GEF
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:57 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
1
New cards
Reasons why Mendel was successful in understanding heredity
He used scientific and quantitative methods
2
New cards
Enclose the flower
Sepals function
3
New cards
Petals
comes in various shapes and colors
4
New cards
Anther
produces pollen
5
New cards
Carpel/pistil
Female reproductive organ
6
New cards
Stigma
pollen deposit
7
New cards
Style
Tube to ovary
8
New cards
Ovary
holds the ovule
9
New cards
Ovule
female gamete
10
New cards
self-pollination
pollen from anther of the same plant to the stigma
11
New cards
cross-pollination
pollen from the anther of another plant to the stigma
12
New cards
Allele
alternative forms of a gene
13
New cards
Trait
appearance of a characteristic
14
New cards
Ratio of phenotype and genotype of monohybrid cross
geno-1:2:1, pheno- 3:1
15
New cards
Ratio of phenotypes in Mendel’s dihybrid cross
pheno- 9:3:3:1
16
New cards
Describe Mendel’s principles of heredity
Each plant possesses two genetic factors or alleles that encode a trait, Alleles are separated with equal probability when a plant forms gametes and one allele is present in one gamete à Both alleles cannot be present in a gamete, When 2 gametes fuse to form a zygote, allele from male parent unites with allele from female parent
17
New cards
Explain how meiosis can explain Independent assortment
In meiosis the there are several combination of possible c’somal arrangements which will alleles to assort independently
18
New cards
Complete Dominance
In heterozygous individuals only one phenotype is detected
19
New cards
Incomplete Dominance
When homozygous individuals do not completely show one phenotype
20
New cards
Codominance
Heterozygous individual display both phenotypes
21
New cards
Penetrance
Probability of phenotype from a genotype
22
New cards
Incomplete penetrance
When a phenotype shown is not expected of genotype
23
New cards
Expressivity
Degree to a trait being expressed
24
New cards
Anticipation
Increasing severity of disease or earlier age of onset of a genetic trait in successive generations
25
New cards
Lethal allele
Allele that causes death of the organism
26
New cards
Blood Type of 1. IA I 2. IA IB 3. ii
1. A
2. AB
3. O
27
New cards
Epistatic gene
Gene that Suppresses another gene
28
New cards
Hypostatic gene
Gene that is suppressed by epistatic gene
29
New cards
double recessive epistasis
Two recessive alleles on two different loci repress a phenotype
30
New cards
Sex linked characteristics
characteristics that are determined by genes directly located on sex chromosomes
31
New cards
Sex-Influenced Characteristics
Characteristics that are more likely toward a certain sex, genes are located in autosome
32
New cards
Sexs-limited Characteristics
Trait encoded on autosomes but are expressed only in one sex.
33
New cards
inheritance of mitochondria and chloroplasts
The male gametes is always degraded leaving only passing of genes from the mother.
34
New cards
cytoplasmic inheritance
Phenotypes displayed are the result of genes of the mitochondria and chloroplast
35
New cards
Maternal effect
Mothers genotype decides the offspring’s phenotype. Explained by mother placing mRNA and proteins in eggs used in early development
36
New cards
Polygeny
Many genes are involved in deciding a phenotype
37
New cards
Pleiotropy
One gene influences multiple genes
38
New cards
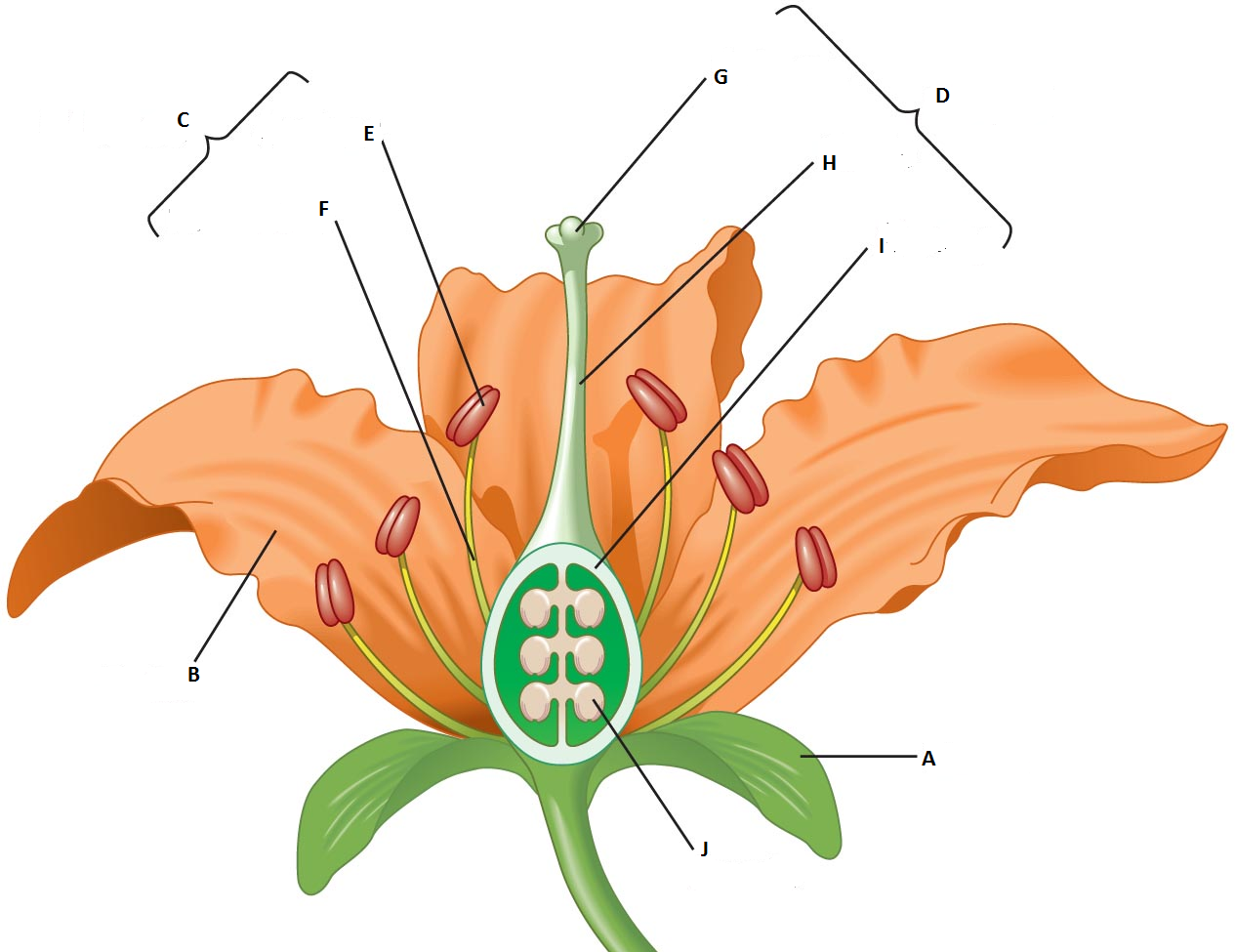
39
New cards
Multifactorial characteristics
Phenotypes decided by genes and environment
40
New cards
Concept of linked genes
2 Traits that cannot assort independently
41
New cards
When are genes considered linked
2 genes that are close together on the same C’some
42
New cards
When does independent assortment occur
Occurs during Meiosis I
43
New cards
Difference between recombinant and nonrecombinant gametes
If crossing over has happened or not
44
New cards
Cis Configuration
same allele type on one C’some dominant or recessive
45
New cards
Trans Configuration
one dominant and one recessive.
46
New cards
Equation to find distance between 2 genes that are on the same chromosome from the number of progeny obtained
(# of recombinant progeny/ # of total progeny)\* 100 = _______ cM
47
New cards
Difference between a genetic (or chromosomal) and physical map
Genetic map – tells where genes are on a C’some. Physical Map- tells what genes are on what C’some
48
New cards
Somatic cell hybridization
Creates a heterokaryon by fusing a human fibroblast and a mouse tumor cell which will create multiple cells lines with different C’somes and analysis the gene product with the C’somes present will let you know which gene is on which C’some.
49
New cards
Deletion mapping
By viewing the karyotype of C’somes with deleted regions it is possible to see if a mutant is there or not in the progeny.
50
New cards
Heterokaryon
Human fibroblast + Mouse tumor cell
51
New cards
Two types of DNA sequencing
Sanger Sequencing, Genome wide sequencing
52
New cards
Test Cross
Cross involving homologous recessive
53
New cards
transposable elements (transposons)
Gene that move within the genome without nonhomologous recombination
54
New cards
Features seen in transposable elements (transposons)
Terminal inverted repeats at the ends, Flanking direct repeat: next to terminal but not part of the transposon
55
New cards
Locations of terminal inverted repeats, flanking direct repeats, and transposase coding sequence
Outer Flanking, inverted, coding sequence
56
New cards
Types of transposons
Class I: Retrotransposons
Class II: DNA transposon
Class II: DNA transposon
57
New cards
transposition general mechanism
DNA is cut making staggered ends, transposons places itself inside the staggered end, gaps are filled by DNA polymerase and creates the flanking direct repeat
58
New cards
Replicative Transposition
Transcription of transposon forms a RNA intermediate which is converted back into DNA and is transposed
59
New cards
Non-replicative Transposition
DNA is excised and is transposed
60
New cards
The transposon is able to move around when an enzyme is able to cleave it at one location and then cut another piece of DNA at another location where it gets inserted. Name the enzyme that is able to mediate this cutting process.
Transposase
61
New cards
Regulation of transposition 2 methods
__Methylating DNA__: prevent the transcription of the transpoase.
regulating translation of transposase enzyme
regulating translation of transposase enzyme
62
New cards
How transposons can influence phenotypes
Transposons placed upstream of a gene may reduce the expression of the genotype
63
New cards
How transposons generate mutations within a gene
places itself inside a gene
64
New cards
How transposons cause chromosomal rearrangements
Two transposome in the same orientation = deletion and opposite orientation = insertion
65
New cards
Definition of epigenetics
Phenotypes and processes that are transmitted to cells in the future but not by DNA differences
66
New cards
DNA methylation (epigenetic)
Promotes Heretrochromatin production and prevents binding of transcriptional regulators
67
New cards
Histone modifications (epigenetic)
Addition of Acetyl group = reduce trans. Or remove = influences trans.
68
New cards
RNA molecules: long noncoding RNA and small RNA like miRNA and siRNA
siRNA- promotes mRNA degradation, miRNA- inhibits translation, Xist long coding RNA- coat C’somes which recruits methyl transferase
69
New cards
Chemicals
likes insecticides, alcohol, cigarettes, the fungicide vinclozin mimics testosterone which causes mice to produce less sperm.
70
New cards
Behavior (epigenetic)
rats being groomed by mother = DNA acetylation = braver rats
71
New cards
Monozygotic twins (epigenetics)
will be different due to epigenetic changes
72
New cards
Genomic imprinting
gene expression depends on sex of the parent that provided it.
73
New cards
Gene conflict hypothesis and genomic imprinting in the context of Igf2 and Igf2R
IGF2 promotes growth and IGF2R counteracts IGF2. IFG2 is expressed when gene is from father. IGF2R is expressed when given from mother.
74
New cards
Gene conflict hypothesis
since the nutrients is provided by the mother IGF2R makes it so that the children do not over burden the mother.
75
New cards
Definition of genotypic frequency
How many people have a certain genotype in a population
76
New cards
Definition of allelic frequency
Prevalence of an allele in a population
77
New cards
Hardy-Weinberg law What does the law state
Allelic frequencies do not change
78
New cards
What factors affect allelic and genotypic frequencies
mutations, matting patterns, migration, population size, natural selection
79
New cards
Relation between mutation and genetic variation
Increases genetic variation due to it create alleles
80
New cards
Types of non-random mating
Positive assorted mating: tendency for like individuals to mate, Negative assorted mating: tenendcy for unlike individuals to mate, inbreeding preference between related individuals
81
New cards
Relationship of inbreeding and homozygotes
Inbreeding raises the likelihood of homozygous genotypes
82
New cards
Definition of gene flow
Influx of alleles from a population
83
New cards
Effect of migration on genetic variation
Increases genetic variance
84
New cards
How migration influences allelic frequencies
Spreads alleles in a population
85
New cards
Definition of genetic drift
Random change of the allele frequency
86
New cards
Causes of genetic drift
population size, founder effect, bottleneck, fixation
87
New cards
Definition of Founder effect
few individuals leave a population make a new population
88
New cards
Definition of Bottleneck effect
population undergoes major reduction in size
89
New cards
Definition of fixation
when the allele frequency reaches 1
90
New cards
Relation between genetic drift and genetic variation
drift reduces the likelihood of genetic variation.
91
New cards
Definition of natural selection
Certain adaptive traits promote survival
92
New cards
Definition of fitness
reproductive success of a genotype
93
New cards
Types of selection (be able to identify and explain): Disruptive, directional, and stabilizing selection,
Disruptive- advantages trait is either extremely large or small not in the middle, Directional- one extreme is promoted only, Stabilizing- the average of the traits is promoted
94
New cards
Anagenesis
Evolution of a single lineage
95
New cards
Cladogenesis
Evolution when one lineage splits to 2
96
New cards
Biological species concept’s definition of species
Group of organisms that care capable of interbreeding but do not breed with other species
97
New cards
Meaning of reproductive isolation
Do not breed with other species
98
New cards
Prezygotic reproductive isolating mechanisms: definition, ways by which the process can occur
Gametes of 2 species cannot fuse, Ecological- habitat location, behavioral-, Temporal- mating occurs at different times, Mechanical- different reproductive structures, Gametic isolation- Gametes cannot fuse
99
New cards
Postzygotic reproductive isolating mechanisms: definition, ways by which the process can occur
Gametes can fuse but hybrid is sterile or inviable, Hybrid inviability- zygote does not develop, Hybird sterility-, Hybrid breakdown- fertility drops with further crossing
100
New cards
speciation
Formation of a new species