OTM IV - Visual Fields
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Visual field
portion of space from which light can enter the eye, reach the retina, stimulate the photoreceptors, and evoke a sensation of light.
Perimetry
systematic measurement of the visual field allowing for detection and quantification of damage to the visual field. Also allows for monitoring change to the visual field over time. Can be automated, manual, static, or kinetic
Static perimetry
perimetry where the location, size, and duration of the stimulus is kept constant and the luminance is gradually increased until the target is seen. Is a measurement of threshold values.
Kinetic perimetry
perimetry where a moving stimulus is present from a non-seeing area to a seeing area and this is repeated at various points around the visual field. Is a measurement of isopters.
-Detection of pathology
-Track progression of disease or medication use affecting the visual field
-Determining efficacy of treatment
-Visual ability testing for driving restrictions
four reasons (not all inclusive) for visual field testing
60
superior visual field
60
nasal visual field
75
inferior visual field
100
temporal visual field
150
total monocular visual field
15, temporally, 5, 7, inferiorly
Physiological blind spot is located ____ degrees ______, and is ____ degrees horizontally and _____ degrees vertically in dimension. It is also displaced slightly _____
Decibel (dB)
the unit for stimulus intensity during visual field testing. It is a logarithmic unit where the lower the number, the brighter the stimulus, where zero is the maximum brightness.
Visual sensitivity
the minimum perceivable brightness
Visual threshold
the minimum quantity of stimulus needed for detection
Isopter
line connecting all the points in the visual field having the same threshold for a given stimulus representing the boundary within which a stimulus can be seen. Are used to construct the hill of vision.
Scotoma
a visual field defect surrounded by a normal visual field
Relative scotoma
scotoma where objects of low luminance cannot be seen, but bright ones can
Absolute scotoma
scotoma where nothing can be seen at all within that area
Depression
area of reduced sensitivity without a surrounding area of normal sensitivity. Patient is not seeing well across their visual field. I.e.) cataract, uncorrected refractive error
33, 1 , 10, 20
Amsler grid testing must be performed at ___ cm in order for each grid square to subtend _____ degree on the retina, ____ degrees on each side of the fixation point, and ____ degrees total
Tangent screen
a manual, kinetic visual field test that is performed monocularly with dim room lightly. A patient sits 1 meter away from a black felt screen and a pin is placed when they indicate a stimulus held up by the examiner is seen.
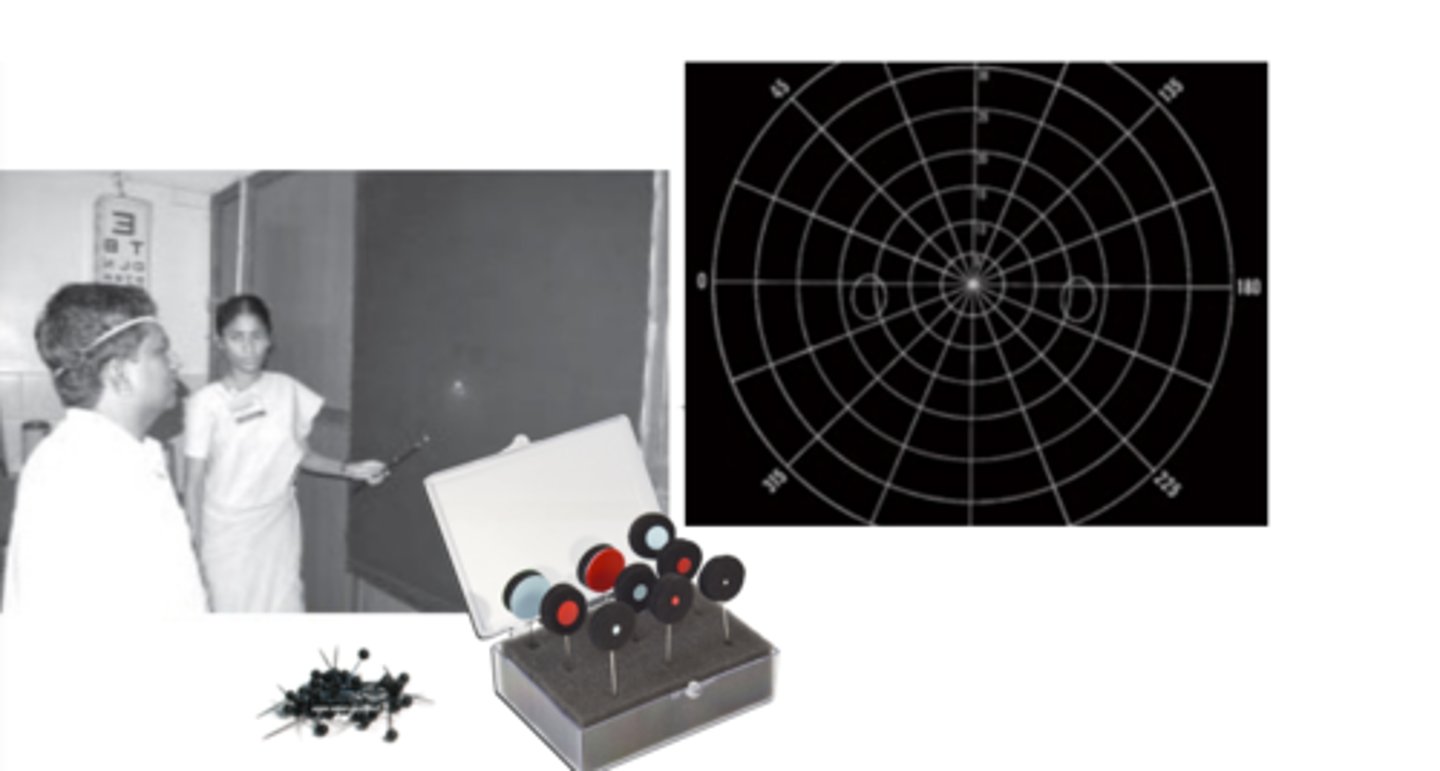

non-biological (hysterical)
Detection of malingering or non-organic visual field loss can be achieved by comparing the visual fields at 1 versus 2 meters. If the visual field remains the same at both distances, this represents a _____ visual field defect.
biological
Detection of malingering or non-organic visual field loss can be achieved by comparing the visual fields at 1 versus 2 meters. If the visual field becomes larger at 2 meters, this represents a ______ visual field defect.
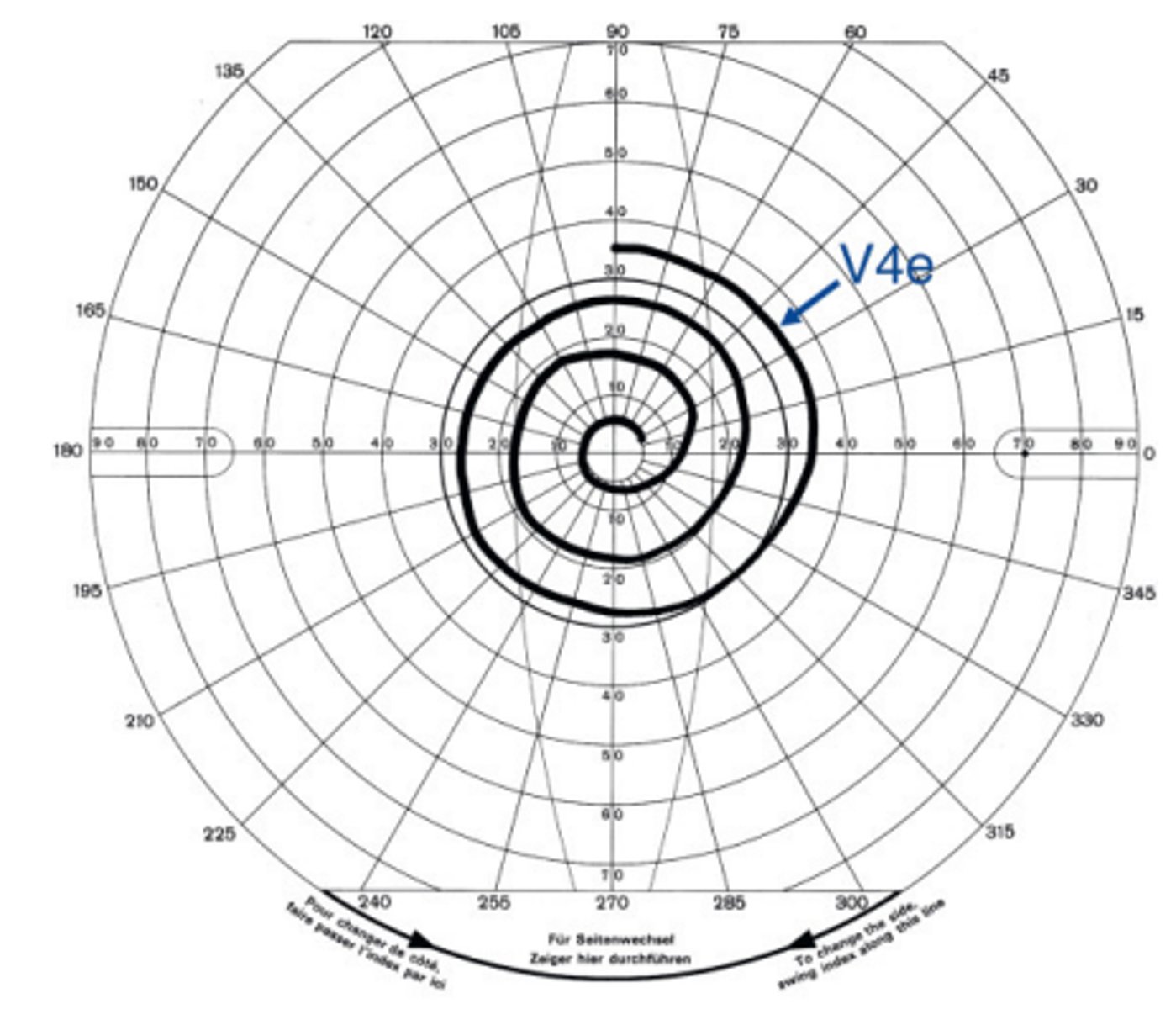
Goldmann perimetry
a manual kinetic perimetry test where a patient is presented a series of targets against a white dome and the isopters are plotted depending on the patient's responses. Requires a trained perimetrist to accurately measure the visual field.
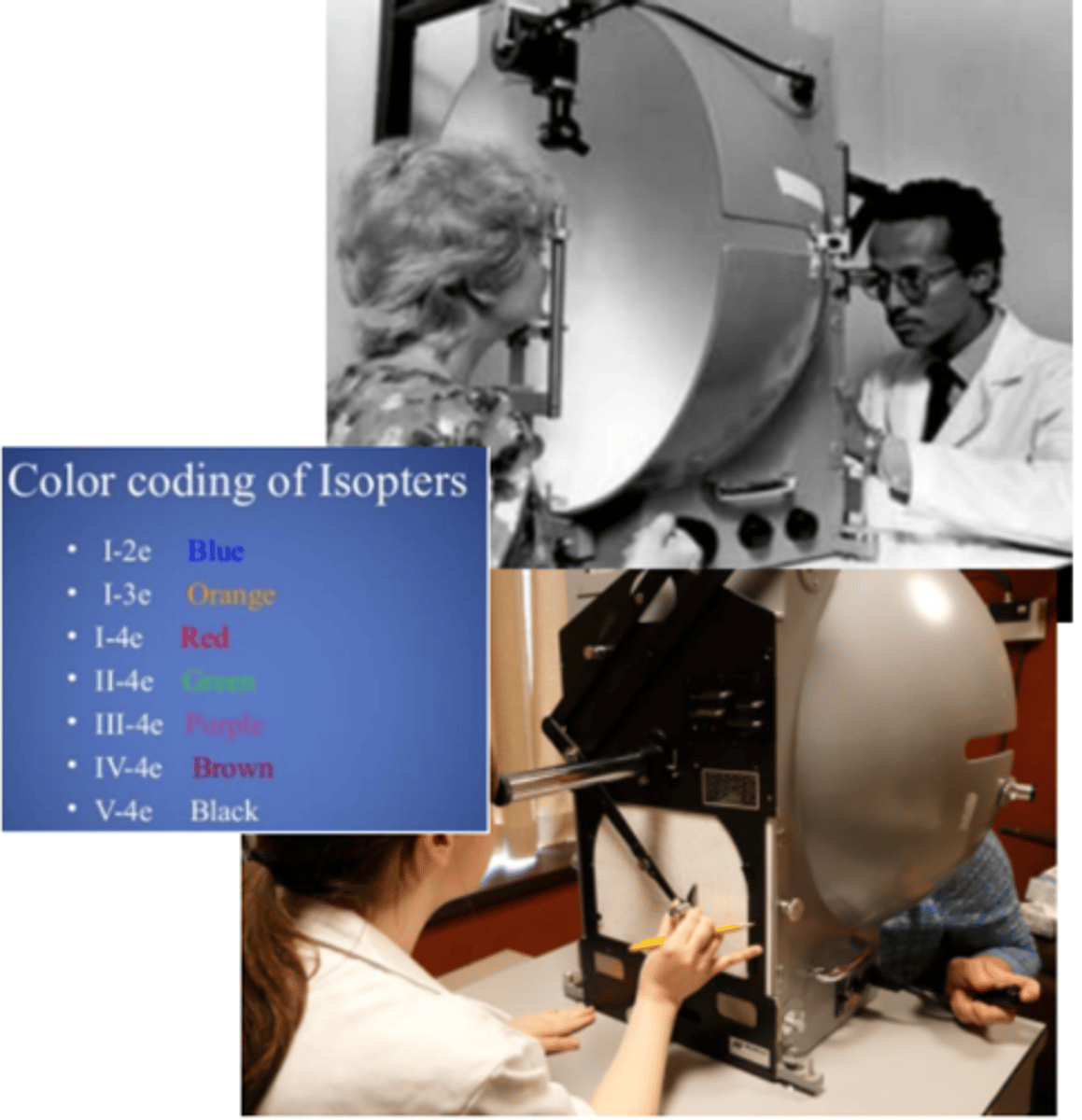
roman numerals
In Goldmann perimetry, target Size is represented with...
numbers
In Goldmann perimetry, target Luminance is represented with...
letters a-e
In Goldmann perimetry, target Filter is represented with...
nasally, horizontal, vertical
Goldmann perimetry is especially useful for specific visual field testing that may reveal particular disease processes. For example, glaucoma will result in decreased visual field sensitivity _____ and tends to have a pattern along the _____ meridian. Whereas, neurological lesions tend to have patterns along the _____ meridian.
non-biological (hysterical)
If Goldmann perimetry results in a spiral shaped visual field, this suggests a ______ visual field defect
Automated Visual Field Testing (standard automated perimetry SAP)
the standard of perimetry testing. Allows for enhanced detection of visual field loss with higher reliability when compared to manual perimetry. Uses a static target with threshold sensitivity presented in decibels. I.e.) Humphrey, octopus
Humphrey visual field
a threshold static automated perimeter which utilizes standardized testing algorithms depending on the test indication.
Glaucoma, neurological defects, retinal disease
three conditions commonly tested and monitored by Humphrey visual field testing.
33 cm
working distance of Humphrey visual field testing. Is used to calculate the trial lens used to correct the patient's refractive error during testing. This is important, as 1D of blur correlates to 1dB of depression of the hill of vision.
200 ms
time that the stimulus is presented during Humphrey visual field testing. Is short enough so that the patient's eye movements are not fast enough to track the target.
5-7, III 0.43, V 1.73
The size of the stimulus presented on Humphrey visual field testing is smaller than the standard blind spot being <___ degrees. The standard, most commonly used size is size ____ degrees. In advanced glaucoma, a larger size ____ degree target is used.
31.5 Abs
standard background illumination of the Humphrey visual field. Is similar to photopic lighting conditions, as we are more interested in cone function rather than rods. Outside room illumination must be dim.
Suprathreshold
Humphrey VF algorithm that is used as a screening tool using a stimulus 4-6 dB brighter than the expected threshold. Is quick and easy, and records whether a location is normal or abnormal and therefore is not sensitivity to early field loss. I.e.) testing for visual function of drivers, visual disability testing for insurance purposes, retinitis pigmentosa, neurological loss, blepharoptosis testing
Esterman test
suprathreshold Humphrey VF algorithm using habitual distance glasses and tested binocularly to imitate driving conditions. Measures up to 150 degrees, but only 120 degrees is required for driving
120 point
suprathreshold Humphrey VF algorithm which is performed monocularly and is used for neurological and disability screening
SITA standard
threshold Humphrey VF algorithm using the 4-2 staircase method, but takes half the time of full threshold testing because it begins by presenting stimuli that are closer to threshold to start. Visual field defects will be slightly shallower than full threhold test results. Is specifically designed for glaucoma.
30-2
Humphrey VF strategy testing the central 30 degrees of the visual field in 76 locations that are placed 6 degrees apart. It tests 2 points on either side of the horizontal axis, and on either side of the vertical axis. Is good for testing points that are further out in the visual field. I.e.) neurological defects
24-2
Humphrey VF strategy testing the central 24 degrees of the visual field in 54 locations that are placed 6 degrees apart. It tests 2 points on either side of the horizontal axis, and on either side of the vertical axis. Commonly used in glaucoma.
24-2C
Humphrey VF strategy that has the speed of the SITA faster with an additional 10 points incorporated into the 24-2 grid which follow the nerve fiber layer pattern.
10-2
Humphrey VF strategy testing the central 10 degrees of the visual field in 68 locations. Allows for detailed analysis of the macula. I.e.) additional glaucoma testing for analysis of central ganglion cells or testing in progressed glaucoma patients having only central vision remaining, Plaquenil use
manually observing
Fixation can be monitored by ____ the patient's eye movements
blind spot
Fixation is monitored by locating the ____, if stimuli are presented to this area and are seen this indicates a fixation loss
gaze tracker
Fixation can be monitored using a ____ which measures gaze direction each time a stimulus is presented with precision of about 1 degree.
Fixation loss
occurs when a patient responds to a stimulus presented in the blind spot. Should be less than or equal to 20%. Can be affected by advanced glaucoma or large blind spots.
False positive
Occurs when a patient pushes the button when no stimulus was presented. Should be less than or equal to 30%
False negative
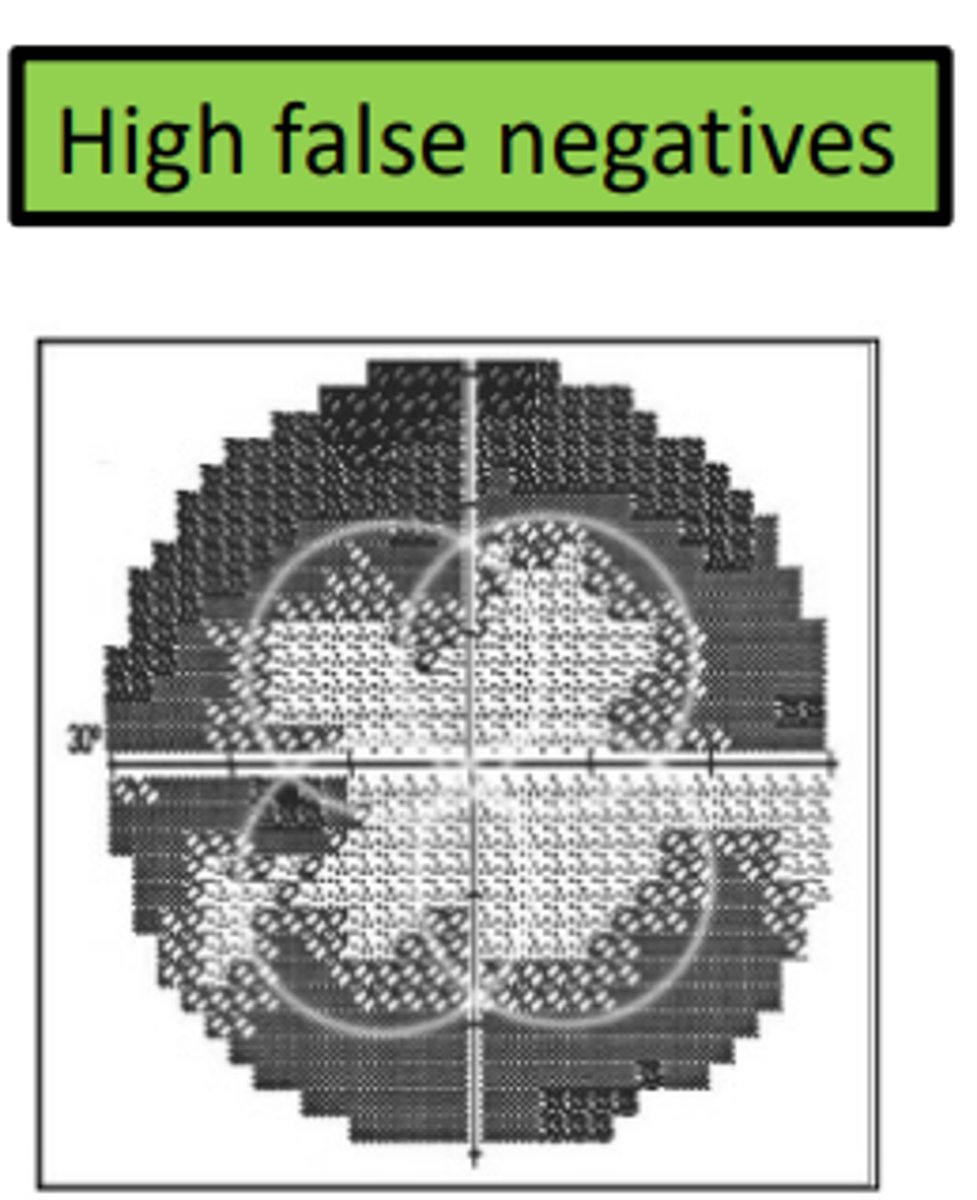
occurs when a patient fails to push the button for a stimulus that should be visible. Is flagged if the stimulus is 9dB, 8x brighter than threshold. Can be affected by true visual field defects, so does not necessarily indicate an unreliable test. Should be less than or equal to 30%.
2, 3
Taking a visual field test for the first time is a learning curve for the patient. The patient will perform better with further testing, peaking after about ___ fields and this is therefore the standard for the establishment of a baseline. Should be less this ___ months apart to eliminate variation caused by disease processes.
ring
If the trial lens is too far from the eye, it will produce a visual field artifact in the shape of a...
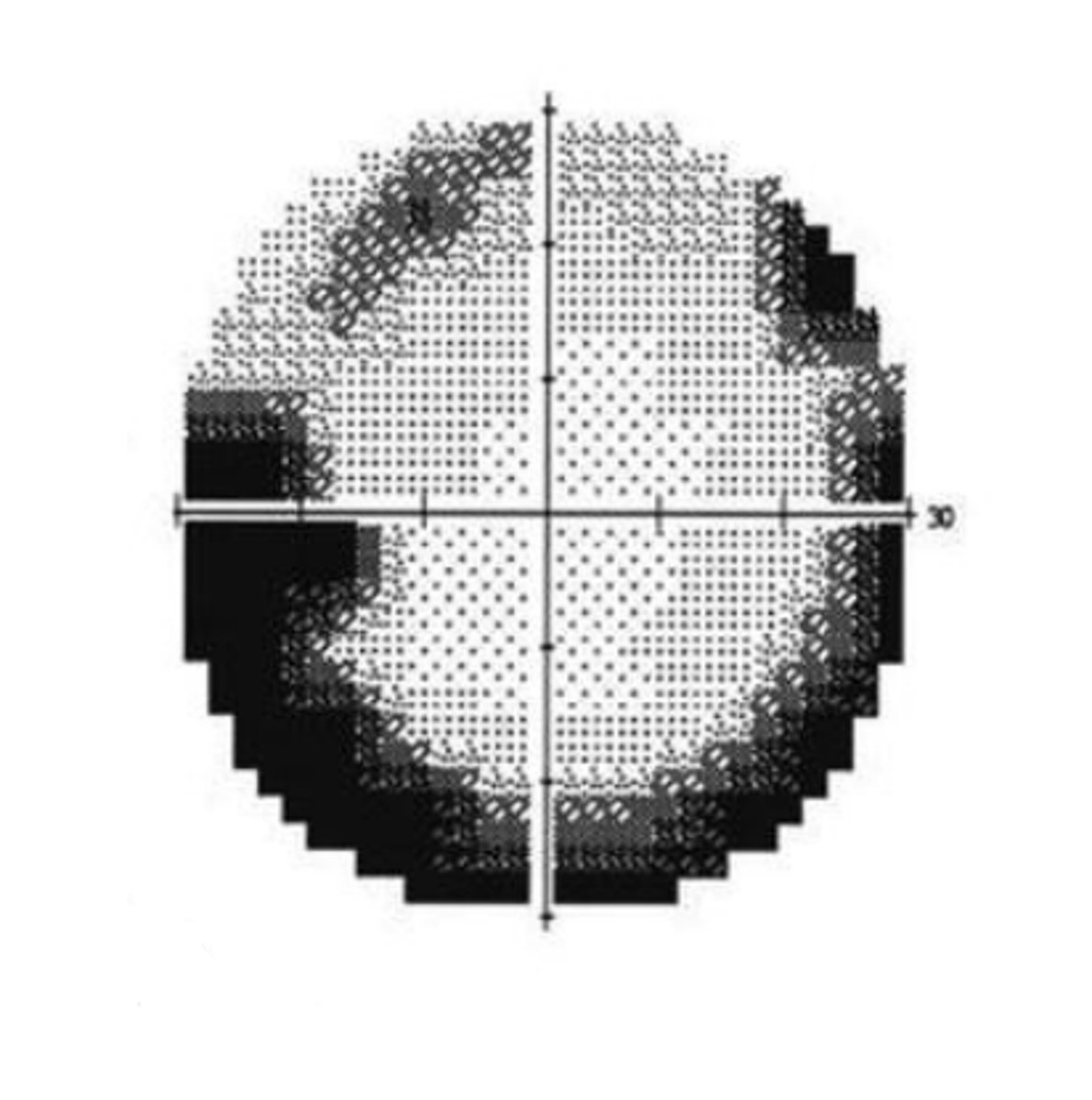
clover
If a patient is fatigued, this will commonly produce a visual field defect in the shape of a _____. This is because the center of the quadrants are tested first.
superiorly
Dermatochalasis will show a visual field defect...
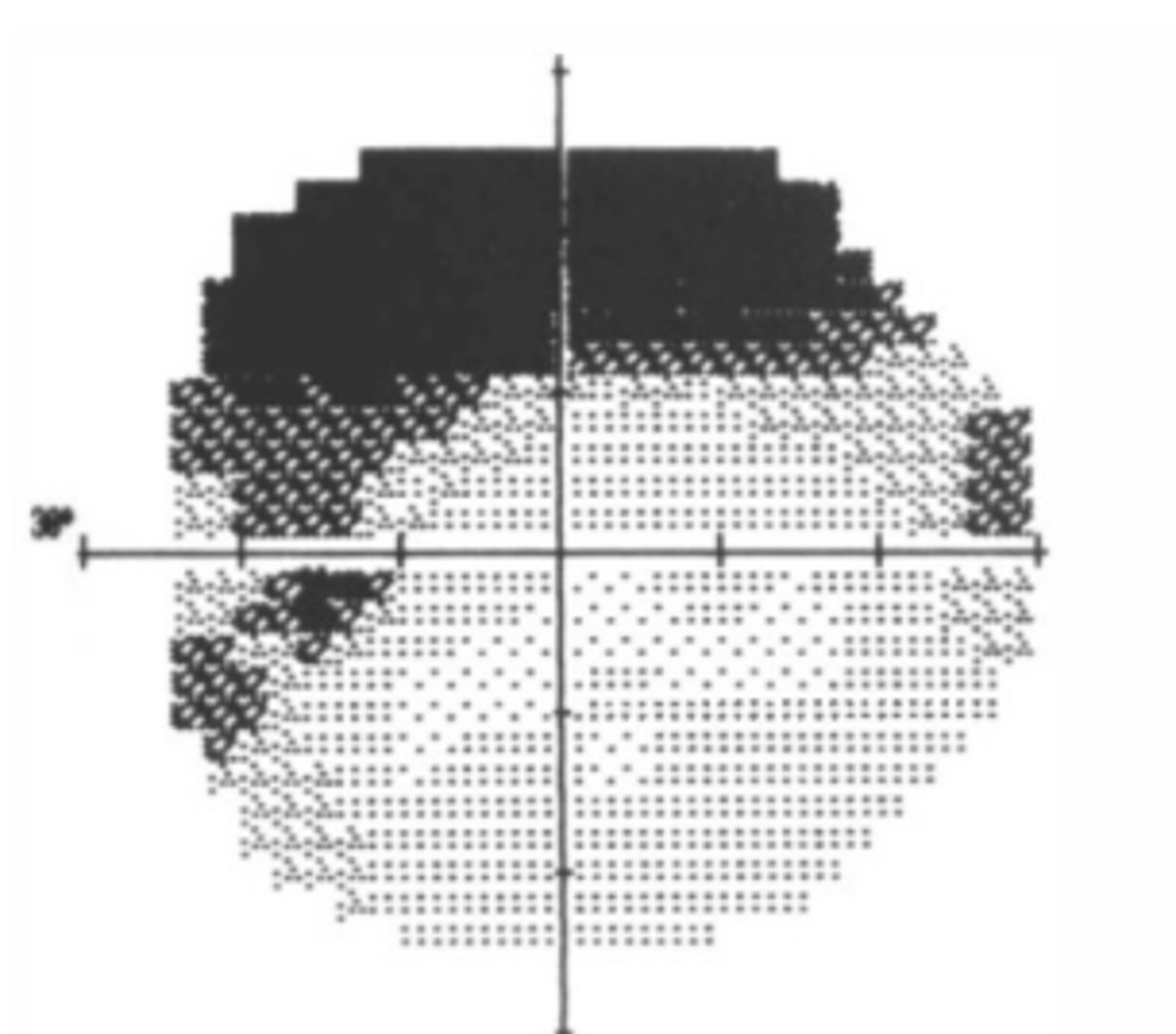
Grayscale
presentation of VF results that gives a visual representation of sensitivity. Is useful for detecting artifacts and overall regions of concerns, but should not be used to assess the actual defect in detail.
Numeric scale
presentation of VF results that shows retinal sensitivities in dB at each location tested. Is useful for evaluating the hill of vision.
Total deviation plot
presentation of VF results that shows the difference (in dB) between test results compared to normative data for the patient's age group. Shows the probability of each point being normal. Does not subtract other ocular defects such as cataracts, refractive error, etc.
Pattern deviation plot
presentation of VF results that shows the overall sensitivity changes in the hill of vision. Subtracts overall depression value from each test point (as seen in cataracts or refractive error) in order to show localized defects.
Probability plots
depict the likely hood of a normal patient having that level of vision
Mean deviation
the overall depression of the field. Should not exceed –2dB. Helps to quantify the visual field loss as mild, moderate, severe, etc.
0 to –5.99 dB
mild visual field defect as classified by mean deviation
-6 to –11.99 dB
moderate visual field defect as classified by mean deviation
Above –12
advanced visual field defect as classified by mean deviation
Pattern standard deviation
presentation of VF results showing the degree of departure from the normal hill of vision. High values can occur due to low test reliability, VF defect, or both. Should not exceed –2dB.
Visual field index
presentation of VF results showing the percent of a normal age adjusted visual field with greater weight given points closer to fixation to adjust for ganglion cell density and visual function. Is less sensitive to cataract and media changes.
Glaucoma hemifield analysis
presentation of VF results comparing corresponding point values across the horizontal where changes are characteristic of glaucoma. Has five anatomical sectors superiorly and inferiorly that follow the arrangement of retinal nerve fibers.
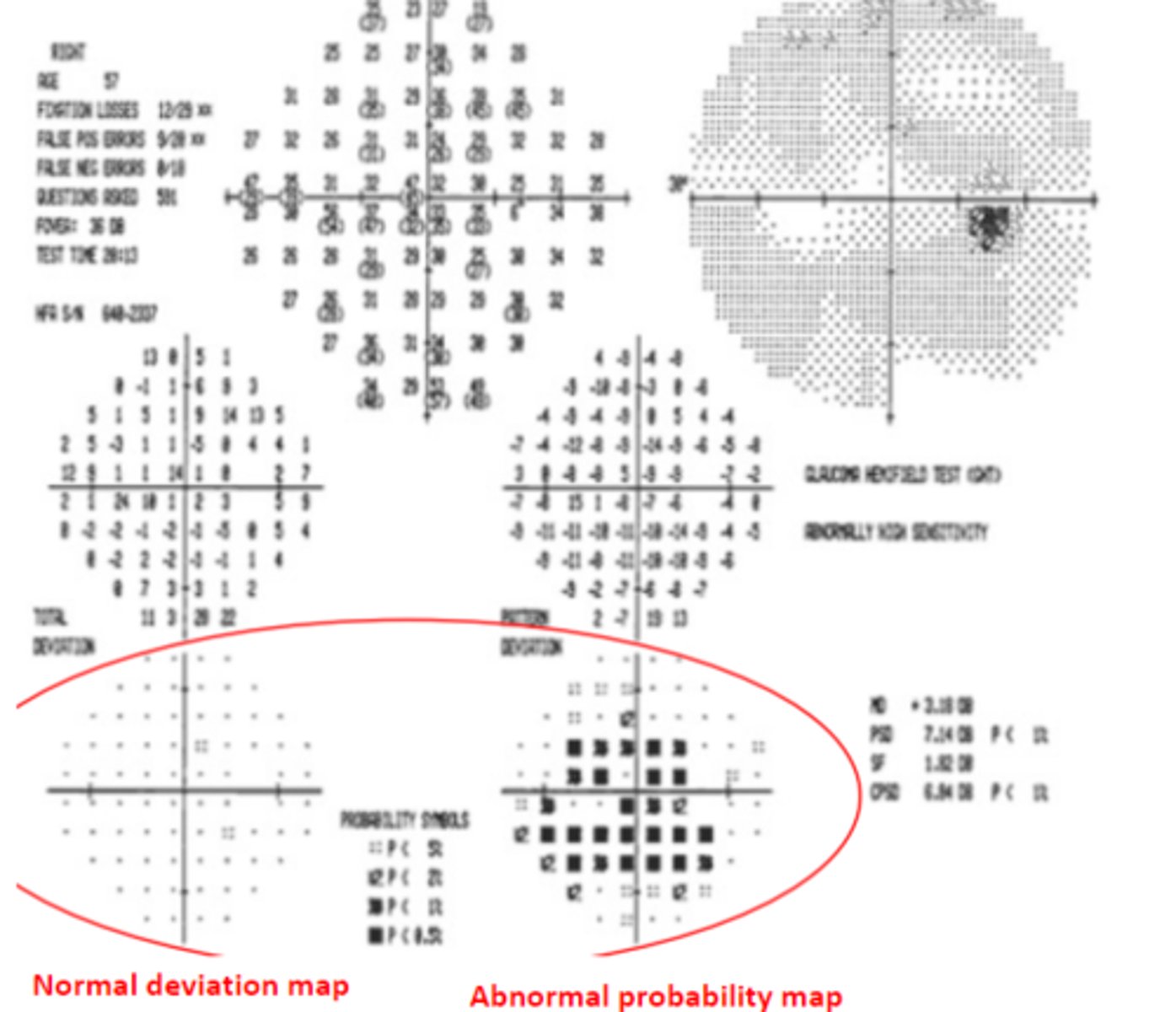
white scotoma
A _____ can be seen when the patient is "trigger happy" and having a high number of false positives. Will also have higher fixation losses and a probably map that looks abnormal with a normal total deviation map.
upward
An ____ bar on the gaze tracking chart indicates fixation disparity, and the size of the bar indicates the magnitude of disparity
short downward
A ____ bar on the gaze tracking chart indicates tracking failure
long downward
A ____ bar on the gaze tracking chart indicates eyelid closure
5
a Central visual field defect is located _____ degrees or less from the fixation point
5-30
a Paracentral visual field defect is located _____ degrees from the fixation point
30
a Peripheral visual field defect is located greater than ____ degrees from the fixation point