Anatomy / Structure
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
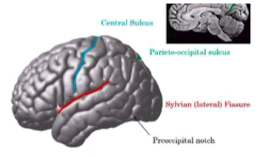
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal
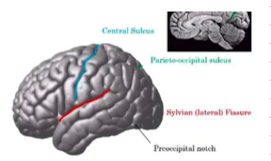
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates parietal and occipital lobe
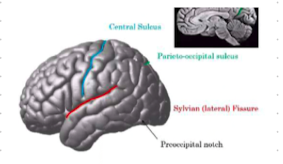
sylvian sulcus
separates frontal and temporal lobe
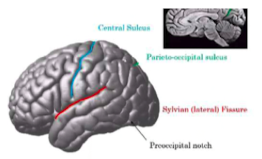
pre occipital notch
separates occipital and temporal lobe
temporal lobes functions
auditory processing
speech comprehension
ventral vision: what pathway
memory
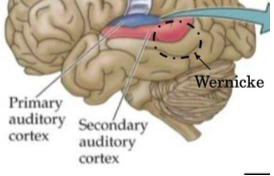
temporal lobe structure
Primary auditory BA 41, 42
Secondary auditory BA 22
temporal lobe sulci
Superior temporal sulcus (STS)
Inferior temporal sulcus (ITS)
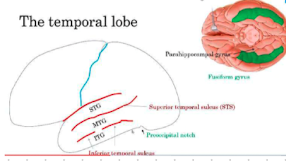
temporal lobe gyri
STG
MTG
IFG
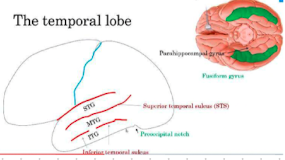
Superior temporal sulcus (STS)
separates STG and MTG
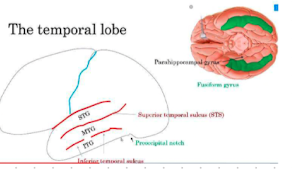
Inferior temporal sulcus (STS)
separates MTG and ITG
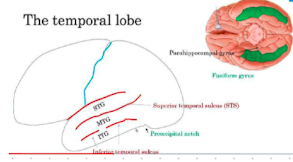
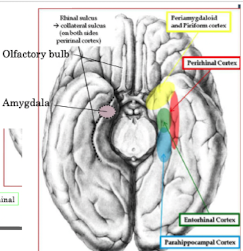
parahippocampal gyrus
• Posterior part: Parahippocampal cortex
• Anterior Part: Entorhinal cortex
• Piriform cortex: Sense o
occipital lobe function
process visual information
occipital lobe structure
• Primary visual cortex BA 17
• Secondary Visual cortex BA 18
• associative visual areas BA 19
parietal lobe functions
somatosensory
• language
• dorsal stream vision: where
• multi sensory integration
parietal lobe structure
inferior parietal lobule
superior parietal lobule
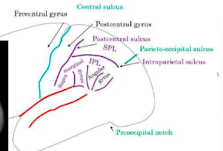
parietal lobe gyri
supramarginal gyrus
angular gyrus
parietal lobe sulcus
intraparietal sulcus
post central sulcus
frontal lobe gyrus
post central gyrus
precentral gyrus
superior forntal gyrus
inferior frontal gyrus
frontal lobe functions
• motor control
• executive functioning
• language
• epoptic processing
• reasoning and emotions
frontal lobe sulcus
central sulcus
precentral sulcus
superior frontal sulcus
inferior forntal sulcus
inferior frontal gyrus
- Pars Opercularis
- Pars Triangularis
- Pars Orbitalis
horizontal ramus
separate ORB and TRI
anterior ascending ramus
separate TRI and OPER
insula strcture
Operculum:
-frontal
-parietal
-temporal
insula function
• hidden within sylvian fissure
• somatic-visceral sensations
• introspection
• gustatory cortex
• socio-emotional
• cognitive
limbic cortex functions
emotional brain involved in behavioral and emotional response
limbic cortex structure
-cingulate cortex
-parahippocampal gyrus/hippocampus
-amygdala
subcortical structure
• Grey matter areas
• not part of cortex islands within white matter
basal ganglia structure
striatum, amygdala, nucleus accumbent
basal ganglia
group of subcortical nuclei
striatum structure
putamen, caudate nucleus, globus pallidus
striatum functions
-involved in initiation and regulation of movements
- motor learning
-muscle tone
amygdala funcitons
memory, emotions, fear
nucleus accumbens
pleasure, reward, motor functions
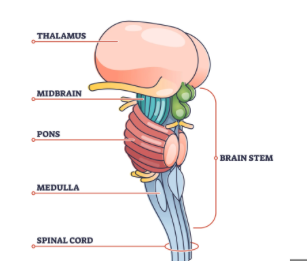
thalamus
relays sensory info to cortex
exception: olfaction→piriform
first order nuclei
lateran geniculate nuclei
medial geniculate nuclei
ventro posterior nuclei
higher order nuclei
- role in higher order cognitive functions and network regulation involving prefrontal cortex
- involved in learning and memory processes
ventro posterior nuclei
relays sensory information from body
lateral geniculate nuclei
visual relay
medial geniculate nuclei
auditory relay
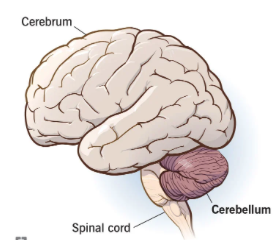
cerebellum function
• production of movement
• balance, posture, coordination
• motor learning
brain stem function
control centers for autonomic vital functions
connects brain to spinal cord
-breathing, heartbeat, sleep, blood pressure
brain stem structure
midbrain
pons
medulla
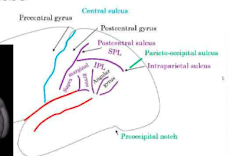
parietal brodmann area
BA 40, 39 SMG, ANG
BA 1,2,3 somatosensory
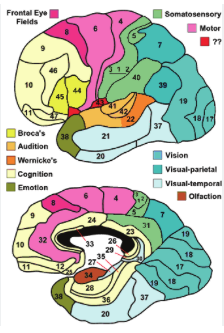
frontal brodmann area
BA 4, 6: motor, premotor
BA 44, 45: Broca = Pars oper, pars tri
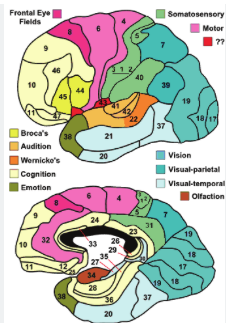
occipital brodmann area
BA 17,18,19 = visual
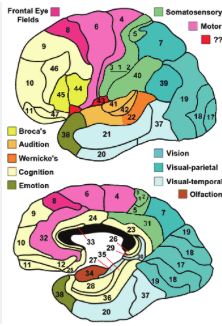
temporal brodmann area
BA 41, 42, 22: auditory
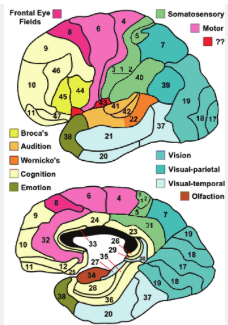
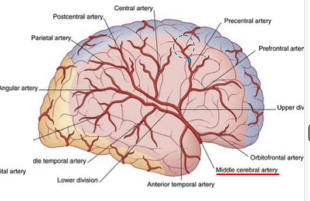
middle cerebral artery
along sylvian fissure
lots of branches
supplies lateral surface: frontal, parietal, partial temporal
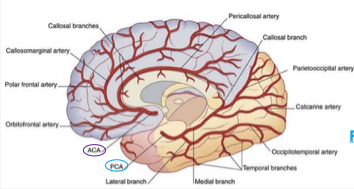
anterior cerebral artery
supplies upper part of medial surface of frontal and parietal lobes
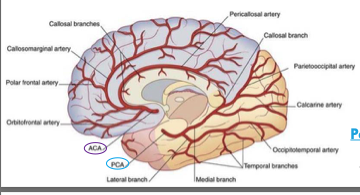
posterior cerebral artery
medial surface of temporal lobe and all of occipital lobe
layer I
molecular layer
comprised of few scatter neurons
layer II
external granular layer
dense layer of very small granular neurons which sometimes appear to be granular
layer III
external pyramidal layer
pyramidal neurons which get larger the deeper into the cortex they go
layer IV
internal granular layer
small round granule cells
layer V
internal pyramidal layer
pyramidal neurons, often denser in upper part than in lower part
layer VI
multiform layer
spindle-shaped neuorns/modified pyramidal cells, lower part often blends with white matter
hypergranular coretx
granular layer 4 and rest of layers appear granular
area 3b, area 17, area 41
dysgranular cortex
slightly granular layer 4 interrupted by pyramidal cells form 3 and 5
area 44
agranular coretx
no granular layer 4
areas 4 and 6
area 47/12
- Typical 6 layer neocortex
- Good granular layer 4
- Active memory retrieval with area 45
area 45
- Distinct granular layer 4
- Large pyramidal cells in the lower part of layer 3 called gamma cells
- Active memory retrieval and processing area
area 44
- Dysgranular layer 4, lots of disruptions
- Broca’s area proper
- Electrical stimulation causes speech arrest
area 6VR
- Premotor cortex
- Agranular cortex
- Difficult to distinguish layers
- No layer 4
area 4
- Agranular area
- Largest neurons in the brain in layer 5 Betz cells
- Poor border with the white matter, seen in anatomical MRI
- Thick cortical ribbon
- Primary motor cortex, large cells go down spinal cord to synapse with efferent cells
area 3b
- Hypergranular cortex (really tiny and appear granular even though they are not)
- Distinct layer 4
- Other layers all granular
- Thin cortical ribbon
- Primary somatosensory cortex
commissural fibres
white matter
connect left and right hemispheres
association fibers
short and long distance
intrahemispheric
one cortical area to another
anterior to posterior
projection fibers
up down orientation
cortex to spinal cord/subcortical areas vice versa
types of commissural fiber
corpus callosum
hippocampal commissure
posterior commissure
anterior commissure
anterior commissure
connects temporal cortex areas and subcortical structures
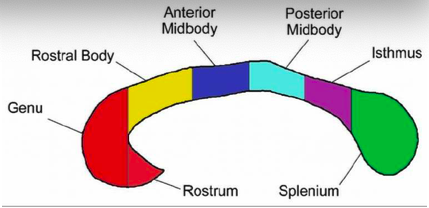
genu and rostrum
connect the orbitofrontal and prefrontal areas
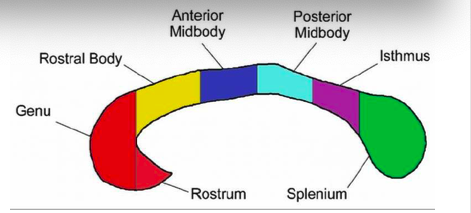
rostral body
premotor and supplementary motor areas
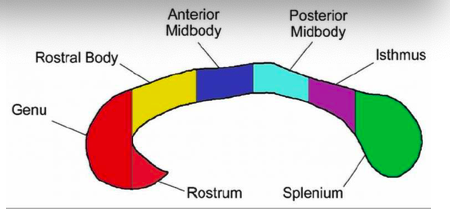
anterior midbody
sensori-motor areas
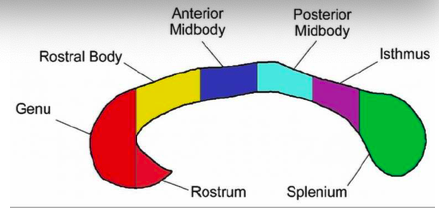
posterior midbody
parietal areas
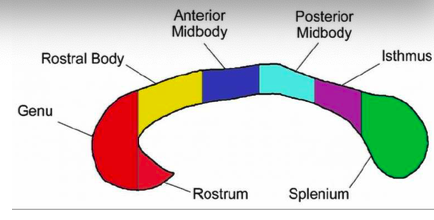
isthmus
posterior parietal and superior temporal areas
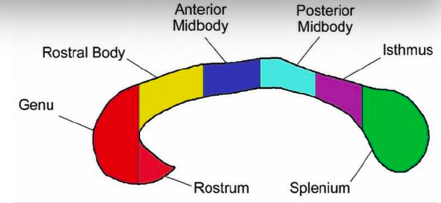
splenium
occipital and inferior temporal areas
types of association fibers
superior longitudinal fasciculus
arcuate fasciculus
middle longitudinal fasciculus
temporo-frontal extreme capsule fasciculus
uncinate fasciculus
inferior longitudinal fasciculus
inferior fronto-occipital fascículos
superior longitudinal fasciculus
frontal to parietal
3 branches
arcuate fasciculus
frontal to posterior temporal areas
middle longitudinal fasciculus
temporal to parietal
temporo-frontal extreme capsule fasciculus (TFexeF)
frontal to intermediate temporal areas
associated with long-term storage of semantic information
ventral stream of language
associated with control retrieval and selection of semantic representations
uncinate fasciculus
orbitofrontal and anterior temporal areas
inferior longitudinal fasciculus
occipito-temporal connections
inferior fronto-occipital fascículos
occipital-frontal connections
external capsule
TFexeF passes through here
motor cortex primarily to putamen
unidirectional
internal capsule
space between subcortical areas and thalamus
bi-directional
inferior frontal language speech
broca’s area
BA 44 and 45
production of langauge
other region’s for speech production
anterior insula
precentral regon
basal ganglia
cerebellum
basal ganglia speech
cognitive control
use of appropriate phonological and articulatory representations of lexical terms
anterior insula
articulation
part of orofacial motor system
precentral region speech
orofacial musculature control
posterior temporal regions
wernicke
wernicke
critical region for auditory language comprehension
superior temporal gyrus
acoustic-phonological analysis of speech input
heschl’s gyrus
posterior superior temporal gyrus and sulcus, secondary cortex
heschl’s gyrus
primary auditory cortex
superior surface of temporal lobe
processes any type of sound
posterior superior temporal gyrus and sulcus
responds to acoustic features of phonetic parameters
differentiates between speech and non speech
MTG and pSTG/STS
comprehension of words
semantics, grammatical aspects
aSTG
processing syntactic structure (sentence structure, therefore not activated for a list of single words)
and semantic processing
ventral branch of AF
connect IFG
dorsal branch of AF
connects more dorsal regions of frontal lobe