CO2026 Gram-Positive Bacteria
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What gram-positive bacteria does the following describe?
-cocci
-catalase positive
-coagulase positive
-mannitol fermentation positive
Staphylococcus aureus
Where is staphyloccocus aureus found?
in normal flora of skin, nose
Bone infections, joint infections, otitis externa (ear infection), folliculits, impetigo abscesses, cellulitis, toxic shock syndrome, and scalded-skin syndrome are all symptoms of being infected by what microbe?
Staphylococcocus aureus
Resistance S.aureus has ______ which is an alternate PBP that beta-lactams cannot bind to.
MecA
Staph aureus has many virulence factors and pathogenetic factors. Name them.
-Protein A which binds to Fc of antibodies (antiphagocytic)
-Pantone-Valentine Leucocidin (destroys white blood cells, necrotic infection, common in skin infections)
-Exfoliative toxin (loss of cell-to-cell contact, Scalded-skin syndrome)
-MecA (methicillin resistance)
What gram-positive bacteria does the following describe?
-cocci
-catalase positive
-coagulase negative
-does not ferment mannitol
Staphylococcus epidermidis
How is Staphyloccocus epidermidis transmitted?
inoculation of normal flora in skin to other areas
What is the only gram-positive cocci that is diplo? (lacent diplococci)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
What is the biggest risk factor for being infected by Staphyloccocus epidermidis? How is the bacteria spread?
foreign materials (prosthetics, catheters); respiratory droplets/aerosols, endogenous spread from our own flora
Slime layer/glycocalyx formation that is sticky as well as MecA are characteristics of what bacteria? What are the symptoms of this infection?
Staphylococcus epidermidis- prosthetic joint/bone infections, wound infections that are opportunistic with slow onset
Which of the following gram-positive bacteria does this describe?
-lacent diplococci
-catalase negative
-hemolysis on blood agar
-capsule
-soluble in bile
Streptoccocus pneumoniae
What can Streptoccocus pneumoniae cause in children? WHat about adults over 65? (HINT: think disease)
children- otitis media, sinusitis
adults over 65 - pneumonia, meningitis
Streptoccocus pneumonia is spread by what?
human-only (oropharnyx)- endogenous spread
What are the 2 virulence factors/pathogenesis that Streptococcus pneumoniae takes?
Polysaccharide capsule (antiphagocytic), IgA protease
How can Streptococcus pneumoniae be prevented?
vaccinations with either polysaccharide capsules conjugated to protein or the capsules only
Which of the gram-positive bacteria does the following described?
-cocci in chains
-catalase-negative
-beta-hemolytic
-bacitracin sensitive
Streptoccocus pyogenes
Where is Streptoccocus pyogenes found? How is it spread?
human-ONLY (oropharynx, transient skin)
-endogenous spread
-respiratory droplets
-direct contact (impetigo)
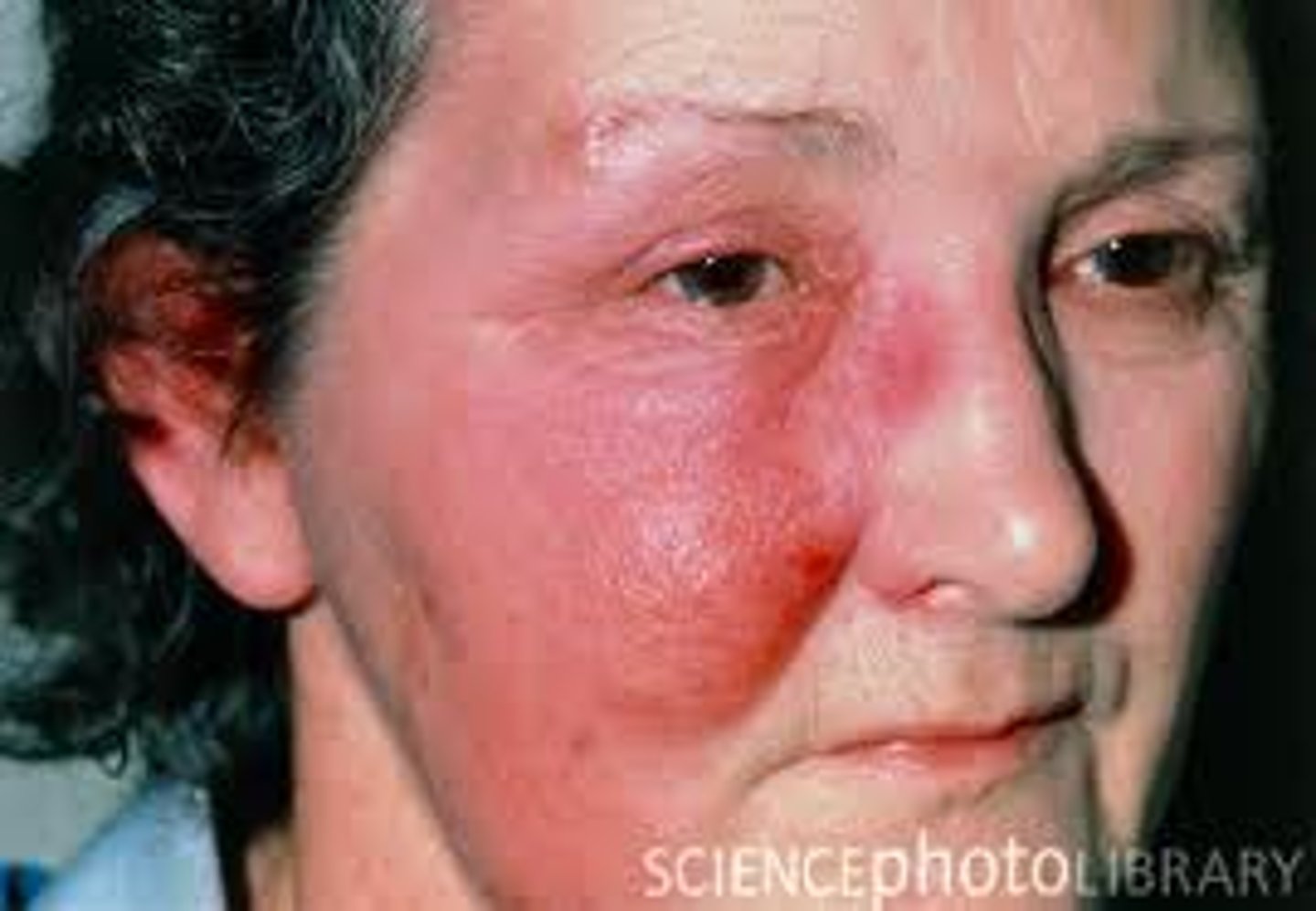
Which bacteria can cause Group A strep, strep throat, impetigo, necrotizing fasciitis, cellulitis, erysipelas, and rheumatic fever (strep throat, scarlet fever, or impetigo)?
Streptoccocus pyogenes (photo of erysipelas)
What can make toxins that cause the rash in Scarlet Fever when infected with Streptoccocus pyogenes?
Pyrogenic exotoxin A or B --> superantigen
What are some of the pathogenesis/virulence factors of Streptoccocus pyogenes?
-hydraluronic capsule
-M protein
-Streptolysin O
-DNase B (deoxyribonuclease)
-Pyogenic exotoxin (superantigen)
Which gram-positive bacteria does the following described?
-cocci in chains
-catalase negative
-alpha hemolytic
-optochin resistant
Viridans Streptococci
Where is Viridans Streptococci found? How is it transmitted?
human-only in oropharynx normal flora; spread endogenously through poor dental hygiene, major surgery
What are some disease caused by being infected with Viridans Streptococci?
dental caries, periodontal disease, endocarditis
Biofilm formation in tooth enamel or heart valve adhesion is commonly seen in what organism?
Viridan Streptococci
Sometimes, dentists will give a _____________ antibiotic prior to major dental surgery to prevent infection of ______ ________.
prophylactic antibiotic to prevent Viridans Streptococci
Which 2 gram-positive rods are obligate anaerobes? Which one is the non-spore former?
Cutibacterium acnes (NON-spore former) and Clostridium perfringes
Where do Cutibacterium acnes live?
fatty acids in sebum (commensal- a part of skin flora)
How is Cutibacterium acnes transmitted? What does it cause?
endogenous overgrowth of skin flora; acne vulgaris
Which gram-positive bacteria does the following describe?
-rods
-obligate anaerobe
-spore-former
Clostridium perfringes
What is the reservoir for Clostridium perfringes? How can it be transmitted?
endospores in soil, environment
-direct inoculation of spores to deep wound
-sharing/using dirty needles
-ingestion of undercooked meat (1 of the most common causes of food poisoning)
What is the biggest risk factor for Clostridium perfringes?
traumatic entry of spores in wounds (deep puncture wound after motorbike accident)
What is the pathogenesis of Clostridium perfringes?
-Alpha toxin- phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase
-Beta toxin- cytotoxin (hole-puncher)
-Invasin enzymes (hyaluronidase)
-capsule
What are some symptoms or physical characteristics of being infected by Clostridium perfringes?
necrotic destruction of muscles/tissues, pockets of air/gas under skin, purple bullae (necrosis)
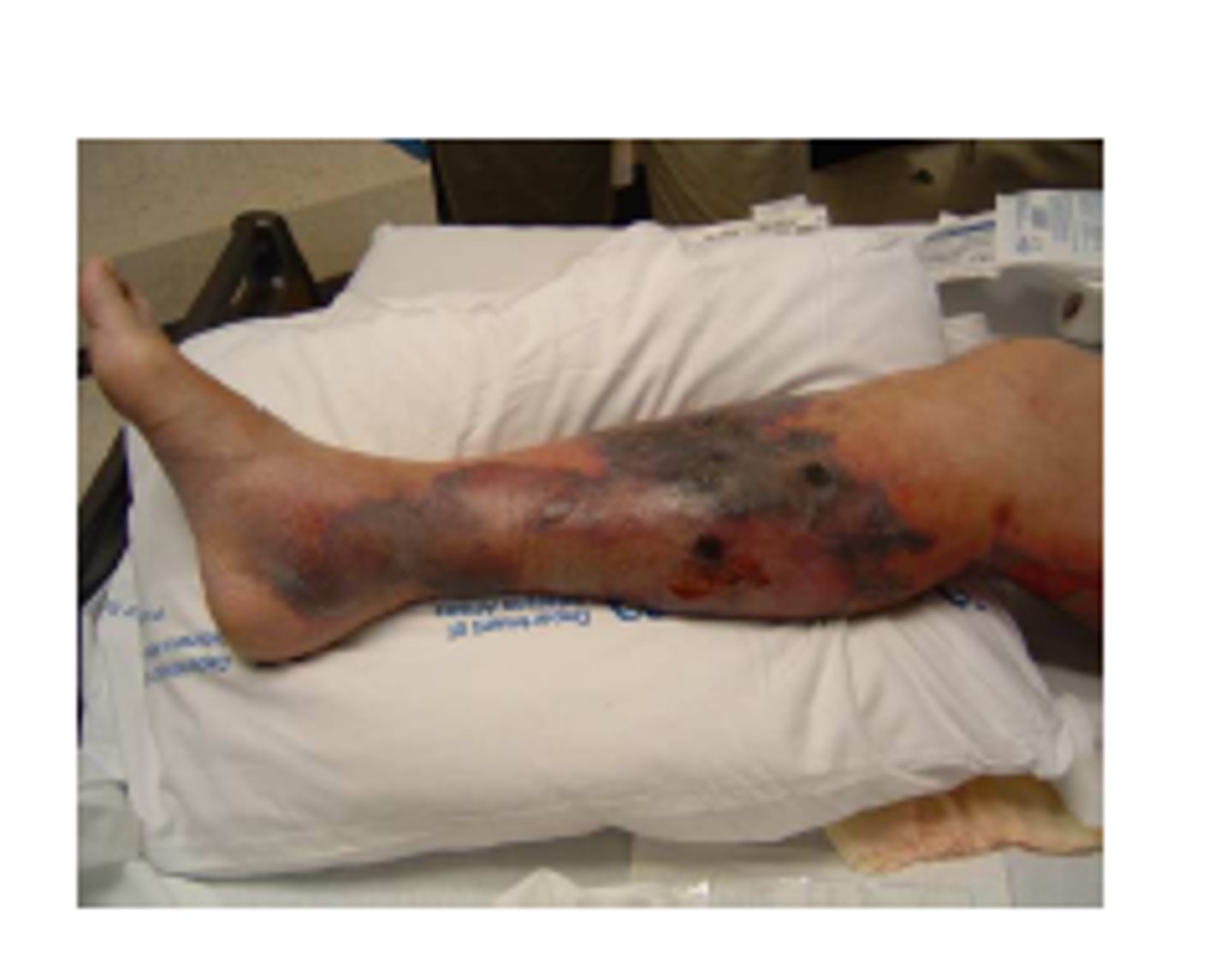
Which gram-positive rod is diagnosed using double hemolysis on blood agar and also detects leicithinase activity (alpha toxin) on egg yolk agar?
Clostridium perfringes
Which gram-positive bacteria has a unique capsule of Poly-D-gamma-glutamic acid?
Bacillus anthracis
Which two gram-positive rods are non-spore forming?
Cutibacterium acnes and cornebacterium diptheriae
Which two gram-positive rods are spore forming?
Bacillus anthracis and clostridium perfringes
What gram-positive bacteria does the following describe?
-rods in chains
-spore-former
-non-motile
-non-hemolytic
-poly-D-gamma-glutamic acid capsule
Bacillus anthracis
Where does Bacillus anthracic exist? How is it transmitted to the cutaneous gastrointestinal and pulmonary?
endospores in environment, soil
-Cutaneous: spore inoculated directly into skin, germinate locally
-GI: spores ingested, germinate in stomach
-Pulmonary: spores are inhaled, germinate in lungs
The epidemiology of this bacteria is zoonotic, particularly ruminate herbivores as they eat the grass where the spores are present. A risk factor for getting infected would be working with livestock. It can also be used as a bioweapon. Which gram-positive bacteria does this best describe?
Bacillus anthracis
What are the symptoms in someone who develops a cutaneous infection of Bacillus anthracis?
painless, pruritic black eschar at inoculation site with massive edema around (necrotic ulceration)
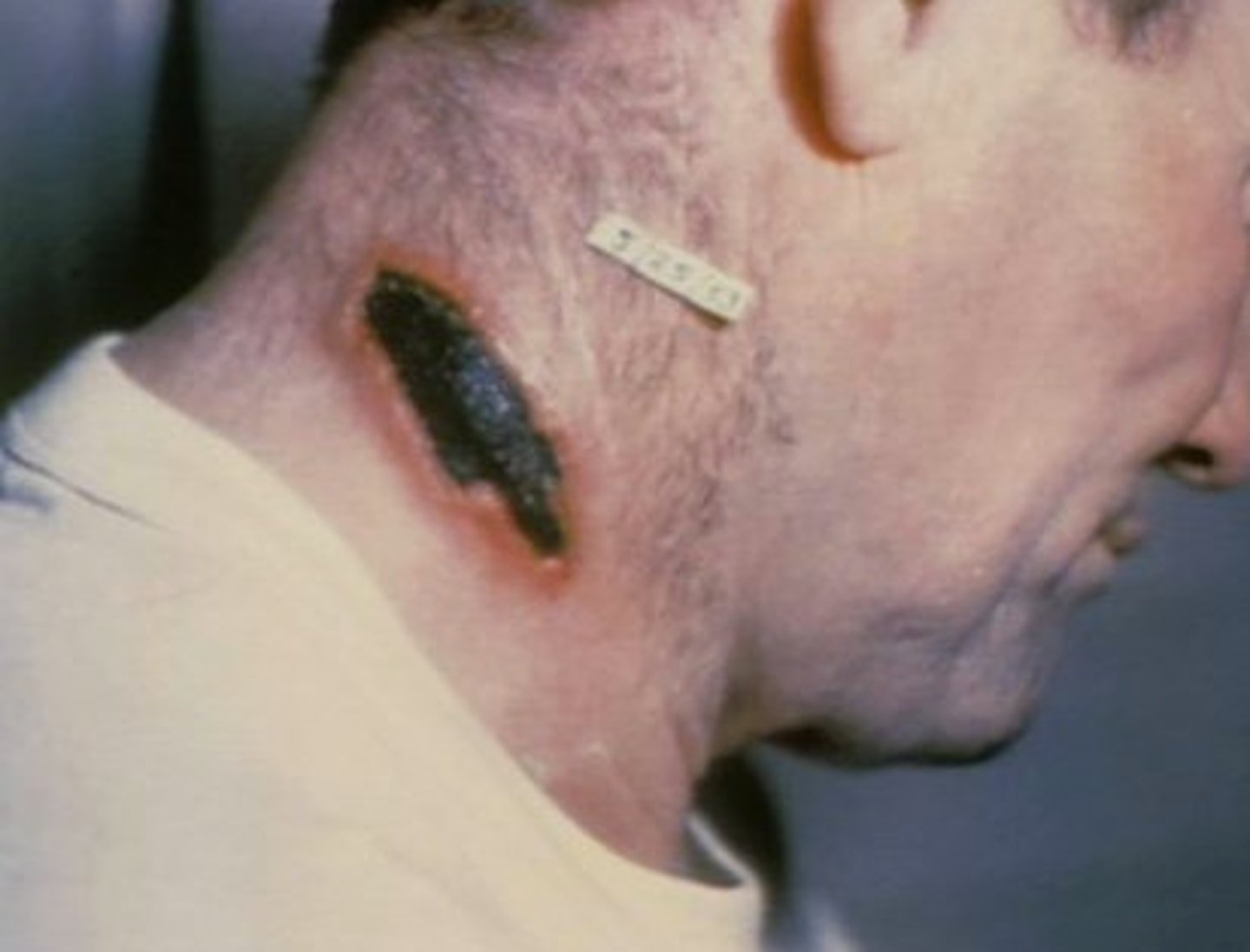
What is the pathogenesis of Bacillus anthracis? How can you diagnose this bacterial infection?
spores, anthrax toxins (protective (B portion of AB), lethal, and edema), capsule with unique poly-D-gamma-glutamic acid; PCR
Which gram-positive is described in the following?
-rods with clubbed ends
-metachromatic granules
-non-spore-former
-non-motile
-aerobic
Corynebacterium diptheriae
Which 2 gram-positive rods are aerobic?
Bacillus anthracis and Corynebacterium diptheriae
What is the reservoir of Corynebacterium diptheriae and how is it transmitted?
reservoir: human only
transmission: person-person through aerosols, respiratory droplets
What areas are endemic to Corynebacterium diptheriae? What are some risk factors in developing the infection?
Epidemiology: Haiti, Dominican Republic, Asia & South Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East
Risk factors: unvaccinated, war or natural disaster, immunocompromised, less than 5 years of age
What are some of the symptoms of Diptheria (caused by Corynebacterium diptheriae)?
Respiratory issues
-First symptoms: sore throat, malaise, low-grade fever, dysphagia
-thick, grey pseudomembrane that can block throat and stop breathing
-Bull neck: swelling of cervical lymph nodes
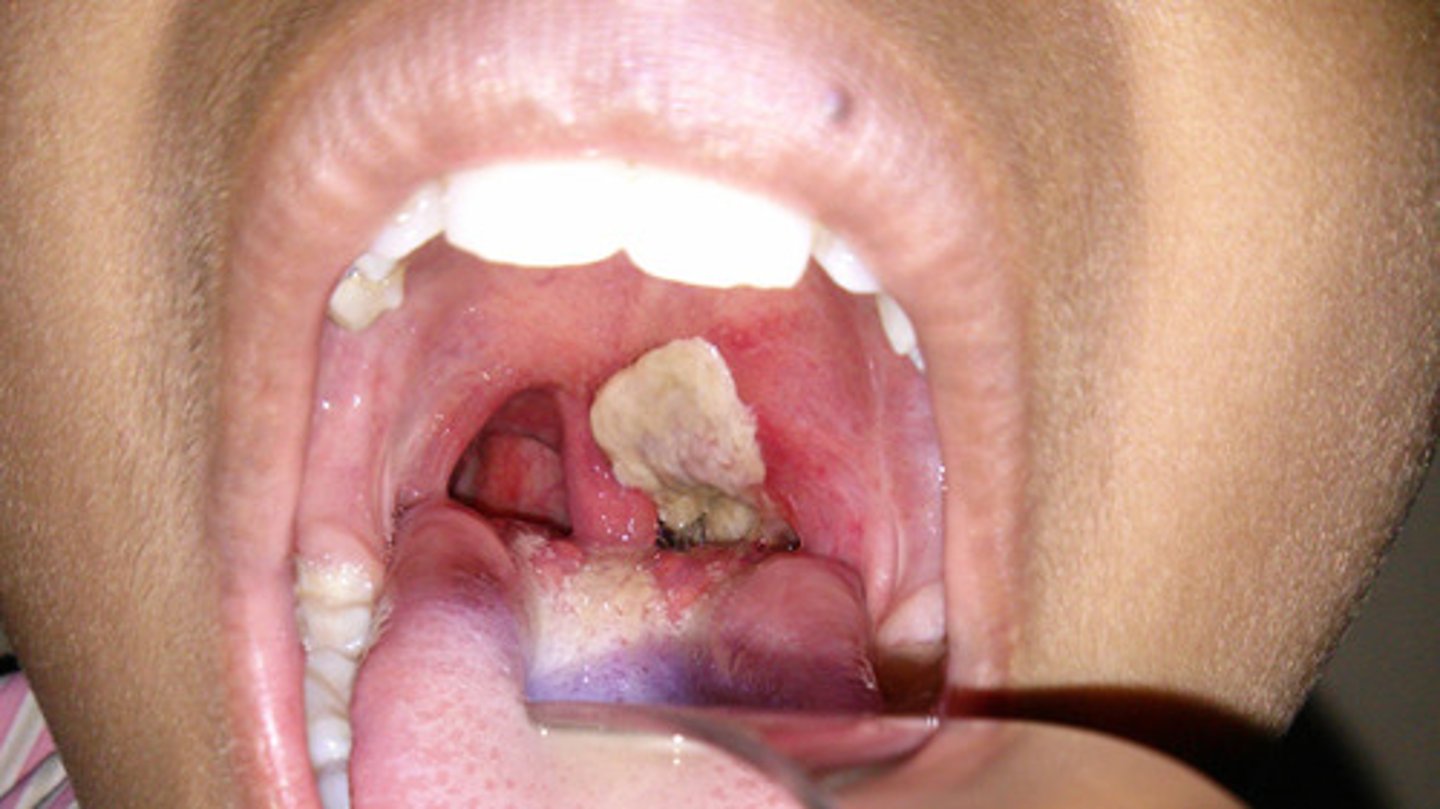
The Diptheria toxin was originally acquired through lysogenic conversion (bacteriophage) transduction. It uses the ___ toxin which inactivates EF2, preventing ___________.
AB toxin; preventing protein synthesis
How do you prevent Corynebacterium diptheriae?
toxoid vaccination