Rating Charts and Cooling Curves (9/20/2023)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
99% of the kinetic energy of electrons is converted to ___ during x-ray production
heat
Amount of heat given off is expressed in ___
Heat Units (HU)
Number of HU produced depends on ___ and ___
the type of generator and the exposure factors used
Explain alternating currents (AC)
current that alternates between positive and negative kv
Why are single phase alternation currents not ideal?
the negative kv is not useful for imaging
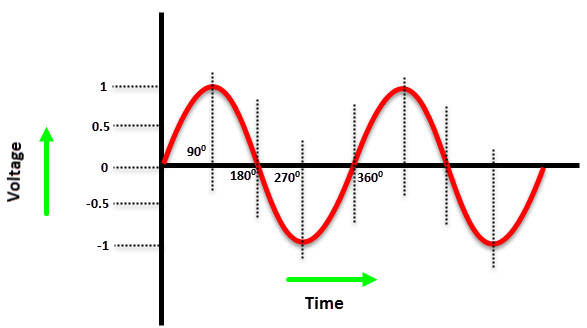
What type of wave/current does the image depict?
single phase alternating current
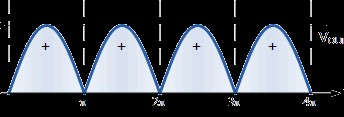
What type of wave/current does the image depict?
single phase rectified current
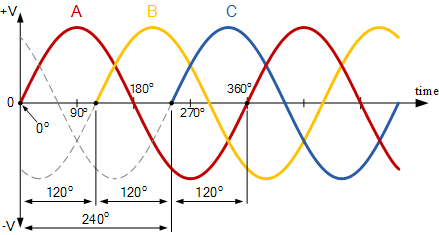
What type of wave/current does the image depict?
3 phase 6 pulse wave form
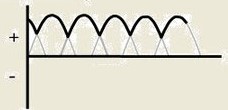
What type of wave/current does the image depict?
3 phase 12 pulse current
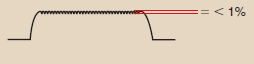
What type of wave/current does the image depict?
high frequency wave form
What type of wave/current is used in all modern equipment? Why?
high frequency wave form; has the least ripple and the highest energy
Define ripple
the fluctuation in voltage output (each bump on the graph)
What is heat load capacity?
the amount of heat that a tube can withstand without damaging the tube components
Heat is produced according to:
technical factors selected
kVp, mA, time
focal spot size
generator type
more powerful generator produces x-rays more efficiently
more powerful generator creates 1.4x more HU
What determines the “quality” of x-rays?
What determines the “quantity” of x-rays?
quality: kVp
quantity: mAs
Generator factor indicates ___
heat production in comparison to the single phase generator
The more efficient the generator, the ___ the HU produced during x-ray production
higher
What is the formula for calculating heat units?
HU = (kVp) (mA) (time in seconds) (generator factor)
What is the generator factor for a single phase generator?
1.00
What is the generator factor for a 3 phase 6 pulse generator?
1.35
What is the generator factor for a 3 phase 12 pulse generator?
1.41
What is the generator factor for a high frequency generator?
1.45
What are the 3 types of rating charts?
tube rating charts
anode cooling charts
housing cooling charts (not used as much)
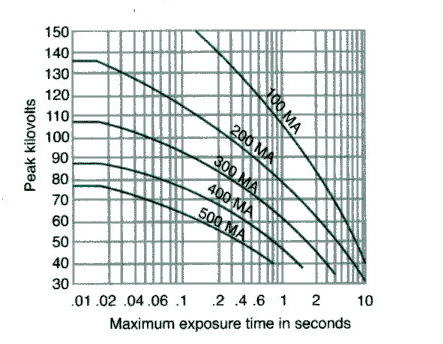
What type of rating chart is shown in the image?
tube rating chart
What is the purpose of a tube rating chart?
determines the technical factors that can be used without overloading tube
What do the vertical axis, horizontal axis, and curved lines represent in a tube rating chart?
vertical axis: kVp
horizontal axis: time (s)
curved lines: mA
How are tube rating charts read?
find the intersection of kVp and time on the graph; any combination of factors at or under the curve is safe
What do the vertical axis, horizontal axis, and curved lines represent in an anode cooling chart?
vertical axis: total heat capacity (HU)
horizontal axis: time (minutes)
curved lines: starting point HU to end time of complete cooling
What is the purpose of an anode cooling chart?
calculates the time it takes for the anode to cool from a given exposure OR the time it will take the anode to cool enough to make an additional exposure
What are some ways you can extend tube life?
warm up anode
depress rotor in one motion
avoid excessive HU production
use lower mA when possible
avoid repeats
handle tube gently
do not move tube when energized
do not use tube if you hear a loud rotor noise