GCSE biology - topic 2 (B1, B2, B3)
1/207
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
whats an example of a cell (plant and animal)?
phloem cell, red blood cells
what is an organ system?
group of organs that work together to perform specific functions. The way in which one organ functions depends on other organs in the system
whats an example of an organism (plant and animal)?
lily, human
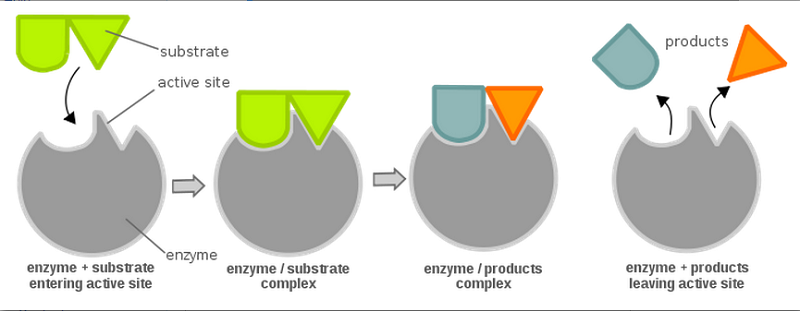
what are enzymes in terms of biological makeup?
large proteins, made up of chains of amino acids. These fold into unique shapes enzymes need to do their jobs
what is enzymes optimal pH (usually, some exceptions, eg. pepsin)
neutral 7 (pepsin-2)
how do you do the practical of investigating the effect of pH on enzyme activity? (8)
put a drop of iodine on each well of a spotting tile
put a beaker of water over a bunsen burner until at 35°
add 1cm³ of amalyse solution and 1cm³ of a buffer solution to a boiling tube.
put the tube into a beaker of water and wait 5 mins.
add 5cm³ of starch solution to the boiling tube.
mix immediately and start a stop clock.
use continuous sampling (add a drop of the solution to the iodine solution every 30s until it stops turning blue/black and remains orange(this means no starch is present))
repeat with different pH values to see how pH affects time.
what are starch, proteins, and fats?
big molecules (too big to pass through the walls of the digestive system, so digestive enzymes break the big molecules into smaller ones (eg. sugars, amino acids, fatty acids), which can pass through easier, allowing them to be absorbed into the bloodstream)
where is bile produced and stored?
produced in the liver, stored in the gall bladder before released into the small intestine
what does bile emulsify
fat ( it breaks the fat into tiny droplets), which gives a bigger surface area for the enzyme lipase to work on - this makes digestion faster.
what does the salivary glands do in the digestive system?
produces amylase enzymes in the saliva
what does the liver do in the digestive system?
produces bile
what does the large intestine do in the digestive system?
where excess water is absorbed from food
what does the small intestine do in the digestive system? (2)
produces protease, amylase, and lipase enzymes to complete digestion
where digested food is absorbed out of the digestive system into the blood
what does the stomach do in the digestive system? (3)
it pummels the food with its muscular walls
it produces pepsin
it produces hydrochloric acid to kill bacteria and to give the right pH for pepsin to work
what is pepsin
a protease enzyme
how do you do the biuret test?
prepare a food sample and add to test tube. add 2cm³ of biuret solution and shake gently
what will happen if your food test does have lipids?
the mixture will separate into 2 layers, with the top layer bright red.
what are the lungs like?
big pink sponges which are protected by the ribcage, while being surrounded by pleural membranes
what happens in the second circulatory system?
the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood around all the other organs of the body. the blood gives up its oxygen at the body cells and the deoxygenated blood returns to the heart to be pumped out to the lungs again
how does the heart use four chambers to pump blood around? (5)
blood flows into 2 atria from the vena cava and the pulmonary vein.
the atria contract, pushing the blood into the ventricles.
the ventricles contract, forcing the blood into pulmonary artery, and the aorta, and out of the heart.
the blood then flows to the organs through arteries and returns through veins.
the atria fill again and the cycle starts over
what branch off the aorta?
coronary arteries which surround the heart, making sure the heart gets all the oxygenated blood it needs
what are the artery adaptions? 4
the heart pumps the blood out at high pressure so the walls are strong and elastic
the walls are thick compared to the size of the lumen
they contain thick layers of muscle to make them strong
they have elastic fibres to allow them to stretch and spring back
what are the capillary adaptions? 4
arteries branch into capillaries which are really tiny. they carry the blood really close to every cell in the body to exchange substances with them
they have permeable walls, so substances can diffuse in and out
they supply food and oxygen, and take away wastes like CO2
their walls are usually only one cell thick, this increases the rate of diffusion by decreasing the distance over which it occurs
what are the vein adaptions? 3
the blood is at the lowest pressure in the veins so the walls dont need to be as thick as artery walls
they have a bigger lumen than arteries to help the blood flow despite the lower pressure
they also have valves to help keep the blood flowing in the right direction
what is the shape of red blood cells?
a biconcave disc (like contact lenses), which gives a large SA for absorbing oxygen. they dont have a nucleus, which allows more room to carry oxygen