Ribs/Sternum Exam
1/91
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
How many pairs of ribs are there?
12
Purpose of ribs
Support walls of pleural cavity and diaphragm; protects heart and lungs
Ribs shape
Conical
Rib bone classification
Flat bone
Costal cartilage
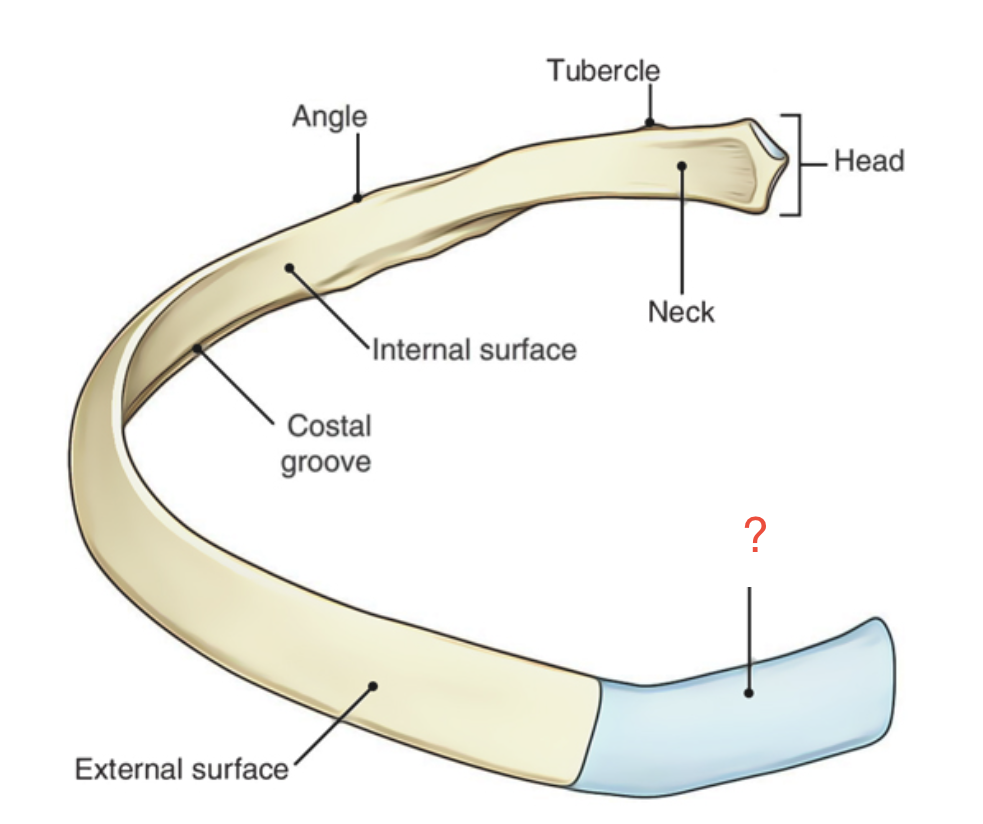
Head of rib
Articulates with body of vertebra
Neck of rib
Flattended area between the head and tubercle
Tubercle of rib
Has a facet that articulates with transverse process of vertebra
Which ribs connected to the sternum?
1-7
Which ribs have costal cartilage?
1-10
Which ribs are “floating” ribs?
11-12
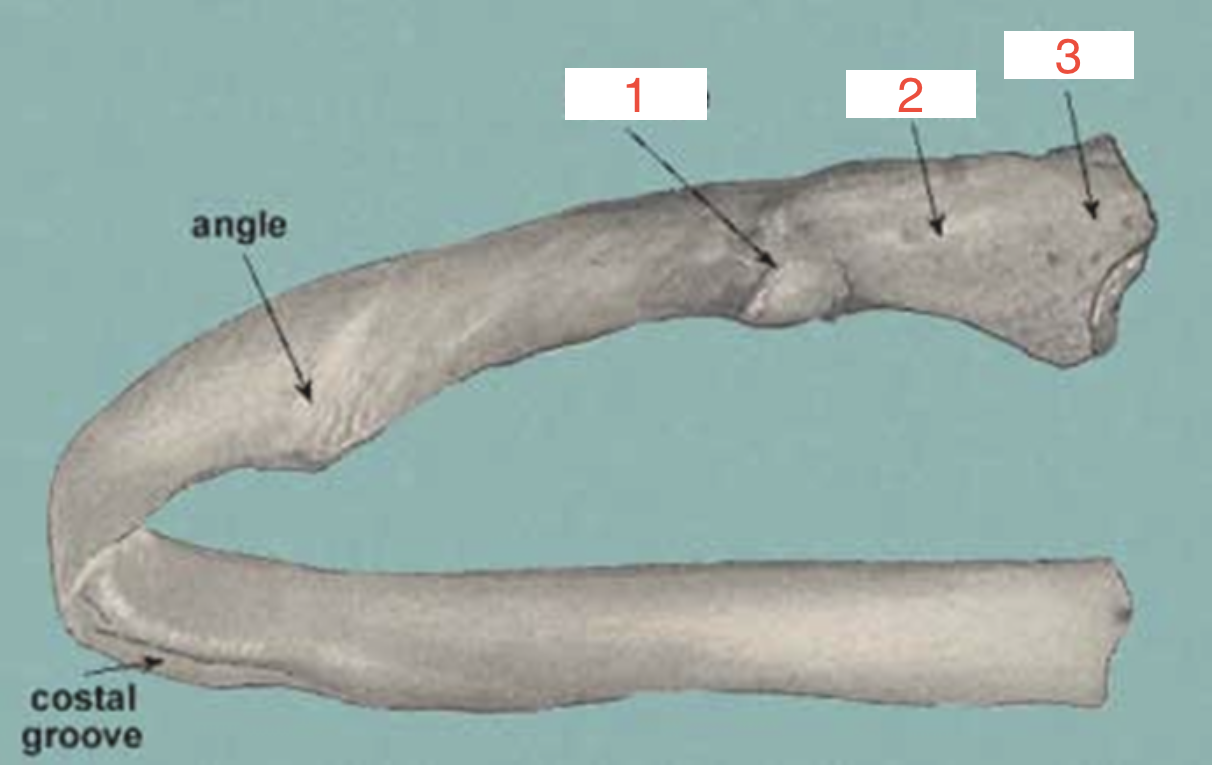
1?
Tubercle
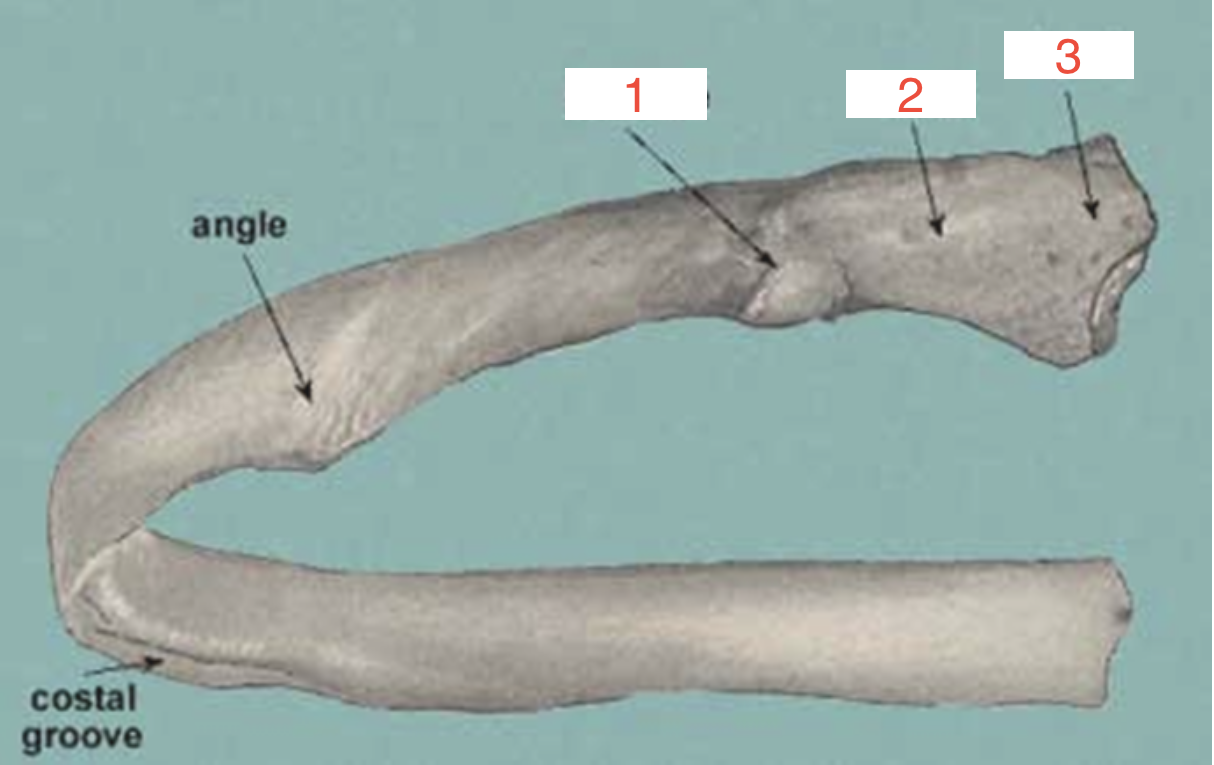
2?
Neck
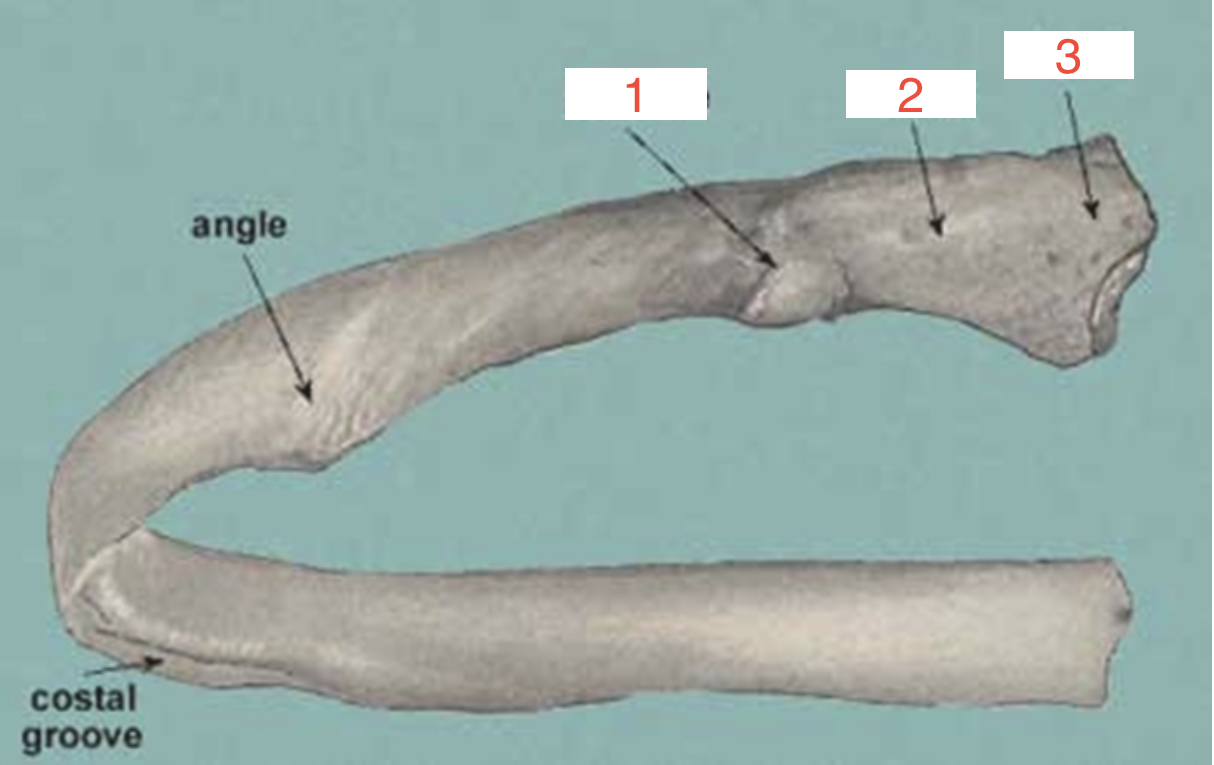
3?
Head
Vertebral end
End of rib which attaches to the thoracic vertebra
Angle of rib
Posteriorly, before connection to vertebra
Body/shaft
Main part of rib
Sternal end
End of rib which attaches anteriorly
Costal groove
Located on the inferior/ internal border containing costal arteries, veins, and nerves; trauma to the ribs can damage this area and cause pain and hemorrhaging
Costovertebral Joint
The head connects to vertebral body; synovial gliding joints
Costotransverse Joint
The tubercle connects to transverse process; synovial gliding joint
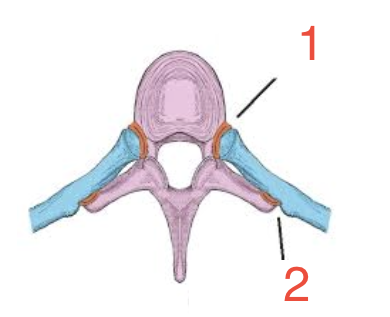
1?
Costovertebral joint
2?
Costotransverse joint
True ribs
1-7
False ribs
8-12
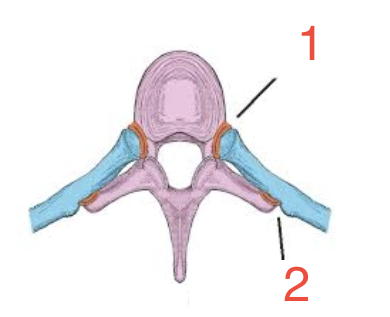
Costochondral Joint
Anterior connection of sternal end of rib with the costal cartilage; cartilaginous synchondroses joints and allow no movement
Costcochondral joint
Interchondral Joints
Between costal cartilages of 6-7, 7-8, 8-9 and 9-10; synoival gliding joint
Intercostal Space
Space between each rib
How much does the diaphragm move between deep inspiration and deep expiration?
1 ½ inches
Ribs located aboce the diaphragm (1-9) are best examined on ______________
Inspiration
Ribs below the diaphragm (8-12) are best examined on ________________
Expiration
Where is the rib cage the widest?
8-9
Sternum bone classification
Flat bone
Cervical rib
Extra rib attached to C7
What are the 3 parts of the sternum?
Manubrium, body and xiphoid process
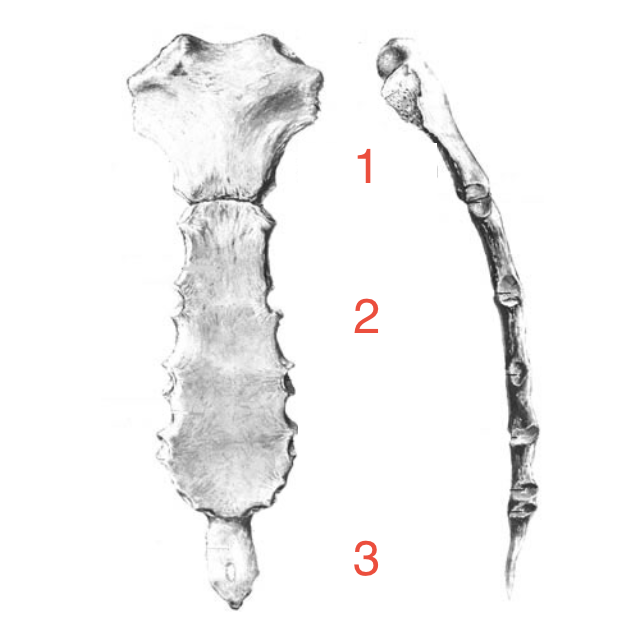
1?
Manubrium
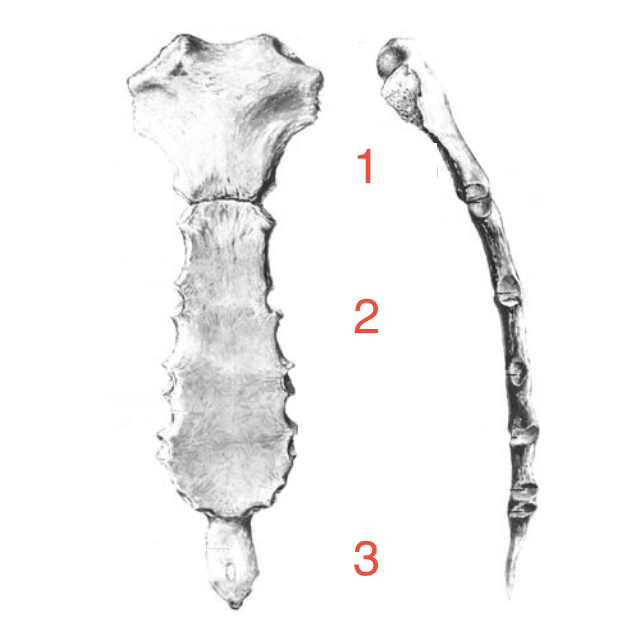
2?
Body
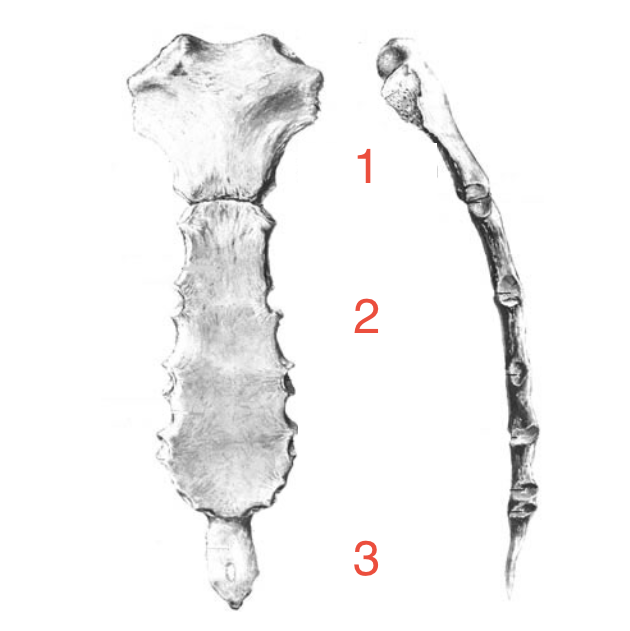
3?
Xiphoid process
Clavicular notches
On the superior lateral sides where the sternal ends of the clavicle articulate
Costal Notch
For the cartilage of the first rib attachment
What vertebra level does the jugular notch correspond with?
T2/T3
Manubriosternal Joint
Joint space between the manubrium and sternal body; cartilaginous symphysis joint with little to no movement
Sternal Angle
At the manubriosternal joint - this area forms a slight angle; makes a palpable transverse ridge
What vertebra does the sternal angle correspond to?
T4/T5
Costal Notches
Attachments of ribs 2-7, sternocostal joints; synovial gliding joints
Xiphoid Process
Cartilaginous early in life then partially or completely ossifies later in life; palpable and corresponds to the superior portion of the liver and inferior aspect of the heart
Xiphisternal Joint
Joint space between the sternal body and xiphoid process; cartilaginous synchondrosis joint which allow little or no movement
Sternum routine
RAO and lateral
What vertebra does the xiphoid process correspond to?
T10
What is the sternum RAO obliquity for a large barrel chest patient?
15 degrees
What is the sternum RAO obliquity for a thin chested patient?
20 degrees
Subcutaneous Emphysema
Presence of air in subcutaneous tissue
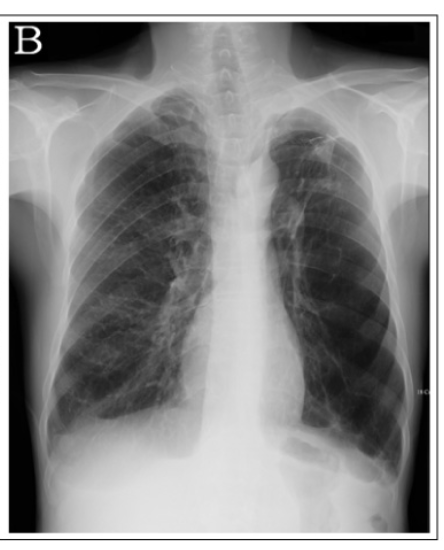
Subcutaneous emphysema
Flail Chest
Two or more contiguous rib fractures with two or more breaks per rib
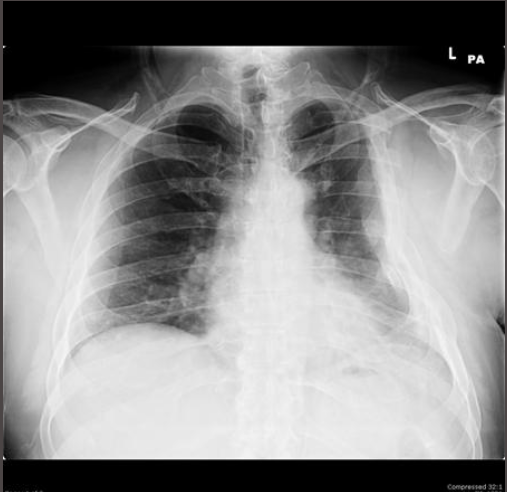
Flail chest
Pectus Carinatum – Pigeon Chest
Uncommon birth defect in which a child's breastbone protrudes outward abnormally
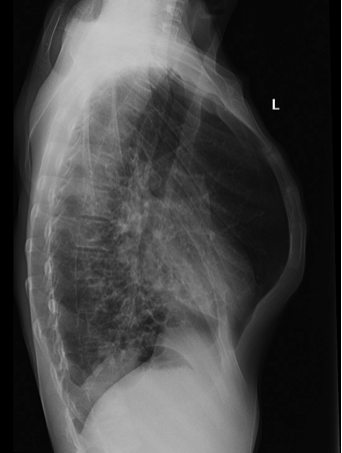
Pectus carinatum pigeon chest
Pectus Excavatum – Funnel Chest
Condition in which the person's breastbone is sunken into the chest
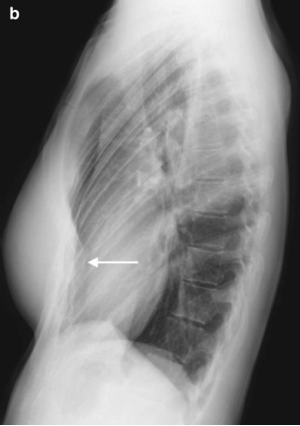
Pectus Excavatum – Funnel Chest
Rib SID
72
What side of ribs goes against the IR
Affected side
What must you annotate on rib images?
Erect
Anterior rib pain position
PA
Posterior rib pain position
AP
What do you do if a patient pin points an area of pain on a rib?
BB
Bilateral rib collimation
17×14
Unilateral rib collimation
14×17
PA rib lower image tube angle
10-15 caudad
If inital rib image is PA, what do you do for oblique?
RAO/LAO
If inital rib image is AP, what do you do for oblique?
RPO/LPO
RAO sternum SID
40
RAO sternum collimation
11×14
RAO sternum technique
81 kVp, center cell (3.2 mAs)
RAO sternum breathing
Suspended expiration
Upper ribs breathing
Suspended inspiration
Lower ribs breathing
Suspended expiration
How much do you rotate the patient for an RAO sternum?
15-20 degrees
Lateral sternum SID
72
Lateral sternum collimation
10×12 L
Lateral sternum technique
81 kVp, center cell (10 mAs)
Lateral sternum breathing
Suspended deep inspiration
AP/PA upper ribs technique
81 kVp, center cell (10 mAs)
AP/PA lower ribs technique
85 kVp, center cell (12.5 mAs)
Upper ribs collimation
14×17
Lower ribs collimation
14×11
Rib SID
72
Supine rib SID
40
AP/PA lower image tube angle
10-15 degrees caudal
Upper oblique technique
81 kVp, center cell (16 mAs)
Lower oblique image
85 kVp, center cell (16 mAs)
AP/PA bilateral ribs collimation
17×14