Climate and Biomes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
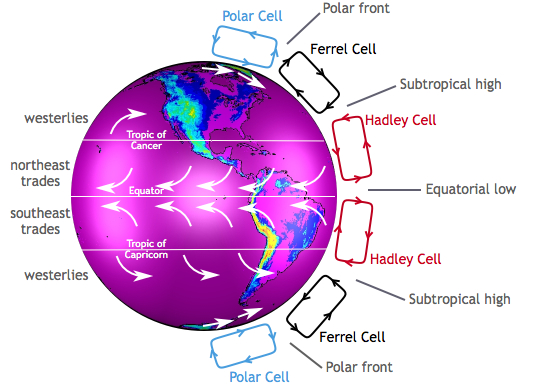
Hadley Cell
At the equator, the sun’s energy is hitting the equator first, so air is also heated. Hot air rises and cold air sinks. Tropical air goes up, loses moisture then comes down as rain; circles back around as dry air
Polar Cells
On each pole, the power to drive those major currents are from cold air descending and then it slowly warms up and moves up; Cold air goes down, slowly warmed up
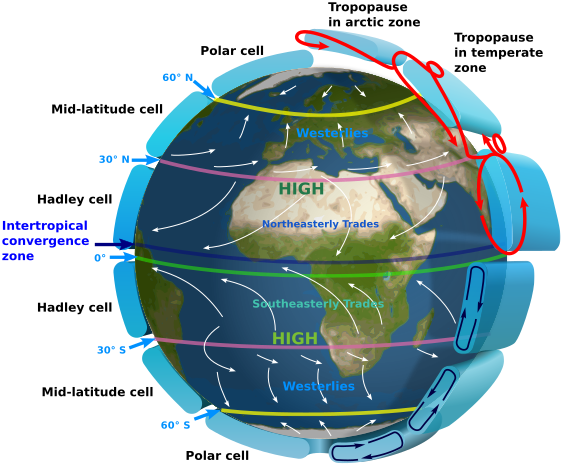
Ferrel Cell
Roughly 30° to 60° latitude; Powered by the Hadley and Polar Cell
Intertropical Convergent Zone
Where the Hadley Cell comes down; most of the water comes down at the equator. Tropics are wet and dry. Water gives up its heat more slowly than land, so it takes more energy to warm up.
Thermohaline Circulation
Cold water from the deep ocean gets shuttle up; movement of deeper water results in higher nutrient levels
Walker Current
A part of Thermohaline Circulation, big ocean current is super cold
El Nino
Weaker winds result in weaker pushing of the ocean current, forcing less of the nutrient-rich colder waters up; average temperature of the waters stays higher
Upwelling
The effect of cold water coming up
Biomes
Distinct habitat types determined by climate and soil; Climate + Soil Type = Biome
Biogeographical Realms
Large spatial regions, geographically isolated and serve as barriers to gene flow
Rainforests
Close to the equator, lots of rain, precipitation changes rather than temperature change
Nutrients in soil gets washed away in the rain; no nutrients in the soil
Buttress Roots
Roots to support the enormous structure of trees competing for light
Tropical Lianas (Vines)
25% of the biomass in the tropics are actually vines; can climb up on other trees and gets access to sunlight
Tropical Deciduous Forest
Deciduous = dropping their leaves every year; never freezes: dry season and wet season; intertropical Convergence Zone comes over them
Warm Deserts
Wet winters, not completely dry; some rainfall
Mediterranean Climate
Drought-tolerant, very dry; plants grow quickly after fires
Continental Climates
Getting so far away from the oceans, so it barely affects the climate; higher temperature changes
Ex. Prairies - soil is very nutritious
Temperate Deciduous Forest
Trees that drop their leaves in the wintertime due to seasonality
Rainshadow
Side of the mountain with no moisture
Adiabatic Cooling
Atmosphere current hits a mountain, it’s warm and has a lot of water in it, then it’s pushed up higher and higher to cooler air. Once it gets to the dew point (where relative humidity is at 100%), then it loses moisture