science test fridy
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Magnetism
the physical phenomenon of attraction or repulsion between objects, caused by the motion of electric charges, like electric currents or spinning electrons, creating magnetic fields that exert forces on other magnetic materials or moving charges
Non Contact Force
a push or pull that acts on an object without physically touching it
Magnet
a piece of iron (or an ore, alloy, or other material) that has its component atoms so ordered that the material exhibits properties of magnetism, such as attracting other iron-containing objects or aligning itself in an external magnetic field
Repel
drive or force (an attack or attacker) back or away
Attract
a force pulls two objects toward each other, causing them to approach or adhere
Iron filings
tiny fragments of iron, often a byproduct of metalworking, used to visualize invisible magnetic fields
Magnetic Field
an invisible force field surrounding magnets, electric currents, or changing electric fields, defined by the influence it exerts on moving electric charges, currents, and magnetic materials, acting as a vector field that maps force direction and strength in space
Magnetic Field lines
imaginary lines used to visually map a magnetic field, showing its direction (where a compass's North pole points) and strength (density of lines), forming continuous closed loops that exit the North pole and enter the South pole, never crossing each other
Compass
an instrument containing a magnetized pointer which shows the direction of magnetic north and bearings from it
Dipolar
having two extremes, most commonly referring to Bipolar Disorder, a mental health condition causing extreme mood swings between emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression)
Earth’s poles
the Geographic Poles (North & South), defined by the planet's rotation axis (Arctic Ocean & Antarctica), and the Magnetic Poles, where the magnetic field points vertically, constantly shifting and located near, but not exactly at, the geographic poles
Magnetosphere
the region surrounding the earth or another astronomical body in which its magnetic field is the predominant effective magnetic field
Electromagnet
temporary magnet created when an electric current flows through a wire, usually coiled around a ferromagnetic core like iron, producing a magnetic field that can be turned on and off
Electric current
the flow or movement of electric charge (like electrons or ions) through a conductor or space, measured as the rate of charge passing a point per unit time, typically in Amperes (A), with a higher ampere number indicating more flow, analogous to more water flowing in a river
What movement can be observed if two magnets:
pulling and pushing force
All magnets are _________blank_____________. They have a north and south magnetic pole.
dipolar
Without a compass, we need iron ________blank__________________ or a computer simulation to help us visualize magnetic fields.
filings
How do the directions of the forces in the field around a magnet change?
____________blank_______________________________________
The direction of magnetic force changes from pushing (repel) with same poles to pulling (attract) with opposite poles, with invisible "field lines" showing the path. They always go out of the north pole and into the south pole, looping around to show the direction, like tiny arrows pointing away from north and towards south.
How would you describe the shape of the magnetic field around the magnet? _________
Continuous, closed loops that emerge from the north pole, curve outwards and around to the south pole.
How is the Earth like a magnet?
An iron inner core and spinning outer core made of liquid iron and nickel creates an invisible magnetic field, like a huge bar magnet, with a north and south pole that guides compasses, protects us from the Sun's harmful rays and helps some migrating animals navigate where they are going.
Draw the 8 compass needle positions based on the magnet below.
The north end of a compass needle points toward the south pole of the magnet.
Magnetic field lines go from N → S outside the magnet.
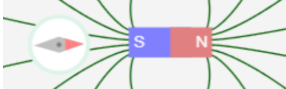
What would a compass needle do next to a south facing magnet? _____________________
Red needle points to the south pole
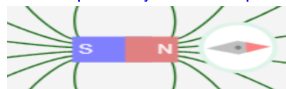
What would a compass needle do next to a north facing magnet? ____________________
Red needle points away from the north pole aligning with the magnetic field
Energy Wave
disturbances that transfer energy through space or a medium (like water, air, or fields) without permanently moving the matter itself
Sound
vibrations that travel through the air or another medium and can be heard when they reach a person's or animal's ear.
Vibrations
rhythmic, oscillatory movements around an equilibrium point
Speaker
a transducer that converts electrical energy into audible sound energy by vibrating a diaphragm, typically using magnetic forces (voice coil moving in a magnetic field) or electrostatic forces, to create pressure waves in the air that we perceive as sound
Electromagnetic Force
a fundamental interaction between electrically charged particles, combining electric and magnetic forces, responsible for everything from atoms to electronics
Crest
the highest point of a surface wave
Trough
the lowest point or valley in a wave (like water or sound), opposite a crest, representing minimum displacement
Wavelength
the distance between two consecutive, identical points on a wave
Amplitude
the maximum displacement or intensity of a wave (like sound, light, or water) from its central, resting (equilibrium) position
Frequency
the number of times a repeating event occurs per unit of time,
Rest line
the equilibrium position or rest position in waves, the undisturbed baseline where a medium settles (like calm water), around which waves oscillate, showing zero displacement
Pitch
the perceived highness or lowness of a sound, directly determined by the frequency of its sound waves
Echolocation
a biological process used by animals like bats and dolphins to locate objects by emitting sounds and interpreting the echoes that bounce back
Volume
the amount of three-dimensional space an object or substance occupies
Compression Wave
a type of longitudinal wave where the particles in the medium move back and forth in the same direction as the wave's travel
Wave speed
the rate at which a wave travels through a medium, defined as the distance a wave crest travels divided by the time it takes
Medium
the substance or material (solid, liquid, gas, or even vacuum) through which energy, waves (like sound or light), or forces travel, acting as a carrier to transfer energy from one point to another
Thunder
the powerful sound produced by the rapid expansion and contraction of super heated air from a lightning flash, creating an acoustic shock wave that we hear as cracks and rumbles as the air vibrates and echoes
Waves transfer (what) through a medium or empty space.
energy
A section of a sound wave where the particles are crowded together is called a
compression
A substance through which a wave can travel is a
medium.
How does a speaker work? Refer to the diagram below.
One of the speaker's magnets is a permanent magnet (meaning that it is always magnetized) and the other is an electromagnet meaning it needs electricity to run through it to work.
When an electrical signal is sent to the speaker, it creates a fluctuating magnetic field that pushes and pulls the coil, (push and pull force) causing it to move back and forth with the attached speaker cone.
The cone vibrates and causes air molecules to collide with each other
transferring energy like a domino effect, until it reaches our ears.
. When you increase the frequency of a transverse wave,
Wavelength will decrease
What can these waves travel through?
Solids Liquids Gases
Explain how bats locate their insect prey with low and high frequency sound waves. Use the word Echolocation.
Using a process called echolocation, bats emit high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) that bounce off objects in the environment, and then interpret the returning echoes to determine the location, size, and shape of its prey.
A (blank) ruler vibrates more slowly, so has a lower frequency. A shorter ruler vibrates more quickly so has a (blank) frequency.
longer, higher