4.6 - Hardware & Software
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is hardware?
the physical components of the computer system
What is software?
program code - sequences of instructions which are executed in order to perform a task
What are some examples of hardware?
monitor, processor, graphics card, webcam, printer
What are some examples of software?
word processor, web browser, image editor, video editor
What are the categories of software?
application software and system software
What is application software?
programs that complete a specific task for the user
What are some examples of application software?
word processors, web browsers, spreadsheet software
What is system software?
it operates, controls and maintains the computer and its components
What does system software include?
the operating system, utility programs, library programs, translators
What is an operating system?
it allows its user to control the computer with ease by providing what’s called a virtual machine and manages and controls access to the computer’s resources, including memory management, processor scheduling and handling interrupts
What are utility programs?
they are used for completing housekeeping tasks in a computer system, such as data backup, defragmenting hard drives, data compression and encryption
What are library programs?
they contain useful functions that are frequently used by a program
Why were high level languages developed?
to make the job for the programmer easier
What are the two categories of low level language?
assembly language and machine code
What is machine code?
it uses 0s and 1s to represent instructions
What are the disadvantages of machine code?
it is very long and extremely difficult for humans to understand, so the programs are prone to errors and difficult to debug
What is machine code useful for?
embedded systems and real-time applications where speed of execution is paramount, as there is no need to translate machine code
What is assembly language?
a simpler way of writing machine code with mnemonics such as ADD or MOV in place of binary instructions of machine code
What are the advantages of assembly language?
more compact and less prone to error than machine code
What are some examples of high level languages?
fortran, pascal, C#, python, java
What are the advantages of high level languages?
they are not platform specific, it is much easier for humans to learn and understand, easier to debug
What are the disadvantages of high level languages?
they need to be translated into machine code by a compiler or interpreter
What makes high level languages easier to debug than low level?
named variables, indentation, commenting, english instructions, mathematical symbols
What is an imperative high level language?
in a similar way to low-level languages, they are formed from instructions that specify how the computer should complete a task, rather than what a computer should do
What are translators?
they translate assembly and high level language into machine code to be executed by the processor
What does an assembler do?
translates assembly language into machine code
What is the relationship between assembly language and machine code?
one to one as one line of assembly language can be represented by one line of machine code
What does a compiler do?
translates high level language into machine code - checks for errors and then translates entire program at once
Which translators are platform specific?
assemblers and compilers
What does an interpreter do?
translates high-level languages into machine code and executes the code line-by-line, checking for errors as they go
What is source code?
programs that are written in high level languages that need to be translated - the input to a translator
What is object code?
executable machine code - the output produced from source code
What are the differences between compilers and interpreters?
compilers check for errors before translating all source code at once - interpreters check for errors, translate and execute line by line; there is no need for source code or compiler to be present when the translated code is executed - but both the source code and the interpreter must be present when the program is executed; compilers protect the source code from extraction - interpreters offer little protection of source code
Why is an intermediate language produced as the final output by some compilers?
it allows for platform independence as then a virtual machine is used to execute the bytecode on different processors
What is an example of an intermediate language?
bytecode
Why is it useful to use an intermediate language?
it only needs to be translated once and can be executed by a variety of processors as they each have their own virtual machine
What are logic circuits made up of?
many logic gates
What is the symbol for a NOT gate?
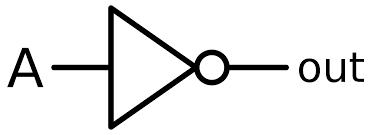
What is the symbol for an AND gate?
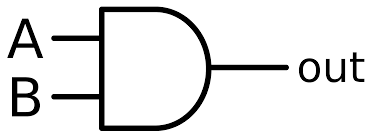
What is the symbol for an OR gate?
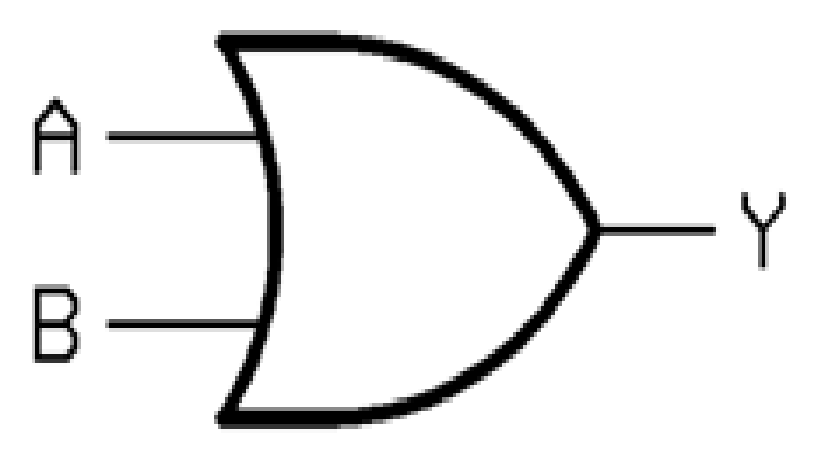
What is the symbol for an XOR gate?
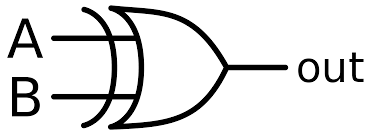
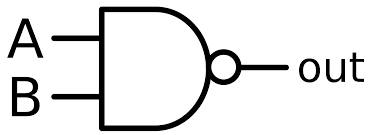
What is the symbol for a NAND gate?
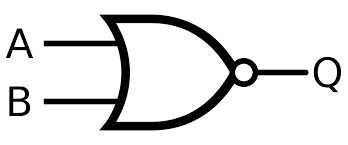
What is the symbol for a NOR gate?
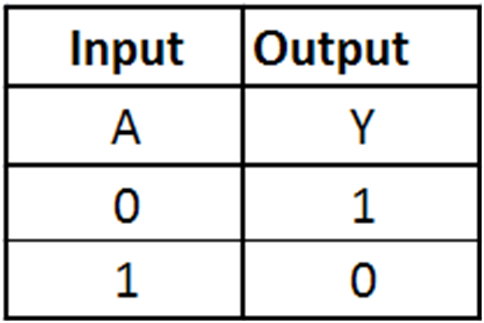
What is the truth table for a NOT gate?
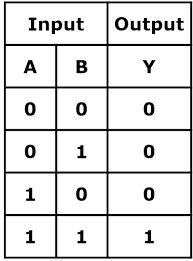
What is the truth table for an AND gate?
What is the truth table for an OR gate?
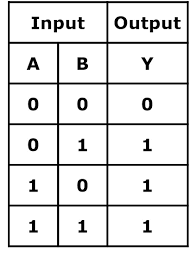
What is the truth table for an XOR gate?
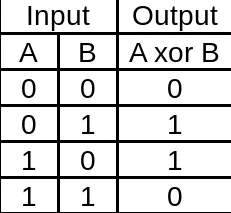
What is the truth table for a NAND gate?
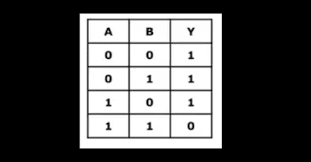
What is the truth table for a NOR gate?
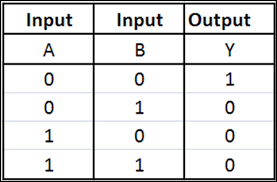
What is an adder?
a logic circuit that can be used to add Boolean values together
What is a half adder?
a logic circuit that adds two numbers using two inputs, two outputs and two logic gates
What are the outputs of a half adder?
sum, which adds the two binary values and carry, which is used for overflow
What does a half adder look like?
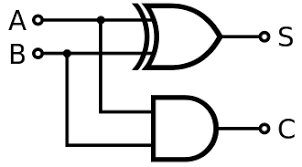
What is a full adder?
a logic circuit that adds numbers which has three inputs and two outputs, enabling it to input two Boolean values and a carry bit from a previous, less significant operation
What are the inputs of a full adder?
A, B and C (carry in), the carry bit from the previous operation
What are the outputs of a full adder?
sum, which adds the two binary values and carry, which is used for overflow
What does a full adder look like?
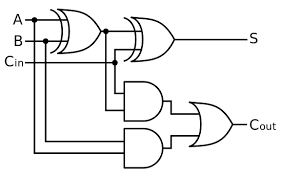
What is an edge-triggered D-type flip-flop?
a logic circuit which can be used as a memory unit for storing the value of a single bit
What are the inputs of an edge-triggered D-type flip-flop?
there are two - one for data and another for a clock signal
What is a clock signal?
a signal generated by the computer and alternates between 0 and 1 at a set frequency
What is the output of an edge-triggered D-type flip-flop?
the value of the stored bit - the value of the data input with each change of the clock signal
What represents a NOT in boolean algebra?
A - a line over the top of the letter
What represents an AND in boolean algebra?
AB - a dot in the middle of the letters or AB - the product of these two letters
What represents an OR in boolean algebra?
A+B - addition symbol
What is the order of precedence in boolean algebra?
brackets, NOT, AND, OR
What are De Morgan’s laws?
NOT(A+B)=A⁻•B⁻ - break the bar and change the sign
What is the distributive law in boolean algebra?
A • (B + C) = A • B + A • C , equivalent to expanding the brackets or factorisation in normal algebra
What is the commutative law in boolean algebra?
variables can be rearranged without affecting the logic of the statement, e.g. X ⋅ Y = Y ⋅ X
What is the associative law in boolean algebra?
allows for the removal and rearrangement of the brackets when all signs are the same e.g. X ⋅ (Y ⋅ Z) = (X ⋅ Y) ⋅ Z and X + (Y + Z) = (X + Y) + Z
What are the absorption rules in boolean algebra?
X + (X ⋅ Y) = X and X ⋅ (X + Y) = X