Homeostasis (Nervous) Slideshows 6.0-8.0
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What is the nervous system?
Collection of neurons found in the body that relay information between the brain and the rest of the body
What 2 components are found in the CNS?
The brain and the spinal cord
The brain and spinal cord are i____s (fill in the blank)
integrators, receive info and decides what to do with it, coordinates activity of all parts of the body.
What term describes all of the other nervous system cells outside the CNS?
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Where does the PNS relay information to?
The CNS
What two subcategories is the PNS split into
The somatic nervous system and the autonomic system
Somatic is v___, autonomic is ____
Voluntary, Automatic
Example of SNS
Muscle flexing, touching an object
Example of ANS
Acts unconsciously and regulates bodily function such as heart rate, digestion, etc…
ANS can be FURTHER split into what 2 subcategories?
Sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic
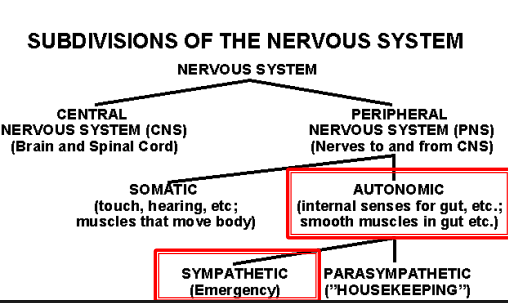
What does the sympathetic nervous system control?
Controls the body’s response to dangerous/stressful situations
What does the parasympathetic nervous system control?
Controls all of the other housekeeping tasks. Sometimes called the rest and digest system.
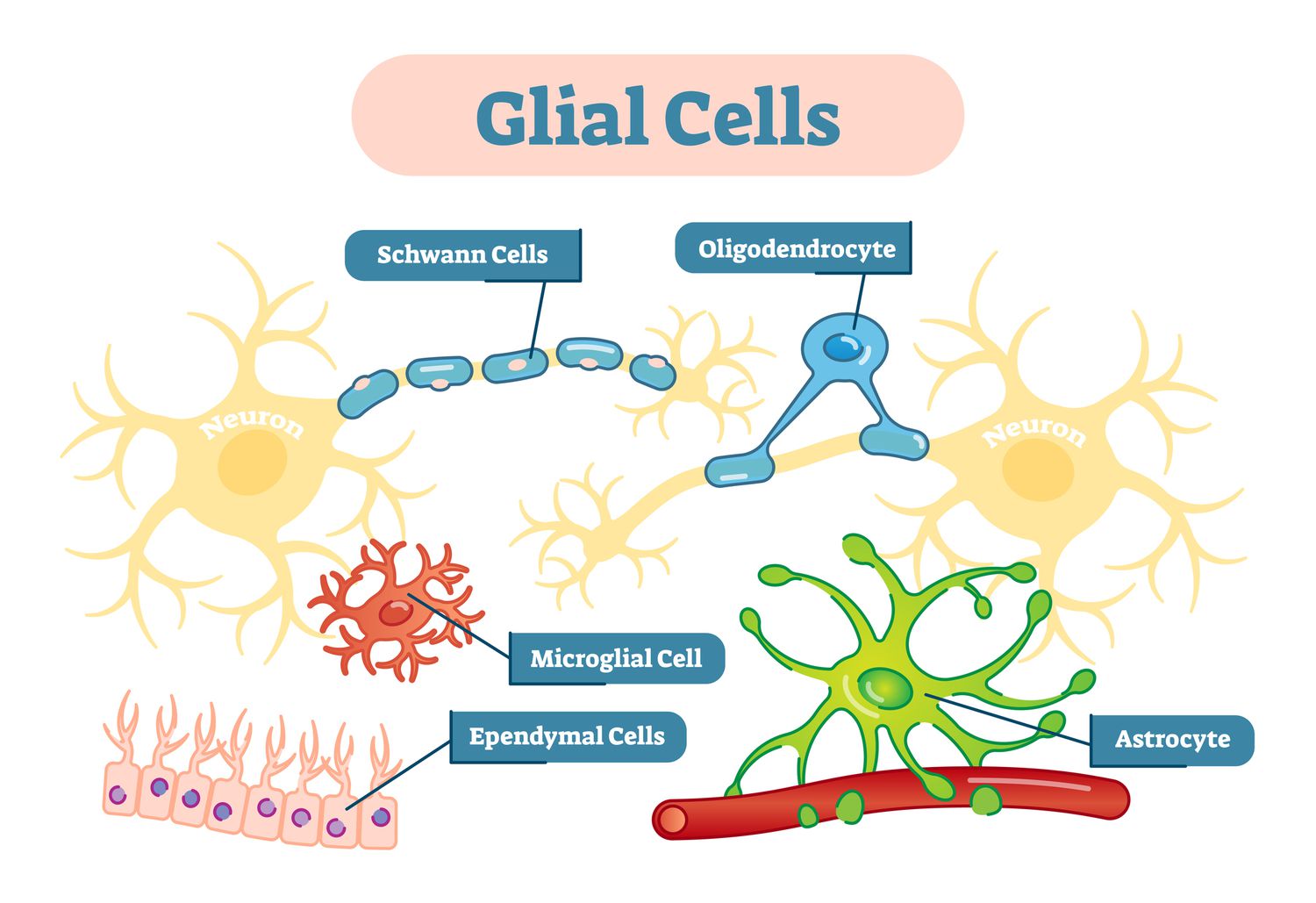
Two types of nervous tissue cells are?
Neurons and glial cells
What are neurons?
Neurons are specialized cells that receive and transmit electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system.
Which type of signaling is more functionally important in neurons: chemical or electrical?
Electrical signaling is more functionally important for rapid signal transmission along neurons.
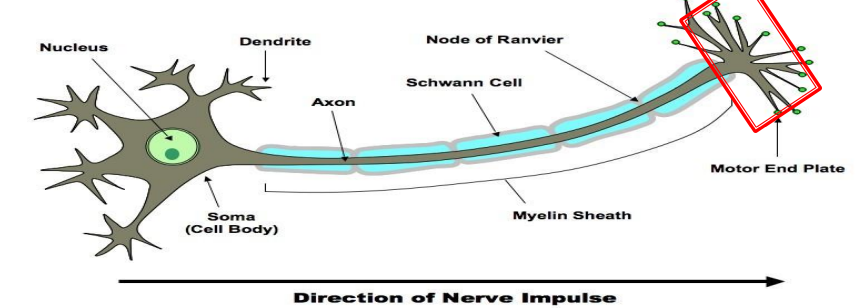
What is the function of dendrites?
Dendrites are branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons.
What is the soma (cell body) of a neuron responsible for?
The soma contains the nucleus and organelles (RER, SER, etc.) and maintains the neuron’s metabolic functions.
What is the axon and what does it do?
The axon is a long, tube-like structure that carries electrical impulses away from the soma.
What is the myelin sheath?
A fatty insulating layer that wraps around axons to increase the speed of signal transmission.
What cells form the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system?
Schwann cells, a type of glial cell.
What is a Node of Ranvier?
Gaps between Schwann cells where ions can move in and out of the axon.
Why are Nodes of Ranvier important?
They allow saltatory conduction, where the nerve impulse “jumps” between nodes, increasing speed.
What is the axon terminal (motor end plate)?
The end of the axon where neurotransmitters are released to communicate with another cell.
What are sensory neurons?
Neurons activated by sensory input from the environment that transmit signals to the nervous system.
What are interneurons?
Neurons that connect sensory and motor neurons, primarily within the spinal cord and brain.
What are motor neurons?
Neurons that transmit signals from the central nervous system to muscles, glands, and organs.
What type of muscles do motor neurons control?
Skeletal and smooth muscle.
What is the typical structure of a motor neuron?
Multipolar, one axon and multiple dendrites.
What are nerves?
Neurons that are bundled together
What is neural signaling?
Communication between neurons via electrical impulses and chemical neurotransmitters.
Can a neuron both receive and send signals?
Yes, a neuron can receive input from other neurons and transmit signals downstream.
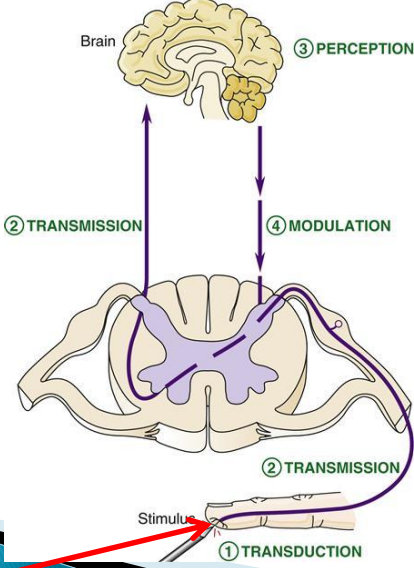
What model describes the pathway for a nerve impulse?
A stimulus response model
What role do receptors play in the stimulus–response model?
They transform stimuli into nerve impulses.
Typical Neural Signalling pathway:
Stimulus —> receptor —> sensory neuron (somatic PNS) —> sent to the spine (CNS) —> to the brain (CNS) —> back to the spine —> motor neuron
What is a reflex action?
An involuntary, rapid response to a stimulus that does not require conscious thought.
What is a reflex arc?
A pathway that involves a sensory neuron sending a signal through the spine directly to the motor neuron bypassing the brain.
Why are reflexes important?
Prevent injury and protects us from danger.
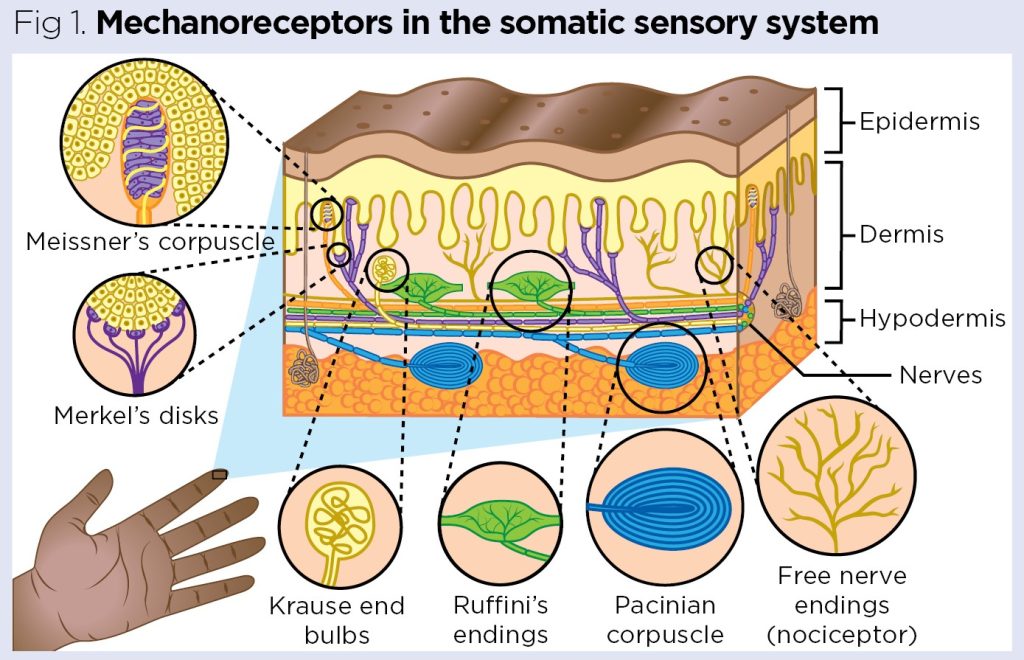
What are the five categories of sensory neurons?
Photo receptors — Light
Nociceptors — Pain
Mechanoreceptors — Pressure, sound waves, and motion
Chemoreceptors — Chemical changes (taste, smell, gas concentration)
Thermoreceptors — Heat
What does a stimulus activate on a neuron?
The stimulus activates a conformational change of a sodium channel protein on the dendrites
What happens as a result of the conformational change of a protein on the sensory neuron?
Causes sodium ions to rush into the dendrites
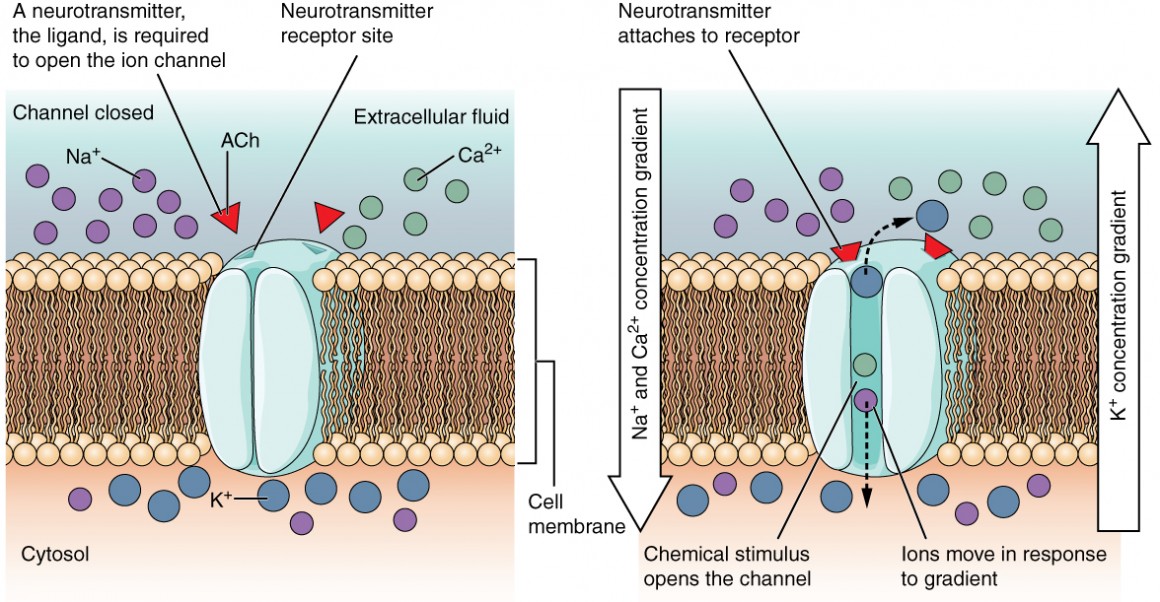
What does a influx of sodium cause?
Creates positive charge in the neuron which allows a signal to be sent down the axon towards the axon terminal.
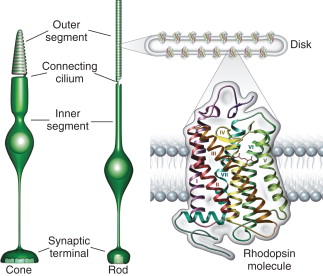
What are the two types of sensory neurons found in the eye?
Cones and rods
Cones detect ____ and are ___ ____ sensitive
Cones detect color and are less light sensitive
Rods detect ____ and are ___ ____ sensitive
Rods detect black and white and are extremely light sensitive
What are photopigment proteins?
Photopigments (receptor proteins) are found in rods and cones; they are activated by photons of specific wavelengths. Sort of similar to how different pigments in plants absorb different wavelengths.
nociceptors detect extremes in t____, p_____, and c_____
nociceptors detect extremes in temperature, pressure, and chemicals
do nociceptors send signals through a reflex arc?
Nociceptors often initiate reflex arcs (withdrawal reflex), but they also send signals to the brain for pain perception.
Mechanoreceptors detect t___, p____, s____, s____ _____, and m___
mechanoreceptors detect touch, pressure, soundwaves, and motion
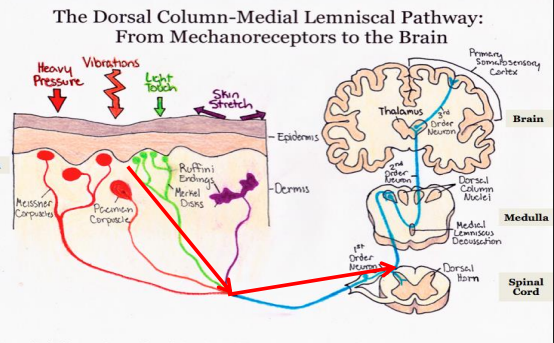
Where are mechanoreceptors found in the skin?
Nociceptors are found both superficially and deep in tissues, including near bone, allowing detection of damage at multiple tissue depths.
Thermoreceptors are..?
Specialized neurons that detect differences in temperature and measure the heat present in the environment relative to the body’s normal temperature
What type of chemoreceptor detects smells in the nasal cavity?
Olfactory receptors detect odors/pheromones in the nasal cavity
What type of chemoreceptor detects taste in the mouth?
Taste receptors detect aqueous chemical compounds in the mouth
What is action potential?
The movement of a positive electric charge down the axon of a neuron towards the axon terminal.
What is it called when the positive charge moves down the axon?
This is called propagation
Potassium channels are u______ and let potassium ___ of the cell
Potassium channels are unidirectional and let potassium out of the cell
Sodium channels are u______ and let sodium ___ the cell
Sodium channels are unidirectional and let sodium into the cell
Sodium potassium requires what to function?
ATP, activated through phosphorylation
Per cycle the sodium potassium pump moves ____ sodium ions ___ of the cell
Per cycle the sodium potassium pump moves 3 sodium ions out of the cell
Per cycle the sodium potassium pump moves ____ potassium ions ___ the cell
Per cycle the sodium potassium pump moves 2 potassium ions into the cell
Polarized refers to a what charge?
Negative charge
The inside of a neuron has a _____ charge relative to the surroundings
The inside of a neuron has a NEGATIVE charge relative to the surroundings
There is a ___ amount of sodium ___ the membrane, and a ___ amount of potassium inside the membrane
High amount of sodium OUTSIDE the membrane, high amount of potassium INSIDE the membrane
The resting potential of the neuron is around ____mV?
-70 mV
During resting membrane potential _____ protein channels are open
NO protein channels are open
Depolarization refers to the process where ____ rushes into the cell and makes it more ____ charged
Sodium ions rush into the cell and makes it more positively charged
Sodium entering into the neuron is an example of what type of transport?
Facillitated diffusion
What is the all or nothing principle?
The all-or-nothing principle states that a neuron will fire an action potential only if the membrane potential reaches a threshold of -55 mV; once triggered, the action potential occurs at a fixed size and strength, regardless of stimulus intensity.
During depolarization ____ channels are open
Sodium ion channels are open during depolarization
Repolarization triggers when cell voltage becomes ____ mV
Above 40 mV
Repolarization cause ___ channels to close and ____ channels to open, causing the charge of the neuron to _____ to about _____ mV
sodium channels to close and potassium channels to open, charge of the neuron to decrease to about -100 mV
What is hyperpolarization?
The state of the neuron where its voltage potential is below -70mV
During hyperpolarization the neuron is in a r_____ p_____ that lasts about ________, during this state the neuron cannot be _____
refractory period that lasts about 2 milliseconds, cannot be stimulated
During the refractory/repolarization phase the adjacent segment of the axon is ….?
While one segment is refractory, the next segment is depolarizing toward threshold, allowing forward signal transmission.
During the refractory period how does the neuron return to its original state before depolarization?
The sodium potassium pump uses ATP to move excess sodium inside neuron to the outside while moving excess potassium outside the membrane inside the neuron membrane.
The refractory period and closing of proteins is important because it prevents ____ action potential
backwards action potential.
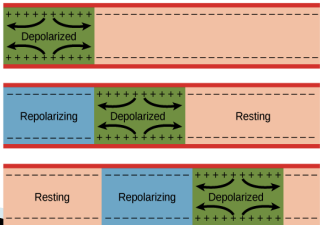
What is saltatory conduction?
The process by which action potentials jump from one node of Ranvier to the next along a myelinated axon.
How does myelination affect action potential speed?
Myelinated axons propagate action potentials much faster than unmyelinated axons due to saltatory conduction.
What role do Schwann cells play in action potential propagation?
Schwann cells create the myelin sheath that insulates the axon and facilitates faster AP propagation.
Why is saltatory conduction faster than continuous conduction?
Because the action potential jumps from node to node, instead of traveling along the entire membrane continuously.
As _______ rushes into the node it creates an _______ force which pushes ions inside the axon toward the next _______
sodium (Na⁺), electrical, node