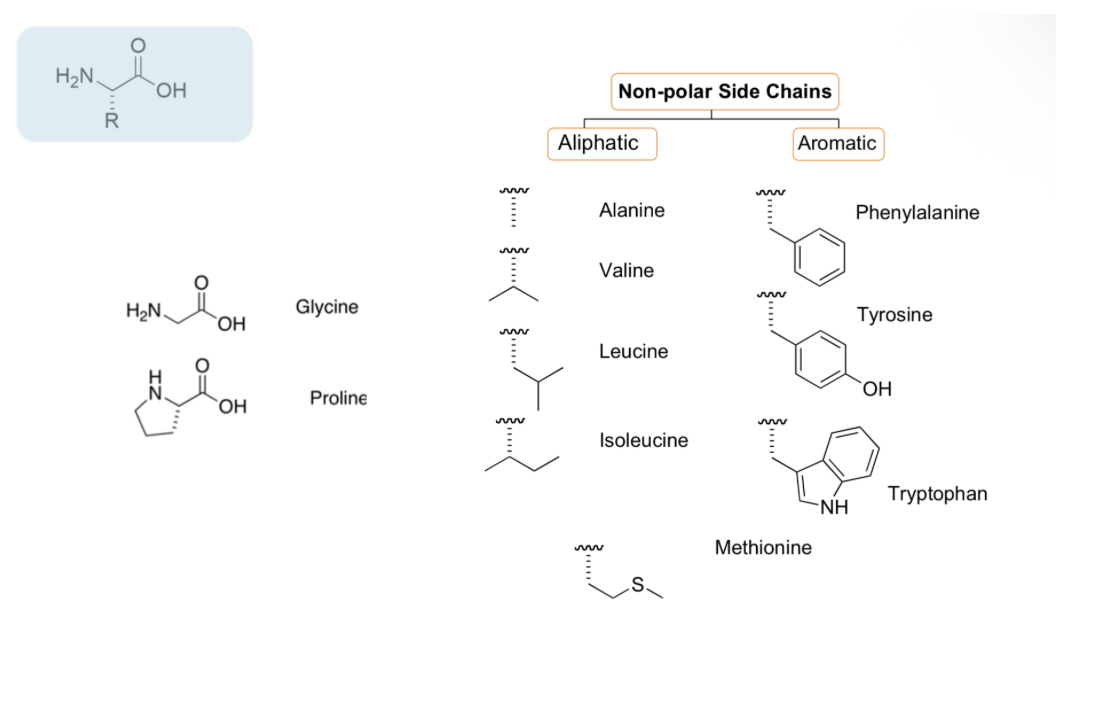
Amino acid side chain properties
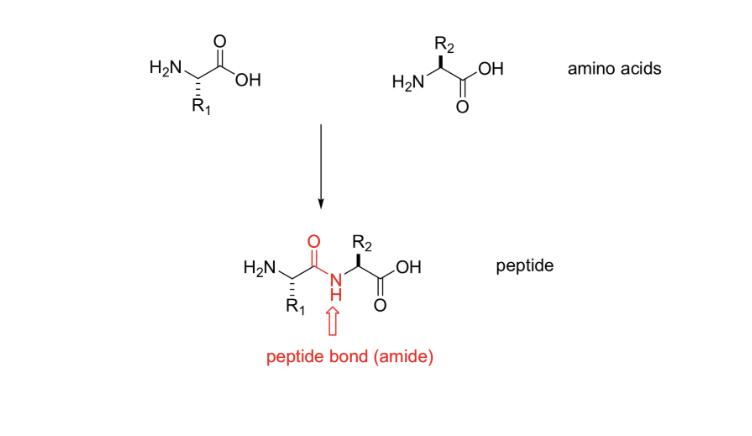
Peptides are linear chains of amino acids
Proteins are long peptides folded into a particular shape
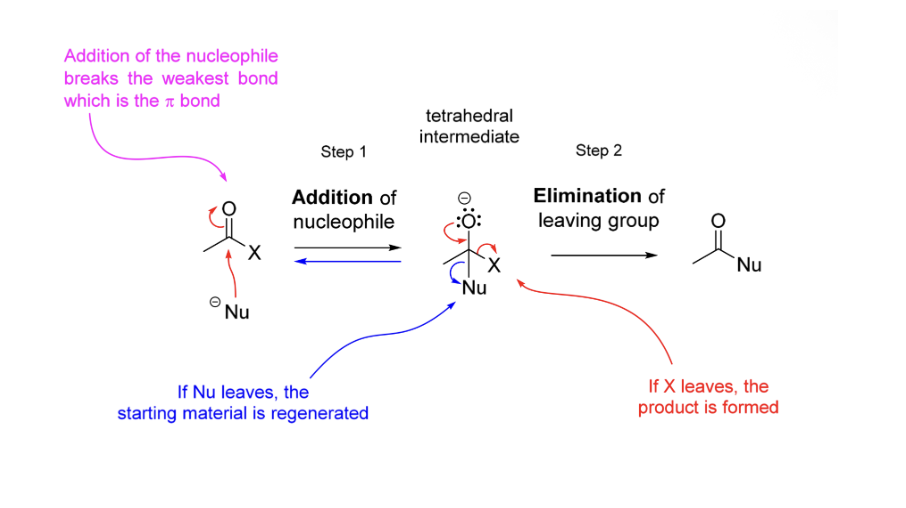
Nucleophilic substitution of carboxylate
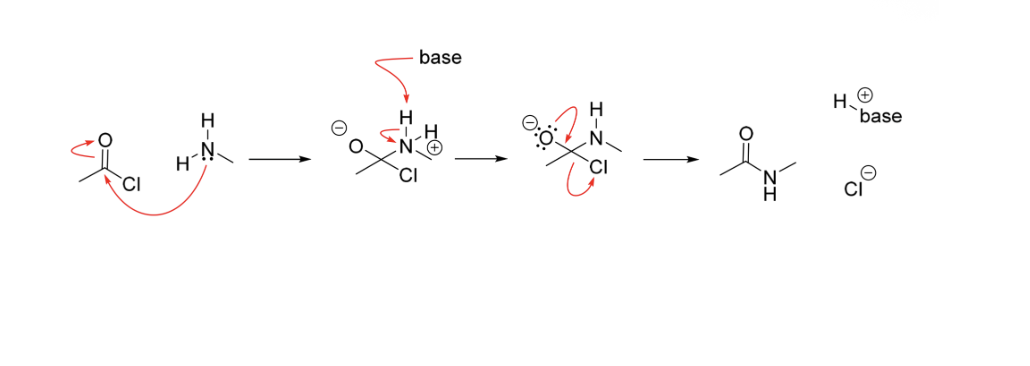
Amide Bond formation - Base catalysis
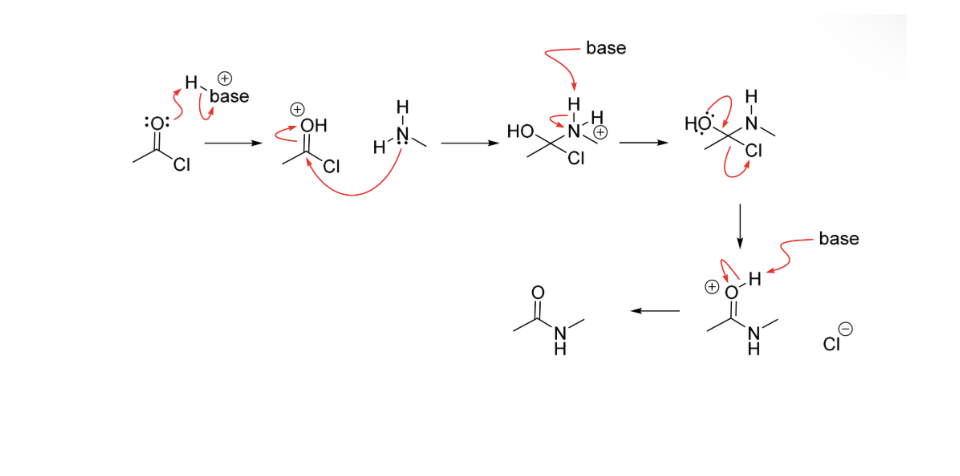
Amide bond formation - Acid catalysis
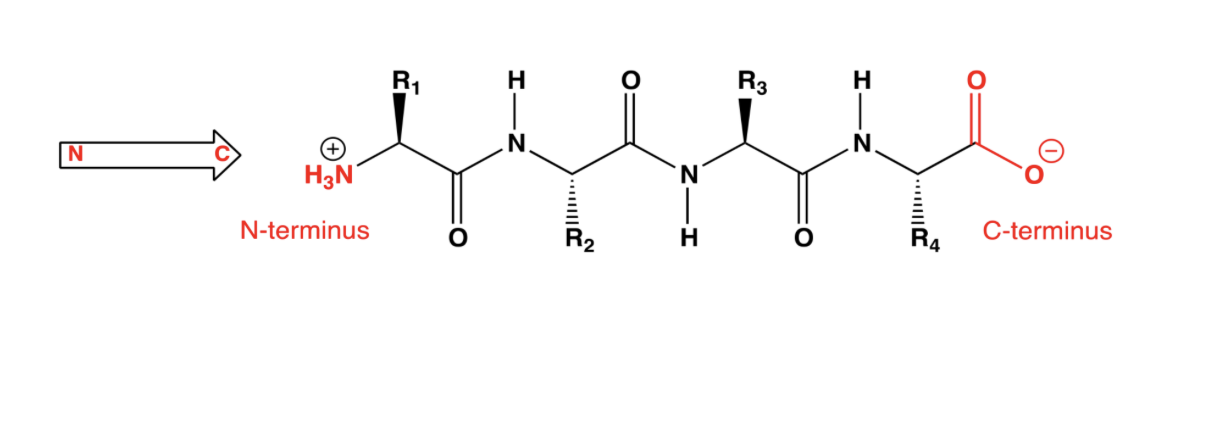
Primary structure of proteins
Sequence of amino acids in a protein
(this is the only information specified by a gene)
Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds (amide bonds)
Primary structure is a list
By convention, amino acids in a protein are listed in order from the N-terminus towards the C-terminus
Secondary structure
Regions of local order in the backbone chain
Forms small-scale structures such as:
A- helix
B- helix
Loop
Turn
Represented in ribbon structures
Origin of secondary structure
Conformational restrictions in amide bonds
Conformation restrictions between amide and a-carbon
Interactions between amide bonds
Intermolecular forces acting in an intramolecule way
Same forces that control solubility
Side chain interactions within a region of the chain
Amide bond has double bond character
Side chain interactions
Negative charges attract positive charges
Hydrogen bonding between side chains and backbones
Non-polar side chains interact with other non-polar chain - steric interactions
The result of these chemical interactions is the folding of the amino acid chain to produce large-scale structures
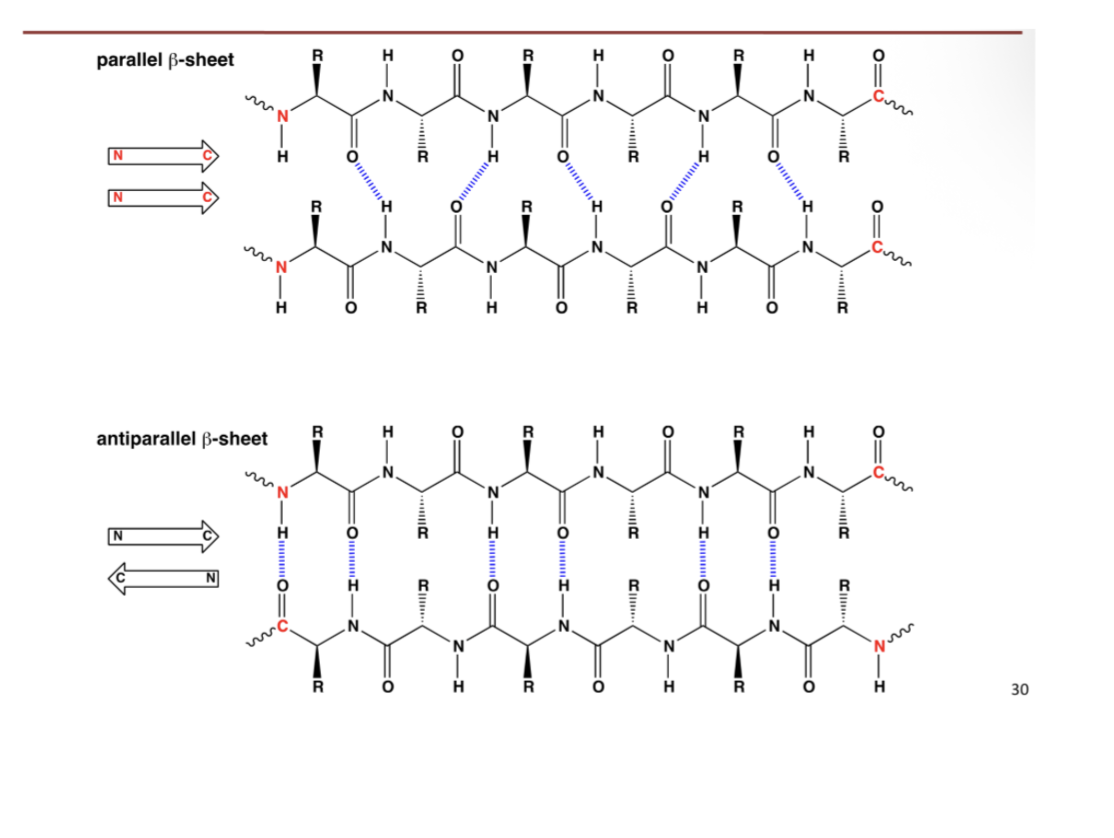
B- structures
B-stands
Backbone atoms are coplanar or “flat’
Several strands can associate to form sheets (B-sheet)
Large sheets can curl around themselves, forming cylinders (B-barrels
B- sheet can be parallel or antiparallel
Loops
Areas with no defined secondary structure
Represented by “spaghetti” on ribbon diagrams
Turns
Several types
May not be explicitly represented on ribbon diagrams
Look for areas where the chain changes direction by a large amount
Tertiary structure
Overall 3-D shape of a protein
Result on interactions between non-adjacent regions
Amino acid side chains
2 secondary structures (two helices)
Contains regions of order
Secondary structure
Contains less ordered regions
Loops
Tertiary structure and attractive forces
Attractions between secondary structures cause the secondary structures to folf back on themselves
These are mostly non-bonding interactions
There are occasional covalent bonds
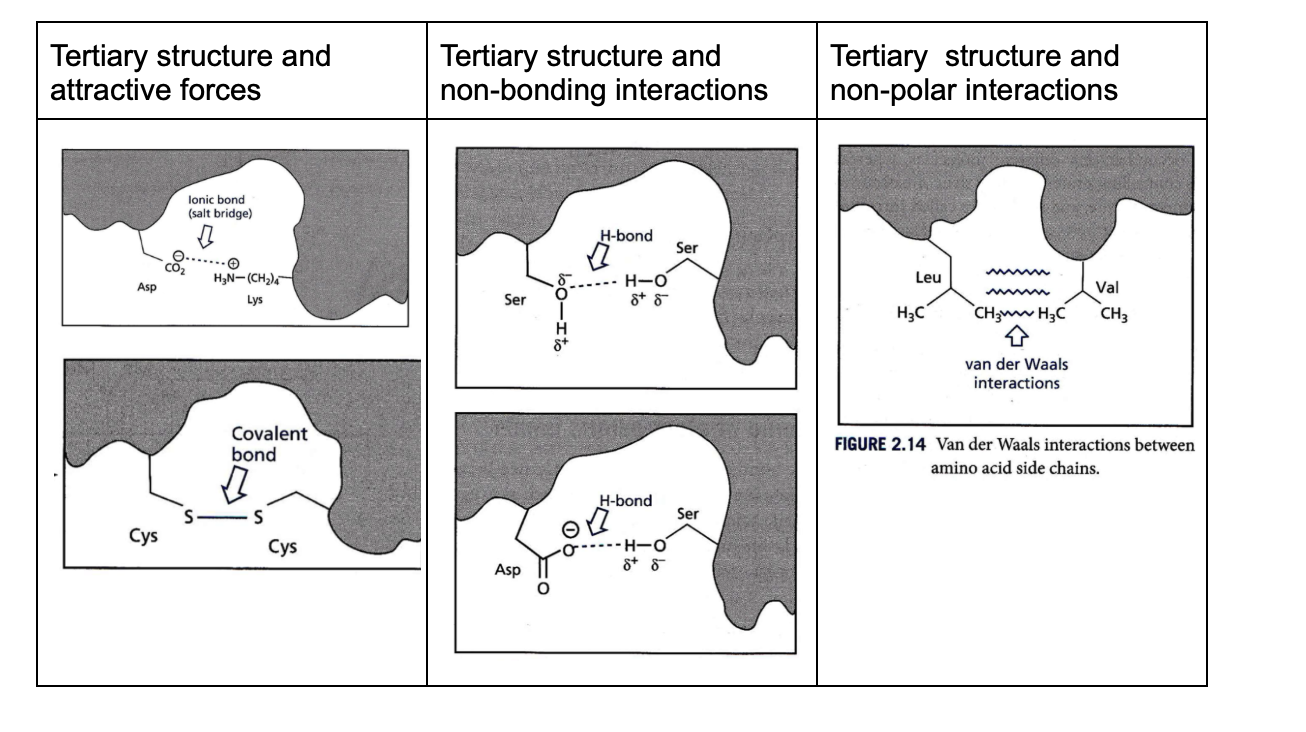
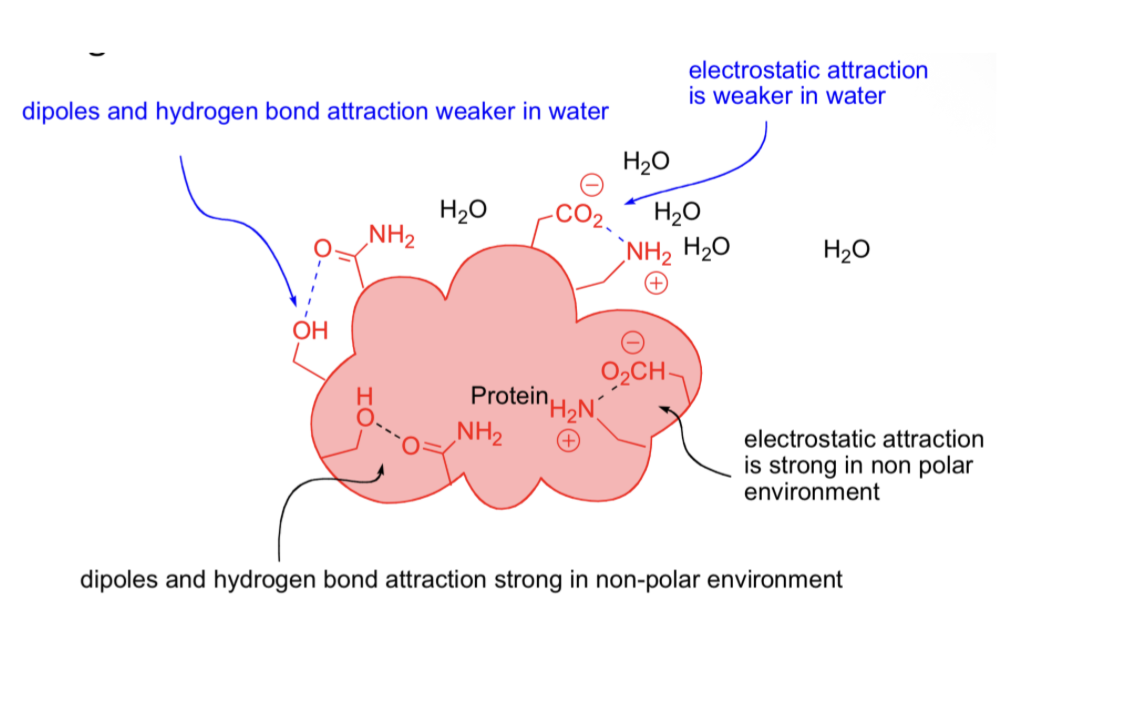
Van Der Waals interactions are very important
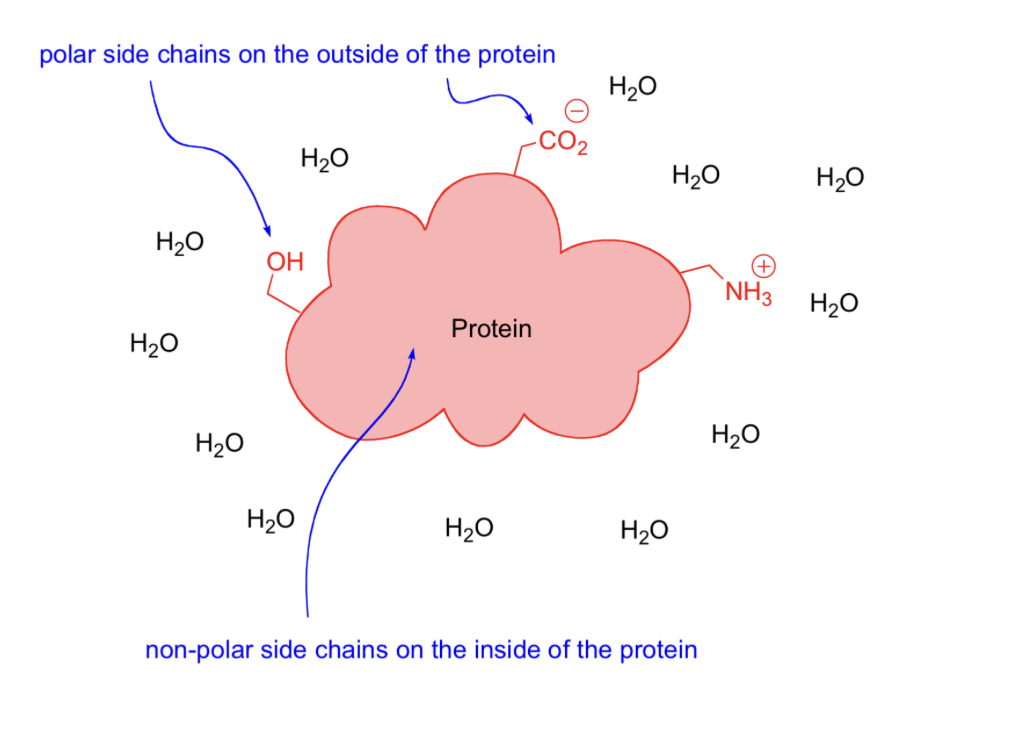
Dipole interactions and H-bonds stronger Inside Hydrophobic environment
Non polar environment critical to holding protein together
Some proteins form Quaternary structures
Two or more proteins bind together
Sub units can be the same or different
Protein-Protein interactions are very strong
Lots of surface contact area
Lots of chemical interactions
Exclusion of water from space between
Proteins stick together well
Difficult to separate some proteins
Overall structures determine function
Most of the molecule is a scaffold
Only a small part is normally “functional”
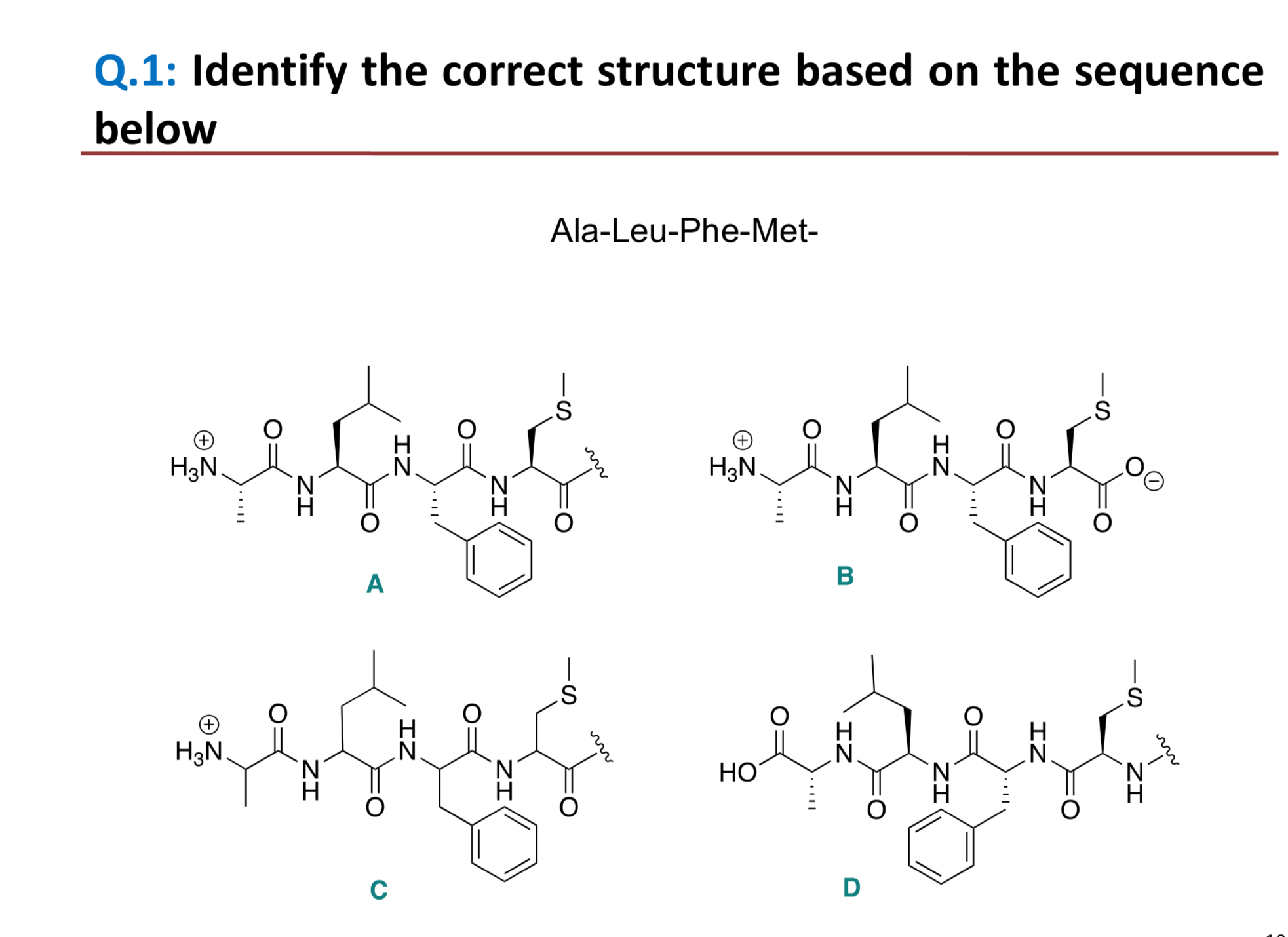
Identify the correct structure based on the sequence below