Exam 2 Material
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pols 207 - 2023 Edition - Jan/May - Chapter 4,5 - Roblyer
Last updated 3:17 AM on 2/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
What are the advantages to multiple levels of government?
* Efficiency
* Equity
* Participation
* Protection against Tyranny
* Choice
* Equity
* Participation
* Protection against Tyranny
* Choice
2
New cards
What is the best description of the No Government Period (1776 - 1850)?
* Rural agrarian settings
* Dispersed population
* People were self-dependence
* County officials were government?
* “best government is least government”
* Dispersed population
* People were self-dependence
* County officials were government?
* “best government is least government”
3
New cards
what does agrarian mean?
cultivated land or an economy that was surrounded by agriculture.
4
New cards
During the No Government Period, what form of government was there?
County officials were government, they preformed traditional roles and kept record of property ownership.
5
New cards
What best describes the Municipal Government Period (1850 - 1895)?
* American cites Grew exponentially
* industrial revolution
* Immigration
* Urbanization
* Corruption grew
* industrial revolution
* Immigration
* Urbanization
* Corruption grew
6
New cards
What are some characteristics of Big cities during the Municipal Governments Period?
* Demand for water
* Increase in Sewage & waste
* Increase in crime
* regulations in health and building codes
* Demand for Education
* Increase in Sewage & waste
* Increase in crime
* regulations in health and building codes
* Demand for Education
7
New cards
During the Municipal Governments Period, what was the population density in some parts of New York?
100,000 people per square mile
8
New cards
what are some characteristics of “State Intercity” period of Government (1895 - 1932)
* Corruption still rooted in cites
* State governments created Dillons rule
* Party machines decline in power
* State governments created Dillons rule
* Party machines decline in power
9
New cards
What did Dillons rule do?
* Local governments are no longer allowed to put down what party they are affiliated with.
* People can now only be hired based on their merit and not their family relationships.
* Separated school districts to be their own sub section of government.
* People can now only be hired based on their merit and not their family relationships.
* Separated school districts to be their own sub section of government.
10
New cards
What are the characteristics of the “Federal Government” era (1932 to Present)
* Economic plumet due to Great Depression, World War 2, and cold war.
* Federal Government became the “Guardian & Protector”
* Imposed social standards
* Taxation & spending allowed the government to move into areas where states couldn’t
* Federal Government became the “Guardian & Protector”
* Imposed social standards
* Taxation & spending allowed the government to move into areas where states couldn’t
11
New cards
What is a Unitary Gov?
When the people and the central government directly communicate, and the central government is the primary source of power.
12
New cards
What is a Confederacy?
The State government are the primary sources of power. The issue with these governments is agreeing with each other so the state and federal level tend not to agree. Example is the Articles of Confederation.
13
New cards
What is a Federal?
The power is distributed between the states and the federal government.
14
New cards
What is federalism?
Allocation of powers between the top and lower level of gov.
15
New cards
What is American Federalism?
Assigns governmental powers to one or both of the State or National Levels. This can sometimes cause issues on allocation of power depending on how people interpret constitutions.
16
New cards
What is New Federalism?
Giving back most power to the states. However, the federal government claimed that the states would have to take on most of the bills. So states backed out.
17
New cards
What are the primary responsibilities of Federal gov.?
* National Defense
* Space Program
* Postal Service
* Space Program
* Postal Service
18
New cards
What are the primary responsibility of State Gov.?
* Education
* highways & transpiration
* Health
* Sanitation
* Fire
* Police
* highways & transpiration
* Health
* Sanitation
* Fire
* Police
19
New cards
What responsibilities are shared between Federal & state gov?
* Welfare
* Employment services
* Unemployment compensation
* Employment services
* Unemployment compensation
20
New cards
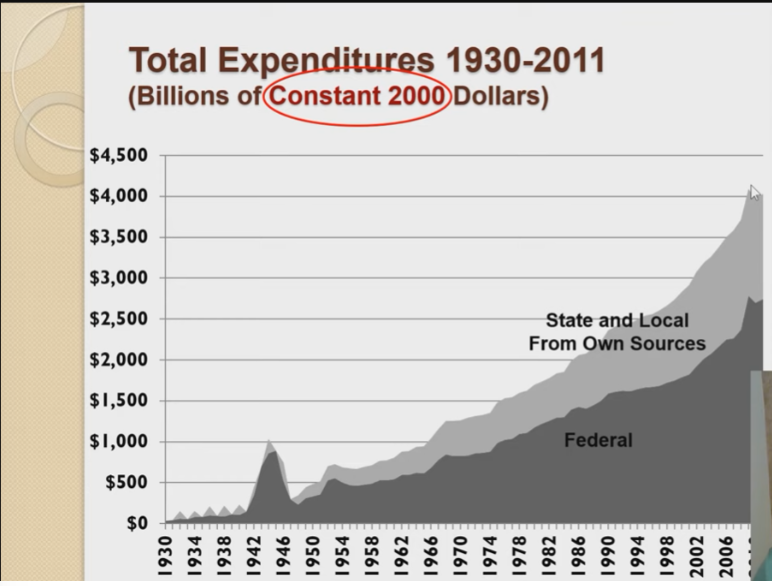
What best describes what the graph shows
* the buying power of 2000 currencies to represent inflation
* read as differences, the federal government spends more than the state gov.
* read as differences, the federal government spends more than the state gov.
21
New cards
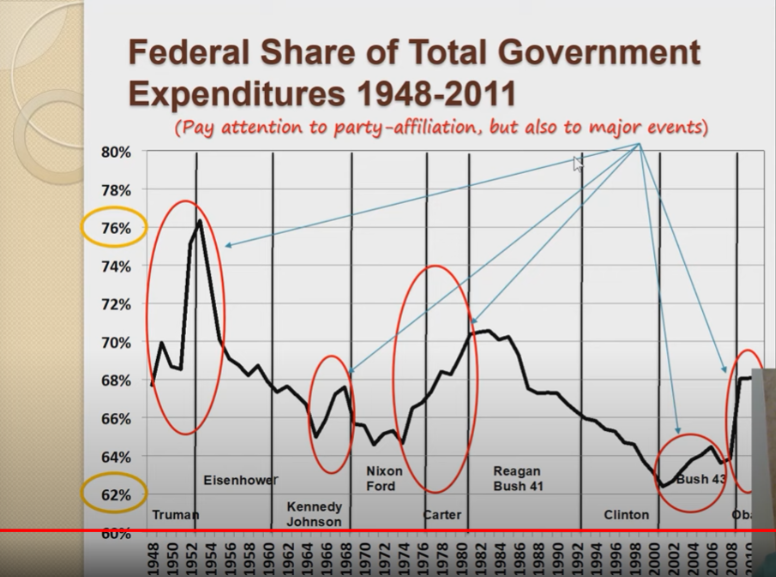
What bests describes the characteristics of the graph?
* Axis starts at 62% to 76% meaning gov. spends most of their funds
* It seems like political party has no correlation with spending.
* 1952, spending went up due to the cold war
* It seems like political party has no correlation with spending.
* 1952, spending went up due to the cold war
22
New cards
What is the Purpose of constituions?
* legitimacy or power
* organization of government
* limiting government power
* organization of government
* limiting government power
23
New cards
What are some similar characteristics of federal and state constitutions?
* separation of powers ( Executives, judicial, and legislative)
* Check and balances between powers
* Bill of rights
* Check and balances between powers
* Bill of rights
24
New cards
Define long constitutions?
have desire to carefully control their government. They contain detailed restrictions on power, and maybe difficult to alter
25
New cards
Define Short constitutions
open for interpretation, flexible with power, and can be changed more easily.
26
New cards
Texas Bill of rights main points
* Freedom & Sovereignty of state - The rights of the state
* Religious test - No religious test is needed to a public office, unless they acknowledge a supreme being.
* Outlawry or transportation offense - no one can be exiled form Texas
* Perpetuities & monopolies - no monopolies allowed.
* Religious test - No religious test is needed to a public office, unless they acknowledge a supreme being.
* Outlawry or transportation offense - no one can be exiled form Texas
* Perpetuities & monopolies - no monopolies allowed.
27
New cards
What is a main criticism of the Texas Constitution?
Disorganized and hard to read. Seems like it was made for mainly the wealthy.
28
New cards
Why is efficiently an advantage to multiple levels of government?
when you have one entity trying to manage an entire country, it become inefficient and you wont meet everyone’s needs. So you need multiple levels of government to manage everyone’s needs in certain everyone’s.
29
New cards
Why is equity an advantage to multiple levels of government?
Imagine a town wanted a park and another town wanted a chickfila. do you think its fair to put all of our fund to a project of another town you don’t know?
30
New cards
Why is **Participation** an advantage of multiple levels of government?
It will be easier to attend school boards and local city council decisions.
31
New cards
Due to Dillions rule what can local cities no longer do?
there projects can be rejected by the state if they agree or disagree with them.
32
New cards
What are nonpartisan city elections?
cannot put you political affiliation for local election. This made political machines ineffective due to most of the population being illiterate.
33
New cards
What are public goods?
they are non-excludable and non-rivaling, everybody can use without denying to others. They are merit goods, which cannot be denied to someone if they cannot pay such as education.
34
New cards
Private goods
excludable and rivaling, only those who pay for them can get these goods.
35
New cards
What is revenue?
Income received by the government through taxes
36
New cards
Expenditures
Goods and services purchased or provided with government funds.
37
New cards
Gross Domestic Product ( GDP)
used to measure the size, health, and power of a nations economy. However it does not tell us the economic health of individuals.
38
New cards
What are characteristics of Taxation?
* a form of government revenue used to purchase public goods and services.
* Taxes directed to those who pay more
* Benefits are public goods and services that are provided to citizens determined by policy.
* Taxes directed to those who pay more
* Benefits are public goods and services that are provided to citizens determined by policy.
39
New cards
Why are taxes required?
If there are public goods, then there is a need of funding.
40
New cards
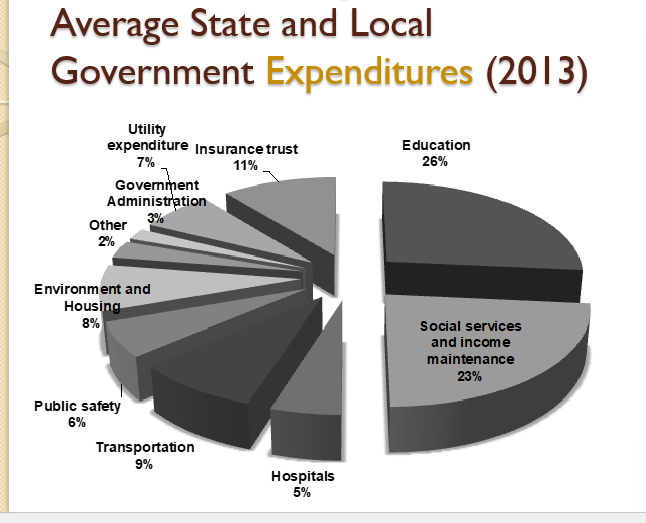
Where does all of the revenue go?
Mainly education and Social Services
41
New cards
How much can debt exceed?
cannot go past 5% of annual amount in capital funds for the past 3 years
42
New cards
What is the welfare spending limit?
it shall not exceed 1% of state budget in any biennium
43
New cards
Who can borrow money?
The Government can and businesses too
44
New cards
What are state leaders of high levels of debt?
They are poor discal managers and they are taking unnecessary risk
45
New cards
What are local government leaders POV on debt
absolutely necessary to provide for real needs and it a low risk high reward
46
New cards
1\. List the types and frequency of different levels of governments in the U.S.
* Federal government
* State Government
* Local governments
* State Government
* Local governments
47
New cards
2\. Explain the different advantages of having multiple levels of government and provide examples.
It provides efficiency and equity amongst the citizens of the US. Example: let's say you live in San Antonio and traffic is a real issue, so you propose to the city to fix transportation by adding a train system. However the city of College station wants an improved bike system. All of a sudden the state issues a better bike system for every city, do you think that's fair?
48
New cards
Characterize the “No Government” period, what America was like at the time, and how this period differs from today’s conservative slogan: “The least government is the best government.”
This era of government did not have a strong central government, everyone lived on agriculture and was independent. Then the only government was courthouses.
49
New cards
Characterize the “Municipal Government” period, how America had changed, and how that altered governments’ functions.
Corruption was high, the industrial revolution began, and immigration was rampant. Thousands of civilians lived in clustered areas.
50
New cards
Describe the role of political machines during this period and how they both abused and inspired the fundamentals of democracy.
Political machines were not actual machines but more of a criminal organization that would gather individuals to vote for their corrupt political party in rapid numbers. So the voter count would go over the actual population count because the same
individuals would go in more than once because they shaved their beard or they changed clothes.
individuals would go in more than once because they shaved their beard or they changed clothes.
51
New cards
Explain what caused the transition between the Municipal Government and the State-Intercity Government periods
State governments gained power by a concept called Dillon's rule, where the government took initiative to manage local governments which trumped local power and weakened political machines by setting more regulations.
52
New cards
Describe the role and the mechanism of Dillon’s Rule then and today.
Dillon's rule still has a significant impact on us today, the state government today has total control over the local governments on how they regulate their taxes, projects, and county borders.
53
New cards
List the reforms that were successful in taming the political machine beasts and describe how they were effective.
* Non partisan city election
* Placed all municipal hires under civil service (merit based)
* Separated school districts
* Placed all municipal hires under civil service (merit based)
* Separated school districts
54
New cards
Explain the causal mechanism that moved the U.S. into the Federal Government period.
During the World Wars the federal government took on the role as guardian and defender of the nation, which allowed the movement to the federal government period which gave presidents more power than ever.
55
New cards
Describe areas of state responsibility that the national government began moving into and how this was possible.
* Imposing norm on society
* Setting standard for the market
* Can go into massive amounts of debt
* Setting standard for the market
* Can go into massive amounts of debt
56
New cards
Diagram the relationships between the public, the states, and the national government in a unitary government, confederacy, and a federal form of government.
* Unitary - people directly communicate with the national government
* Confederacy - states hold most of the power
* federal government - it's a chain of government going up. People to state to central government
* Confederacy - states hold most of the power
* federal government - it's a chain of government going up. People to state to central government
57
New cards
Explain the basis for disagreements about the divisions between state and national government responsibilities and powers.
The constitution can be interpreted differently from other states, and different perspectives on the allocation of power
58
New cards
Explain the major events that coincided with the largest increases in Federal spending from 1948 until 2011.
* Cold War, Vietnam war, recovering from great depression
* 9/11 recession of 2008
* FDR Great new deal which involved Medicare, Medicaid, social security, disability, etc.…
* Energy crisis with the embargo act of Saudis
* 9/11 recession of 2008
* FDR Great new deal which involved Medicare, Medicaid, social security, disability, etc.…
* Energy crisis with the embargo act of Saudis
59
New cards
Explain the purposes of a constitution.
To set the foundation for how a state or national government is structures with a set of definitive rules with a set of governmental power
60
New cards
Describe the similarities between all state constitutions and the U.S. Constitution.
* Mostly all state have the same length as the US constitution
* They have the same structure of power such as the executive, the judicial, and the legislative
* Both have a form of Bill of rights
* They have the same structure of power such as the executive, the judicial, and the legislative
* Both have a form of Bill of rights
61
New cards
Characterize the range of sizes of state constitutions and why a state might choose to have a very long constitution.
Texas being the 2nd biggest constitution choose to have multiple scenarios accounted for and be strict with their power as a state
62
New cards
Explain the relationship between state constitutional laws, statutory laws, and local ordinances.
* Hierarchy:
* Constitution
* State Statutes
* Local Government Ordinances
* Constitution
* State Statutes
* Local Government Ordinances
63
New cards
Describe the relationship between the U.S. Bill of Rights and the bills of rights in state constitutions, both in their nature and their specific content.
With the standard bill of rights, there are your regular 10 amendments and with Texas it reiterates these with some minor details
64
New cards
Explain the reasons that many southern states have rewritten their constitutions more often than other states.
Assuming their history with slavery and with their conflicts with the national government after the civil war.
65
New cards
Summarize the differences between how the federal and state constitutions empower their respective governments
* The federal government has a flexibility with power, having the smallest constitution than most states, and being able to take on many different roles
* State governments restrict themselves of power due to the federal government and set the standards of their citizens in the country.
* State governments restrict themselves of power due to the federal government and set the standards of their citizens in the country.
66
New cards
Explain how government budgets are highly accurate policy statements.
· Comparing budgetary policy is important way to measure political differences between states. \n \n · "Follow the money" to learn the actual priorities of any government
67
New cards
Define public and private goods in terms of *rivaling* and *excludability*, then explain what that means.
Public goods are non excludable which means no one can deny you these goods. Private goods can be denied from you and people compete for these goods.
68
New cards
Describe merit goods and how they differ across democracies.
Goods which should not be denied to people who cannot pay for them like like education.
other nations differ by allowing free healthcare
other nations differ by allowing free healthcare
69
New cards
Explain what GDP does and does not measure.
usually a term of measure for economic power of a nation or a state, it talks about the health and the power of the nation. However it does not include the microeconomics of a nation, such as the average family income of a nation
70
New cards
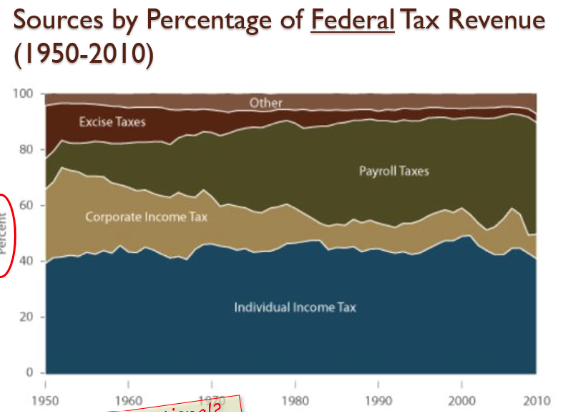
Draw and explain the profiles from 1950-2010 of the 3 largest sources of federal tax revenue.
Individual income tax made up about 40%. \n · Corporate income tax made up 25% at the beginning and started trending downwards. \n · Payroll Taxes (paid by employer and employee and go into the trust fund for Medicare and social security) started off at about 10% and has been increasing up to 40%.
71
New cards
List the most common sources of revenue for state governments.
· Taxes (e.g., property, income, sales, excise, severance) \n · Federal grants \n · Fees and licenses (e.g., auto registration, barber license) \n · Interest on investments \n · Direct sales (e.g., state-owned liquor stores) \n · Borrowing \n · Gambling/lottery
72
New cards
Explain the composition of state & local revenue sources in 2009, then again in 2013, and explain the differences.
· Great recession of 2008 only impacted 2013 revenue sources so federal support increased. \n \n · 2009: State and local Taxes (51%), Federal support (25%), Other state and local sources (24%) \n \n · 2013: Federal support (43%), Other state and local sources (40%), State and local taxes (17%)
73
New cards
Diagram the major sources of state revenue vs. local revenue in 2009 and describe the pattern that appears.
State government: Own revenue (75%), Federal (24%) \n \n · Local government: Own revenue (73%), State (24%)
74
New cards
Explain the term a state’s “own revenue” or “revenue from own sources” and how that broke out into key components in 2009.
· Own revenue makes up 75% and that can be broken down into: \n \n Fees and licence’s (35%), Sales Tax (32%), Income Tax (26%), Employment Trust Funds (6%), Property Tax (1%)
75
New cards
Describe the time cycles of Texas state budgets and the means of generating revenue estimates that can be used by the legislature to build the budget.
· Written and approved by the legislature every 2 years. \n \n · Assumes a specific amount of revenue from various sources. \n \n · Directs how expenditures will be made (on what and how much)
76
New cards
List the three major sources of revenue in Comptroller’s projection. Explain each one.
· Taxes ($77). \n · Federal Income ($70, grants). \n · Fees, Interest and other income ($30.8)
77
New cards
Explain how the total projected state revenue is split into Dedicated and General Revenue groups and the purpose and restrictions on each.
· Dedicated Revenue ($100, must go for pre-specified purposed). \n · General revenue ($77, available for legislature to spend)
78
New cards
4\. Explain the purpose of the Rainy Day Fund and how it is funded.
Economic stabilization funded by General revenue set aside for emergencies such as natural disasters or inflation
79
New cards
Describe how the final estimate of funds available to the legislature for budgeting is determined, starting with the General Revenue amount.
Subtract the amount of rainy day fund and overrun from previous year from the General revenue
80
New cards
Characterize the degree of success that Texas state comptrollers have making successful estimates of tax revenues across the years. Explain the risks associated with estimates that are significantly too high or too low.
· Estimates have to be very close. \n · Good to have collected more than you expected. However it's bad if you underestimate tax revenue by a lot because that means you could've spent a lot more money.
81
New cards
Explain how the Texas projected revenues for 2012-2013 compared to the revenue breakdown of the average state in 2009. Provide reasons that may account for significant differences.
Texas has more federal income than the average state because they don't collect as much taxes from their own state residents. This data was taken after the recession of 2008
82
New cards
Characterize the changes in the mix of three major revenue sources in Texas revenue projections from 2012-2013 to the following biennium. Also describe them in terms of the mixes that existed from 2006 on.
Keep increasing. However we need to consider inflation in 2021 we made less than 2017 due to inflation.
83
New cards
Describe the changes in total revenue and funds available for budgeting during the biennium’s from 2012 to 2021.
Total revenue increases but stay the same in terms of percentage.
84
New cards
Explain the major types of taxes used in Texas, the state’s reliance on them, and what their profiles looked like during and after the Great Recession.
· Income tax (none in TX) \n · Sales tax \n · Property tax \n · Severance tax - Applies to minerals "severed" from the land \n · "Tax Shifting"
85
New cards
Describe how tax shifting occurs and why it is used.
Gains revenue for a state or locality by taxing people or entities outside of that state/locality (ex: hotel rooms)
86
New cards
Characterize how and why different states use different type of taxes and weight them differently than other states.
It depends on the population, what the citizens demand for, and how their constitution is written.
87
New cards
Explain how taxes are based on an ability-to-pay model and what that means about contribution and benefit distributions.
· Those-who-have pay the costs \n · Often, those-with-more pay more \n · Policy determines who needs to pay, and how much they pay
88
New cards
Describe how taxes redistribute wealth and who makes the decisions behind that redistribution.
· They use money (from those who pay more) to provide services \n \n · Tax policy (which varies within each state and locality) determines where this redistribution happens, and to what degree
89
New cards
Compare and contrast taxes and user fees. Provide examples, including services and resources where both are used.
· Taxes are required if there are public goods: Public goods are "nonexcludable," markets would fail if they tried to pay for them (K-12 education) \n \n · User fees distribute benefits only to those who pay: Ex: User fees for hunting licenses, barbering license, fishing license, etc.
90
New cards
Characterize the rationale for taxes with respect to public goods. Use public education as an example.
The state of Texas fund their school districts by using property taxes, with these taxes we are able to fund schools with the hopes the children would receive the proper education they need
91
New cards
Explain why normative language is often used when commenting about taxes and how this can obscure empirical facts related to taxes.
· Comparisons (right, wrong, high, low) because details are too hard to know. \n \n · Absence of empirical analysis can create illogical conclusions: \n \n Ex: Taxes are too high but government needs to do more for us (want to pay less but get more benefits)
92
New cards
Describe a “zero-sum” game as it applies to taxes and why it is hard to generate interest in addressing tax-related problems for the non-winners in a society.
· No services exist without someone paying the bill \n \n · Want to increase services? Bill must increase, too!
93
New cards
Characterize how the tax brackets work in the federal income tax system.
· You belong in a certain tax bracket based on income. Higher brackets pay in for all of the brackets they passed. \n \n · Rich people use capital gains (buy something and sell it later gain money due to inflation) because they are taxed less.
94
New cards
Tax Base
The item/amount subject to taxation \n \n Example: You don't pay federal income tax on your entire income.
95
New cards
Tax Rate
· The % set by legislature for states (1st point) \n \n · Progressive Tax Rate- Higher the base, the higher the rate (don't have regressive because it's unfair to tax lower base a higher rate) \n \n · Fixed Tax Rate- Same rate, independent
96
New cards
Tax Bill
Taxes paid in a year by a person or business (2ndpoint). Tax base multiplied by tax rate
97
New cards
Total Value
Total income, total value of property, etc.
98
New cards
Tax Burden
\n Tax Bill divided by Total Value. Accurate because you look at all the money you made in a year.
99
New cards
Difference between tax burden and tax incidence.
Tax incidence compares tax burdens across income groups.
100
New cards
Explain how a taxation system with progressive tax rates and still create a regressive tax incidence.
Because a citizen with a higher income pays a smaller proportion of their income in taxes therefore making their tax burden lower.