Lectures 2 + 3: Cells of the Nervous System
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Define neurons
Excitable cells that conduct impulses, purpose is to integrate + relay info within a neural circuit.
Define glia
Keeps neurons healthy, is the space around neurons, helps integrate neuronal signals, can proliferate throughout life.
Describe nissl staining
Can distinguish between neurons + glia, nucleolus of all cells are stained, binds to RNA in nucleus + cell body, allows visualisation of variation in size, density + distribution of neurons.
Describe the soma
Aka cell body, perikaryon. Has high density of mitochondria as neurons need lots of ATP for AT of ions etc. Has organelles for proteins synthesis + processing: ribosomes, RER + Golgi apparatus.
Describe silver chromate
Stain that binds to diff parts of neurons, good for seeing diff processes + neurons in detail, only picks out some neurons so can’t see all.
What structures ensures axons are stable?
Microtubules, microfilaments + neurofilaments.
Describe microtubules
Made of lots of monomers of tubular, forms follow tube that runs longitudinally down neurities.
Define axon hillock
Connects cell body to rest of axon.
Defiene axon initial segment
After axon hillock, has specific + high density of certain ion channels as is where APs are generated, impacts neurons ability to send APs along axon.
Define axon collaterals
Branches, thinner than main axon, means signal can move in diff directions, functions of neurons depends on number of collaterals.
Describe some features of axons
No RER/fewer free ribosomes = low protein production.
Range in lengths (<1mm to > 1m) = longer = needs to get from brain to bottom of spinal cord + feet.
1um - 25um diameter.
membrane composition different.
Describe immunohistochemsitry
Uses antibodies, wanted protein has specific structure = makes primary antibody that recognises + binds to wanted protein, then makes secondary antibody that binds to the primary antibody + has fluorescent tag = can see see/make image.
White = colours expressed in the same place = axon initial segment.
Why can’t you put a tag on a primary antibody when doing immunohistochemistry?
Causes background signal + less specific.
Describe the structure of axons
Thicker, can be myelinated, axons with many collaterals have high levels of divergence.
Define divergence
Signal is spread out to lots of different places, is useful if want to coordinate repose over different areas.
Describe the presynaptic terminal
At end of axon, where AP turns to NT. Has many mitochondria as very active, has specialised proteins that can help recycle proteins + NTs and help vesicles bind. Has synaptic vesicles.
Why do some neurons use axoplasmic transport?
Everything the presynaptic terminal needs to function comes from the cell body.
How was fast axoplasmic transport discovered?
By adding radioactive a.a in cell body + tracking them. Saw kinesin ‘walks’ along microtubules + carries vesicles which needs ATP.
Define anterograde transport
Travel from cell body to terminal.
Define retrograde transport
Travel from terminal to cell body.
How can axoplasmic transport be manipulated to visualise cells?
**come back to**
Define axoplasmic transport
Moving of substances down the axon.
Define convergence
Many different outputs can converge onto one neuron = integrates lots of info before creating a response.
What do dendritic branches come together to form?
Dendritic trees.
What happens when dendritic spines don’t develop properly?
Cognitive impairment.
What is a dendritic spine?
Occurs when a dendrite swells out into a spine + where synapse forms.
Why do you classify neurons?
Makes it easier to build hypothesis about types of neurons.
What features are considered when classifying neurons by structure?
Number of neuritis (= no of axons + dendrites), dendritic geometry (size + planes of dendritic trees), connections, axon length (if local or project).
Define unipolar neurite
Only has one process/neurite coming off cell body. Small area for receiving synaptic input = highly specialised function. Reliable relay of info
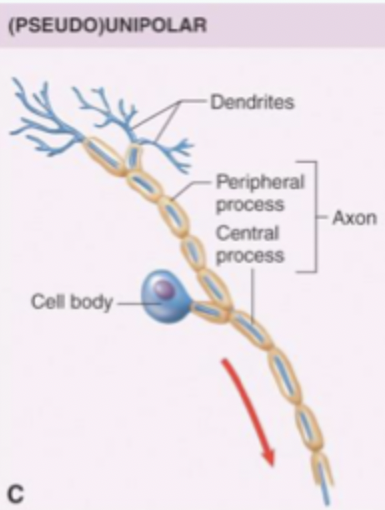
Define pseudounipolar neurite
Neurites comes off then split at one end which converts to a dendrite while the other end stays as an axon. Function is to transmit signal with very little modification. Found in periphery.
Define dorsal root ganglion
Bulge which sits on outside of dorsal aspect that has lots of cell bodies. Axon goes towards dorsal of spinal cord. Part that turns into dendrite goes out towards skin - eventually becomes sensory receptors. Affrent neuron.
Define ganglion
Group of neuronal cell bodies in periphery.
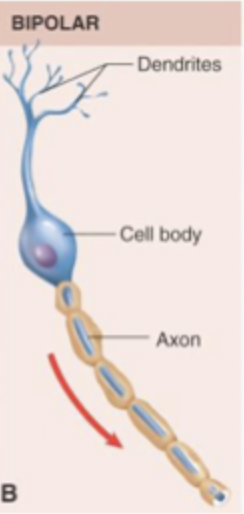
Describe bipolar neurites
Simple type of cells. Small areas for receiving synaptic input = highly specialised function. Reliable relay of info. Not found in many areas. Have cell body with one neurite coming off each side. Has 2 poles (axon + dendritic). Small dendritic tree = not much integration.
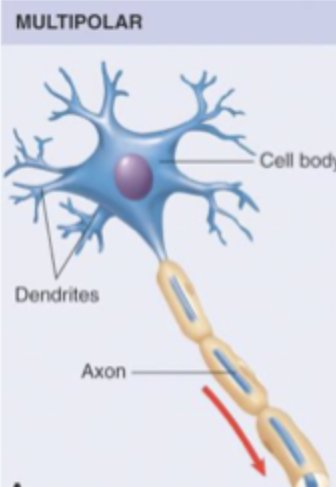
Describe multipolar neurite
Most common type, especially in CNS. One axon + many dendrites coming off cell body = large area for receiving synaptic input = high level of convergence.
Define stellate multipolar neurons
Star shape, dendrites coming off in many directions.
Define pyramidal multipolar neurons
Triangle cell body, have some apical dendrites around cell + long dendrite with smaller ones coming off = can integrate info from many diff areas.
Describe the connections of sensory neurons
Dendrite periphery, input into spinal cord or some straight to brain (e.g cranial nerves), axonal portion goes to CNS.
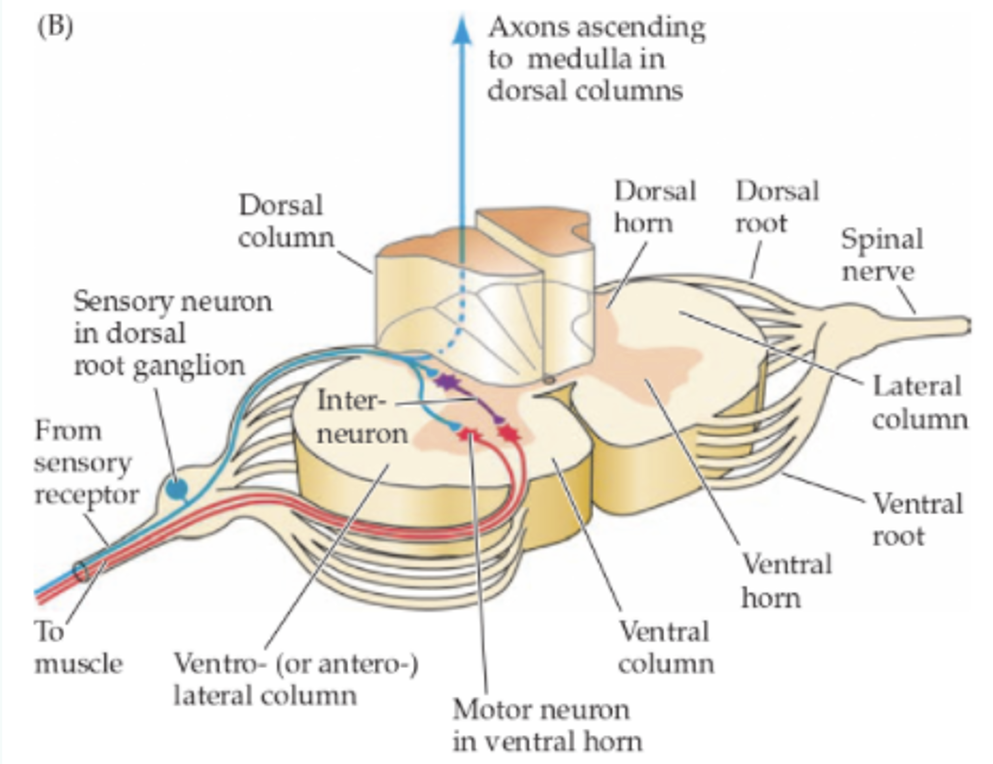
Describe the connections of motor neurons
Cell body in CNS, presynaptic terminal in periphery.
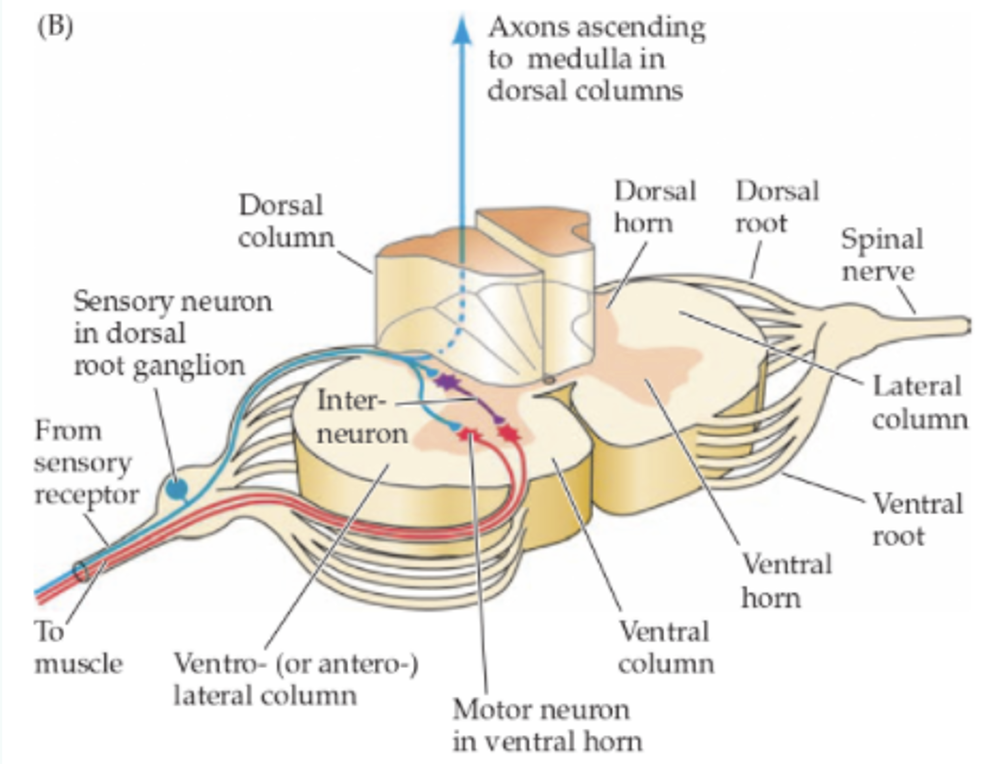
Describe connections of interneurons
Relay/projection interneurons (neurons stay in CNA but moves info between brain regions or to spinal cord). Local interneurons (short axons, process info in local circuits).
Define astrocytes
Control environment surrounding neurons, spatial domains, GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein is unique marker, don’t have define cell bodies,
Define spatial domains
Small cell body with processes going off but don’t tend to overlap each astrocytes as each astrocytes ‘looks after’ areas.
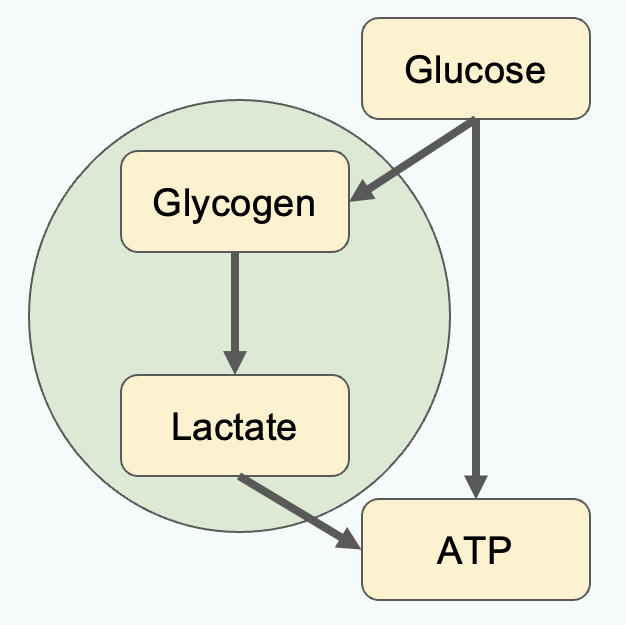
How do astrocytes act as fuel suppliers?
Acts as a glycogen store when excess glucose in blood. Metabolise glycogen + supply lactate. Endfeet can loop around BVs to take up glucose. Detect if glucose concentration of a neutron is low.
Define tripartite synapse
Terminates NT activity. Recycles NTs to presynaptic terminals.
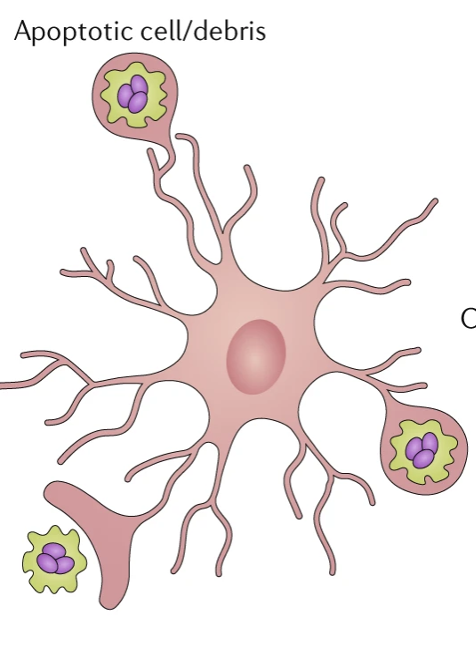
Describe microglia
Macrophages of the CNS. Key role in tissue surveillance + phagocytosis. Can have harmful roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Detects cell = sends out process = engulfs dead cell.
Define oligodendrocytes
Myelinating cells of the CNS, form myelin sheaths. Can myeline multiple axons. Can have 15-30 processes from cell body to myelin sheath.

Define Schwann cells
Glial cells that form myelin sheaths of the PNS. One Schwann cell provides one myelin segment to a single axon.
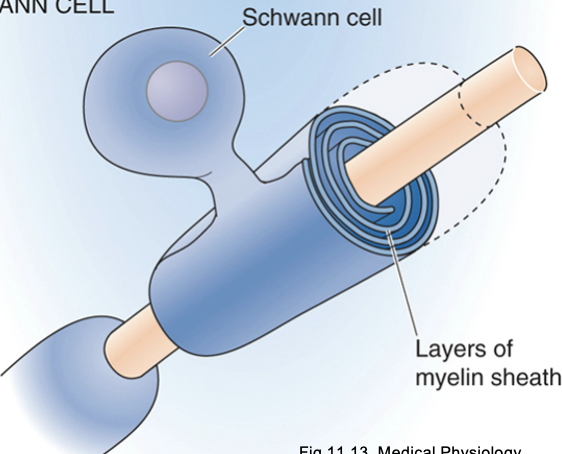
Describe the myelin sheath formation
Process of oligo cytoplasm wraps many times around the axon, cytoplasm is squeezed out of laters by compaction. Maintains contact with glial cells for nourishment.
State the function of myelin
Is insulating + creates nodes of ranvier enabling saltatory conduction.