PAC555 Clinical Applications Quiz 2
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
Two views at __________ degree angles to each other (orthogonal) are typically the best approach to x-ray
90
When imaging a joint, image the bone __________ and __________
Above; Below
The perimeter of normal bone forms a __________, __________ line
Smooth; White
The bone __________ is thicker in some areas than in others
Cortex
The inner portion of the bone is spongy, or __________, and appears in darker grayscale than the __________
Cancellous; Cortex
The cancellous of the bone has a __________-like appearance
Net
The __________ between the cortex and medullary cavity is readily visualized
Junction
The __________ is the shaft of the bone
Diaphysis
The __________ is the cap on either end of the bone
Epiphysis
The __________ is where the diaphysis and epiphysis meet. It is the site of epiphyseal growth plate in children (adds length to bone)
Metaphysis
The __________ is the growth center that allows growth of a bony prominent for insertion of tendons or ligaments
Apophysis
The __________ is the closest bony surface to the joint space, seen well on x-ray
Articular cortex
The __________ lies just below the articular cortex
Subchondral bone
The __________ and __________ are not seen on an x-ray but occupy joint space. These are seen better on MRI
Articular Cartilage; Synovial fluid
True or False: Synovial membranes and joint capsules can be seen on x-ray
False
Bone __________ and __________ can change in response to disease or pathologic stress. This is due to bone being a living organ that undergoes ongoing turnover
Density; Composition
__________ reabsorb, or break down, old bone and reduce bone density
Osteoclasts
__________ produce new bone matrix
Osteoblasts
Diseases that increase bone density produce lesions referred to as __________ or __________ lesions
Blastic; Sclerotic
Diseases that decrease bone density produce lesions referred to as __________ lesions
Osteolytic
What are the two main types of diseases that increase bone density?
-Diffuse
-Focal
What is the main diffuse disease that increases bone density?
Osteoblastic metastases
What are the 3 main focal diseases that decrease bone density?
-Osteoblastic metastases
-Avascular necrosis of bone
-Paget disease of the bone
In osteoblastic metastatic disease, bony metastases are common from carcinomas of the __________ or __________
Prostate; Breast
Osteoblastic metastatic disease produces __________ that can be focal or diffuse
Sclerosis (increased whiteness)
In osteoblastic metastatic disease, there is a loss of the __________ boundary
Corticomedullary
Avascular necrosis of bones occurs when bone loses __________ supply
Blood
Avascular necrosis of bone has necrotic bony tissues that collapses and becomes __________, in turn appearing whited on x-ray
Denser
Avascular necrosis of bone usually is a __________ rather than __________ lesion
Focal; Diffuse
Paget disease of bone occurs mostly in older __________ and is due to chronic __________ infection
Men; Paramyxoviral
Paget disease of bone forms __________ bone though it is more brittle and susceptible to fracture
Denser
Paget disease of bone is often __________ lesions in one or a few bones
Focal
On x-ray, paget disease of bone appears as thickening of the bony cortex, thicken of trabecular pattern in __________ bone, and a gradual increase in size of affected bones
Cancellous
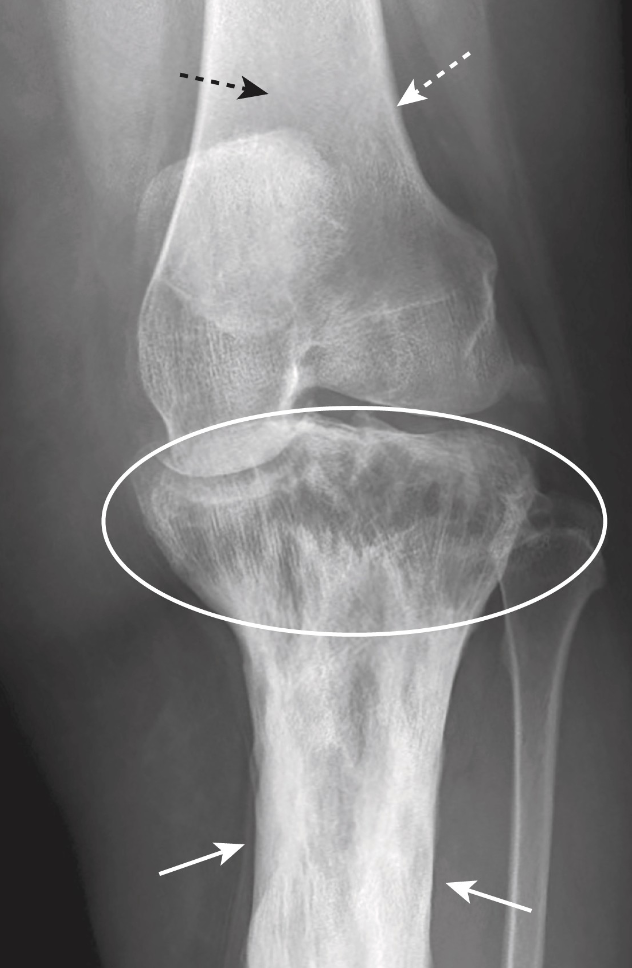
What are the 2 main diffuse diseases that decrease bone density?
-Osteoporosis
-Hyperparathyroidism
What are the 3 main focal diseases that decrease bone density?
-Localized osteolytic metastases
-Multiple myeloma
-Osteomyelitis
What are the 7 main risk factors for osteoporosis?
-Postmenopausal state
-Advanced age
-Steroid medications
-Cushing disease
-Estrogen deficiency
-Inadequate physical activity
-Alcoholism
X-ray has poor sensitivity to diagnose osteoporosis, so individuals must have __________ loss of bone mass before it is recognizable
50%
Osteoporosis is best diagnosed by __________
DEXA scans
In osteoporosis, there is decreased bone density, thinning of __________, decreased visible trabecular, and increased contrast between cortex and __________
Cortex; Medullary cavity
The increased contrast between the cortex and medullary cavity in osteoporosis is due to __________ density of medullary cavity, not __________ density of cortex
Decreased; Increased
In hyperparathyroidism, the parathyroid hormone stimulates __________ activity that removes calcium from bone to deposit into the __________
Osteoclastic; Bloodstream
In hyperparathyroidism, there is an overall __________ in bone density
Decrease
In hyperparathyroidism, there is __________ bone resorption most common on the radial side of middle phalanges of index and middle fingers
Subperiosteal
In hyperparathyroidism, there is erosion of distal __________ and lytic lesions in __________ bones
Clavicle; Long
In hyperparathyroidism, lytic lesions are often called __________
Brown tumors
Brown tumors are named for the high content of __________ pigment which gives the tumors a brown color
Hemosiderin
For lytic lesions of hyperparathyroidism to occur, cortical bone is replaced with __________ and blood
Fibrous tissue
In osteolytic metastatic disease, the __________ is almost always involved
Medullary cavity
In osteolytic metastatic disease, lesions are __________ and __________ shaped
Lucent; Irregularly
What are the 4 commonly involved malignancies in osteolytic metastatic disease?
-Some lung cancers
-Ewing’s sarcoma
-Myeloma
-Leukemia
In myeloma, there is malignancy of __________ cells affects calcium metabolism and bone density
Plasma
X-ray is more sensitive than __________ for detecting myeloma lesions
Radionuclide bone scan
What are the 2 characteristic radiographic findings of myeloma?
-Diffuse and severe osteoporosis
-Multiple, small, “punched out” lesions
In osteomyelitis there is focal destruction of bone due to infection, usually by __________
Staphylococcus aureus
What are the 3 main radiographic findings of osteomyelitis?
-Focal cortical bone destruction
-Soft-tissue swelling
-Focal osteoporosis
Osteomyelitis is detected up to 10 days earlier by __________ or nuclear medicine than by x-ray
MRI
What are the 3 broad categories of radiographic findings in arthritis?
-Hypertrophic arthritis
-Erosive arthritis
-Infectious arthritis
Hypertrophic arthritis is characterized by bone __________ at the affected site
Formation
Hypertrophic arthritic bone formation may either be __________ or __________
Subchondral sclerosis; Osteophyte formation
__________ refers to new bone formation within the parent bone. It is common in hypertrophic arthritis
Subchondral sclerosis
__________ refers to new bone formation that protrudes from the parent bone. It is common in hypertrophic arthritis
Osteophyte formation
What are the 4 main radiographic features of hypertrophic arthritis; osteoarthritis?
-Subchondral sclerosis
-Subchondral cysts
-Osteophyte formation at joint margin
-Narrowed joint space
__________ results from chronic impaction and bone necrosis
Subchondral cysts
Erosive arthritis is characterized by small, irregularly shaped __________ lesions around the joint space
Lytic
The prototype disease of hypertrophic arthritis is __________
Osteoarthritis
The prototype disease of erosive arthritis is __________
Gout
In erosive arthritis, __________ occurs due to deposition of urate crystals in the joint
Arthropathy
What are the 3 radiographic features erosive arthritis?
-Sharp erosions adjacent to joints
-Soft tissue nodules (top) containing irate crystals may be seen in severe cases
-Joint space narrowing usually not seen until late in course of disease
Sharp erosions adjacent to the joints in erosive arthritis is said to resemble __________
Rat bites
Soft tissue nodules of erosive arthritis that contain urate crystal are called __________
Tophi
Infectious arthritis is characterized by joint swelling, __________, and destruction of the __________
Osteopenia; Articular cortex
Infectious arthritis is classified as either __________ or __________
Pyogenic; Nonpyogenic
Pyogenic infectious arthritis is caused by __________ and __________ organisms
Staphylococcal; Gonococcal
Nonpyogenic infectious arthritis is caused by __________
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
X-ray has low-sensitivity for septic arthritis and osteomyelitis. A diagnosis is usually made with a combination of __________ and joint __________
MRI; aspiration
What are the 2 radiographic features of acute fractures?
-Fracture lines
-Abrupt discontinuity of bony cortex
__________ are areas of increased lucency (appear blacker) compared to normal bone
Fracture lines
Naturally occurring lines in bone tend to follow an irregular, meandering course when they change __________
Direction
Fracture lines are generally __________, but when they change direction, they do so abruptly
Straight
__________ are naturally occurring anatomic variants that can mimic a fracture, but are not pathological
Fracture imposters
What are the 3 fracture imposters?
-Sesamoid bones
-Accessory ossicles
-Apophyses
__________ are bony inclusions that form in tendon as it passes over a joint. These are usually bilateral
Sesamoid bones
The most common sesamoid bone is the __________. Others include the thumb, great toe, and posterolateral knee
Patella
__________ are epiphyseal or apophyseal ossification centers that do not fuse with parent bone
Accessory ossicles
Accessory ossicles are most common in the __________ and are usually bilaterally symmetric
Foot
__________ are growth centers that add prominences to a bone where tendons or ligaments insert. These are usually bilaterally symmetric
Apophyses
Dislocations and subluxations occur only at __________
Joints
__________ occur when bones that form the joint are no longer in apposition
Dislocation
__________ occur when bones that form the joint are still in partial contact with each other
Subluxation
What are the 4 things fractures are usually described according to?
-Degree of fracture (complete vs incomplete)
-Number of bony fragments
-Fracture line direction
-Relationship of fragments
__________ fractures fully break the bony cortex, separating the fracture bone into two pieces
Complete
__________ fractures only break a part of the bony cortex
Incomplete
Incomplete fractures usually occur in incompletely __________ bone or in bone that is weaker due to disease
Calcified
Incomplete fractures are more common in __________
Children
What are the 2 types of incomplete fractures?
-Greenstick fracture
-Torus (or buckle) fracture
Greenstick fractures occur most commonly in __________
Children
__________ fractures appear as a bulge that disrupts the smooth outer contour of the bony cortex. This occurs due to __________ of the bony cortex
Torus (buckle); Compression
__________ fractures divide a bone into only two fragments
Simple
__________ fractures divide a single bone in 3 or more fragments
Comminuted
What are the two types of comminuted fractures?
-Segmental fracture
-Butterfly fragment